Zhiding Liang
Beyond Affinity: A Benchmark of 1D, 2D, and 3D Methods Reveals Critical Trade-offs in Structure-Based Drug Design
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Currently, the field of structure-based drug design is dominated by three main types of algorithms: search-based algorithms, deep generative models, and reinforcement learning. While existing works have typically focused on comparing models within a single algorithmic category, cross-algorithm comparisons remain scarce. In this paper, to fill the gap, we establish a benchmark to evaluate the performance of fifteen models across these different algorithmic foundations by assessing the pharmaceutical properties of the generated molecules and their docking affinities and poses with specified target proteins. We highlight the unique advantages of each algorithmic approach and offer recommendations for the design of future SBDD models. We emphasize that 1D/2D ligand-centric drug design methods can be used in SBDD by treating the docking function as a black-box oracle, which is typically neglected. Our evaluation reveals distinct patterns across model categories. 3D structure-based models excel in binding affinities but show inconsistencies in chemical validity and pose quality. 1D models demonstrate reliable performance in standard molecular metrics but rarely achieve optimal binding affinities. 2D models offer balanced performance, maintaining high chemical validity while achieving moderate binding scores. Through detailed analysis across multiple protein targets, we identify key improvement areas for each model category, providing insights for researchers to combine strengths of different approaches while addressing their limitations. All the code that are used for benchmarking is available in https://github.com/zkysfls/2025-sbdd-benchmark
TITAN: A Trajectory-Informed Technique for Adaptive Parameter Freezing in Large-Scale VQE
Sep 18, 2025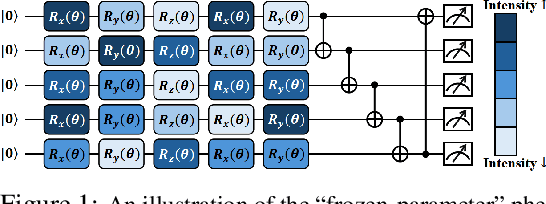
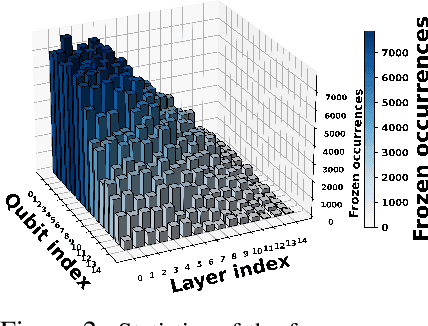
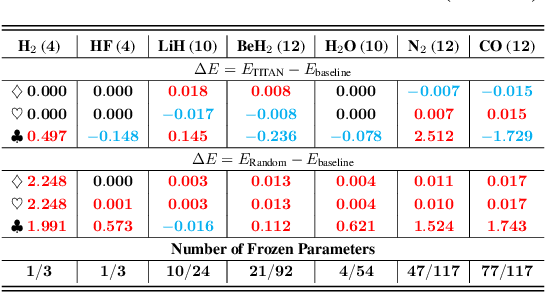
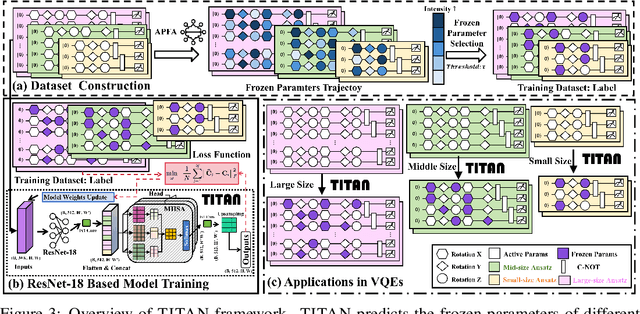
Abstract:Variational quantum Eigensolver (VQE) is a leading candidate for harnessing quantum computers to advance quantum chemistry and materials simulations, yet its training efficiency deteriorates rapidly for large Hamiltonians. Two issues underlie this bottleneck: (i) the no-cloning theorem imposes a linear growth in circuit evaluations with the number of parameters per gradient step; and (ii) deeper circuits encounter barren plateaus (BPs), leading to exponentially increasing measurement overheads. To address these challenges, here we propose a deep learning framework, dubbed Titan, which identifies and freezes inactive parameters of a given ansatze at initialization for a specific class of Hamiltonians, reducing the optimization overhead without sacrificing accuracy. The motivation of Titan starts with our empirical findings that a subset of parameters consistently has a negligible influence on training dynamics. Its design combines a theoretically grounded data construction strategy, ensuring each training example is informative and BP-resilient, with an adaptive neural architecture that generalizes across ansatze of varying sizes. Across benchmark transverse-field Ising models, Heisenberg models, and multiple molecule systems up to 30 qubits, Titan achieves up to 3 times faster convergence and 40% to 60% fewer circuit evaluations than state-of-the-art baselines, while matching or surpassing their estimation accuracy. By proactively trimming parameter space, Titan lowers hardware demands and offers a scalable path toward utilizing VQE to advance practical quantum chemistry and materials science.
HybridQ: Hybrid Classical-Quantum Generative Adversarial Network for Skin Disease Image Generation
Jun 26, 2025Abstract:Machine learning-assisted diagnosis is gaining traction in skin disease detection, but training effective models requires large amounts of high-quality data. Skin disease datasets often suffer from class imbalance, privacy concerns, and object bias, making data augmentation essential. While classical generative models are widely used, they demand extensive computational resources and lengthy training time. Quantum computing offers a promising alternative, but existing quantum-based image generation methods can only yield grayscale low-quality images. Through a novel classical-quantum latent space fusion technique, our work overcomes this limitation and introduces the first classical-quantum generative adversarial network (GAN) capable of generating color medical images. Our model outperforms classical deep convolutional GANs and existing hybrid classical-quantum GANs in both image generation quality and classification performance boost when used as data augmentation. Moreover, the performance boost is comparable with that achieved using state-of-the-art classical generative models, yet with over 25 times fewer parameters and 10 times fewer training epochs. Such results suggest a promising future for quantum image generation as quantum hardware advances. Finally, we demonstrate the robust performance of our model on real IBM quantum machine with hardware noise.
Introduction to Quantum Machine Learning and Quantum Architecture Search
Apr 21, 2025



Abstract:Recent advancements in quantum computing (QC) and machine learning (ML) have fueled significant research efforts aimed at integrating these two transformative technologies. Quantum machine learning (QML), an emerging interdisciplinary field, leverages quantum principles to enhance the performance of ML algorithms. Concurrently, the exploration of systematic and automated approaches for designing high-performance quantum circuit architectures for QML tasks has gained prominence, as these methods empower researchers outside the quantum computing domain to effectively utilize quantum-enhanced tools. This tutorial will provide an in-depth overview of recent breakthroughs in both areas, highlighting their potential to expand the application landscape of QML across diverse fields.
QCS-ADME: Quantum Circuit Search for Drug Property Prediction with Imbalanced Data and Regression Adaptation
Mar 02, 2025Abstract:The biomedical field is beginning to explore the use of quantum machine learning (QML) for tasks traditionally handled by classical machine learning, especially in predicting ADME (absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion) properties, which are essential in drug evaluation. However, ADME tasks pose unique challenges for existing quantum computing systems (QCS) frameworks, as they involve both classification with unbalanced dataset and regression problems. These dual requirements make it necessary to adapt and refine current QCS frameworks to effectively address the complexities of ADME predictions. We propose a novel training-free scoring mechanism to evaluate QML circuit performance on imbalanced classification and regression tasks. Our mechanism demonstrates significant correlation between scoring metrics and test performance on imbalanced classification tasks. Additionally, we develop methods to quantify continuous similarity relationships between quantum states, enabling performance prediction for regression tasks. This represents the first comprehensive approach to searching and evaluating QCS circuits specifically for regression applications. Validation on representative ADME tasks-one imbalanced classification and one regression-demonstrates moderate positive correlation between our scoring metrics and circuit performance, significantly outperforming baseline scoring methods that show negligible correlation.
Quantum-inspired Reinforcement Learning for Synthesizable Drug Design
Sep 13, 2024Abstract:Synthesizable molecular design (also known as synthesizable molecular optimization) is a fundamental problem in drug discovery, and involves designing novel molecular structures to improve their properties according to drug-relevant oracle functions (i.e., objective) while ensuring synthetic feasibility. However, existing methods are mostly based on random search. To address this issue, in this paper, we introduce a novel approach using the reinforcement learning method with quantum-inspired simulated annealing policy neural network to navigate the vast discrete space of chemical structures intelligently. Specifically, we employ a deterministic REINFORCE algorithm using policy neural networks to output transitional probability to guide state transitions and local search using genetic algorithm to refine solutions to a local optimum within each iteration. Our methods are evaluated with the Practical Molecular Optimization (PMO) benchmark framework with a 10K query budget. We further showcase the competitive performance of our method by comparing it against the state-of-the-art genetic algorithms-based method.
Quantum-machine-assisted Drug Discovery: Survey and Perspective
Aug 24, 2024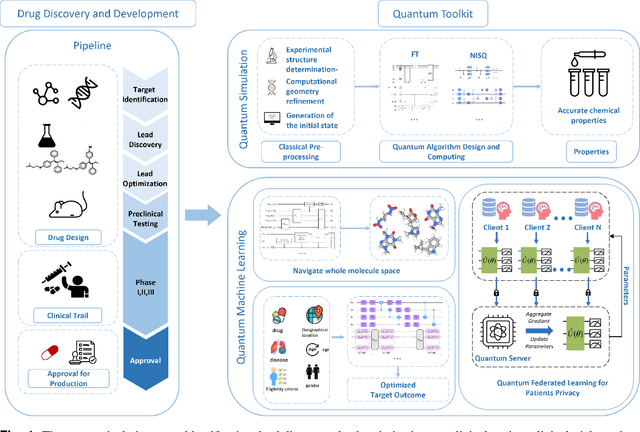

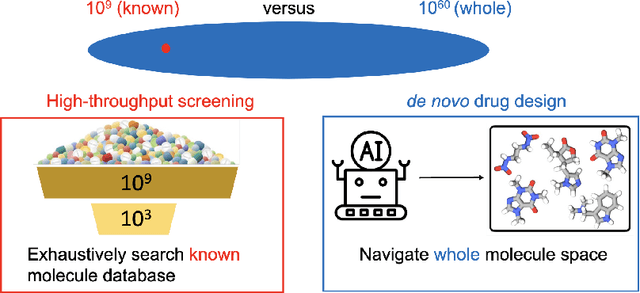
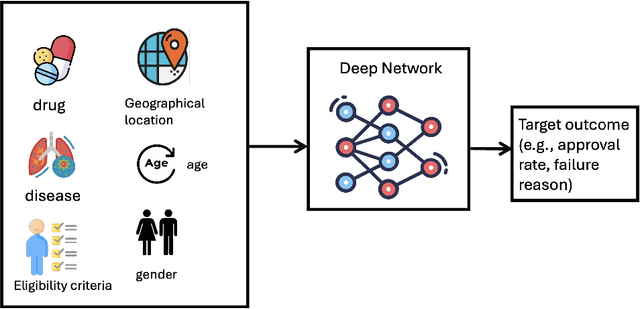
Abstract:Drug discovery and development is a highly complex and costly endeavor, typically requiring over a decade and substantial financial investment to bring a new drug to market. Traditional computer-aided drug design (CADD) has made significant progress in accelerating this process, but the development of quantum computing offers potential due to its unique capabilities. This paper discusses the integration of quantum computing into drug discovery and development, focusing on how quantum technologies might accelerate and enhance various stages of the drug development cycle. Specifically, we explore the application of quantum computing in addressing challenges related to drug discovery, such as molecular simulation and the prediction of drug-target interactions, as well as the optimization of clinical trial outcomes. By leveraging the inherent capabilities of quantum computing, we might be able to reduce the time and cost associated with bringing new drugs to market, ultimately benefiting public health.
Qsco: A Quantum Scoring Module for Open-set Supervised Anomaly Detection
May 25, 2024Abstract:Open set anomaly detection (OSAD) is a crucial task that aims to identify abnormal patterns or behaviors in data sets, especially when the anomalies observed during training do not represent all possible classes of anomalies. The recent advances in quantum computing in handling complex data structures and improving machine learning models herald a paradigm shift in anomaly detection methodologies. This study proposes a Quantum Scoring Module (Qsco), embedding quantum variational circuits into neural networks to enhance the model's processing capabilities in handling uncertainty and unlabeled data. Extensive experiments conducted across eight real-world anomaly detection datasets demonstrate our model's superior performance in detecting anomalies across varied settings and reveal that integrating quantum simulators does not result in prohibitive time complexities. Our study validates the feasibility of quantum-enhanced anomaly detection methods in practical applications.
Graph Learning for Parameter Prediction of Quantum Approximate Optimization Algorithm
Mar 05, 2024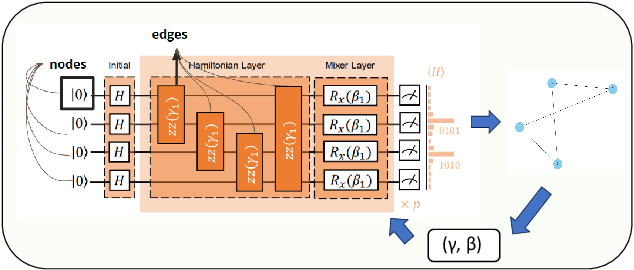
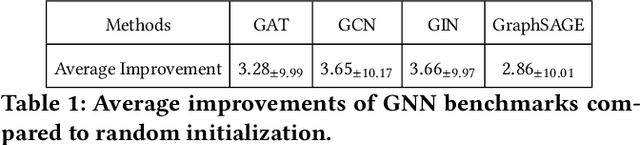
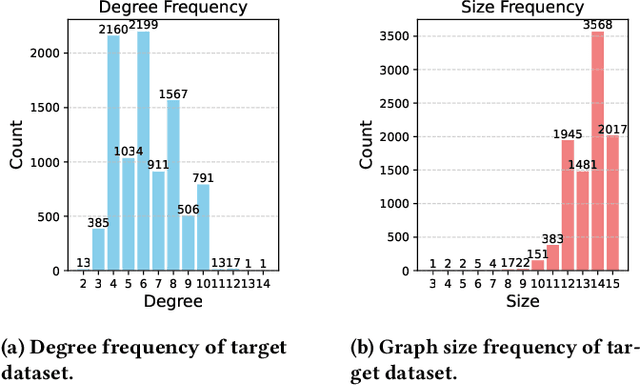
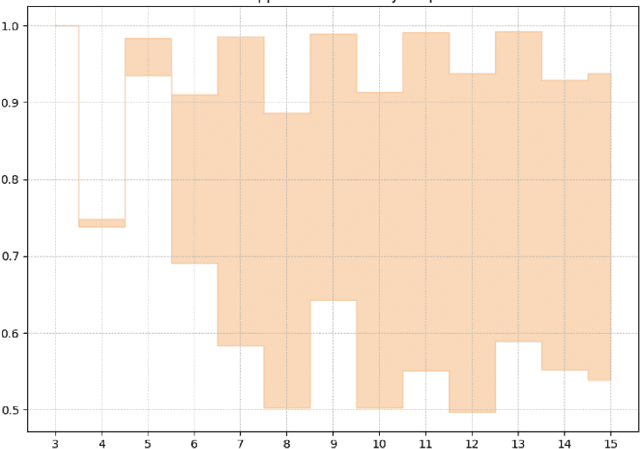
Abstract:In recent years, quantum computing has emerged as a transformative force in the field of combinatorial optimization, offering novel approaches to tackling complex problems that have long challenged classical computational methods. Among these, the Quantum Approximate Optimization Algorithm (QAOA) stands out for its potential to efficiently solve the Max-Cut problem, a quintessential example of combinatorial optimization. However, practical application faces challenges due to current limitations on quantum computational resource. Our work optimizes QAOA initialization, using Graph Neural Networks (GNN) as a warm-start technique. This sacrifices affordable computational resource on classical computer to reduce quantum computational resource overhead, enhancing QAOA's effectiveness. Experiments with various GNN architectures demonstrate the adaptability and stability of our framework, highlighting the synergy between quantum algorithms and machine learning. Our findings show GNN's potential in improving QAOA performance, opening new avenues for hybrid quantum-classical approaches in quantum computing and contributing to practical applications.
RobustState: Boosting Fidelity of Quantum State Preparation via Noise-Aware Variational Training
Nov 27, 2023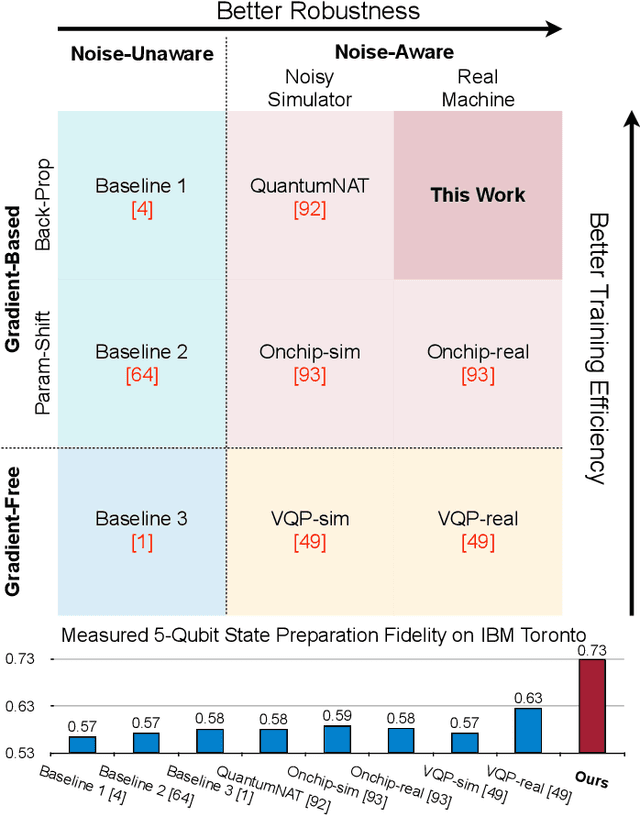
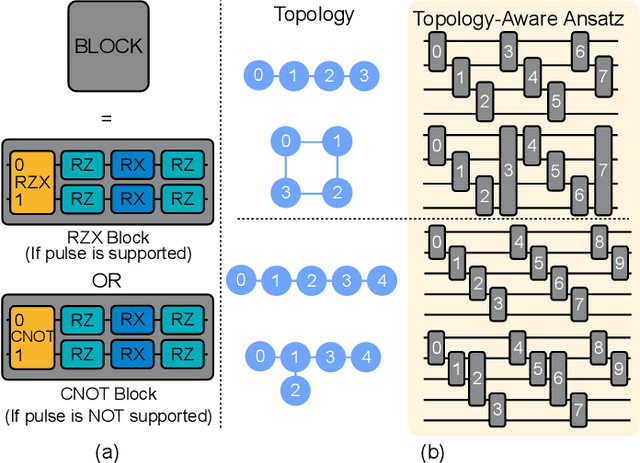
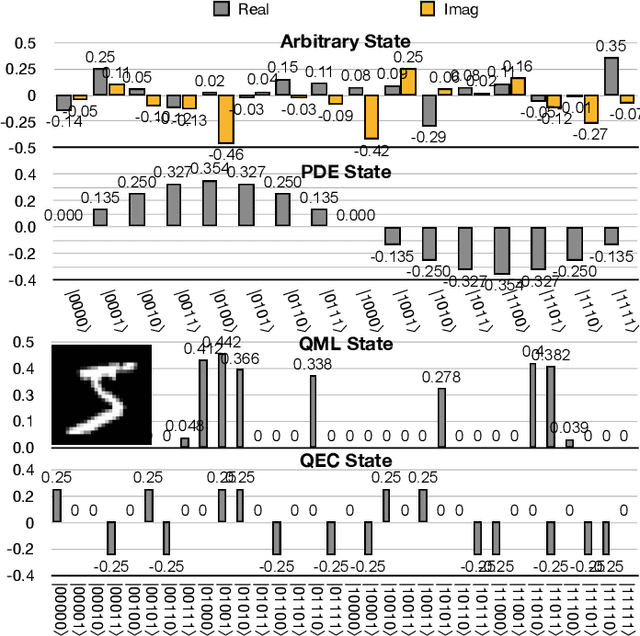
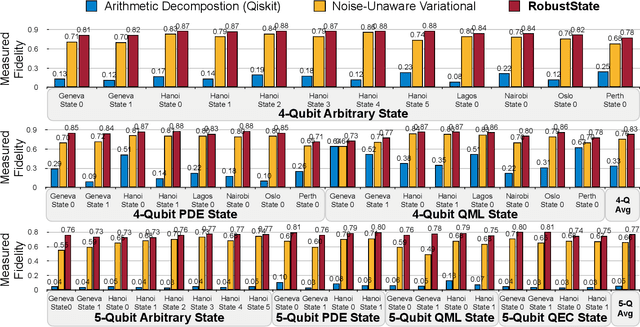
Abstract:Quantum state preparation, a crucial subroutine in quantum computing, involves generating a target quantum state from initialized qubits. Arbitrary state preparation algorithms can be broadly categorized into arithmetic decomposition (AD) and variational quantum state preparation (VQSP). AD employs a predefined procedure to decompose the target state into a series of gates, whereas VQSP iteratively tunes ansatz parameters to approximate target state. VQSP is particularly apt for Noisy-Intermediate Scale Quantum (NISQ) machines due to its shorter circuits. However, achieving noise-robust parameter optimization still remains challenging. We present RobustState, a novel VQSP training methodology that combines high robustness with high training efficiency. The core idea involves utilizing measurement outcomes from real machines to perform back-propagation through classical simulators, thus incorporating real quantum noise into gradient calculations. RobustState serves as a versatile, plug-and-play technique applicable for training parameters from scratch or fine-tuning existing parameters to enhance fidelity on target machines. It is adaptable to various ansatzes at both gate and pulse levels and can even benefit other variational algorithms, such as variational unitary synthesis. Comprehensive evaluation of RobustState on state preparation tasks for 4 distinct quantum algorithms using 10 real quantum machines demonstrates a coherent error reduction of up to 7.1 $\times$ and state fidelity improvement of up to 96\% and 81\% for 4-Q and 5-Q states, respectively. On average, RobustState improves fidelity by 50\% and 72\% for 4-Q and 5-Q states compared to baseline approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge