Yongshan Ding
Efficient Quantum Gradient and Higher-order Derivative Estimation via Generalized Hadamard Test
Aug 10, 2024Abstract:In the context of Noisy Intermediate-Scale Quantum (NISQ) computing, parameterized quantum circuits (PQCs) represent a promising paradigm for tackling challenges in quantum sensing, optimal control, optimization, and machine learning on near-term quantum hardware. Gradient-based methods are crucial for understanding the behavior of PQCs and have demonstrated substantial advantages in the convergence rates of Variational Quantum Algorithms (VQAs) compared to gradient-free methods. However, existing gradient estimation methods, such as Finite Difference, Parameter Shift Rule, Hadamard Test, and Direct Hadamard Test, often yield suboptimal gradient circuits for certain PQCs. To address these limitations, we introduce the Flexible Hadamard Test, which, when applied to first-order gradient estimation methods, can invert the roles of ansatz generators and observables. This inversion facilitates the use of measurement optimization techniques to efficiently compute PQC gradients. Additionally, to overcome the exponential cost of evaluating higher-order partial derivatives, we propose the $k$-fold Hadamard Test, which computes the $k^{th}$-order partial derivative using a single circuit. Furthermore, we introduce Quantum Automatic Differentiation (QAD), a unified gradient method that adaptively selects the best gradient estimation technique for individual parameters within a PQC. This represents the first implementation, to our knowledge, that departs from the conventional practice of uniformly applying a single method to all parameters. Through rigorous numerical experiments, we demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed first-order gradient methods, showing up to an $O(N)$ factor improvement in circuit execution count for real PQC applications. Our research contributes to the acceleration of VQA computations, offering practical utility in the NISQ era of quantum computing.
RobustState: Boosting Fidelity of Quantum State Preparation via Noise-Aware Variational Training
Nov 27, 2023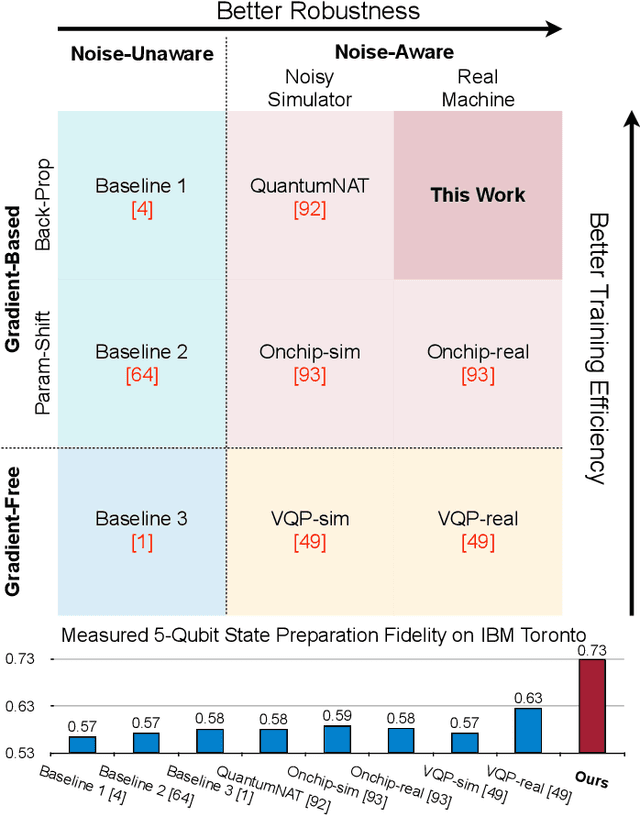
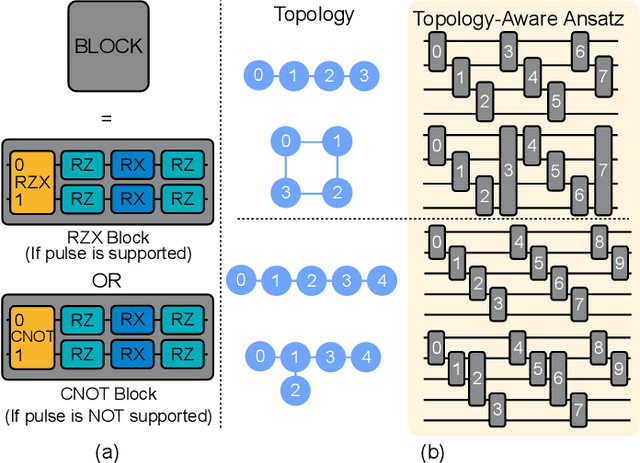
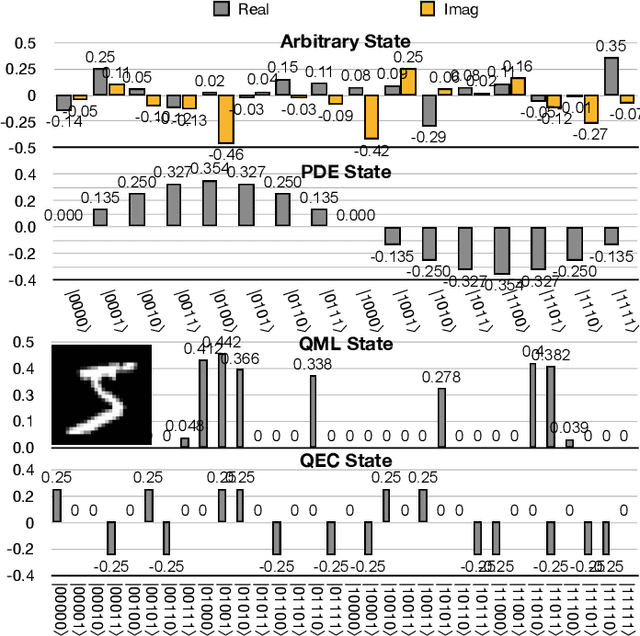
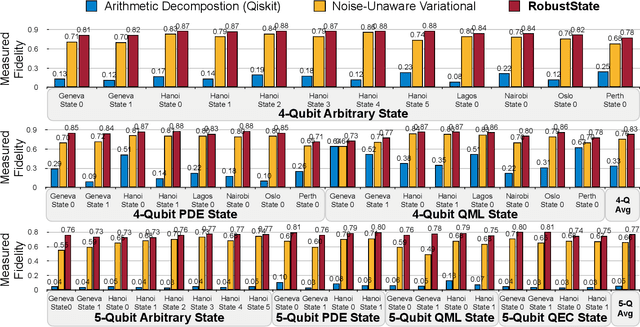
Abstract:Quantum state preparation, a crucial subroutine in quantum computing, involves generating a target quantum state from initialized qubits. Arbitrary state preparation algorithms can be broadly categorized into arithmetic decomposition (AD) and variational quantum state preparation (VQSP). AD employs a predefined procedure to decompose the target state into a series of gates, whereas VQSP iteratively tunes ansatz parameters to approximate target state. VQSP is particularly apt for Noisy-Intermediate Scale Quantum (NISQ) machines due to its shorter circuits. However, achieving noise-robust parameter optimization still remains challenging. We present RobustState, a novel VQSP training methodology that combines high robustness with high training efficiency. The core idea involves utilizing measurement outcomes from real machines to perform back-propagation through classical simulators, thus incorporating real quantum noise into gradient calculations. RobustState serves as a versatile, plug-and-play technique applicable for training parameters from scratch or fine-tuning existing parameters to enhance fidelity on target machines. It is adaptable to various ansatzes at both gate and pulse levels and can even benefit other variational algorithms, such as variational unitary synthesis. Comprehensive evaluation of RobustState on state preparation tasks for 4 distinct quantum algorithms using 10 real quantum machines demonstrates a coherent error reduction of up to 7.1 $\times$ and state fidelity improvement of up to 96\% and 81\% for 4-Q and 5-Q states, respectively. On average, RobustState improves fidelity by 50\% and 72\% for 4-Q and 5-Q states compared to baseline approaches.
Transformer-QEC: Quantum Error Correction Code Decoding with Transferable Transformers
Nov 27, 2023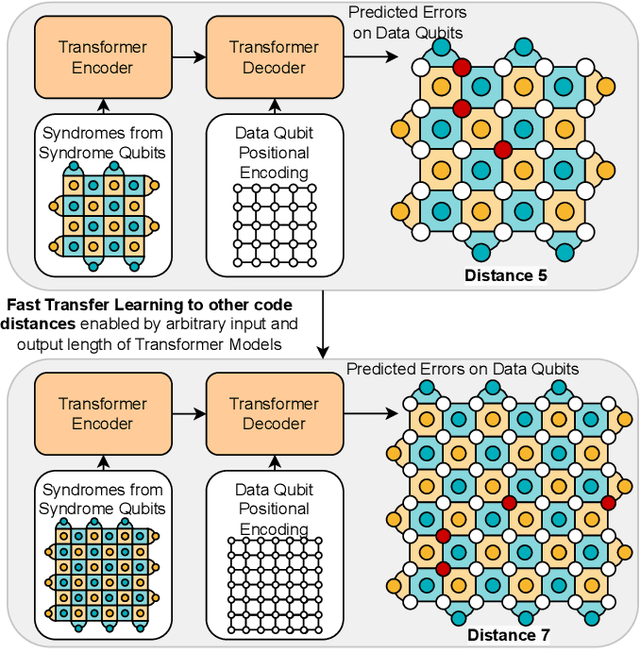
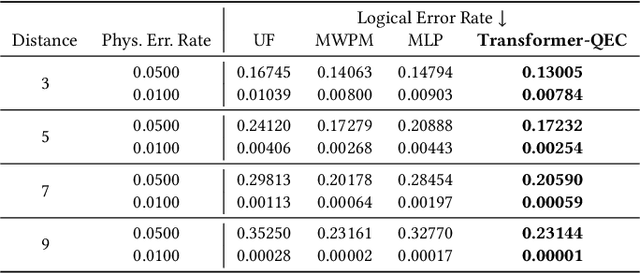
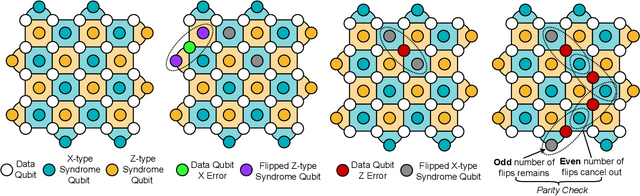
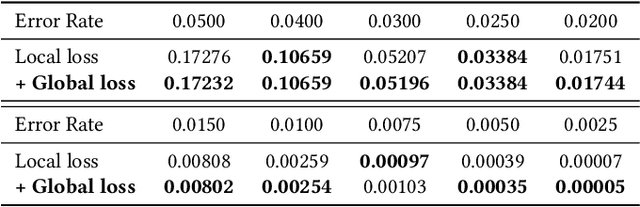
Abstract:Quantum computing has the potential to solve problems that are intractable for classical systems, yet the high error rates in contemporary quantum devices often exceed tolerable limits for useful algorithm execution. Quantum Error Correction (QEC) mitigates this by employing redundancy, distributing quantum information across multiple data qubits and utilizing syndrome qubits to monitor their states for errors. The syndromes are subsequently interpreted by a decoding algorithm to identify and correct errors in the data qubits. This task is complex due to the multiplicity of error sources affecting both data and syndrome qubits as well as syndrome extraction operations. Additionally, identical syndromes can emanate from different error sources, necessitating a decoding algorithm that evaluates syndromes collectively. Although machine learning (ML) decoders such as multi-layer perceptrons (MLPs) and convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have been proposed, they often focus on local syndrome regions and require retraining when adjusting for different code distances. We introduce a transformer-based QEC decoder which employs self-attention to achieve a global receptive field across all input syndromes. It incorporates a mixed loss training approach, combining both local physical error and global parity label losses. Moreover, the transformer architecture's inherent adaptability to variable-length inputs allows for efficient transfer learning, enabling the decoder to adapt to varying code distances without retraining. Evaluation on six code distances and ten different error configurations demonstrates that our model consistently outperforms non-ML decoders, such as Union Find (UF) and Minimum Weight Perfect Matching (MWPM), and other ML decoders, thereby achieving best logical error rates. Moreover, the transfer learning can save over 10x of training cost.
QuEst: Graph Transformer for Quantum Circuit Reliability Estimation
Oct 30, 2022Abstract:Among different quantum algorithms, PQC for QML show promises on near-term devices. To facilitate the QML and PQC research, a recent python library called TorchQuantum has been released. It can construct, simulate, and train PQC for machine learning tasks with high speed and convenient debugging supports. Besides quantum for ML, we want to raise the community's attention on the reversed direction: ML for quantum. Specifically, the TorchQuantum library also supports using data-driven ML models to solve problems in quantum system research, such as predicting the impact of quantum noise on circuit fidelity and improving the quantum circuit compilation efficiency. This paper presents a case study of the ML for quantum part. Since estimating the noise impact on circuit reliability is an essential step toward understanding and mitigating noise, we propose to leverage classical ML to predict noise impact on circuit fidelity. Inspired by the natural graph representation of quantum circuits, we propose to leverage a graph transformer model to predict the noisy circuit fidelity. We firstly collect a large dataset with a variety of quantum circuits and obtain their fidelity on noisy simulators and real machines. Then we embed each circuit into a graph with gate and noise properties as node features, and adopt a graph transformer to predict the fidelity. Evaluated on 5 thousand random and algorithm circuits, the graph transformer predictor can provide accurate fidelity estimation with RMSE error 0.04 and outperform a simple neural network-based model by 0.02 on average. It can achieve 0.99 and 0.95 R$^2$ scores for random and algorithm circuits, respectively. Compared with circuit simulators, the predictor has over 200X speedup for estimating the fidelity.
PAN: Pulse Ansatz on NISQ Machines
Aug 02, 2022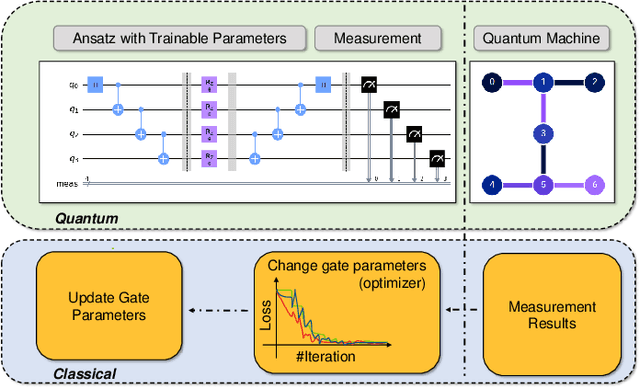
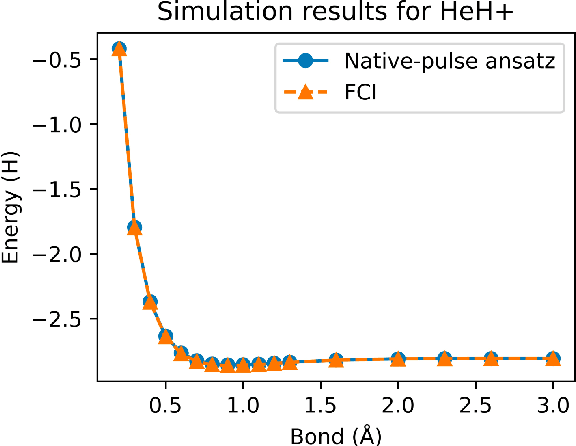
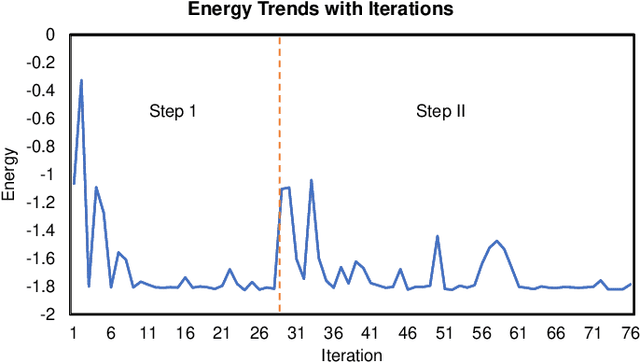
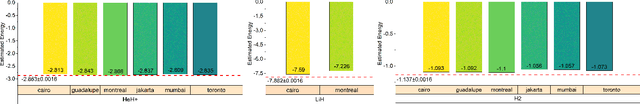
Abstract:Variational quantum algorithms (VQAs) have demonstrated great potentials in the NISQ era. In the workflow of VQA, the parameters of ansatz are iteratively updated to approximate the desired quantum states. We have seen various efforts to draft better ansatz with less gates. In quantum computers, the gate ansatz will eventually be transformed into control signals such as microwave pulses on transmons. And the control pulses need elaborate calibration to minimize the errors such as over-rotation and under-rotation. In the case of VQAs, this procedure will introduce redundancy, but the variational properties of VQAs can naturally handle problems of over-rotation and under-rotation by updating the amplitude and frequency parameters. Therefore, we propose PAN, a native-pulse ansatz generator framework for VQAs. We generate native-pulse ansatz with trainable parameters for amplitudes and frequencies. In our proposed PAN, we are tuning parametric pulses, which are natively supported on NISQ computers. Considering that parameter-shift rules do not hold for native-pulse ansatz, we need to deploy non-gradient optimizers. To constrain the number of parameters sent to the optimizer, we adopt a progressive way to generate our native-pulse ansatz. Experiments are conducted on both simulators and quantum devices to validate our methods. When adopted on NISQ machines, PAN obtained improved the performance with decreased latency by an average of 86%. PAN is able to achieve 99.336% and 96.482% accuracy for VQE tasks on H2 and HeH+ respectively, even with considerable noises in NISQ machines.
On-chip QNN: Towards Efficient On-Chip Training of Quantum Neural Networks
Feb 26, 2022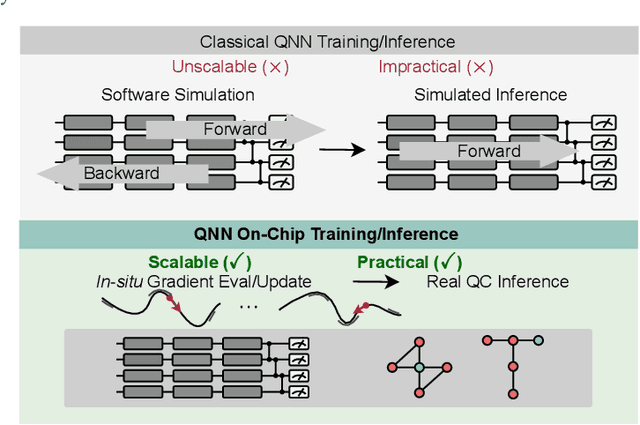
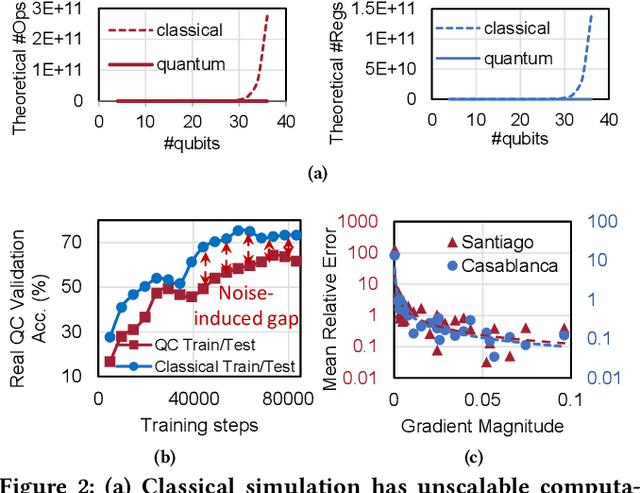
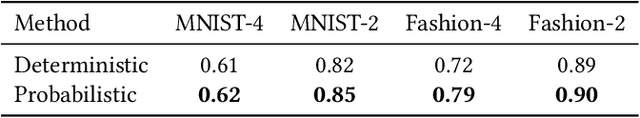
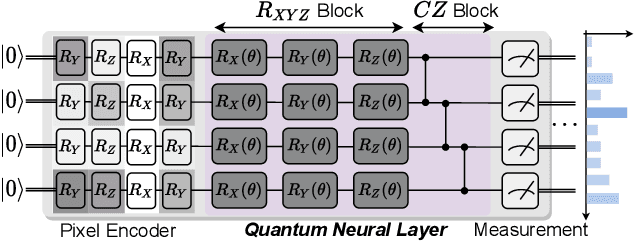
Abstract:Quantum Neural Network (QNN) is drawing increasing research interest thanks to its potential to achieve quantum advantage on near-term Noisy Intermediate Scale Quantum (NISQ) hardware. In order to achieve scalable QNN learning, the training process needs to be offloaded to real quantum machines instead of using exponential-cost classical simulators. One common approach to obtain QNN gradients is parameter shift whose cost scales linearly with the number of qubits. We present On-chip QNN, the first experimental demonstration of practical on-chip QNN training with parameter shift. Nevertheless, we find that due to the significant quantum errors (noises) on real machines, gradients obtained from naive parameter shift have low fidelity and thus degrade the training accuracy. To this end, we further propose probabilistic gradient pruning to firstly identify gradients with potentially large errors and then remove them. Specifically, small gradients have larger relative errors than large ones, thus having a higher probability to be pruned. We perform extensive experiments on 5 classification tasks with 5 real quantum machines. The results demonstrate that our on-chip training achieves over 90% and 60% accuracy for 2-class and 4-class image classification tasks. The probabilistic gradient pruning brings up to 7% QNN accuracy improvements over no pruning. Overall, we successfully obtain similar on-chip training accuracy compared with noise-free simulation but have much better training scalability. The code for parameter shift on-chip training is available in the TorchQuantum library.
RoQNN: Noise-Aware Training for Robust Quantum Neural Networks
Oct 21, 2021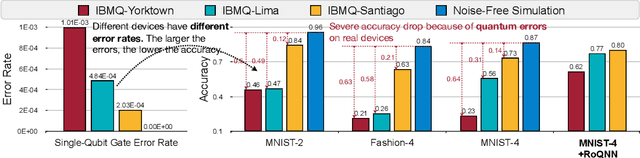
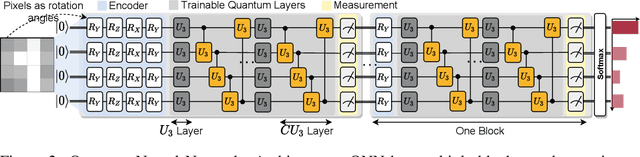
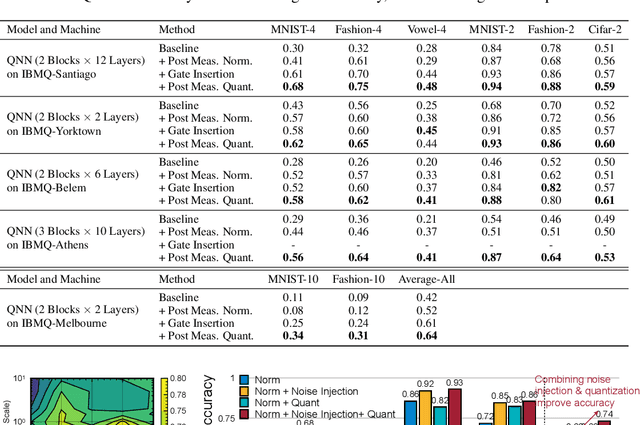
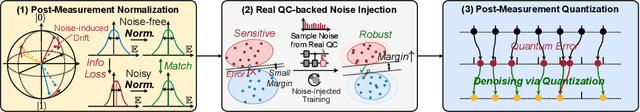
Abstract:Quantum Neural Network (QNN) is a promising application towards quantum advantage on near-term quantum hardware. However, due to the large quantum noises (errors), the performance of QNN models has a severe degradation on real quantum devices. For example, the accuracy gap between noise-free simulation and noisy results on IBMQ-Yorktown for MNIST-4 classification is over 60%. Existing noise mitigation methods are general ones without leveraging unique characteristics of QNN and are only applicable to inference; on the other hand, existing QNN work does not consider noise effect. To this end, we present RoQNN, a QNN-specific framework to perform noise-aware optimizations in both training and inference stages to improve robustness. We analytically deduct and experimentally observe that the effect of quantum noise to QNN measurement outcome is a linear map from noise-free outcome with a scaling and a shift factor. Motivated by that, we propose post-measurement normalization to mitigate the feature distribution differences between noise-free and noisy scenarios. Furthermore, to improve the robustness against noise, we propose noise injection to the training process by inserting quantum error gates to QNN according to realistic noise models of quantum hardware. Finally, post-measurement quantization is introduced to quantize the measurement outcomes to discrete values, achieving the denoising effect. Extensive experiments on 8 classification tasks using 6 quantum devices demonstrate that RoQNN improves accuracy by up to 43%, and achieves over 94% 2-class, 80% 4-class, and 34% 10-class MNIST classification accuracy measured on real quantum computers. We also open-source our PyTorch library for construction and noise-aware training of QNN at https://github.com/mit-han-lab/pytorch-quantum .
QuantumNAS: Noise-Adaptive Search for Robust Quantum Circuits
Aug 02, 2021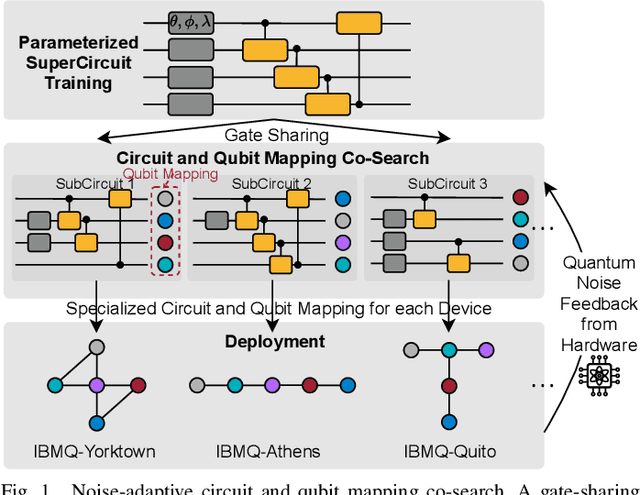
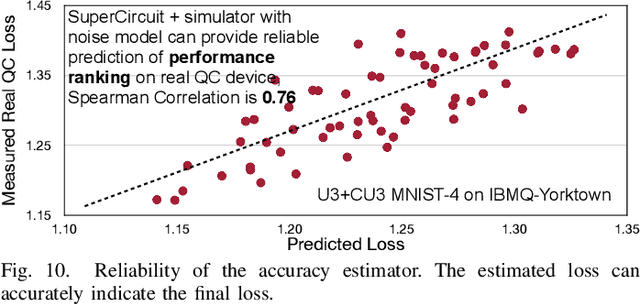
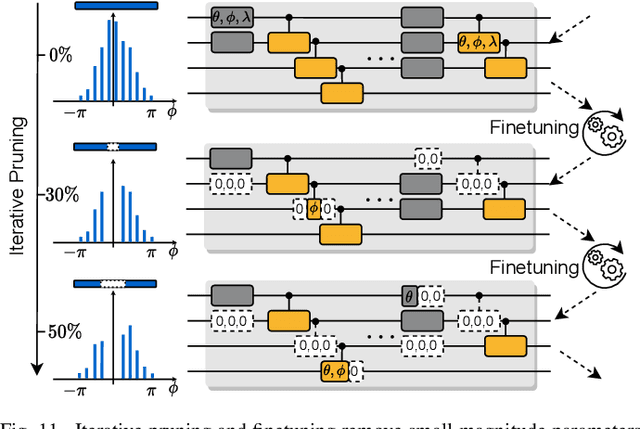
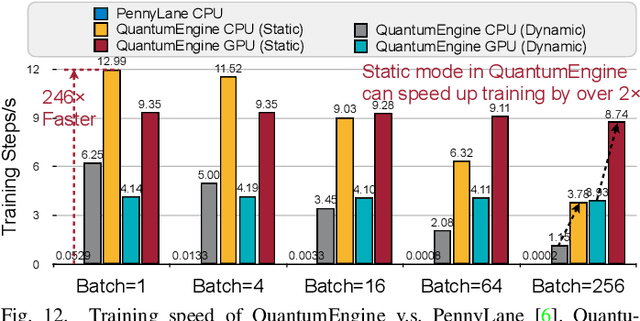
Abstract:Quantum noise is the key challenge in Noisy Intermediate-Scale Quantum (NISQ) computers. Previous work for mitigating noise has primarily focused on gate-level or pulse-level noise-adaptive compilation. However, limited research efforts have explored a higher level of optimization by making the quantum circuits themselves resilient to noise. We propose QuantumNAS, a comprehensive framework for noise-adaptive co-search of the variational circuit and qubit mapping. Variational quantum circuits are a promising approach for constructing QML and quantum simulation. However, finding the best variational circuit and its optimal parameters is challenging due to the large design space and parameter training cost. We propose to decouple the circuit search and parameter training by introducing a novel SuperCircuit. The SuperCircuit is constructed with multiple layers of pre-defined parameterized gates and trained by iteratively sampling and updating the parameter subsets (SubCircuits) of it. It provides an accurate estimation of SubCircuits performance trained from scratch. Then we perform an evolutionary co-search of SubCircuit and its qubit mapping. The SubCircuit performance is estimated with parameters inherited from SuperCircuit and simulated with real device noise models. Finally, we perform iterative gate pruning and finetuning to remove redundant gates. Extensively evaluated with 12 QML and VQE benchmarks on 10 quantum comput, QuantumNAS significantly outperforms baselines. For QML, QuantumNAS is the first to demonstrate over 95% 2-class, 85% 4-class, and 32% 10-class classification accuracy on real QC. It also achieves the lowest eigenvalue for VQE tasks on H2, H2O, LiH, CH4, BeH2 compared with UCCSD. We also open-source QuantumEngine (https://github.com/mit-han-lab/pytorch-quantum) for fast training of parameterized quantum circuits to facilitate future research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge