Zhenhe Zhang
Pangu Ultra: Pushing the Limits of Dense Large Language Models on Ascend NPUs
Apr 10, 2025



Abstract:We present Pangu Ultra, a Large Language Model (LLM) with 135 billion parameters and dense Transformer modules trained on Ascend Neural Processing Units (NPUs). Although the field of LLM has been witnessing unprecedented advances in pushing the scale and capability of LLM in recent years, training such a large-scale model still involves significant optimization and system challenges. To stabilize the training process, we propose depth-scaled sandwich normalization, which effectively eliminates loss spikes during the training process of deep models. We pre-train our model on 13.2 trillion diverse and high-quality tokens and further enhance its reasoning capabilities during post-training. To perform such large-scale training efficiently, we utilize 8,192 Ascend NPUs with a series of system optimizations. Evaluations on multiple diverse benchmarks indicate that Pangu Ultra significantly advances the state-of-the-art capabilities of dense LLMs such as Llama 405B and Mistral Large 2, and even achieves competitive results with DeepSeek-R1, whose sparse model structure contains much more parameters. Our exploration demonstrates that Ascend NPUs are capable of efficiently and effectively training dense models with more than 100 billion parameters. Our model and system will be available for our commercial customers.
AIGS: Generating Science from AI-Powered Automated Falsification
Nov 17, 2024



Abstract:Rapid development of artificial intelligence has drastically accelerated the development of scientific discovery. Trained with large-scale observation data, deep neural networks extract the underlying patterns in an end-to-end manner and assist human researchers with highly-precised predictions in unseen scenarios. The recent rise of Large Language Models (LLMs) and the empowered autonomous agents enable scientists to gain help through interaction in different stages of their research, including but not limited to literature review, research ideation, idea implementation, and academic writing. However, AI researchers instantiated by foundation model empowered agents with full-process autonomy are still in their infancy. In this paper, we study $\textbf{AI-Generated Science}$ (AIGS), where agents independently and autonomously complete the entire research process and discover scientific laws. By revisiting the definition of scientific research, we argue that $\textit{falsification}$ is the essence of both human research process and the design of an AIGS system. Through the lens of falsification, prior systems attempting towards AI-Generated Science either lack the part in their design, or rely heavily on existing verification engines that narrow the use in specialized domains. In this work, we propose Baby-AIGS as a baby-step demonstration of a full-process AIGS system, which is a multi-agent system with agents in roles representing key research process. By introducing FalsificationAgent, which identify and then verify possible scientific discoveries, we empower the system with explicit falsification. Experiments on three tasks preliminarily show that Baby-AIGS could produce meaningful scientific discoveries, though not on par with experienced human researchers. Finally, we discuss on the limitations of current Baby-AIGS, actionable insights, and related ethical issues in detail.
PANDA: Preference Adaptation for Enhancing Domain-Specific Abilities of LLMs
Feb 20, 2024Abstract:While Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated considerable capabilities across various natural language tasks, they often fall short of the performance achieved by domain-specific state-of-the-art models. One potential approach to enhance domain-specific capabilities of LLMs involves fine-tuning them using corresponding datasets. However, this method can be both resource and time-intensive, and not applicable to closed-source commercial LLMs. In this paper, we propose Preference Adaptation for Enhancing Domain-specific Abilities of LLMs (PANDA), a method designed to augment the domain-specific capabilities of LLMs by leveraging insights from the response preference of expert models without requiring fine-tuning. Our experimental results reveal that PANDA significantly enhances the domain-specific ability of LLMs on text classification and interactive decision tasks. Moreover, LLM with PANDA even outperforms the expert model that being learned on 4 tasks of ScienceWorld. This finding highlights the potential of exploring tuning-free approaches to achieve weak-to-strong generalization.
Towards Unified Alignment Between Agents, Humans, and Environment
Feb 14, 2024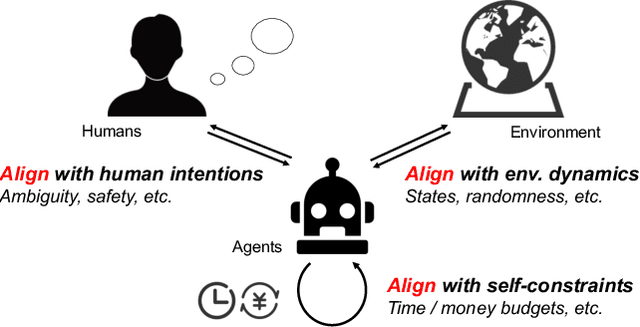
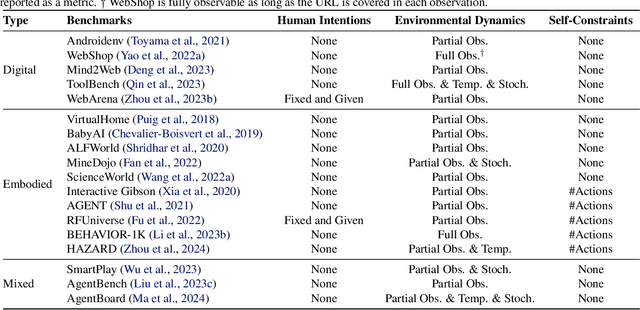
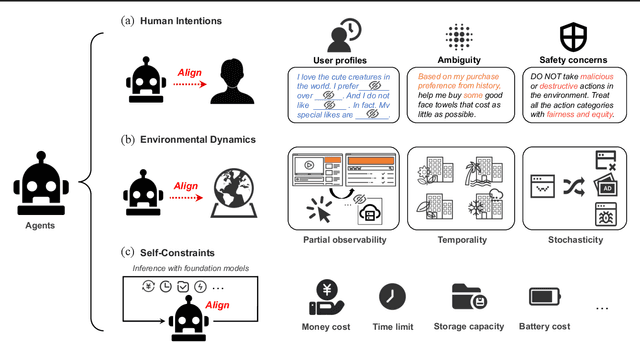

Abstract:The rapid progress of foundation models has led to the prosperity of autonomous agents, which leverage the universal capabilities of foundation models to conduct reasoning, decision-making, and environmental interaction. However, the efficacy of agents remains limited when operating in intricate, realistic environments. In this work, we introduce the principles of $\mathbf{U}$nified $\mathbf{A}$lignment for $\mathbf{A}$gents ($\mathbf{UA}^2$), which advocate for the simultaneous alignment of agents with human intentions, environmental dynamics, and self-constraints such as the limitation of monetary budgets. From the perspective of $\mathbf{UA}^2$, we review the current agent research and highlight the neglected factors in existing agent benchmarks and method candidates. We also conduct proof-of-concept studies by introducing realistic features to WebShop, including user profiles to demonstrate intentions, personalized reranking for complex environmental dynamics, and runtime cost statistics to reflect self-constraints. We then follow the principles of $\mathbf{UA}^2$ to propose an initial design of our agent, and benchmark its performance with several candidate baselines in the retrofitted WebShop. The extensive experimental results further prove the importance of the principles of $\mathbf{UA}^2$. Our research sheds light on the next steps of autonomous agent research with improved general problem-solving abilities.
SPIRAL: Self-supervised Perturbation-Invariant Representation Learning for Speech Pre-Training
Jan 29, 2022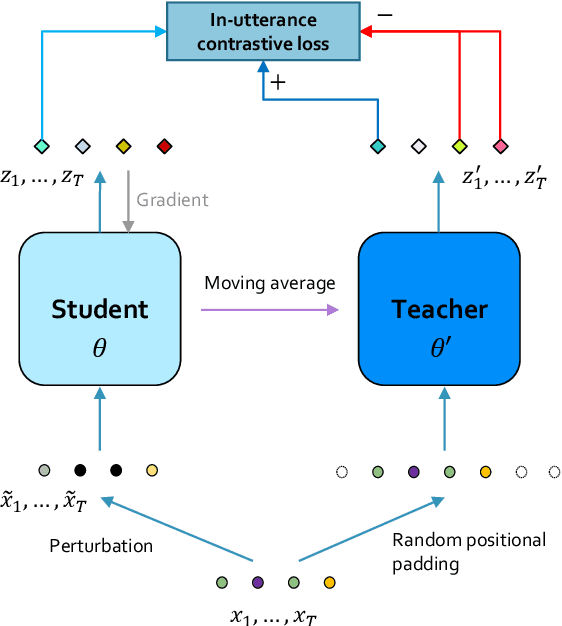
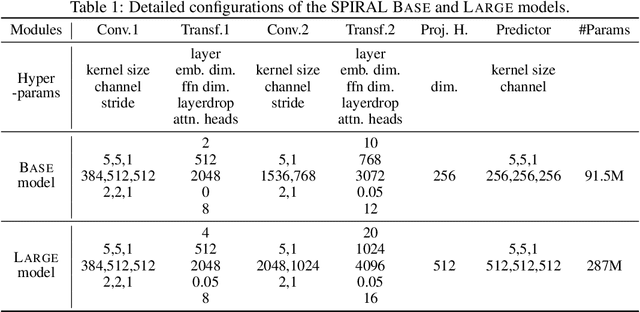
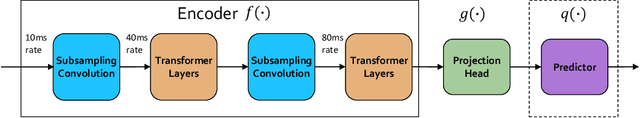
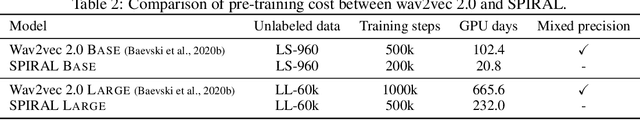
Abstract:We introduce a new approach for speech pre-training named SPIRAL which works by learning denoising representation of perturbed data in a teacher-student framework. Specifically, given a speech utterance, we first feed the utterance to a teacher network to obtain corresponding representation. Then the same utterance is perturbed and fed to a student network. The student network is trained to output representation resembling that of the teacher. At the same time, the teacher network is updated as moving average of student's weights over training steps. In order to prevent representation collapse, we apply an in-utterance contrastive loss as pre-training objective and impose position randomization on the input to the teacher. SPIRAL achieves competitive or better results compared to state-of-the-art speech pre-training method wav2vec 2.0, with significant reduction of training cost (80% for Base model, 65% for Large model). Furthermore, we address the problem of noise-robustness that is critical to real-world speech applications. We propose multi-condition pre-training by perturbing the student's input with various types of additive noise. We demonstrate that multi-condition pre-trained SPIRAL models are more robust to noisy speech (9.0% - 13.3% relative word error rate reduction on real noisy test data), compared to applying multi-condition training solely in the fine-tuning stage. The code will be released after publication.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge