Zhao Ren
Beyond saliency: enhancing explanation of speech emotion recognition with expert-referenced acoustic cues
Nov 12, 2025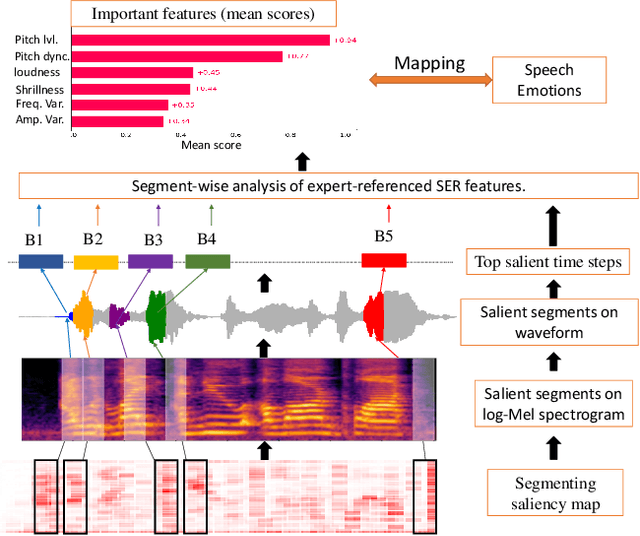

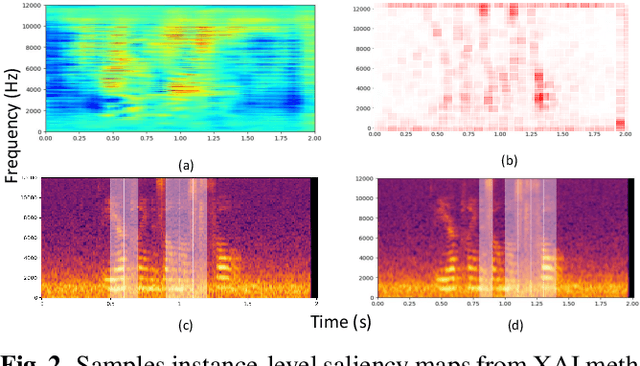
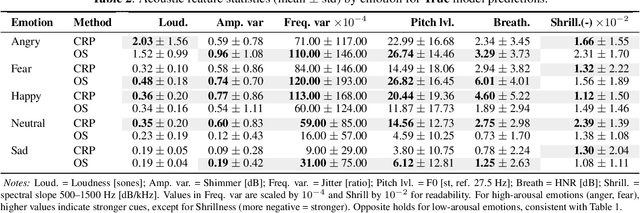
Abstract:Explainable AI (XAI) for Speech Emotion Recognition (SER) is critical for building transparent, trustworthy models. Current saliency-based methods, adapted from vision, highlight spectrogram regions but fail to show whether these regions correspond to meaningful acoustic markers of emotion, limiting faithfulness and interpretability. We propose a framework that overcomes these limitations by quantifying the magnitudes of cues within salient regions. This clarifies "what" is highlighted and connects it to "why" it matters, linking saliency to expert-referenced acoustic cues of speech emotions. Experiments on benchmark SER datasets show that our approach improves explanation quality by explicitly linking salient regions to theory-driven speech emotions expert-referenced acoustics. Compared to standard saliency methods, it provides more understandable and plausible explanations of SER models, offering a foundational step towards trustworthy speech-based affective computing.
Machine Unlearning in Speech Emotion Recognition via Forget Set Alone
Oct 05, 2025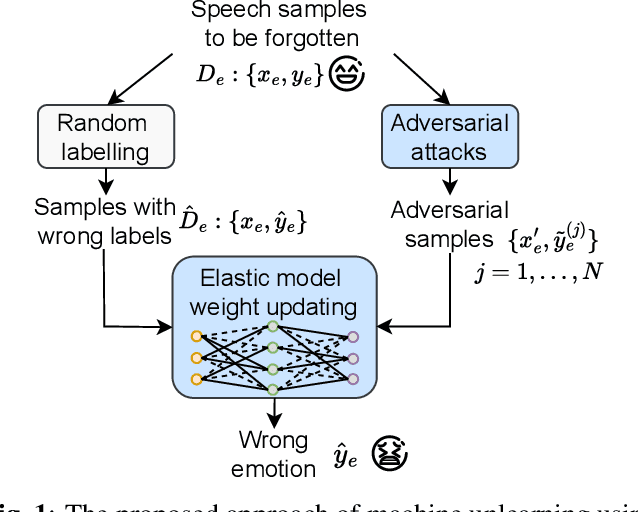
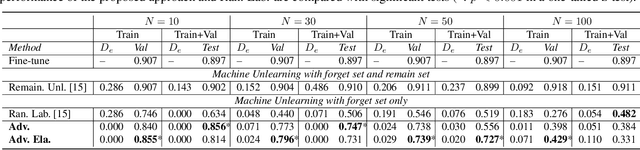

Abstract:Speech emotion recognition aims to identify emotional states from speech signals and has been widely applied in human-computer interaction, education, healthcare, and many other fields. However, since speech data contain rich sensitive information, partial data can be required to be deleted by speakers due to privacy concerns. Current machine unlearning approaches largely depend on data beyond the samples to be forgotten. However, this reliance poses challenges when data redistribution is restricted and demands substantial computational resources in the context of big data. We propose a novel adversarial-attack-based approach that fine-tunes a pre-trained speech emotion recognition model using only the data to be forgotten. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed approach can effectively remove the knowledge of the data to be forgotten from the model, while preserving high model performance on the test set for emotion recognition.
End-to-end Acoustic-linguistic Emotion and Intent Recognition Enhanced by Semi-supervised Learning
Jul 10, 2025Abstract:Emotion and intent recognition from speech is essential and has been widely investigated in human-computer interaction. The rapid development of social media platforms, chatbots, and other technologies has led to a large volume of speech data streaming from users. Nevertheless, annotating such data manually is expensive, making it challenging to train machine learning models for recognition purposes. To this end, we propose applying semi-supervised learning to incorporate a large scale of unlabelled data alongside a relatively smaller set of labelled data. We train end-to-end acoustic and linguistic models, each employing multi-task learning for emotion and intent recognition. Two semi-supervised learning approaches, including fix-match learning and full-match learning, are compared. The experimental results demonstrate that the semi-supervised learning approaches improve model performance in speech emotion and intent recognition from both acoustic and text data. The late fusion of the best models outperforms the acoustic and text baselines by joint recognition balance metrics of 12.3% and 10.4%, respectively.
Instruction-Guided Editing Controls for Images and Multimedia: A Survey in LLM era
Nov 15, 2024



Abstract:The rapid advancement of large language models (LLMs) and multimodal learning has transformed digital content creation and manipulation. Traditional visual editing tools require significant expertise, limiting accessibility. Recent strides in instruction-based editing have enabled intuitive interaction with visual content, using natural language as a bridge between user intent and complex editing operations. This survey provides an overview of these techniques, focusing on how LLMs and multimodal models empower users to achieve precise visual modifications without deep technical knowledge. By synthesizing over 100 publications, we explore methods from generative adversarial networks to diffusion models, examining multimodal integration for fine-grained content control. We discuss practical applications across domains such as fashion, 3D scene manipulation, and video synthesis, highlighting increased accessibility and alignment with human intuition. Our survey compares existing literature, emphasizing LLM-empowered editing, and identifies key challenges to stimulate further research. We aim to democratize powerful visual editing across various industries, from entertainment to education. Interested readers are encouraged to access our repository at https://github.com/tamlhp/awesome-instruction-editing.
Investigating Effective Speaker Property Privacy Protection in Federated Learning for Speech Emotion Recognition
Oct 17, 2024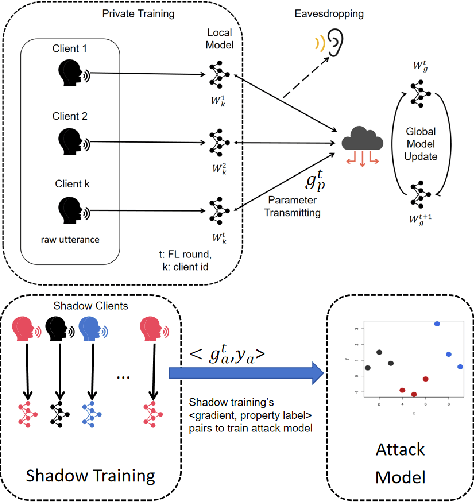
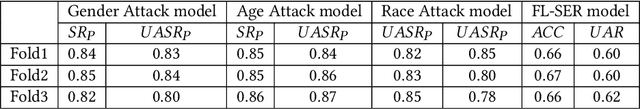
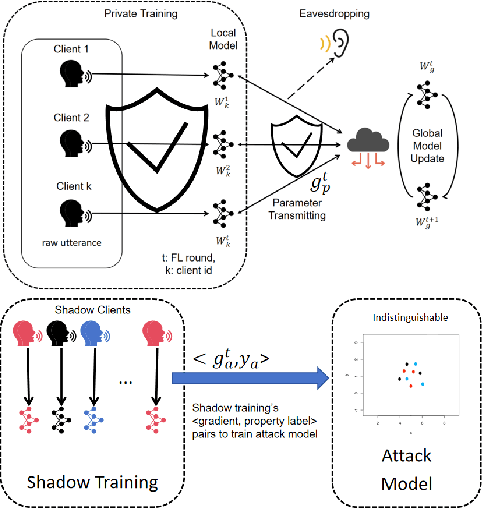
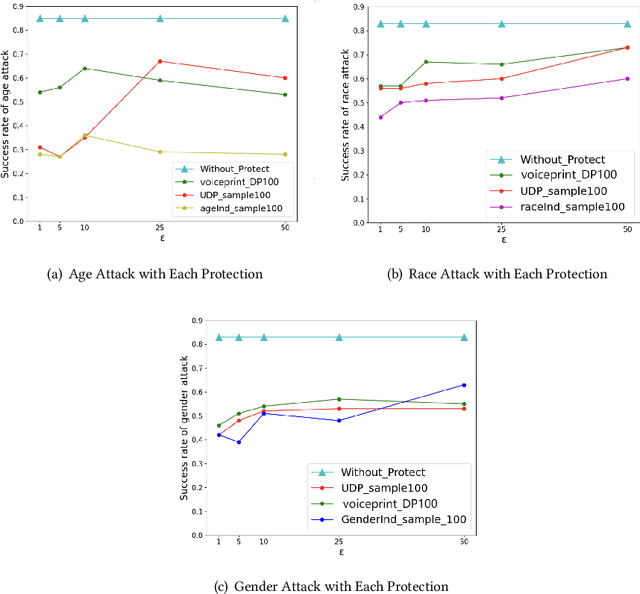
Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) is a privacy-preserving approach that allows servers to aggregate distributed models transmitted from local clients rather than training on user data. More recently, FL has been applied to Speech Emotion Recognition (SER) for secure human-computer interaction applications. Recent research has found that FL is still vulnerable to inference attacks. To this end, this paper focuses on investigating the security of FL for SER concerning property inference attacks. We propose a novel method to protect the property information in speech data by decomposing various properties in the sound and adding perturbations to these properties. Our experiments show that the proposed method offers better privacy-utility trade-offs than existing methods. The trade-offs enable more effective attack prevention while maintaining similar FL utility levels. This work can guide future work on privacy protection methods in speech processing.
Optimizing Cox Models with Stochastic Gradient Descent: Theoretical Foundations and Practical Guidances
Aug 05, 2024



Abstract:Optimizing Cox regression and its neural network variants poses substantial computational challenges in large-scale studies. Stochastic gradient descent (SGD), known for its scalability in model optimization, has recently been adapted to optimize Cox models. Unlike its conventional application, which typically targets a sum of independent individual loss, SGD for Cox models updates parameters based on the partial likelihood of a subset of data. Despite its empirical success, the theoretical foundation for optimizing Cox partial likelihood with SGD is largely underexplored. In this work, we demonstrate that the SGD estimator targets an objective function that is batch-size-dependent. We establish that the SGD estimator for the Cox neural network (Cox-NN) is consistent and achieves the optimal minimax convergence rate up to a polylogarithmic factor. For Cox regression, we further prove the $\sqrt{n}$-consistency and asymptotic normality of the SGD estimator, with variance depending on the batch size. Furthermore, we quantify the impact of batch size on Cox-NN training and its effect on the SGD estimator's asymptotic efficiency in Cox regression. These findings are validated by extensive numerical experiments and provide guidance for selecting batch sizes in SGD applications. Finally, we demonstrate the effectiveness of SGD in a real-world application where GD is unfeasible due to the large scale of data.
Speech Emotion Recognition under Resource Constraints with Data Distillation
Jun 21, 2024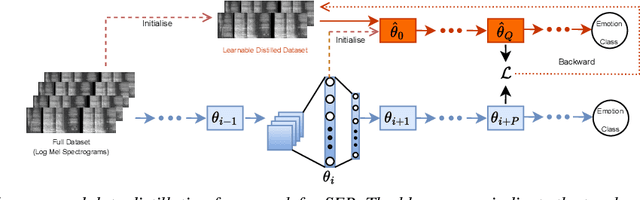
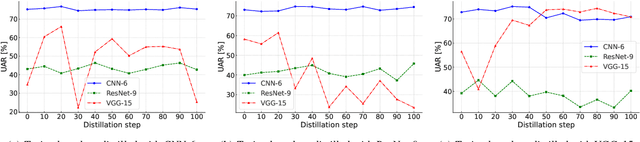
Abstract:Speech emotion recognition (SER) plays a crucial role in human-computer interaction. The emergence of edge devices in the Internet of Things (IoT) presents challenges in constructing intricate deep learning models due to constraints in memory and computational resources. Moreover, emotional speech data often contains private information, raising concerns about privacy leakage during the deployment of SER models. To address these challenges, we propose a data distillation framework to facilitate efficient development of SER models in IoT applications using a synthesised, smaller, and distilled dataset. Our experiments demonstrate that the distilled dataset can be effectively utilised to train SER models with fixed initialisation, achieving performances comparable to those developed using the original full emotional speech dataset.
Diff-ETS: Learning a Diffusion Probabilistic Model for Electromyography-to-Speech Conversion
May 11, 2024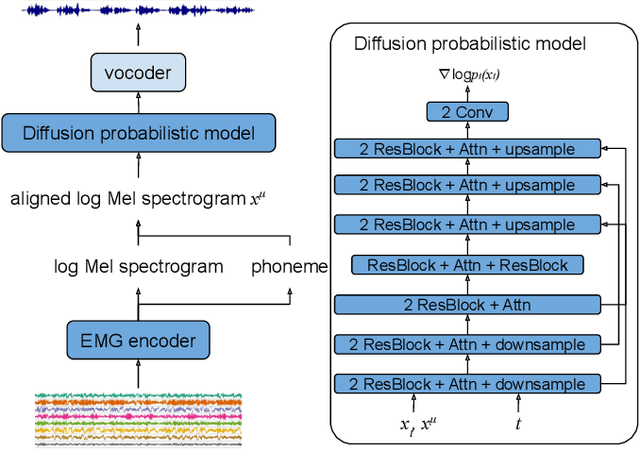
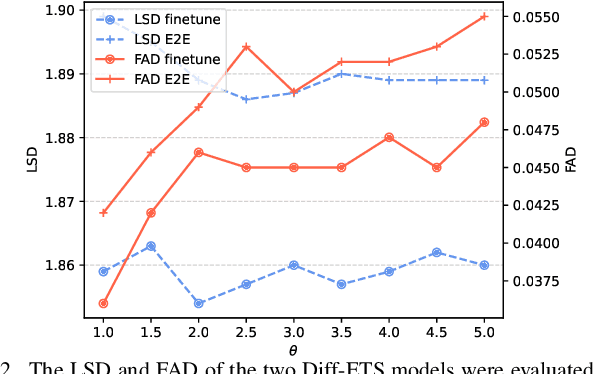
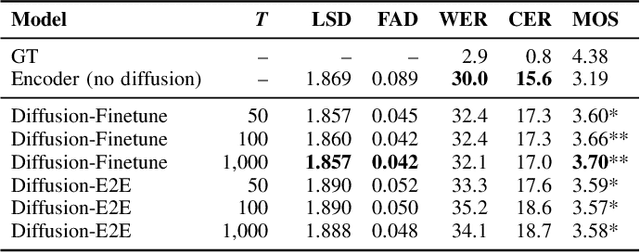
Abstract:Electromyography-to-Speech (ETS) conversion has demonstrated its potential for silent speech interfaces by generating audible speech from Electromyography (EMG) signals during silent articulations. ETS models usually consist of an EMG encoder which converts EMG signals to acoustic speech features, and a vocoder which then synthesises the speech signals. Due to an inadequate amount of available data and noisy signals, the synthesised speech often exhibits a low level of naturalness. In this work, we propose Diff-ETS, an ETS model which uses a score-based diffusion probabilistic model to enhance the naturalness of synthesised speech. The diffusion model is applied to improve the quality of the acoustic features predicted by an EMG encoder. In our experiments, we evaluated fine-tuning the diffusion model on predictions of a pre-trained EMG encoder, and training both models in an end-to-end fashion. We compared Diff-ETS with a baseline ETS model without diffusion using objective metrics and a listening test. The results indicated the proposed Diff-ETS significantly improved speech naturalness over the baseline.
A Survey of Privacy-Preserving Model Explanations: Privacy Risks, Attacks, and Countermeasures
Mar 31, 2024



Abstract:As the adoption of explainable AI (XAI) continues to expand, the urgency to address its privacy implications intensifies. Despite a growing corpus of research in AI privacy and explainability, there is little attention on privacy-preserving model explanations. This article presents the first thorough survey about privacy attacks on model explanations and their countermeasures. Our contribution to this field comprises a thorough analysis of research papers with a connected taxonomy that facilitates the categorisation of privacy attacks and countermeasures based on the targeted explanations. This work also includes an initial investigation into the causes of privacy leaks. Finally, we discuss unresolved issues and prospective research directions uncovered in our analysis. This survey aims to be a valuable resource for the research community and offers clear insights for those new to this domain. To support ongoing research, we have established an online resource repository, which will be continuously updated with new and relevant findings. Interested readers are encouraged to access our repository at https://github.com/tamlhp/awesome-privex.
STAA-Net: A Sparse and Transferable Adversarial Attack for Speech Emotion Recognition
Feb 02, 2024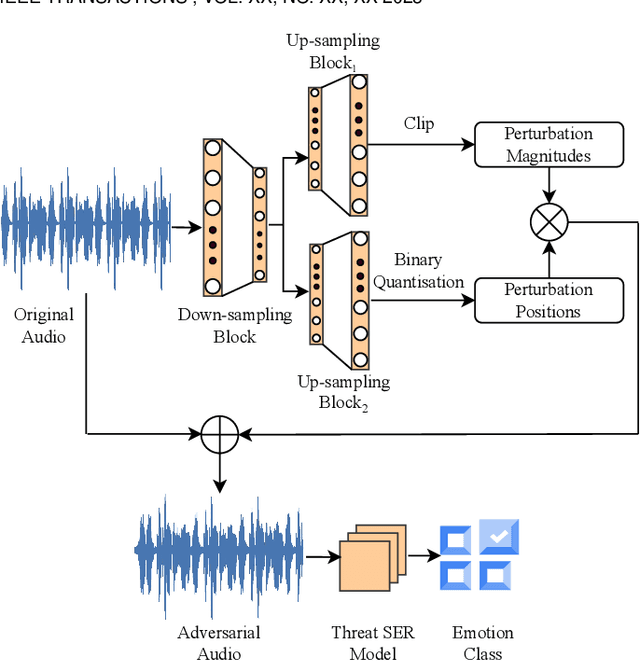
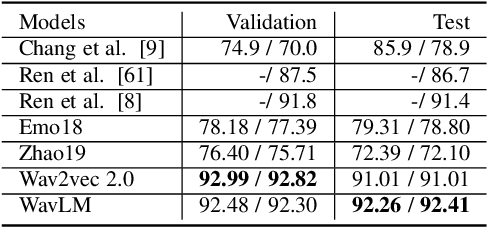
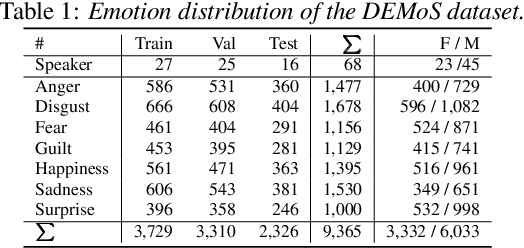
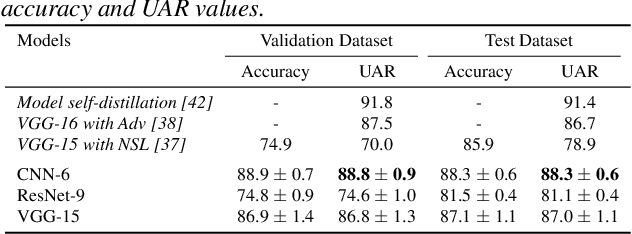
Abstract:Speech contains rich information on the emotions of humans, and Speech Emotion Recognition (SER) has been an important topic in the area of human-computer interaction. The robustness of SER models is crucial, particularly in privacy-sensitive and reliability-demanding domains like private healthcare. Recently, the vulnerability of deep neural networks in the audio domain to adversarial attacks has become a popular area of research. However, prior works on adversarial attacks in the audio domain primarily rely on iterative gradient-based techniques, which are time-consuming and prone to overfitting the specific threat model. Furthermore, the exploration of sparse perturbations, which have the potential for better stealthiness, remains limited in the audio domain. To address these challenges, we propose a generator-based attack method to generate sparse and transferable adversarial examples to deceive SER models in an end-to-end and efficient manner. We evaluate our method on two widely-used SER datasets, Database of Elicited Mood in Speech (DEMoS) and Interactive Emotional dyadic MOtion CAPture (IEMOCAP), and demonstrate its ability to generate successful sparse adversarial examples in an efficient manner. Moreover, our generated adversarial examples exhibit model-agnostic transferability, enabling effective adversarial attacks on advanced victim models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge