Zeyuan Yang
Semantically Aware UAV Landing Site Assessment from Remote Sensing Imagery via Multimodal Large Language Models
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Safe UAV emergency landing requires more than just identifying flat terrain; it demands understanding complex semantic risks (e.g., crowds, temporary structures) invisible to traditional geometric sensors. In this paper, we propose a novel framework leveraging Remote Sensing (RS) imagery and Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) for global context-aware landing site assessment. Unlike local geometric methods, our approach employs a coarse-to-fine pipeline: first, a lightweight semantic segmentation module efficiently pre-screens candidate areas; second, a vision-language reasoning agent fuses visual features with Point-of-Interest (POI) data to detect subtle hazards. To validate this approach, we construct and release the Emergency Landing Site Selection (ELSS) benchmark. Experiments demonstrate that our framework significantly outperforms geometric baselines in risk identification accuracy. Furthermore, qualitative results confirm its ability to generate human-like, interpretable justifications, enhancing trust in automated decision-making. The benchmark dataset is publicly accessible at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/ELSS-dataset-43D7.
The Maximum Coverage Model and Recommendation System for UAV Vertiports Location Planning
Aug 18, 2025Abstract:As urban aerial mobility (UAM) infrastructure development accelerates globally, cities like Shenzhen are planning large-scale vertiport networks (e.g., 1,200+ facilities by 2026). Existing planning frameworks remain inadequate for this complexity due to historical limitations in data granularity and real-world applicability. This paper addresses these gaps by first proposing the Capacitated Dynamic Maximum Covering Location Problem (CDMCLP), a novel optimization framework that simultaneously models urban-scale spatial-temporal demand, heterogeneous user behaviors, and infrastructure capacity constraints. Building on this foundation, we introduce an Integrated Planning Recommendation System that combines CDMCLP with socio-economic factors and dynamic clustering initialization. This system leverages adaptive parameter tuning based on empirical user behavior to generate practical planning solutions. Validation in a Chinese center city demonstrates the effectiveness of the new optimization framework and recommendation system. Under the evaluation and optimization of CDMCLP, the quantitative performance of traditional location methods are exposed and can be improved by 38\%--52\%, while the recommendation system shows user-friendliness and the effective integration of complex elements. By integrating mathematical rigor with practical implementation considerations, this hybrid approach bridges the gap between theoretical location modeling and real-world UAM infrastructure planning, offering municipalities a pragmatic tool for vertiport network design.
VCA: Video Curious Agent for Long Video Understanding
Dec 12, 2024
Abstract:Long video understanding poses unique challenges due to their temporal complexity and low information density. Recent works address this task by sampling numerous frames or incorporating auxiliary tools using LLMs, both of which result in high computational costs. In this work, we introduce a curiosity-driven video agent with self-exploration capability, dubbed as VCA. Built upon VLMs, VCA autonomously navigates video segments and efficiently builds a comprehensive understanding of complex video sequences. Instead of directly sampling frames, VCA employs a tree-search structure to explore video segments and collect frames. Rather than relying on external feedback or reward, VCA leverages VLM's self-generated intrinsic reward to guide its exploration, enabling it to capture the most crucial information for reasoning. Experimental results on multiple long video benchmarks demonstrate our approach's superior effectiveness and efficiency.
UBSoft: A Simulation Platform for Robotic Skill Learning in Unbounded Soft Environments
Nov 19, 2024Abstract:It is desired to equip robots with the capability of interacting with various soft materials as they are ubiquitous in the real world. While physics simulations are one of the predominant methods for data collection and robot training, simulating soft materials presents considerable challenges. Specifically, it is significantly more costly than simulating rigid objects in terms of simulation speed and storage requirements. These limitations typically restrict the scope of studies on soft materials to small and bounded areas, thereby hindering the learning of skills in broader spaces. To address this issue, we introduce UBSoft, a new simulation platform designed to support unbounded soft environments for robot skill acquisition. Our platform utilizes spatially adaptive resolution scales, where simulation resolution dynamically adjusts based on proximity to active robotic agents. Our framework markedly reduces the demand for extensive storage space and computation costs required for large-scale scenarios involving soft materials. We also establish a set of benchmark tasks in our platform, including both locomotion and manipulation tasks, and conduct experiments to evaluate the efficacy of various reinforcement learning algorithms and trajectory optimization techniques, both gradient-based and sampling-based. Preliminary results indicate that sampling-based trajectory optimization generally achieves better results for obtaining one trajectory to solve the task. Additionally, we conduct experiments in real-world environments to demonstrate that advancements made in our UBSoft simulator could translate to improved robot interactions with large-scale soft material. More videos can be found at https://vis-www.cs.umass.edu/ubsoft/.
Towards Unified Alignment Between Agents, Humans, and Environment
Feb 14, 2024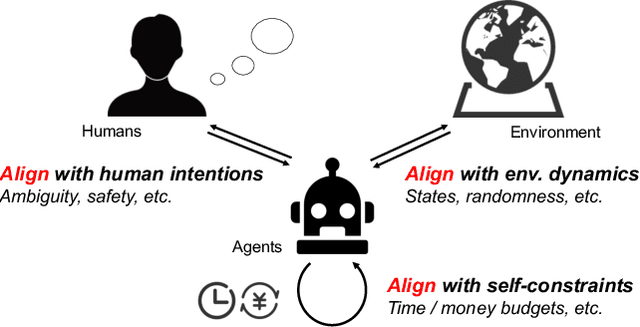
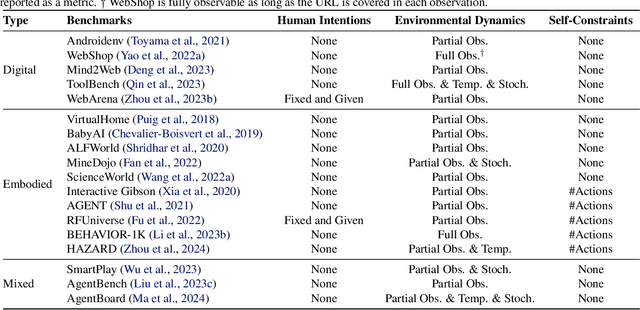
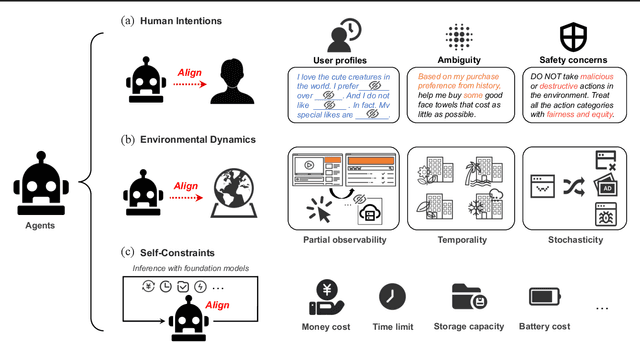

Abstract:The rapid progress of foundation models has led to the prosperity of autonomous agents, which leverage the universal capabilities of foundation models to conduct reasoning, decision-making, and environmental interaction. However, the efficacy of agents remains limited when operating in intricate, realistic environments. In this work, we introduce the principles of $\mathbf{U}$nified $\mathbf{A}$lignment for $\mathbf{A}$gents ($\mathbf{UA}^2$), which advocate for the simultaneous alignment of agents with human intentions, environmental dynamics, and self-constraints such as the limitation of monetary budgets. From the perspective of $\mathbf{UA}^2$, we review the current agent research and highlight the neglected factors in existing agent benchmarks and method candidates. We also conduct proof-of-concept studies by introducing realistic features to WebShop, including user profiles to demonstrate intentions, personalized reranking for complex environmental dynamics, and runtime cost statistics to reflect self-constraints. We then follow the principles of $\mathbf{UA}^2$ to propose an initial design of our agent, and benchmark its performance with several candidate baselines in the retrofitted WebShop. The extensive experimental results further prove the importance of the principles of $\mathbf{UA}^2$. Our research sheds light on the next steps of autonomous agent research with improved general problem-solving abilities.
Failures Pave the Way: Enhancing Large Language Models through Tuning-free Rule Accumulation
Oct 24, 2023



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have showcased impressive performance. However, due to their inability to capture relationships among samples, these frozen LLMs inevitably keep repeating similar mistakes. In this work, we propose our Tuning-free Rule Accumulation (TRAN) framework, which guides LLMs in improving their performance by learning from previous mistakes. Considering data arrives sequentially, LLMs gradually accumulate rules from incorrect cases, forming a rule collection. These rules are then utilized by the LLMs to avoid making similar mistakes when processing subsequent inputs. Moreover, the rules remain independent of the primary prompts, seamlessly complementing prompt design strategies. Experimentally, we show that TRAN improves over recent baselines by a large margin.
Restricted Orthogonal Gradient Projection for Continual Learning
Jan 28, 2023Abstract:Continual learning aims to avoid catastrophic forgetting and effectively leverage learned experiences to master new knowledge. Existing gradient projection approaches impose hard constraints on the optimization space for new tasks to minimize interference, which simultaneously hinders forward knowledge transfer. To address this issue, recent methods reuse frozen parameters with a growing network, resulting in high computational costs. Thus, it remains a challenge whether we can improve forward knowledge transfer for gradient projection approaches using a fixed network architecture. In this work, we propose the Restricted Orthogonal Gradient prOjection (ROGO) framework. The basic idea is to adopt a restricted orthogonal constraint allowing parameters optimized in the direction oblique to the whole frozen space to facilitate forward knowledge transfer while consolidating previous knowledge. Our framework requires neither data buffers nor extra parameters. Extensive experiments have demonstrated the superiority of our framework over several strong baselines. We also provide theoretical guarantees for our relaxing strategy.
Machine Learning for Intelligent Optical Networks: A Comprehensive Survey
Mar 11, 2020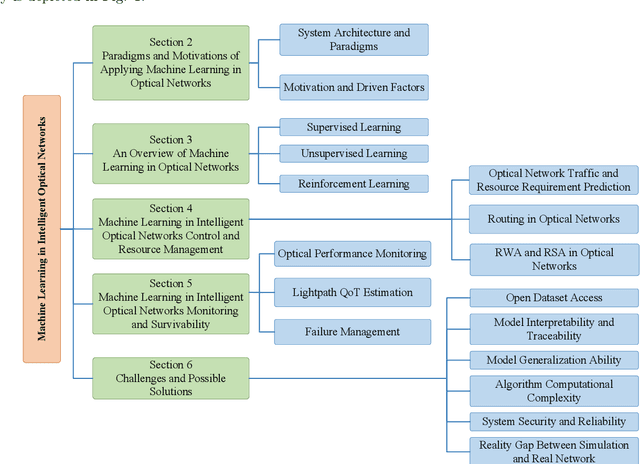
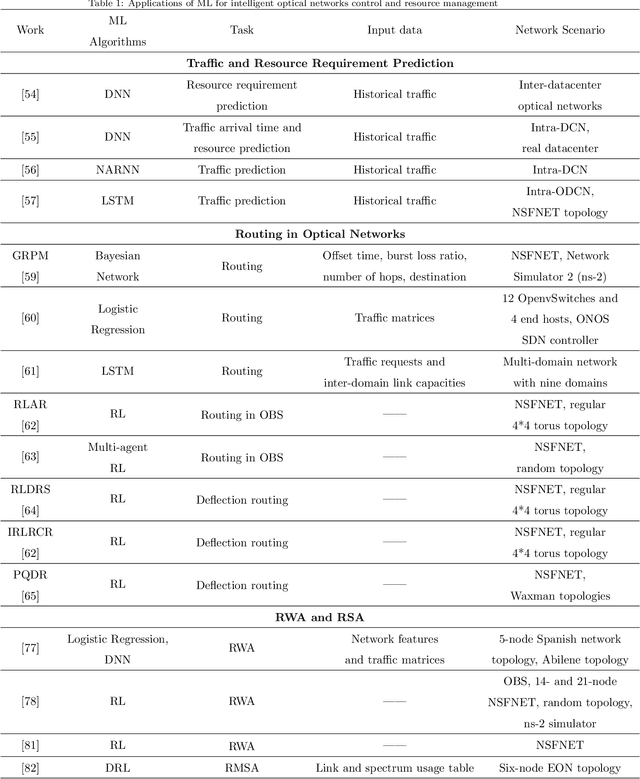
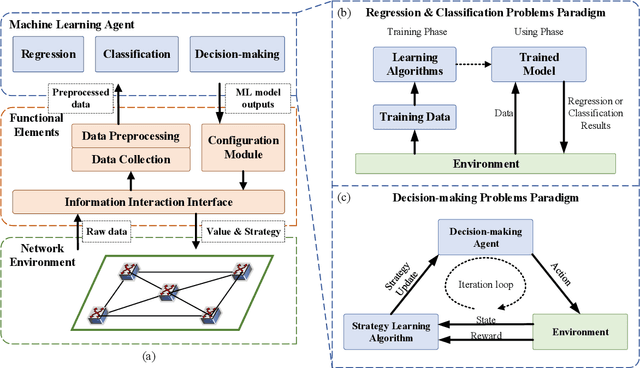
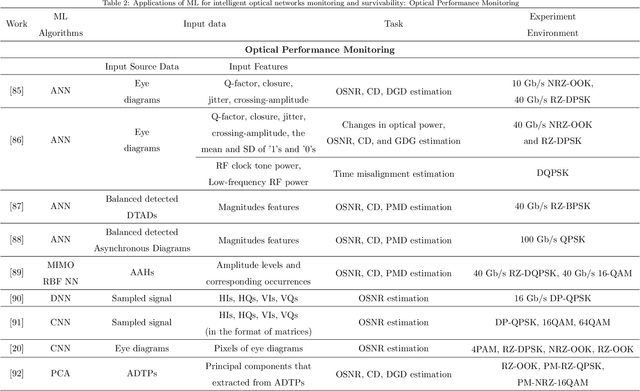
Abstract:With the rapid development of Internet and communication systems, both in services and technologies, communication networks have been suffering increasing complexity. It is imperative to improve intelligence in communication network, and several aspects have been incorporating with Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML). Optical network, which plays an important role both in core and access network in communication networks, also faces great challenges of system complexity and the requirement of manual operations. To overcome the current limitations and address the issues of future optical networks, it is essential to deploy more intelligence capability to enable autonomous and exible network operations. ML techniques are proved to have superiority on solving complex problems; and thus recently, ML techniques have been used for many optical network applications. In this paper, a detailed survey of existing applications of ML for intelligent optical networks is presented. The applications of ML are classified in terms of their use cases, which are categorized into optical network control and resource management, and optical networks monitoring and survivability. The use cases are analyzed and compared according to the used ML techniques. Besides, a tutorial for ML applications is provided from the aspects of the introduction of common ML algorithms, paradigms of ML, and motivations of applying ML. Lastly, challenges and possible solutions of ML application in optical networks are also discussed, which intends to inspire future innovations in leveraging ML to build intelligent optical networks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge