Zhenyuan Yang
Knowledge Distillation and Dataset Distillation of Large Language Models: Emerging Trends, Challenges, and Future Directions
Apr 20, 2025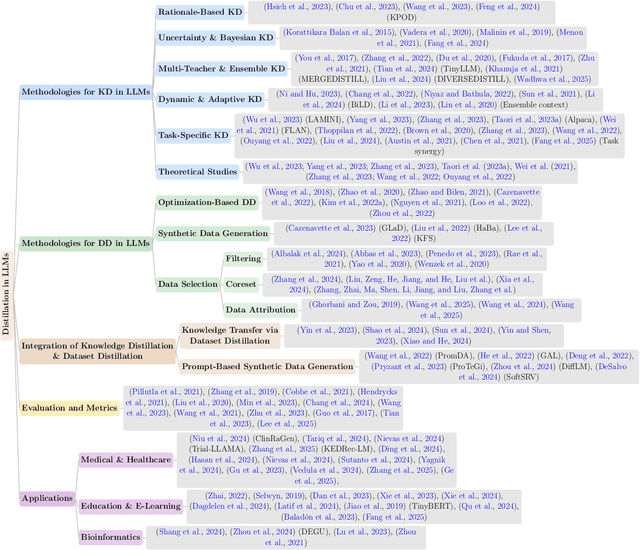
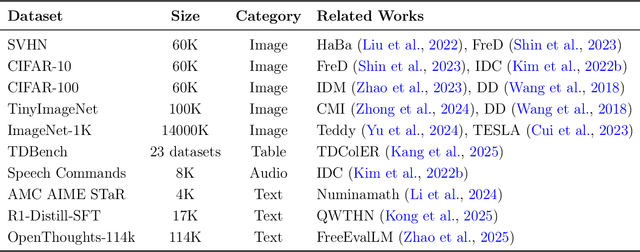
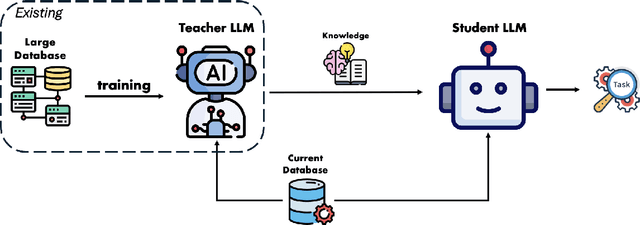
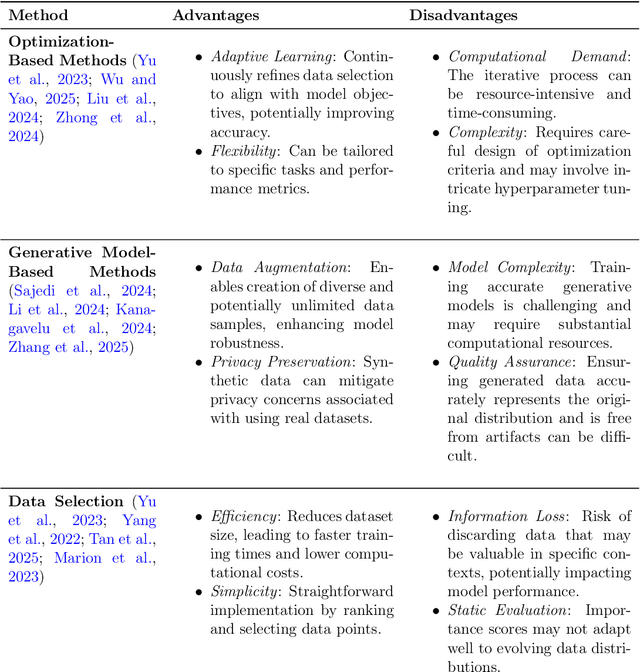
Abstract:The exponential growth of Large Language Models (LLMs) continues to highlight the need for efficient strategies to meet ever-expanding computational and data demands. This survey provides a comprehensive analysis of two complementary paradigms: Knowledge Distillation (KD) and Dataset Distillation (DD), both aimed at compressing LLMs while preserving their advanced reasoning capabilities and linguistic diversity. We first examine key methodologies in KD, such as task-specific alignment, rationale-based training, and multi-teacher frameworks, alongside DD techniques that synthesize compact, high-impact datasets through optimization-based gradient matching, latent space regularization, and generative synthesis. Building on these foundations, we explore how integrating KD and DD can produce more effective and scalable compression strategies. Together, these approaches address persistent challenges in model scalability, architectural heterogeneity, and the preservation of emergent LLM abilities. We further highlight applications across domains such as healthcare and education, where distillation enables efficient deployment without sacrificing performance. Despite substantial progress, open challenges remain in preserving emergent reasoning and linguistic diversity, enabling efficient adaptation to continually evolving teacher models and datasets, and establishing comprehensive evaluation protocols. By synthesizing methodological innovations, theoretical foundations, and practical insights, our survey charts a path toward sustainable, resource-efficient LLMs through the tighter integration of KD and DD principles.
Large Language Models for Bioinformatics
Jan 10, 2025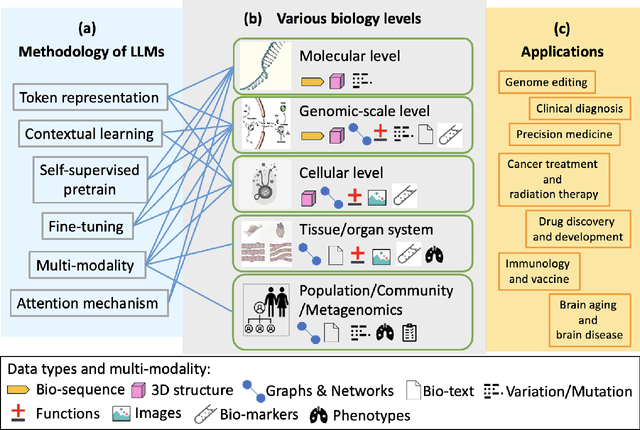
Abstract:With the rapid advancements in large language model (LLM) technology and the emergence of bioinformatics-specific language models (BioLMs), there is a growing need for a comprehensive analysis of the current landscape, computational characteristics, and diverse applications. This survey aims to address this need by providing a thorough review of BioLMs, focusing on their evolution, classification, and distinguishing features, alongside a detailed examination of training methodologies, datasets, and evaluation frameworks. We explore the wide-ranging applications of BioLMs in critical areas such as disease diagnosis, drug discovery, and vaccine development, highlighting their impact and transformative potential in bioinformatics. We identify key challenges and limitations inherent in BioLMs, including data privacy and security concerns, interpretability issues, biases in training data and model outputs, and domain adaptation complexities. Finally, we highlight emerging trends and future directions, offering valuable insights to guide researchers and clinicians toward advancing BioLMs for increasingly sophisticated biological and clinical applications.
Opportunities and Challenges of Large Language Models for Low-Resource Languages in Humanities Research
Dec 09, 2024Abstract:Low-resource languages serve as invaluable repositories of human history, embodying cultural evolution and intellectual diversity. Despite their significance, these languages face critical challenges, including data scarcity and technological limitations, which hinder their comprehensive study and preservation. Recent advancements in large language models (LLMs) offer transformative opportunities for addressing these challenges, enabling innovative methodologies in linguistic, historical, and cultural research. This study systematically evaluates the applications of LLMs in low-resource language research, encompassing linguistic variation, historical documentation, cultural expressions, and literary analysis. By analyzing technical frameworks, current methodologies, and ethical considerations, this paper identifies key challenges such as data accessibility, model adaptability, and cultural sensitivity. Given the cultural, historical, and linguistic richness inherent in low-resource languages, this work emphasizes interdisciplinary collaboration and the development of customized models as promising avenues for advancing research in this domain. By underscoring the potential of integrating artificial intelligence with the humanities to preserve and study humanity's linguistic and cultural heritage, this study fosters global efforts towards safeguarding intellectual diversity.
Legal Evalutions and Challenges of Large Language Models
Nov 15, 2024



Abstract:In this paper, we review legal testing methods based on Large Language Models (LLMs), using the OPENAI o1 model as a case study to evaluate the performance of large models in applying legal provisions. We compare current state-of-the-art LLMs, including open-source, closed-source, and legal-specific models trained specifically for the legal domain. Systematic tests are conducted on English and Chinese legal cases, and the results are analyzed in depth. Through systematic testing of legal cases from common law systems and China, this paper explores the strengths and weaknesses of LLMs in understanding and applying legal texts, reasoning through legal issues, and predicting judgments. The experimental results highlight both the potential and limitations of LLMs in legal applications, particularly in terms of challenges related to the interpretation of legal language and the accuracy of legal reasoning. Finally, the paper provides a comprehensive analysis of the advantages and disadvantages of various types of models, offering valuable insights and references for the future application of AI in the legal field.
Evaluation of OpenAI o1: Opportunities and Challenges of AGI
Sep 27, 2024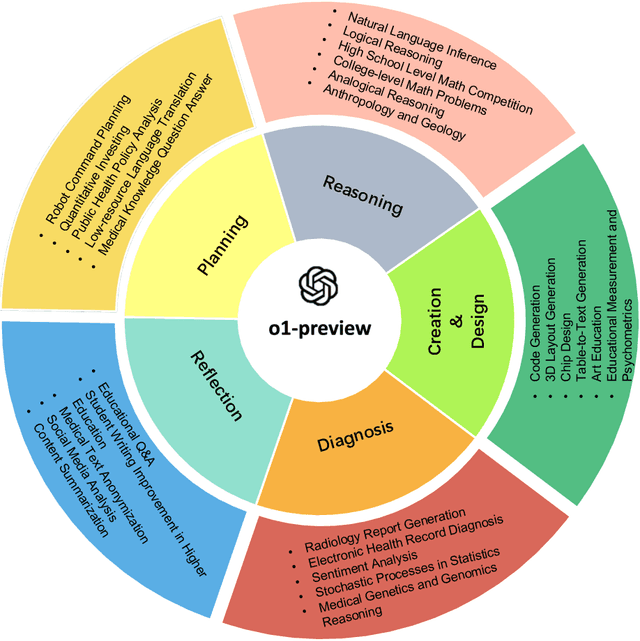
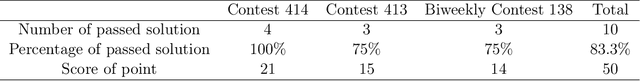
Abstract:This comprehensive study evaluates the performance of OpenAI's o1-preview large language model across a diverse array of complex reasoning tasks, spanning multiple domains, including computer science, mathematics, natural sciences, medicine, linguistics, and social sciences. Through rigorous testing, o1-preview demonstrated remarkable capabilities, often achieving human-level or superior performance in areas ranging from coding challenges to scientific reasoning and from language processing to creative problem-solving. Key findings include: -83.3% success rate in solving complex competitive programming problems, surpassing many human experts. -Superior ability in generating coherent and accurate radiology reports, outperforming other evaluated models. -100% accuracy in high school-level mathematical reasoning tasks, providing detailed step-by-step solutions. -Advanced natural language inference capabilities across general and specialized domains like medicine. -Impressive performance in chip design tasks, outperforming specialized models in areas such as EDA script generation and bug analysis. -Remarkable proficiency in anthropology and geology, demonstrating deep understanding and reasoning in these specialized fields. -Strong capabilities in quantitative investing. O1 has comprehensive financial knowledge and statistical modeling skills. -Effective performance in social media analysis, including sentiment analysis and emotion recognition. The model excelled particularly in tasks requiring intricate reasoning and knowledge integration across various fields. While some limitations were observed, including occasional errors on simpler problems and challenges with certain highly specialized concepts, the overall results indicate significant progress towards artificial general intelligence.
Examining the Commitments and Difficulties Inherent in Multimodal Foundation Models for Street View Imagery
Aug 23, 2024



Abstract:The emergence of Large Language Models (LLMs) and multimodal foundation models (FMs) has generated heightened interest in their applications that integrate vision and language. This paper investigates the capabilities of ChatGPT-4V and Gemini Pro for Street View Imagery, Built Environment, and Interior by evaluating their performance across various tasks. The assessments include street furniture identification, pedestrian and car counts, and road width measurement in Street View Imagery; building function classification, building age analysis, building height analysis, and building structure classification in the Built Environment; and interior room classification, interior design style analysis, interior furniture counts, and interior length measurement in Interior. The results reveal proficiency in length measurement, style analysis, question answering, and basic image understanding, but highlight limitations in detailed recognition and counting tasks. While zero-shot learning shows potential, performance varies depending on the problem domains and image complexities. This study provides new insights into the strengths and weaknesses of multimodal foundation models for practical challenges in Street View Imagery, Built Environment, and Interior. Overall, the findings demonstrate foundational multimodal intelligence, emphasizing the potential of FMs to drive forward interdisciplinary applications at the intersection of computer vision and language.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge