Ruixuan Wang
DCAC: Dynamic Class-Aware Cache Creates Stronger Out-of-Distribution Detectors
Jan 18, 2026Abstract:Out-of-distribution (OOD) detection remains a fundamental challenge for deep neural networks, particularly due to overconfident predictions on unseen OOD samples during testing. We reveal a key insight: OOD samples predicted as the same class, or given high probabilities for it, are visually more similar to each other than to the true in-distribution (ID) samples. Motivated by this class-specific observation, we propose DCAC (Dynamic Class-Aware Cache), a training-free, test-time calibration module that maintains separate caches for each ID class to collect high-entropy samples and calibrate the raw predictions of input samples. DCAC leverages cached visual features and predicted probabilities through a lightweight two-layer module to mitigate overconfident predictions on OOD samples. This module can be seamlessly integrated with various existing OOD detection methods across both unimodal and vision-language models while introducing minimal computational overhead. Extensive experiments on multiple OOD benchmarks demonstrate that DCAC significantly enhances existing methods, achieving substantial improvements, i.e., reducing FPR95 by 6.55% when integrated with ASH-S on ImageNet OOD benchmark.
Representation Calibration and Uncertainty Guidance for Class-Incremental Learning based on Vision Language Model
Dec 10, 2025Abstract:Class-incremental learning requires a learning system to continually learn knowledge of new classes and meanwhile try to preserve previously learned knowledge of old classes. As current state-of-the-art methods based on Vision-Language Models (VLMs) still suffer from the issue of differentiating classes across learning tasks. Here a novel VLM-based continual learning framework for image classification is proposed. In this framework, task-specific adapters are added to the pre-trained and frozen image encoder to learn new knowledge, and a novel cross-task representation calibration strategy based on a mixture of light-weight projectors is used to help better separate all learned classes in a unified feature space, alleviating class confusion across tasks. In addition, a novel inference strategy guided by prediction uncertainty is developed to more accurately select the most appropriate image feature for class prediction. Extensive experiments on multiple datasets under various settings demonstrate the superior performance of our method compared to existing ones.
Hierarchical Vision-Language Learning for Medical Out-of-Distribution Detection
Aug 25, 2025


Abstract:In trustworthy medical diagnosis systems, integrating out-of-distribution (OOD) detection aims to identify unknown diseases in samples, thereby mitigating the risk of misdiagnosis. In this study, we propose a novel OOD detection framework based on vision-language models (VLMs), which integrates hierarchical visual information to cope with challenging unknown diseases that resemble known diseases. Specifically, a cross-scale visual fusion strategy is proposed to couple visual embeddings from multiple scales. This enriches the detailed representation of medical images and thus improves the discrimination of unknown diseases. Moreover, a cross-scale hard pseudo-OOD sample generation strategy is proposed to benefit OOD detection maximally. Experimental evaluations on three public medical datasets support that the proposed framework achieves superior OOD detection performance compared to existing methods. The source code is available at https://openi.pcl.ac.cn/OpenMedIA/HVL.
Decoupling Continual Semantic Segmentation
Aug 07, 2025Abstract:Continual Semantic Segmentation (CSS) requires learning new classes without forgetting previously acquired knowledge, addressing the fundamental challenge of catastrophic forgetting in dense prediction tasks. However, existing CSS methods typically employ single-stage encoder-decoder architectures where segmentation masks and class labels are tightly coupled, leading to interference between old and new class learning and suboptimal retention-plasticity balance. We introduce DecoupleCSS, a novel two-stage framework for CSS. By decoupling class-aware detection from class-agnostic segmentation, DecoupleCSS enables more effective continual learning, preserving past knowledge while learning new classes. The first stage leverages pre-trained text and image encoders, adapted using LoRA, to encode class-specific information and generate location-aware prompts. In the second stage, the Segment Anything Model (SAM) is employed to produce precise segmentation masks, ensuring that segmentation knowledge is shared across both new and previous classes. This approach improves the balance between retention and adaptability in CSS, achieving state-of-the-art performance across a variety of challenging tasks. Our code is publicly available at: https://github.com/euyis1019/Decoupling-Continual-Semantic-Segmentation.
Class Incremental Learning with Task-Specific Batch Normalization and Out-of-Distribution Detection
Nov 01, 2024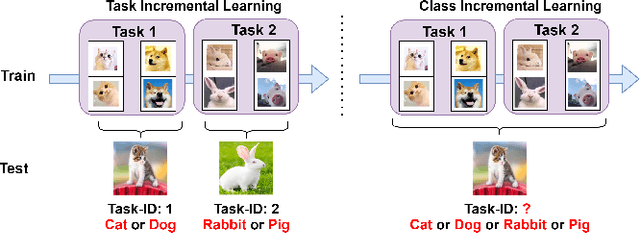
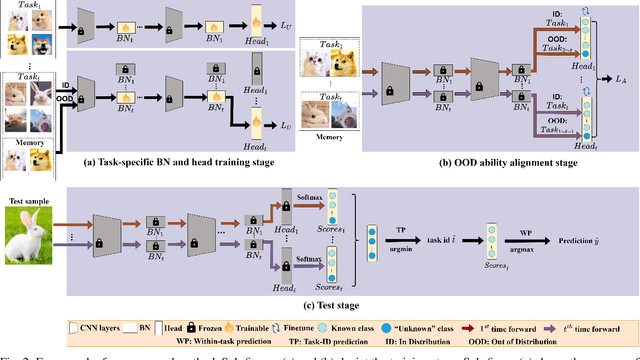
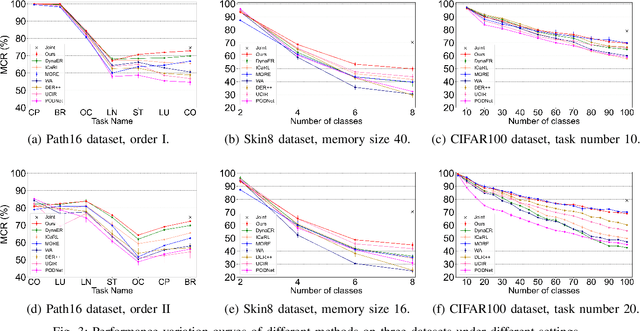
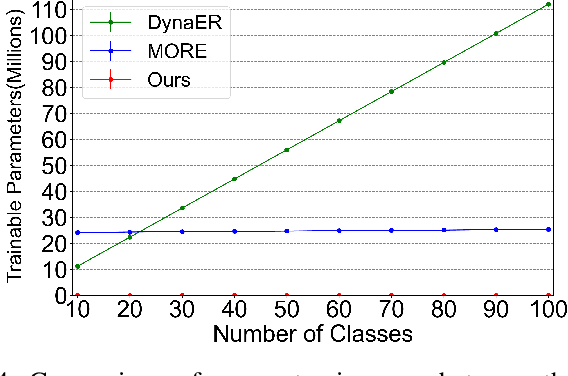
Abstract:This study focuses on incremental learning for image classification, exploring how to reduce catastrophic forgetting of all learned knowledge when access to old data is restricted due to memory or privacy constraints. The challenge of incremental learning lies in achieving an optimal balance between plasticity, the ability to learn new knowledge, and stability, the ability to retain old knowledge. Based on whether the task identifier (task-ID) of an image can be obtained during the test stage, incremental learning for image classifcation is divided into two main paradigms, which are task incremental learning (TIL) and class incremental learning (CIL). The TIL paradigm has access to the task-ID, allowing it to use multiple task-specific classification heads selected based on the task-ID. Consequently, in CIL, where the task-ID is unavailable, TIL methods must predict the task-ID to extend their application to the CIL paradigm. Our previous method for TIL adds task-specific batch normalization and classification heads incrementally. This work extends the method by predicting task-ID through an "unknown" class added to each classification head. The head with the lowest "unknown" probability is selected, enabling task-ID prediction and making the method applicable to CIL. The task-specific batch normalization (BN) modules effectively adjust the distribution of output feature maps across different tasks, enhancing the model's plasticity.Moreover, since BN has much fewer parameters compared to convolutional kernels, by only modifying the BN layers as new tasks arrive, the model can effectively manage parameter growth while ensuring stability across tasks. The innovation of this study lies in the first-time introduction of task-specific BN into CIL and verifying the feasibility of extending TIL methods to CIL through task-ID prediction with state-of-the-art performance on multiple datasets.
Generalizable Two-Branch Framework for Image Class-Incremental Learning
Mar 13, 2024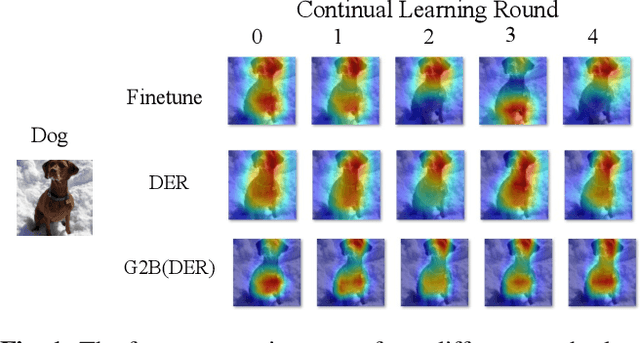
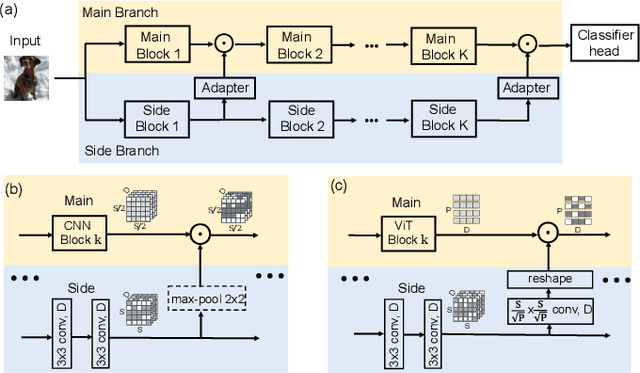
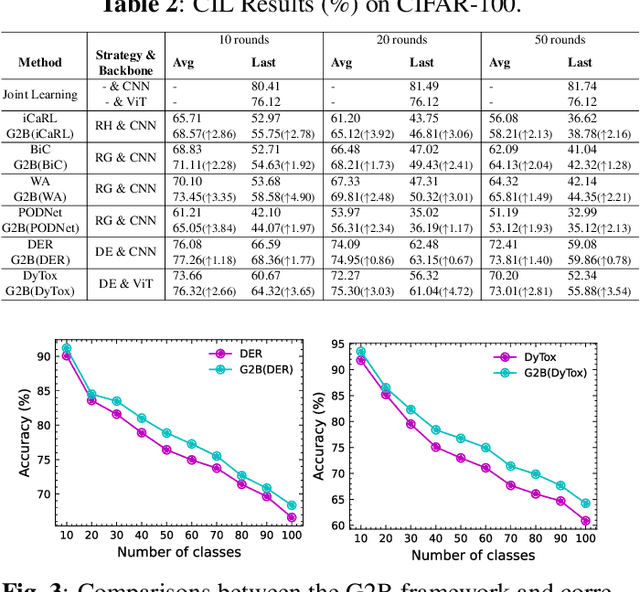
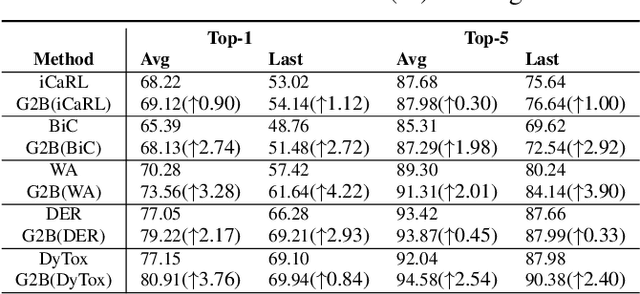
Abstract:Deep neural networks often severely forget previously learned knowledge when learning new knowledge. Various continual learning (CL) methods have been proposed to handle such a catastrophic forgetting issue from different perspectives and achieved substantial improvements. In this paper, a novel two-branch continual learning framework is proposed to further enhance most existing CL methods. Specifically, the main branch can be any existing CL model and the newly introduced side branch is a lightweight convolutional network. The output of each main branch block is modulated by the output of the corresponding side branch block. Such a simple two-branch model can then be easily implemented and learned with the vanilla optimization setting without whistles and bells. Extensive experiments with various settings on multiple image datasets show that the proposed framework yields consistent improvements over state-of-the-art methods.
Intensive Vision-guided Network for Radiology Report Generation
Feb 06, 2024Abstract:Automatic radiology report generation is booming due to its huge application potential for the healthcare industry. However, existing computer vision and natural language processing approaches to tackle this problem are limited in two aspects. First, when extracting image features, most of them neglect multi-view reasoning in vision and model single-view structure of medical images, such as space-view or channel-view. However, clinicians rely on multi-view imaging information for comprehensive judgment in daily clinical diagnosis. Second, when generating reports, they overlook context reasoning with multi-modal information and focus on pure textual optimization utilizing retrieval-based methods. We aim to address these two issues by proposing a model that better simulates clinicians' perspectives and generates more accurate reports. Given the above limitation in feature extraction, we propose a Globally-intensive Attention (GIA) module in the medical image encoder to simulate and integrate multi-view vision perception. GIA aims to learn three types of vision perception: depth view, space view, and pixel view. On the other hand, to address the above problem in report generation, we explore how to involve multi-modal signals to generate precisely matched reports, i.e., how to integrate previously predicted words with region-aware visual content in next word prediction. Specifically, we design a Visual Knowledge-guided Decoder (VKGD), which can adaptively consider how much the model needs to rely on visual information and previously predicted text to assist next word prediction. Hence, our final Intensive Vision-guided Network (IVGN) framework includes a GIA-guided Visual Encoder and the VKGD. Experiments on two commonly-used datasets IU X-Ray and MIMIC-CXR demonstrate the superior ability of our method compared with other state-of-the-art approaches.
A Target Detection Algorithm in Traffic Scenes Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning
Dec 25, 2023Abstract:This research presents a novel active detection model utilizing deep reinforcement learning to accurately detect traffic objects in real-world scenarios. The model employs a deep Q-network based on LSTM-CNN that identifies and aligns target zones with specific categories of traffic objects through implementing a top-down approach with efficient feature extraction of the environment. The model integrates historical and current actions and observations to make a comprehensive analysis. The design of the state space and reward function takes into account the impact of time steps to enable the model to complete the task in fewer steps. Tests conducted demonstrate the model's proficiency, exhibiting exceptional precision and performance in locating traffic signal lights and speed limit signs. The findings of this study highlight the efficacy and potential of the deep reinforcement learning-based active detection model in traffic-related applications, underscoring its robust detection abilities and promising performance.
Classifier-head Informed Feature Masking and Prototype-based Logit Smoothing for Out-of-Distribution Detection
Oct 27, 2023Abstract:Out-of-distribution (OOD) detection is essential when deploying neural networks in the real world. One main challenge is that neural networks often make overconfident predictions on OOD data. In this study, we propose an effective post-hoc OOD detection method based on a new feature masking strategy and a novel logit smoothing strategy. Feature masking determines the important features at the penultimate layer for each in-distribution (ID) class based on the weights of the ID class in the classifier head and masks the rest features. Logit smoothing computes the cosine similarity between the feature vector of the test sample and the prototype of the predicted ID class at the penultimate layer and uses the similarity as an adaptive temperature factor on the logit to alleviate the network's overconfidence prediction for OOD data. With these strategies, we can reduce feature activation of OOD data and enlarge the gap in OOD score between ID and OOD data. Extensive experiments on multiple standard OOD detection benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness of our method and its compatibility with existing methods, with new state-of-the-art performance achieved from our method. The source code will be released publicly.
Class Attention to Regions of Lesion for Imbalanced Medical Image Recognition
Jul 20, 2023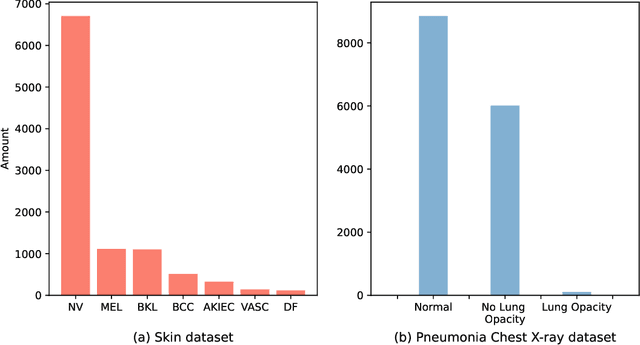
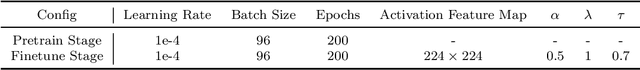
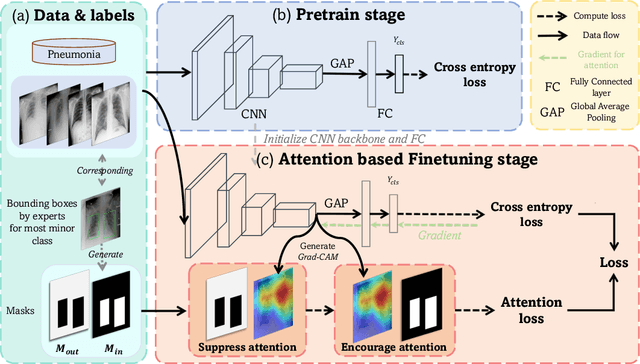
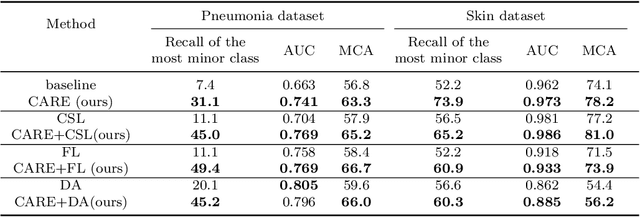
Abstract:Automated medical image classification is the key component in intelligent diagnosis systems. However, most medical image datasets contain plenty of samples of common diseases and just a handful of rare ones, leading to major class imbalances. Currently, it is an open problem in intelligent diagnosis to effectively learn from imbalanced training data. In this paper, we propose a simple yet effective framework, named \textbf{C}lass \textbf{A}ttention to \textbf{RE}gions of the lesion (CARE), to handle data imbalance issues by embedding attention into the training process of \textbf{C}onvolutional \textbf{N}eural \textbf{N}etworks (CNNs). The proposed attention module helps CNNs attend to lesion regions of rare diseases, therefore helping CNNs to learn their characteristics more effectively. In addition, this attention module works only during the training phase and does not change the architecture of the original network, so it can be directly combined with any existing CNN architecture. The CARE framework needs bounding boxes to represent the lesion regions of rare diseases. To alleviate the need for manual annotation, we further developed variants of CARE by leveraging the traditional saliency methods or a pretrained segmentation model for bounding box generation. Results show that the CARE variants with automated bounding box generation are comparable to the original CARE framework with \textit{manual} bounding box annotations. A series of experiments on an imbalanced skin image dataset and a pneumonia dataset indicates that our method can effectively help the network focus on the lesion regions of rare diseases and remarkably improves the classification performance of rare diseases.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge