Zhenyu Hu
SCUBA: Salesforce Computer Use Benchmark
Sep 30, 2025

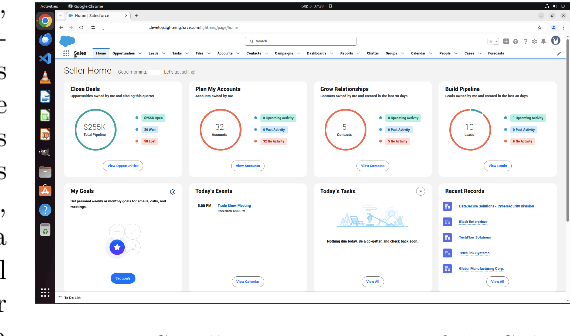
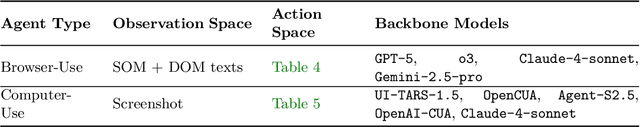
Abstract:We introduce SCUBA, a benchmark designed to evaluate computer-use agents on customer relationship management (CRM) workflows within the Salesforce platform. SCUBA contains 300 task instances derived from real user interviews, spanning three primary personas, platform administrators, sales representatives, and service agents. The tasks test a range of enterprise-critical abilities, including Enterprise Software UI navigation, data manipulation, workflow automation, information retrieval, and troubleshooting. To ensure realism, SCUBA operates in Salesforce sandbox environments with support for parallel execution and fine-grained evaluation metrics to capture milestone progress. We benchmark a diverse set of agents under both zero-shot and demonstration-augmented settings. We observed huge performance gaps in different agent design paradigms and gaps between the open-source model and the closed-source model. In the zero-shot setting, open-source model powered computer-use agents that have strong performance on related benchmarks like OSWorld only have less than 5\% success rate on SCUBA, while methods built on closed-source models can still have up to 39% task success rate. In the demonstration-augmented settings, task success rates can be improved to 50\% while simultaneously reducing time and costs by 13% and 16%, respectively. These findings highlight both the challenges of enterprise tasks automation and the promise of agentic solutions. By offering a realistic benchmark with interpretable evaluation, SCUBA aims to accelerate progress in building reliable computer-use agents for complex business software ecosystems.
Unifying Dimensions: A Linear Adaptive Approach to Lightweight Image Super-Resolution
Sep 26, 2024Abstract:Window-based transformers have demonstrated outstanding performance in super-resolution tasks due to their adaptive modeling capabilities through local self-attention (SA). However, they exhibit higher computational complexity and inference latency than convolutional neural networks. In this paper, we first identify that the adaptability of the Transformers is derived from their adaptive spatial aggregation and advanced structural design, while their high latency results from the computational costs and memory layout transformations associated with the local SA. To simulate this aggregation approach, we propose an effective convolution-based linear focal separable attention (FSA), allowing for long-range dynamic modeling with linear complexity. Additionally, we introduce an effective dual-branch structure combined with an ultra-lightweight information exchange module (IEM) to enhance the aggregation of information by the Token Mixer. Finally, with respect to the structure, we modify the existing spatial-gate-based feedforward neural networks by incorporating a self-gate mechanism to preserve high-dimensional channel information, enabling the modeling of more complex relationships. With these advancements, we construct a convolution-based Transformer framework named the linear adaptive mixer network (LAMNet). Extensive experiments demonstrate that LAMNet achieves better performance than existing SA-based Transformer methods while maintaining the computational efficiency of convolutional neural networks, which can achieve a \(3\times\) speedup of inference time. The code will be publicly available at: https://github.com/zononhzy/LAMNet.
Strengthened Symbol Binding Makes Large Language Models Reliable Multiple-Choice Selectors
Jun 03, 2024Abstract:Multiple-Choice Questions (MCQs) constitute a critical area of research in the study of Large Language Models (LLMs). Previous works have investigated the selection bias problem in MCQs within few-shot scenarios, in which the LLM's performance may be influenced by the presentation of answer choices, leaving the selection bias during Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) unexplored. In this paper, we reveal that selection bias persists in the SFT phase , primarily due to the LLM's inadequate Multiple Choice Symbol Binding (MCSB) ability. This limitation implies that the model struggles to associate the answer options with their corresponding symbols (e.g., A/B/C/D) effectively. To enhance the model's MCSB capability, we first incorporate option contents into the loss function and subsequently adjust the weights of the option symbols and contents, guiding the model to understand the option content of the current symbol. Based on this, we introduce an efficient SFT algorithm for MCQs, termed Point-wise Intelligent Feedback (PIF). PIF constructs negative instances by randomly combining the incorrect option contents with all candidate symbols, and proposes a point-wise loss to provide feedback on these negative samples into LLMs. Our experimental results demonstrate that PIF significantly reduces the model's selection bias by improving its MCSB capability. Remarkably, PIF exhibits a substantial enhancement in the accuracy for MCQs.
* Accept at ACL2024 Main
Enhancing Reinforcement Learning with Label-Sensitive Reward for Natural Language Understanding
May 30, 2024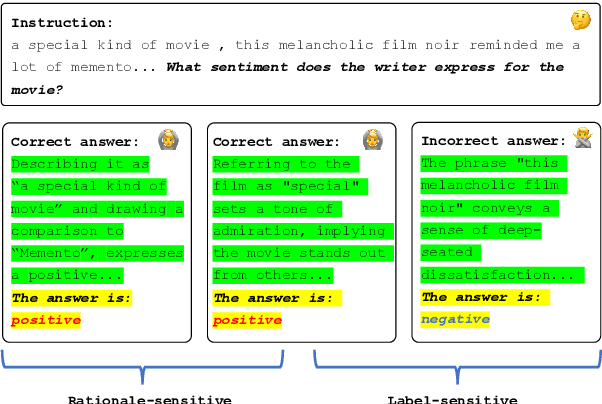



Abstract:Recent strides in large language models (LLMs) have yielded remarkable performance, leveraging reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) to significantly enhance generation and alignment capabilities. However, RLHF encounters numerous challenges, including the objective mismatch issue, leading to suboptimal performance in Natural Language Understanding (NLU) tasks. To address this limitation, we propose a novel Reinforcement Learning framework enhanced with Label-sensitive Reward (RLLR) to amplify the performance of LLMs in NLU tasks. By incorporating label-sensitive pairs into reinforcement learning, our method aims to adeptly capture nuanced label-sensitive semantic features during RL, thereby enhancing natural language understanding. Experiments conducted on five diverse foundation models across eight tasks showcase promising results. In comparison to Supervised Fine-tuning models (SFT), RLLR demonstrates an average performance improvement of 1.54%. Compared with RLHF models, the improvement averages at 0.69%. These results reveal the effectiveness of our method for LLMs in NLU tasks. Code and data available at: https://github.com/MagiaSN/ACL2024_RLLR.
Weaver: Foundation Models for Creative Writing
Jan 30, 2024

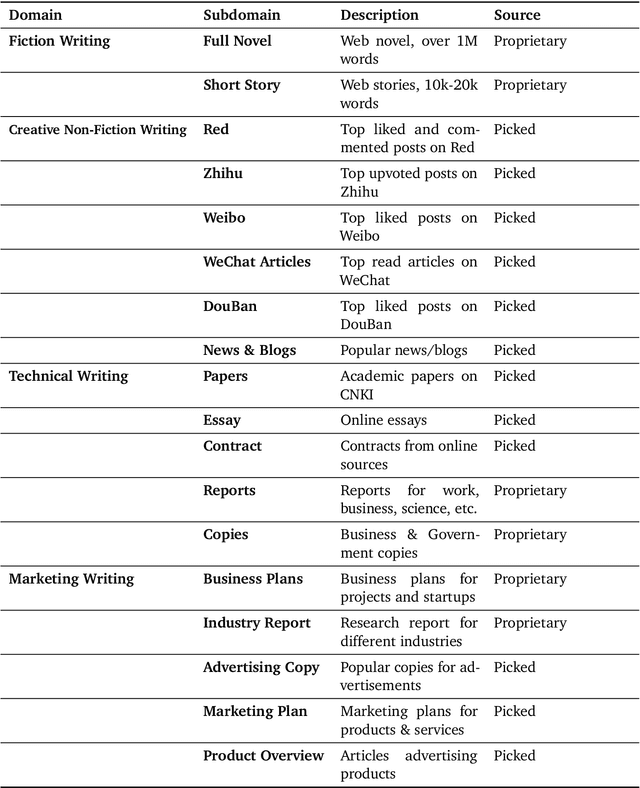

Abstract:This work introduces Weaver, our first family of large language models (LLMs) dedicated to content creation. Weaver is pre-trained on a carefully selected corpus that focuses on improving the writing capabilities of large language models. We then fine-tune Weaver for creative and professional writing purposes and align it to the preference of professional writers using a suit of novel methods for instruction data synthesis and LLM alignment, making it able to produce more human-like texts and follow more diverse instructions for content creation. The Weaver family consists of models of Weaver Mini (1.8B), Weaver Base (6B), Weaver Pro (14B), and Weaver Ultra (34B) sizes, suitable for different applications and can be dynamically dispatched by a routing agent according to query complexity to balance response quality and computation cost. Evaluation on a carefully curated benchmark for assessing the writing capabilities of LLMs shows Weaver models of all sizes outperform generalist LLMs several times larger than them. Notably, our most-capable Weaver Ultra model surpasses GPT-4, a state-of-the-art generalist LLM, on various writing scenarios, demonstrating the advantage of training specialized LLMs for writing purposes. Moreover, Weaver natively supports retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) and function calling (tool usage). We present various use cases of these abilities for improving AI-assisted writing systems, including integration of external knowledge bases, tools, or APIs, and providing personalized writing assistance. Furthermore, we discuss and summarize a guideline and best practices for pre-training and fine-tuning domain-specific LLMs.
E^2VTS: Energy-Efficient Video Text Spotting from Unmanned Aerial Vehicles
Jun 05, 2022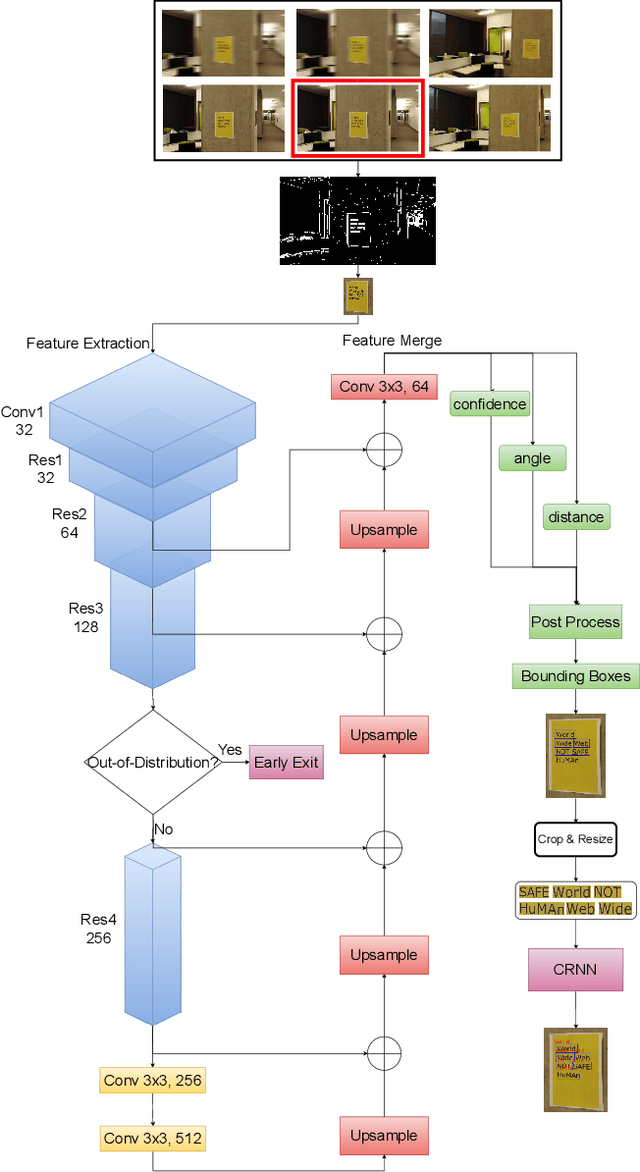
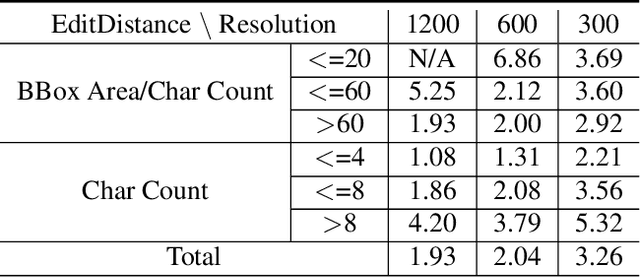

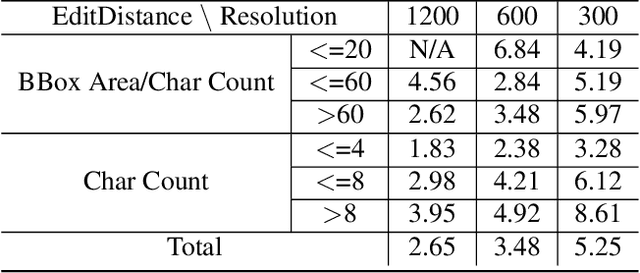
Abstract:Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) based video text spotting has been extensively used in civil and military domains. UAV's limited battery capacity motivates us to develop an energy-efficient video text spotting solution. In this paper, we first revisit RCNN's crop & resize training strategy and empirically find that it outperforms aligned RoI sampling on a real-world video text dataset captured by UAV. To reduce energy consumption, we further propose a multi-stage image processor that takes videos' redundancy, continuity, and mixed degradation into account. Lastly, the model is pruned and quantized before deployed on Raspberry Pi. Our proposed energy-efficient video text spotting solution, dubbed as E^2VTS, outperforms all previous methods by achieving a competitive tradeoff between energy efficiency and performance. All our codes and pre-trained models are available at https://github.com/wuzhenyusjtu/LPCVC20-VideoTextSpotting.
E^2TAD: An Energy-Efficient Tracking-based Action Detector
Apr 09, 2022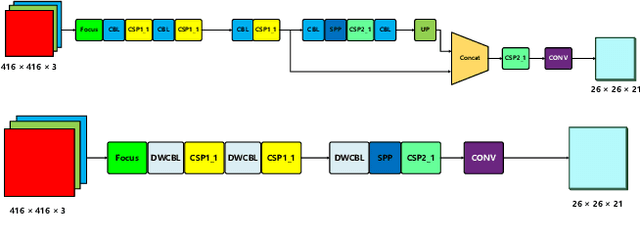
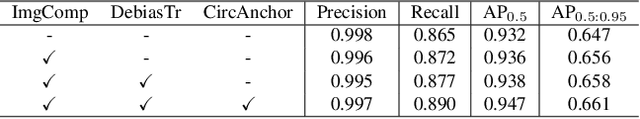
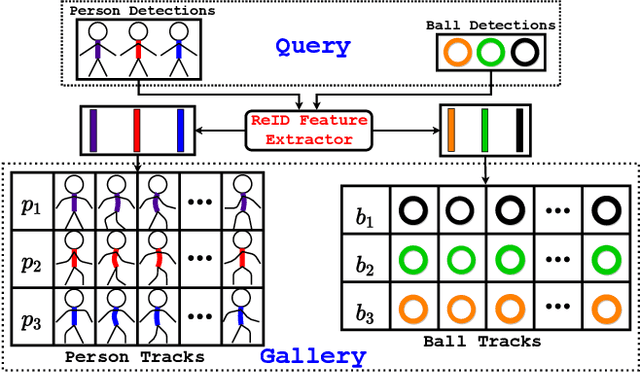
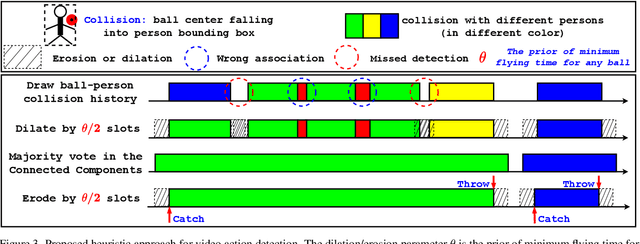
Abstract:Video action detection (spatio-temporal action localization) is usually the starting point for human-centric intelligent analysis of videos nowadays. It has high practical impacts for many applications across robotics, security, healthcare, etc. The two-stage paradigm of Faster R-CNN inspires a standard paradigm of video action detection in object detection, i.e., firstly generating person proposals and then classifying their actions. However, none of the existing solutions could provide fine-grained action detection to the "who-when-where-what" level. This paper presents a tracking-based solution to accurately and efficiently localize predefined key actions spatially (by predicting the associated target IDs and locations) and temporally (by predicting the time in exact frame indices). This solution won first place in the UAV-Video Track of 2021 Low-Power Computer Vision Challenge (LPCVC).
ExAD: An Ensemble Approach for Explanation-based Adversarial Detection
Mar 22, 2021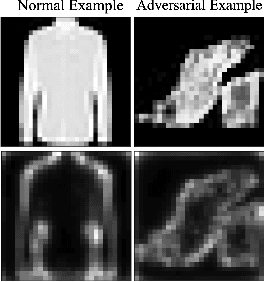
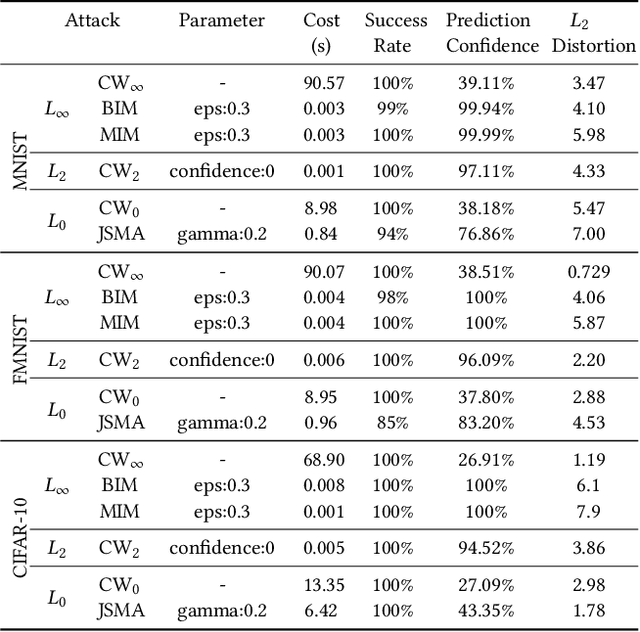
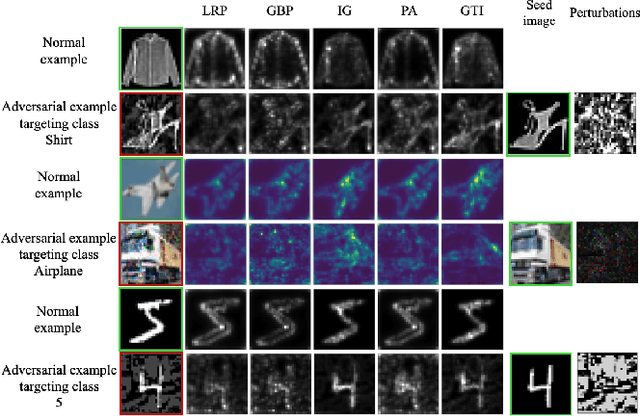
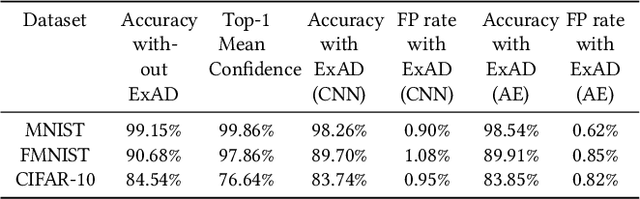
Abstract:Recent research has shown Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) to be vulnerable to adversarial examples that induce desired misclassifications in the models. Such risks impede the application of machine learning in security-sensitive domains. Several defense methods have been proposed against adversarial attacks to detect adversarial examples at test time or to make machine learning models more robust. However, while existing methods are quite effective under blackbox threat model, where the attacker is not aware of the defense, they are relatively ineffective under whitebox threat model, where the attacker has full knowledge of the defense. In this paper, we propose ExAD, a framework to detect adversarial examples using an ensemble of explanation techniques. Each explanation technique in ExAD produces an explanation map identifying the relevance of input variables for the model's classification. For every class in a dataset, the system includes a detector network, corresponding to each explanation technique, which is trained to distinguish between normal and abnormal explanation maps. At test time, if the explanation map of an input is detected as abnormal by any detector model of the classified class, then we consider the input to be an adversarial example. We evaluate our approach using six state-of-the-art adversarial attacks on three image datasets. Our extensive evaluation shows that our mechanism can effectively detect these attacks under blackbox threat model with limited false-positives. Furthermore, we find that our approach achieves promising results in limiting the success rate of whitebox attacks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge