Junhuan Yang
A Novel Diffusion Model for Pairwise Geoscience Data Generation with Unbalanced Training Dataset
Jan 01, 2025



Abstract:Recently, the advent of generative AI technologies has made transformational impacts on our daily lives, yet its application in scientific applications remains in its early stages. Data scarcity is a major, well-known barrier in data-driven scientific computing, so physics-guided generative AI holds significant promise. In scientific computing, most tasks study the conversion of multiple data modalities to describe physical phenomena, for example, spatial and waveform in seismic imaging, time and frequency in signal processing, and temporal and spectral in climate modeling; as such, multi-modal pairwise data generation is highly required instead of single-modal data generation, which is usually used in natural images (e.g., faces, scenery). Moreover, in real-world applications, the unbalance of available data in terms of modalities commonly exists; for example, the spatial data (i.e., velocity maps) in seismic imaging can be easily simulated, but real-world seismic waveform is largely lacking. While the most recent efforts enable the powerful diffusion model to generate multi-modal data, how to leverage the unbalanced available data is still unclear. In this work, we use seismic imaging in subsurface geophysics as a vehicle to present ``UB-Diff'', a novel diffusion model for multi-modal paired scientific data generation. One major innovation is a one-in-two-out encoder-decoder network structure, which can ensure pairwise data is obtained from a co-latent representation. Then, the co-latent representation will be used by the diffusion process for pairwise data generation. Experimental results on the OpenFWI dataset show that UB-Diff significantly outperforms existing techniques in terms of Fr\'{e}chet Inception Distance (FID) score and pairwise evaluation, indicating the generation of reliable and useful multi-modal pairwise data.
Data-Algorithm-Architecture Co-Optimization for Fair Neural Networks on Skin Lesion Dataset
Jul 18, 2024Abstract:As Artificial Intelligence (AI) increasingly integrates into our daily lives, fairness has emerged as a critical concern, particularly in medical AI, where datasets often reflect inherent biases due to social factors like the underrepresentation of marginalized communities and socioeconomic barriers to data collection. Traditional approaches to mitigating these biases have focused on data augmentation and the development of fairness-aware training algorithms. However, this paper argues that the architecture of neural networks, a core component of Machine Learning (ML), plays a crucial role in ensuring fairness. We demonstrate that addressing fairness effectively requires a holistic approach that simultaneously considers data, algorithms, and architecture. Utilizing Automated ML (AutoML) technology, specifically Neural Architecture Search (NAS), we introduce a novel framework, BiaslessNAS, designed to achieve fair outcomes in analyzing skin lesion datasets. BiaslessNAS incorporates fairness considerations at every stage of the NAS process, leading to the identification of neural networks that are not only more accurate but also significantly fairer. Our experiments show that BiaslessNAS achieves a 2.55% increase in accuracy and a 65.50% improvement in fairness compared to traditional NAS methods, underscoring the importance of integrating fairness into neural network architecture for better outcomes in medical AI applications.
APS-USCT: Ultrasound Computed Tomography on Sparse Data via AI-Physic Synergy
Jul 18, 2024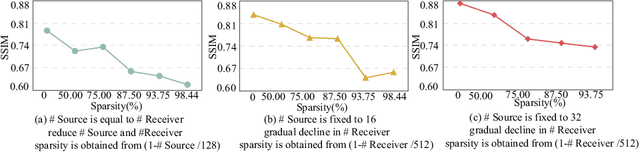
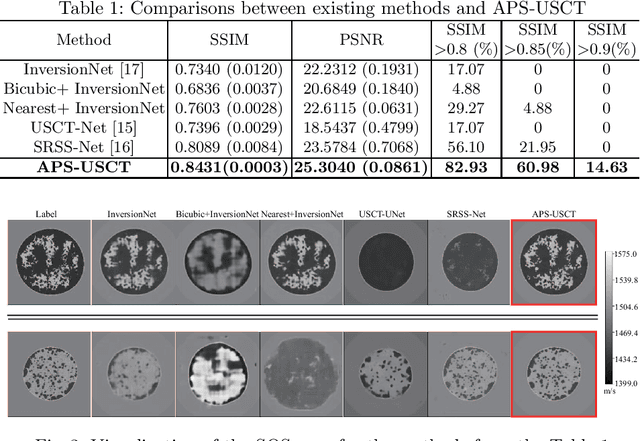
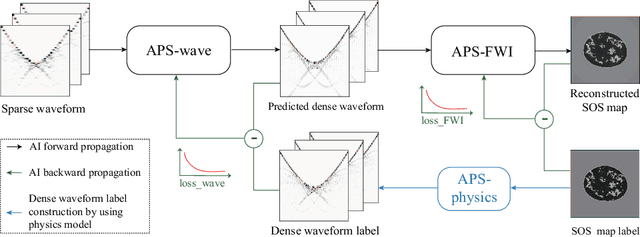
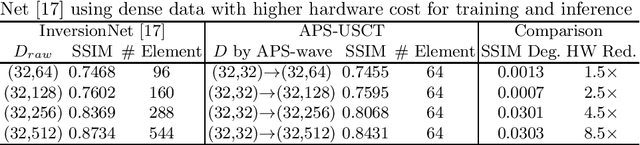
Abstract:Ultrasound computed tomography (USCT) is a promising technique that achieves superior medical imaging reconstruction resolution by fully leveraging waveform information, outperforming conventional ultrasound methods. Despite its advantages, high-quality USCT reconstruction relies on extensive data acquisition by a large number of transducers, leading to increased costs, computational demands, extended patient scanning times, and manufacturing complexities. To mitigate these issues, we propose a new USCT method called APS-USCT, which facilitates imaging with sparse data, substantially reducing dependence on high-cost dense data acquisition. Our APS-USCT method consists of two primary components: APS-wave and APS-FWI. The APS-wave component, an encoder-decoder system, preprocesses the waveform data, converting sparse data into dense waveforms to augment sample density prior to reconstruction. The APS-FWI component, utilizing the InversionNet, directly reconstructs the speed of sound (SOS) from the ultrasound waveform data. We further improve the model's performance by incorporating Squeeze-and-Excitation (SE) Blocks and source encoding techniques. Testing our method on a breast cancer dataset yielded promising results. It demonstrated outstanding performance with an average Structural Similarity Index (SSIM) of 0.8431. Notably, over 82% of samples achieved an SSIM above 0.8, with nearly 61% exceeding 0.85, highlighting the significant potential of our approach in improving USCT image reconstruction by efficiently utilizing sparse data.
A Physics-guided Generative AI Toolkit for Geophysical Monitoring
Jan 06, 2024Abstract:Full-waveform inversion (FWI) plays a vital role in geoscience to explore the subsurface. It utilizes the seismic wave to image the subsurface velocity map. As the machine learning (ML) technique evolves, the data-driven approaches using ML for FWI tasks have emerged, offering enhanced accuracy and reduced computational cost compared to traditional physics-based methods. However, a common challenge in geoscience, the unprivileged data, severely limits ML effectiveness. The issue becomes even worse during model pruning, a step essential in geoscience due to environmental complexities. To tackle this, we introduce the EdGeo toolkit, which employs a diffusion-based model guided by physics principles to generate high-fidelity velocity maps. The toolkit uses the acoustic wave equation to generate corresponding seismic waveform data, facilitating the fine-tuning of pruned ML models. Our results demonstrate significant improvements in SSIM scores and reduction in both MAE and MSE across various pruning ratios. Notably, the ML model fine-tuned using data generated by EdGeo yields superior quality of velocity maps, especially in representing unprivileged features, outperforming other existing methods.
Muffin: A Framework Toward Multi-Dimension AI Fairness by Uniting Off-the-Shelf Models
Aug 26, 2023



Abstract:Model fairness (a.k.a., bias) has become one of the most critical problems in a wide range of AI applications. An unfair model in autonomous driving may cause a traffic accident if corner cases (e.g., extreme weather) cannot be fairly regarded; or it will incur healthcare disparities if the AI model misdiagnoses a certain group of people (e.g., brown and black skin). In recent years, there have been emerging research works on addressing unfairness, and they mainly focus on a single unfair attribute, like skin tone; however, real-world data commonly have multiple attributes, among which unfairness can exist in more than one attribute, called 'multi-dimensional fairness'. In this paper, we first reveal a strong correlation between the different unfair attributes, i.e., optimizing fairness on one attribute will lead to the collapse of others. Then, we propose a novel Multi-Dimension Fairness framework, namely Muffin, which includes an automatic tool to unite off-the-shelf models to improve the fairness on multiple attributes simultaneously. Case studies on dermatology datasets with two unfair attributes show that the existing approach can achieve 21.05% fairness improvement on the first attribute while it makes the second attribute unfair by 1.85%. On the other hand, the proposed Muffin can unite multiple models to achieve simultaneously 26.32% and 20.37% fairness improvement on both attributes; meanwhile, it obtains 5.58% accuracy gain.
The Larger The Fairer? Small Neural Networks Can Achieve Fairness for Edge Devices
Feb 23, 2022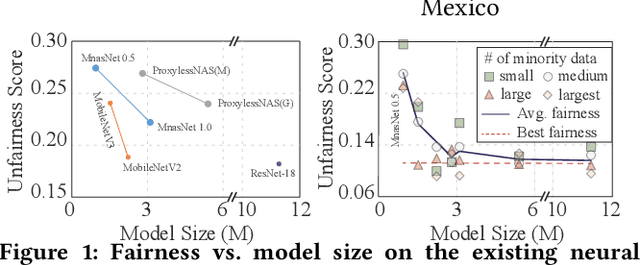
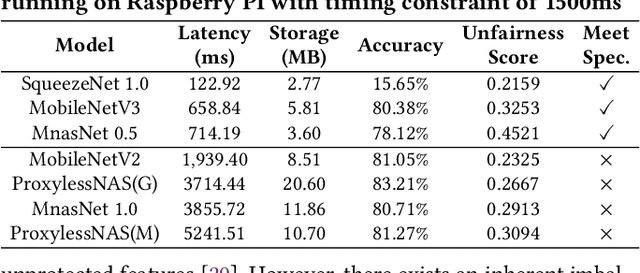
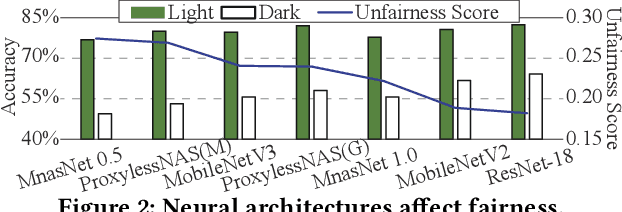
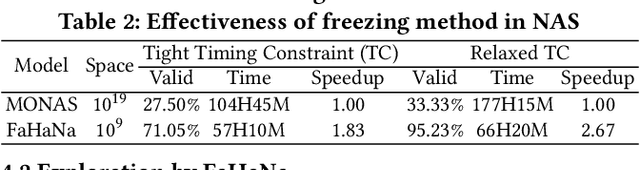
Abstract:Along with the progress of AI democratization, neural networks are being deployed more frequently in edge devices for a wide range of applications. Fairness concerns gradually emerge in many applications, such as face recognition and mobile medical. One fundamental question arises: what will be the fairest neural architecture for edge devices? By examining the existing neural networks, we observe that larger networks typically are fairer. But, edge devices call for smaller neural architectures to meet hardware specifications. To address this challenge, this work proposes a novel Fairness- and Hardware-aware Neural architecture search framework, namely FaHaNa. Coupled with a model freezing approach, FaHaNa can efficiently search for neural networks with balanced fairness and accuracy, while guaranteed to meet hardware specifications. Results show that FaHaNa can identify a series of neural networks with higher fairness and accuracy on a dermatology dataset. Target edge devices, FaHaNa finds a neural architecture with slightly higher accuracy, 5.28x smaller size, 15.14% higher fairness score, compared with MobileNetV2; meanwhile, on Raspberry PI and Odroid XU-4, it achieves 5.75x and 5.79x speedup.
Automated Architecture Search for Brain-inspired Hyperdimensional Computing
Feb 11, 2022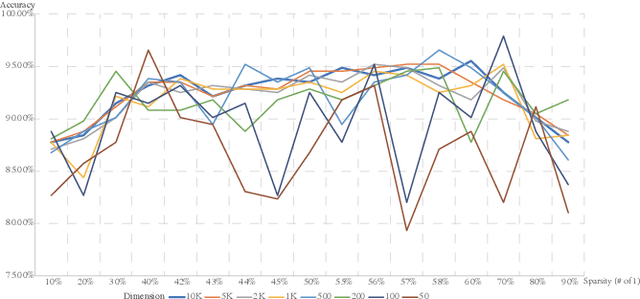
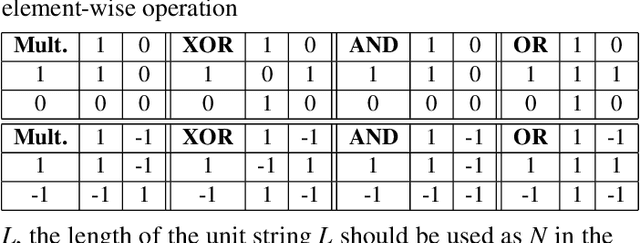
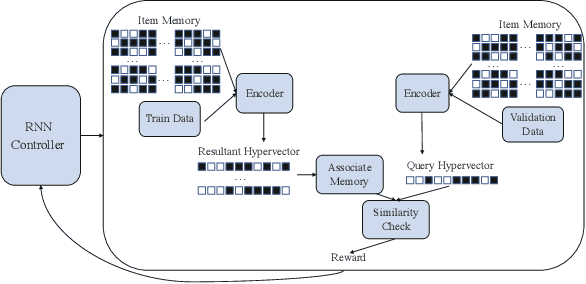
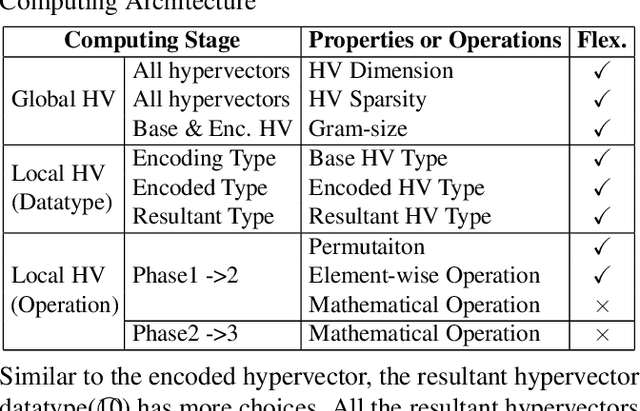
Abstract:This paper represents the first effort to explore an automated architecture search for hyperdimensional computing (HDC), a type of brain-inspired neural network. Currently, HDC design is largely carried out in an application-specific ad-hoc manner, which significantly limits its application. Furthermore, the approach leads to inferior accuracy and efficiency, which suggests that HDC cannot perform competitively against deep neural networks. Herein, we present a thorough study to formulate an HDC architecture search space. On top of the search space, we apply reinforcement-learning to automatically explore the HDC architectures. The searched HDC architectures show competitive performance on case studies involving a drug discovery dataset and a language recognition task. On the Clintox dataset, which tries to learn features from developed drugs that passed/failed clinical trials for toxicity reasons, the searched HDC architecture obtains the state-of-the-art ROC-AUC scores, which are 0.80% higher than the manually designed HDC and 9.75% higher than conventional neural networks. Similar results are achieved on the language recognition task, with 1.27% higher performance than conventional methods.
Detecting Gender Bias in Transformer-based Models: A Case Study on BERT
Oct 15, 2021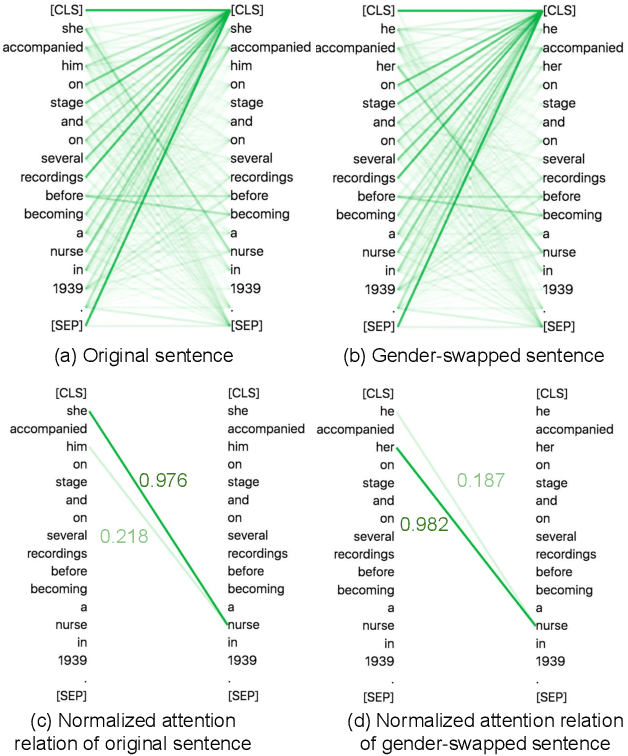
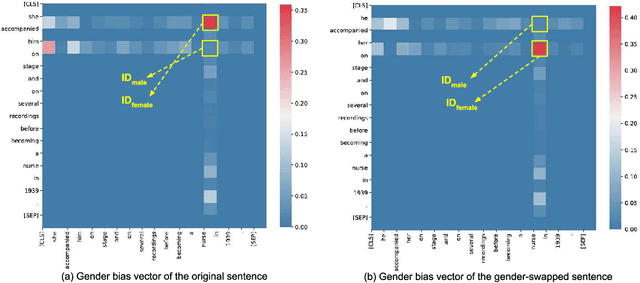
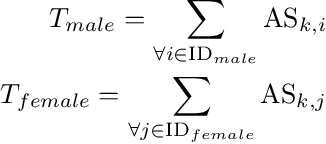
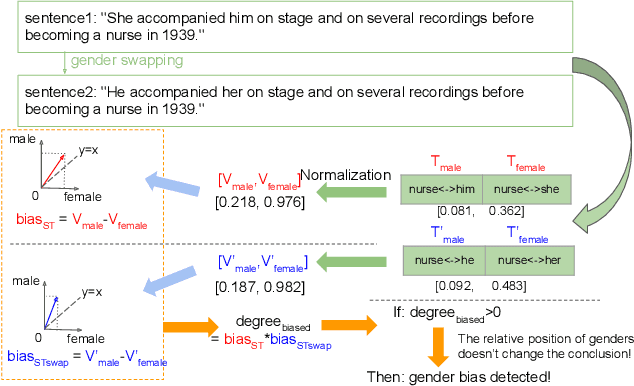
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel gender bias detection method by utilizing attention map for transformer-based models. We 1) give an intuitive gender bias judgement method by comparing the different relation degree between the genders and the occupation according to the attention scores, 2) design a gender bias detector by modifying the attention module, 3) insert the gender bias detector into different positions of the model to present the internal gender bias flow, and 4) draw the consistent gender bias conclusion by scanning the entire Wikipedia, a BERT pretraining dataset. We observe that 1) the attention matrices, Wq and Wk introduce much more gender bias than other modules (including the embedding layer) and 2) the bias degree changes periodically inside of the model (attention matrix Q, K, V, and the remaining part of the attention layer (including the fully-connected layer, the residual connection, and the layer normalization module) enhance the gender bias while the averaged attentions reduces the bias).
Can Noise on Qubits Be Learned in Quantum Neural Network? A Case Study on QuantumFlow
Sep 08, 2021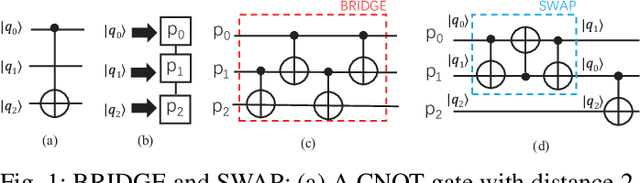
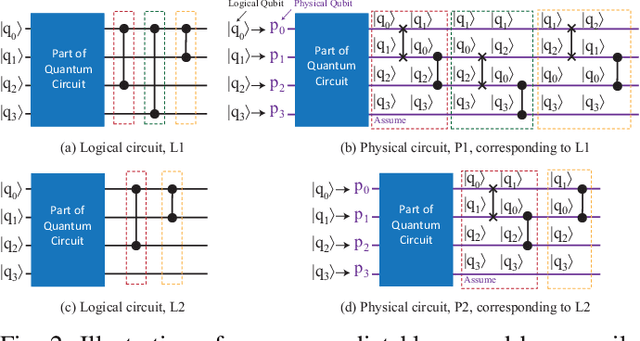
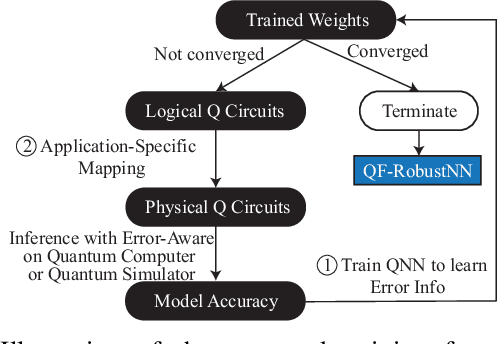
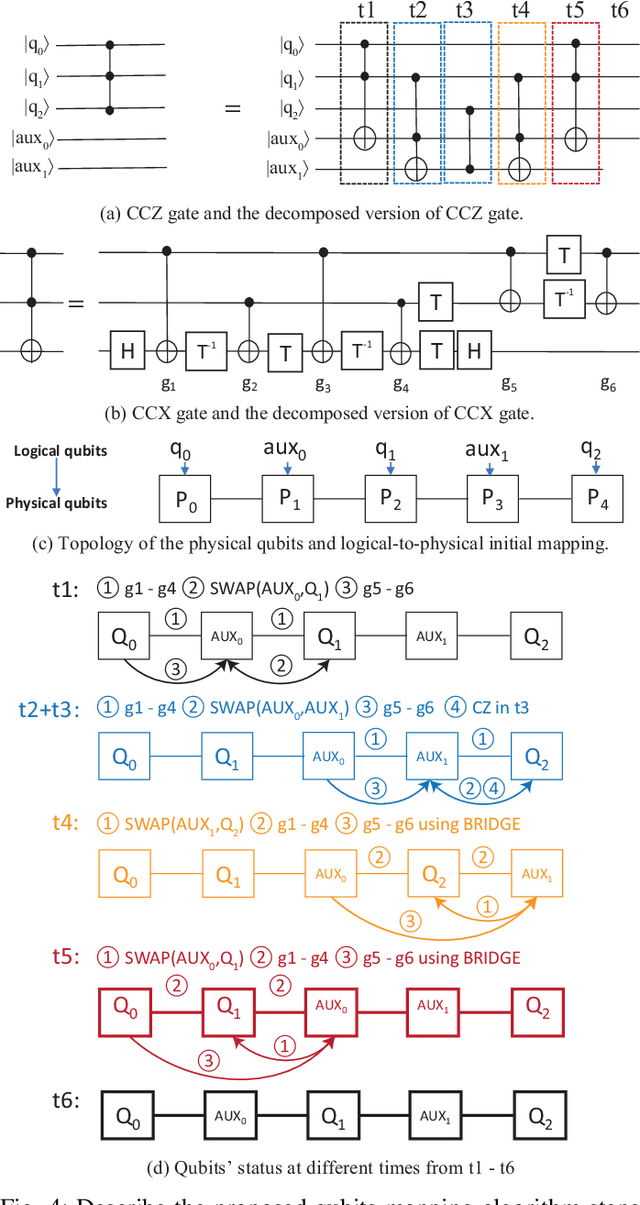
Abstract:In the noisy intermediate-scale quantum (NISQ) era, one of the key questions is how to deal with the high noise level existing in physical quantum bits (qubits). Quantum error correction is promising but requires an extensive number (e.g., over 1,000) of physical qubits to create one "perfect" qubit, exceeding the capacity of the existing quantum computers. This paper aims to tackle the noise issue from another angle: instead of creating perfect qubits for general quantum algorithms, we investigate the potential to mitigate the noise issue for dedicate algorithms. Specifically, this paper targets quantum neural network (QNN), and proposes to learn the errors in the training phase, so that the identified QNN model can be resilient to noise. As a result, the implementation of QNN needs no or a small number of additional physical qubits, which is more realistic for the near-term quantum computers. To achieve this goal, an application-specific compiler is essential: on the one hand, the error cannot be learned if the mapping from logical qubits to physical qubits exists randomness; on the other hand, the compiler needs to be efficient so that the lengthy training procedure can be completed in a reasonable time. In this paper, we utilize the recent QNN framework, QuantumFlow, as a case study. Experimental results show that the proposed approach can optimize QNN models for different errors in qubits, achieving up to 28% accuracy improvement compared with the model obtained by the error-agnostic training.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge