Mengge Xue
Strengthened Symbol Binding Makes Large Language Models Reliable Multiple-Choice Selectors
Jun 03, 2024Abstract:Multiple-Choice Questions (MCQs) constitute a critical area of research in the study of Large Language Models (LLMs). Previous works have investigated the selection bias problem in MCQs within few-shot scenarios, in which the LLM's performance may be influenced by the presentation of answer choices, leaving the selection bias during Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) unexplored. In this paper, we reveal that selection bias persists in the SFT phase , primarily due to the LLM's inadequate Multiple Choice Symbol Binding (MCSB) ability. This limitation implies that the model struggles to associate the answer options with their corresponding symbols (e.g., A/B/C/D) effectively. To enhance the model's MCSB capability, we first incorporate option contents into the loss function and subsequently adjust the weights of the option symbols and contents, guiding the model to understand the option content of the current symbol. Based on this, we introduce an efficient SFT algorithm for MCQs, termed Point-wise Intelligent Feedback (PIF). PIF constructs negative instances by randomly combining the incorrect option contents with all candidate symbols, and proposes a point-wise loss to provide feedback on these negative samples into LLMs. Our experimental results demonstrate that PIF significantly reduces the model's selection bias by improving its MCSB capability. Remarkably, PIF exhibits a substantial enhancement in the accuracy for MCQs.
* Accept at ACL2024 Main
Enhancing Reinforcement Learning with Label-Sensitive Reward for Natural Language Understanding
May 30, 2024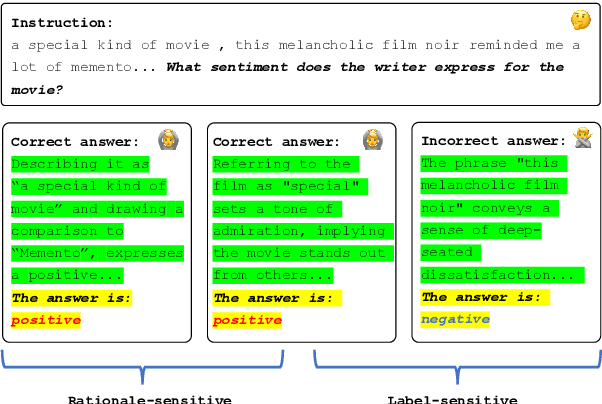



Abstract:Recent strides in large language models (LLMs) have yielded remarkable performance, leveraging reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) to significantly enhance generation and alignment capabilities. However, RLHF encounters numerous challenges, including the objective mismatch issue, leading to suboptimal performance in Natural Language Understanding (NLU) tasks. To address this limitation, we propose a novel Reinforcement Learning framework enhanced with Label-sensitive Reward (RLLR) to amplify the performance of LLMs in NLU tasks. By incorporating label-sensitive pairs into reinforcement learning, our method aims to adeptly capture nuanced label-sensitive semantic features during RL, thereby enhancing natural language understanding. Experiments conducted on five diverse foundation models across eight tasks showcase promising results. In comparison to Supervised Fine-tuning models (SFT), RLLR demonstrates an average performance improvement of 1.54%. Compared with RLHF models, the improvement averages at 0.69%. These results reveal the effectiveness of our method for LLMs in NLU tasks. Code and data available at: https://github.com/MagiaSN/ACL2024_RLLR.
Improving Distantly-Supervised Named Entity Recognition with Self-Collaborative Denoising Learning
Oct 09, 2021



Abstract:Distantly supervised named entity recognition (DS-NER) efficiently reduces labor costs but meanwhile intrinsically suffers from the label noise due to the strong assumption of distant supervision. Typically, the wrongly labeled instances comprise numbers of incomplete and inaccurate annotation noise, while most prior denoising works are only concerned with one kind of noise and fail to fully explore useful information in the whole training set. To address this issue, we propose a robust learning paradigm named Self-Collaborative Denoising Learning (SCDL), which jointly trains two teacher-student networks in a mutually-beneficial manner to iteratively perform noisy label refinery. Each network is designed to exploit reliable labels via self denoising, and two networks communicate with each other to explore unreliable annotations by collaborative denoising. Extensive experimental results on five real-world datasets demonstrate that SCDL is superior to state-of-the-art DS-NER denoising methods.
Coarse-to-Fine Pre-training for Named Entity Recognition
Oct 16, 2020



Abstract:More recently, Named Entity Recognition hasachieved great advances aided by pre-trainingapproaches such as BERT. However, currentpre-training techniques focus on building lan-guage modeling objectives to learn a gen-eral representation, ignoring the named entity-related knowledge. To this end, we proposea NER-specific pre-training framework to in-ject coarse-to-fine automatically mined entityknowledge into pre-trained models. Specifi-cally, we first warm-up the model via an en-tity span identification task by training it withWikipedia anchors, which can be deemed asgeneral-typed entities. Then we leverage thegazetteer-based distant supervision strategy totrain the model extract coarse-grained typedentities. Finally, we devise a self-supervisedauxiliary task to mine the fine-grained namedentity knowledge via clustering.Empiricalstudies on three public NER datasets demon-strate that our framework achieves significantimprovements against several pre-trained base-lines, establishing the new state-of-the-art per-formance on three benchmarks. Besides, weshow that our framework gains promising re-sults without using human-labeled trainingdata, demonstrating its effectiveness in label-few and low-resource scenarios
Enhancing Pre-trained Chinese Character Representation with Word-aligned Attention
Nov 07, 2019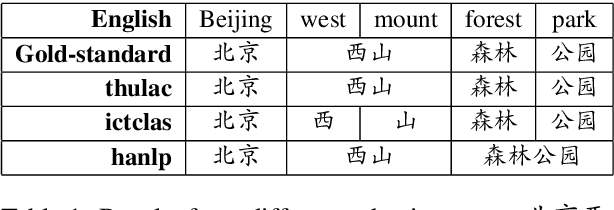
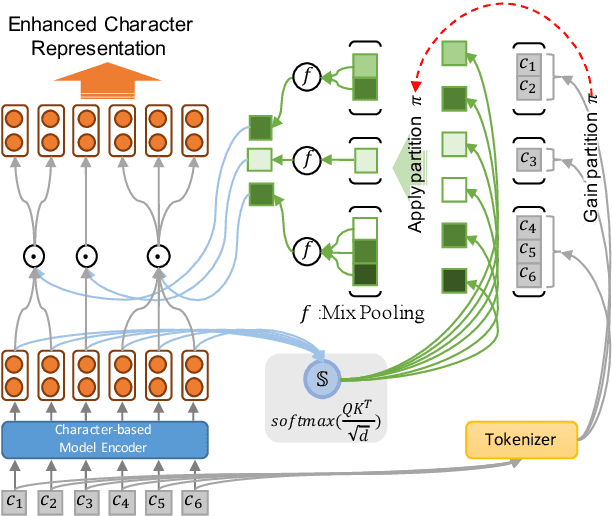
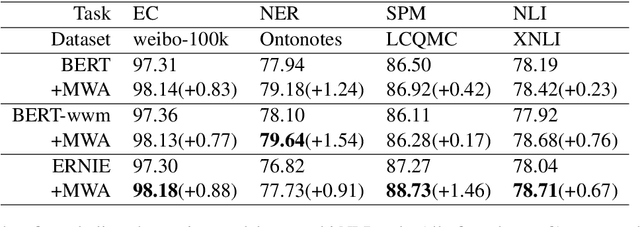
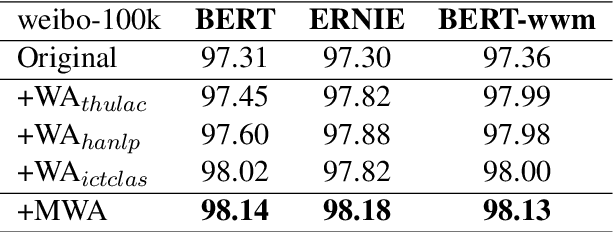
Abstract:Most Chinese pre-trained encoders take a character as a basic unit and learn representations according to character's external contexts, ignoring the semantics expressed in the word, which is the smallest meaningful unit in Chinese. Hence, we propose a novel word aligned attention to incorporate word segmentation information, which is complementary to various Chinese pre-trained language models. Specifically, we devise a mixed-pooling strategy to align the character level attention to the word level, and propose an effective fusion method to solve the potential issue of segmentation error propagation. As a result, word and character information are explicitly integrated at the fine-tuning procedure. Experimental results on various Chinese NLP benchmarks demonstrate that our model could bring another significant gain over several pre-trained models.
Neural Collective Entity Linking Based on Recurrent Random Walk Network Learning
Jun 20, 2019



Abstract:Benefiting from the excellent ability of neural networks on learning semantic representations, existing studies for entity linking (EL) have resorted to neural networks to exploit both the local mention-to-entity compatibility and the global interdependence between different EL decisions for target entity disambiguation. However, most neural collective EL methods depend entirely upon neural networks to automatically model the semantic dependencies between different EL decisions, which lack of the guidance from external knowledge. In this paper, we propose a novel end-to-end neural network with recurrent random-walk layers for collective EL, which introduces external knowledge to model the semantic interdependence between different EL decisions. Specifically, we first establish a model based on local context features, and then stack random-walk layers to reinforce the evidence for related EL decisions into high-probability decisions, where the semantic interdependence between candidate entities is mainly induced from an external knowledge base. Finally, a semantic regularizer that preserves the collective EL decisions consistency is incorporated into the conventional objective function, so that the external knowledge base can be fully exploited in collective EL decisions. Experimental results and in-depth analysis on various datasets show that our model achieves better performance than other state-of-the-art models. Our code and data are released at \url{https://github.com/DeepLearnXMU/RRWEL}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge