Zehong Cao
Cross-Domain Few-Shot Learning for Hyperspectral Image Classification Based on Mixup Foundation Model
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Although cross-domain few-shot learning (CDFSL) for hyper-spectral image (HSI) classification has attracted significant research interest, existing works often rely on an unrealistic data augmentation procedure in the form of external noise to enlarge the sample size, thus greatly simplifying the issue of data scarcity. They involve a large number of parameters for model updates, being prone to the overfitting problem. To the best of our knowledge, none has explored the strength of the foundation model, having strong generalization power to be quickly adapted to downstream tasks. This paper proposes the MIxup FOundation MOdel (MIFOMO) for CDFSL of HSI classifications. MIFOMO is built upon the concept of a remote sensing (RS) foundation model, pre-trained across a large scale of RS problems, thus featuring generalizable features. The notion of coalescent projection (CP) is introduced to quickly adapt the foundation model to downstream tasks while freezing the backbone network. The concept of mixup domain adaptation (MDM) is proposed to address the extreme domain discrepancy problem. Last but not least, the label smoothing concept is implemented to cope with noisy pseudo-label problems. Our rigorous experiments demonstrate the advantage of MIFOMO, where it beats prior arts with up to 14% margin. The source code of MIFOMO is open-sourced in https://github.com/Naeem- Paeedeh/MIFOMO for reproducibility and convenient further study.
Pretraining Large Brain Language Model for Active BCI: Silent Speech
Apr 29, 2025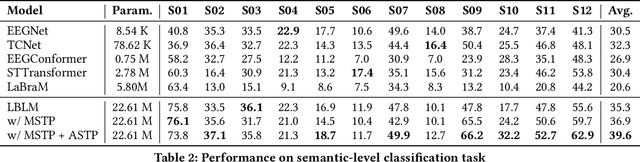
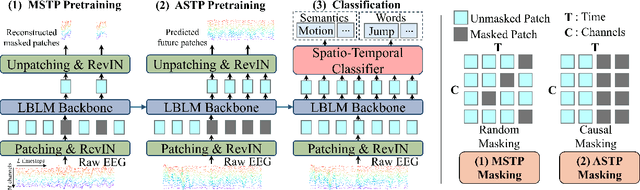
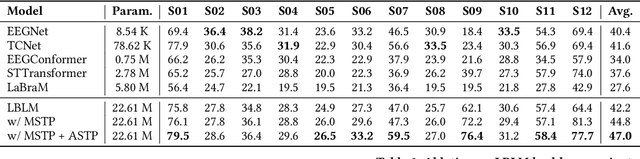
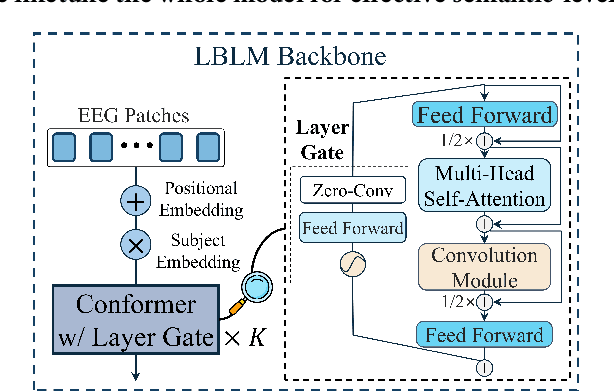
Abstract:This paper explores silent speech decoding in active brain-computer interface (BCI) systems, which offer more natural and flexible communication than traditional BCI applications. We collected a new silent speech dataset of over 120 hours of electroencephalogram (EEG) recordings from 12 subjects, capturing 24 commonly used English words for language model pretraining and decoding. Following the recent success of pretraining large models with self-supervised paradigms to enhance EEG classification performance, we propose Large Brain Language Model (LBLM) pretrained to decode silent speech for active BCI. To pretrain LBLM, we propose Future Spectro-Temporal Prediction (FSTP) pretraining paradigm to learn effective representations from unlabeled EEG data. Unlike existing EEG pretraining methods that mainly follow a masked-reconstruction paradigm, our proposed FSTP method employs autoregressive modeling in temporal and frequency domains to capture both temporal and spectral dependencies from EEG signals. After pretraining, we finetune our LBLM on downstream tasks, including word-level and semantic-level classification. Extensive experiments demonstrate significant performance gains of the LBLM over fully-supervised and pretrained baseline models. For instance, in the difficult cross-session setting, our model achieves 47.0\% accuracy on semantic-level classification and 39.6\% in word-level classification, outperforming baseline methods by 5.4\% and 7.3\%, respectively. Our research advances silent speech decoding in active BCI systems, offering an innovative solution for EEG language model pretraining and a new dataset for fundamental research.
A Self-Constructing Multi-Expert Fuzzy System for High-dimensional Data Classification
Oct 17, 2024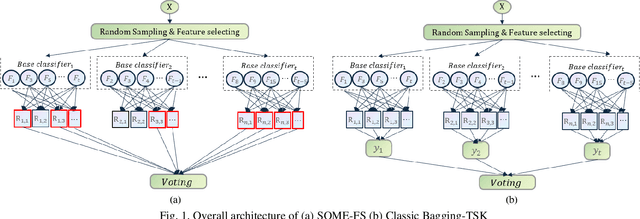
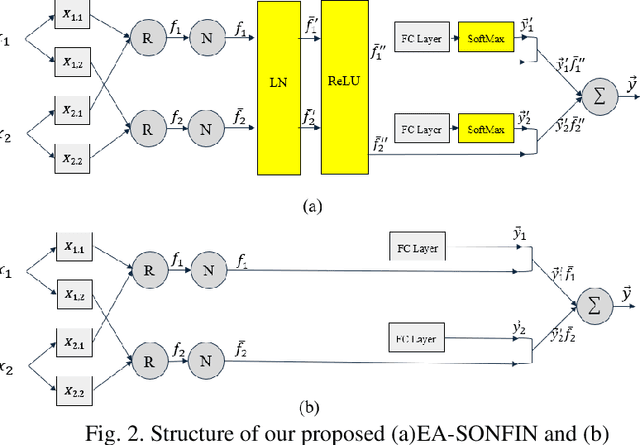
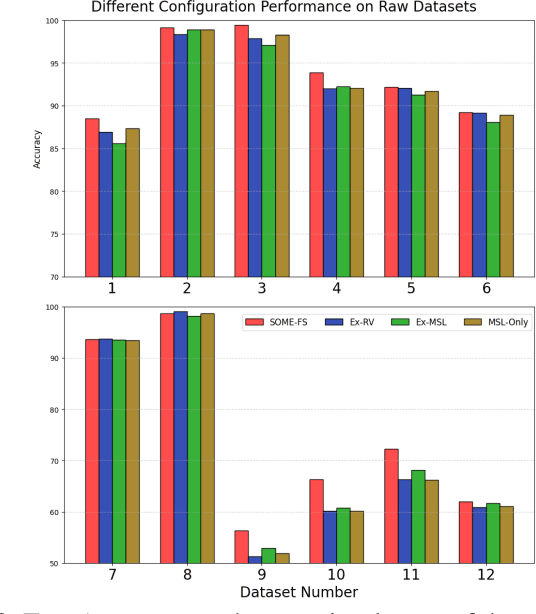
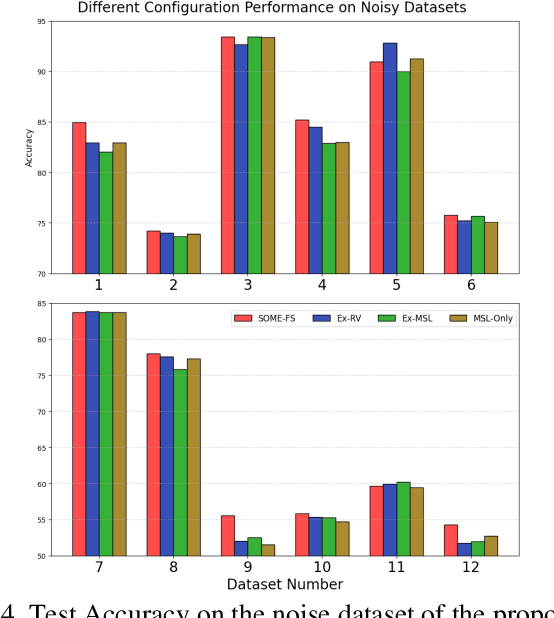
Abstract:Fuzzy Neural Networks (FNNs) are effective machine learning models for classification tasks, commonly based on the Takagi-Sugeno-Kang (TSK) fuzzy system. However, when faced with high-dimensional data, especially with noise, FNNs encounter challenges such as vanishing gradients, excessive fuzzy rules, and limited access to prior knowledge. To address these challenges, we propose a novel fuzzy system, the Self-Constructing Multi-Expert Fuzzy System (SOME-FS). It combines two learning strategies: mixed structure learning and multi-expert advanced learning. The former enables each base classifier to effectively determine its structure without requiring prior knowledge, while the latter tackles the issue of vanishing gradients by enabling each rule to focus on its local region, thereby enhancing the robustness of the fuzzy classifiers. The overall ensemble architecture enhances the stability and prediction performance of the fuzzy system. Our experimental results demonstrate that the proposed SOME-FS is effective in high-dimensional tabular data, especially in dealing with uncertainty. Moreover, our stable rule mining process can identify concise and core rules learned by the SOME-FS.
Knowledge-Guided Prompt Learning for Lifespan Brain MR Image Segmentation
Jul 31, 2024



Abstract:Automatic and accurate segmentation of brain MR images throughout the human lifespan into tissue and structure is crucial for understanding brain development and diagnosing diseases. However, challenges arise from the intricate variations in brain appearance due to rapid early brain development, aging, and disorders, compounded by the limited availability of manually-labeled datasets. In response, we present a two-step segmentation framework employing Knowledge-Guided Prompt Learning (KGPL) for brain MRI. Specifically, we first pre-train segmentation models on large-scale datasets with sub-optimal labels, followed by the incorporation of knowledge-driven embeddings learned from image-text alignment into the models. The introduction of knowledge-wise prompts captures semantic relationships between anatomical variability and biological processes, enabling models to learn structural feature embeddings across diverse age groups. Experimental findings demonstrate the superiority and robustness of our proposed method, particularly noticeable when employing Swin UNETR as the backbone. Our approach achieves average DSC values of 95.17% and 94.19% for brain tissue and structure segmentation, respectively. Our code is available at https://github.com/TL9792/KGPL.
Cross-Domain Few-Shot Learning via Adaptive Transformer Networks
Jan 25, 2024Abstract:Most few-shot learning works rely on the same domain assumption between the base and the target tasks, hindering their practical applications. This paper proposes an adaptive transformer network (ADAPTER), a simple but effective solution for cross-domain few-shot learning where there exist large domain shifts between the base task and the target task. ADAPTER is built upon the idea of bidirectional cross-attention to learn transferable features between the two domains. The proposed architecture is trained with DINO to produce diverse, and less biased features to avoid the supervision collapse problem. Furthermore, the label smoothing approach is proposed to improve the consistency and reliability of the predictions by also considering the predicted labels of the close samples in the embedding space. The performance of ADAPTER is rigorously evaluated in the BSCD-FSL benchmarks in which it outperforms prior arts with significant margins.
Hunting imaging biomarkers in pulmonary fibrosis: Benchmarks of the AIIB23 challenge
Dec 21, 2023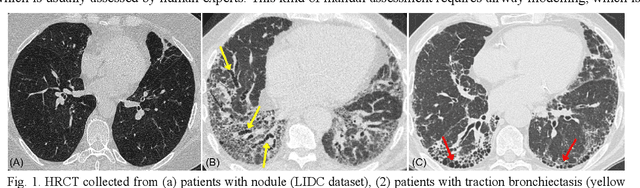
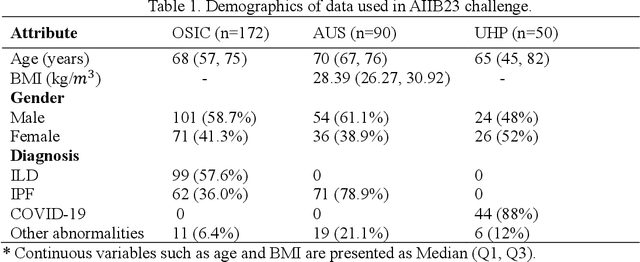
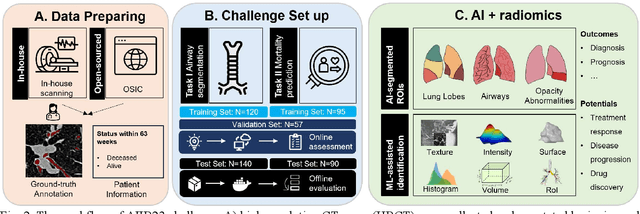
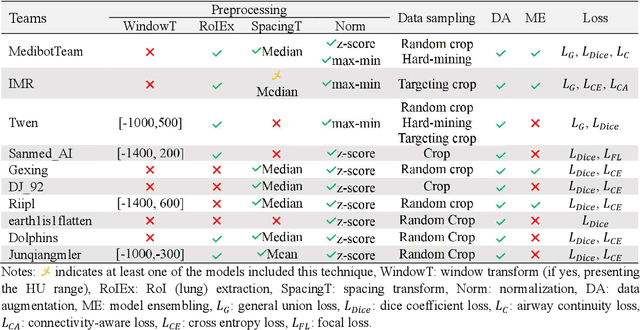
Abstract:Airway-related quantitative imaging biomarkers are crucial for examination, diagnosis, and prognosis in pulmonary diseases. However, the manual delineation of airway trees remains prohibitively time-consuming. While significant efforts have been made towards enhancing airway modelling, current public-available datasets concentrate on lung diseases with moderate morphological variations. The intricate honeycombing patterns present in the lung tissues of fibrotic lung disease patients exacerbate the challenges, often leading to various prediction errors. To address this issue, the 'Airway-Informed Quantitative CT Imaging Biomarker for Fibrotic Lung Disease 2023' (AIIB23) competition was organized in conjunction with the official 2023 International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI). The airway structures were meticulously annotated by three experienced radiologists. Competitors were encouraged to develop automatic airway segmentation models with high robustness and generalization abilities, followed by exploring the most correlated QIB of mortality prediction. A training set of 120 high-resolution computerised tomography (HRCT) scans were publicly released with expert annotations and mortality status. The online validation set incorporated 52 HRCT scans from patients with fibrotic lung disease and the offline test set included 140 cases from fibrosis and COVID-19 patients. The results have shown that the capacity of extracting airway trees from patients with fibrotic lung disease could be enhanced by introducing voxel-wise weighted general union loss and continuity loss. In addition to the competitive image biomarkers for prognosis, a strong airway-derived biomarker (Hazard ratio>1.5, p<0.0001) was revealed for survival prognostication compared with existing clinical measurements, clinician assessment and AI-based biomarkers.
Distributed Semi-supervised Fuzzy Regression with Interpolation Consistency Regularization
Sep 18, 2022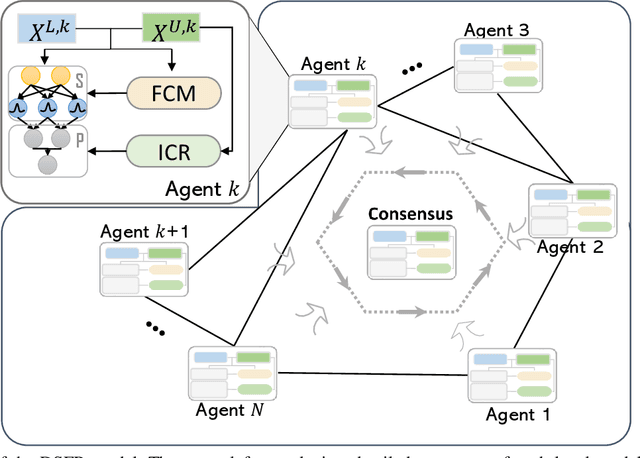
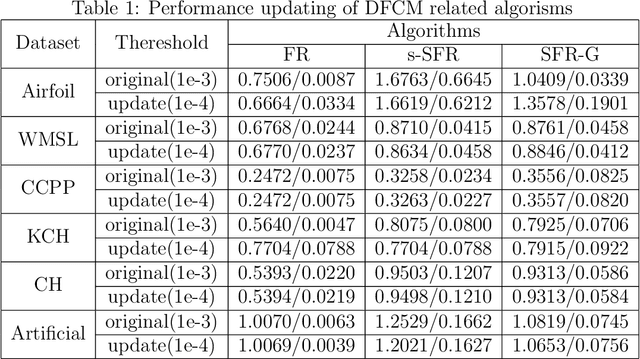
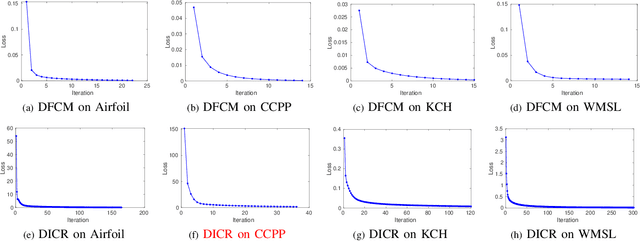
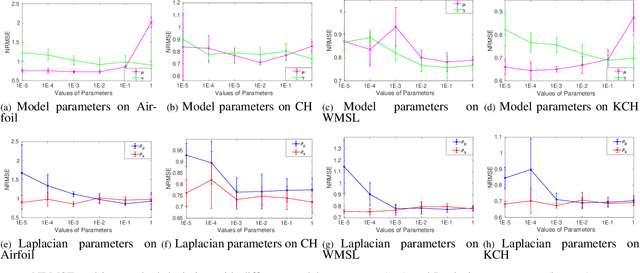
Abstract:Recently, distributed semi-supervised learning (DSSL) algorithms have shown their effectiveness in leveraging unlabeled samples over interconnected networks, where agents cannot share their original data with each other and can only communicate non-sensitive information with their neighbors. However, existing DSSL algorithms cannot cope with data uncertainties and may suffer from high computation and communication overhead problems. To handle these issues, we propose a distributed semi-supervised fuzzy regression (DSFR) model with fuzzy if-then rules and interpolation consistency regularization (ICR). The ICR, which was proposed recently for semi-supervised problem, can force decision boundaries to pass through sparse data areas, thus increasing model robustness. However, its application in distributed scenarios has not been considered yet. In this work, we proposed a distributed Fuzzy C-means (DFCM) method and a distributed interpolation consistency regularization (DICR) built on the well-known alternating direction method of multipliers to respectively locate parameters in antecedent and consequent components of DSFR. Notably, the DSFR model converges very fast since it does not involve back-propagation procedure and is scalable to large-scale datasets benefiting from the utilization of DFCM and DICR. Experiments results on both artificial and real-world datasets show that the proposed DSFR model can achieve much better performance than the state-of-the-art DSSL algorithm in terms of both loss value and computational cost.
Self-Awareness Safety of Deep Reinforcement Learning in Road Traffic Junction Driving
Jan 20, 2022



Abstract:Autonomous driving has been at the forefront of public interest, and a pivotal debate to widespread concerns is safety in the transportation system. Deep reinforcement learning (DRL) has been applied to autonomous driving to provide solutions for obstacle avoidance. However, in a road traffic junction scenario, the vehicle typically receives partial observations from the transportation environment, while DRL needs to rely on long-term rewards to train a reliable model by maximising the cumulative rewards, which may take the risk when exploring new actions and returning either a positive reward or a penalty in the case of collisions. Although safety concerns are usually considered in the design of a reward function, they are not fully considered as the critical metric to directly evaluate the effectiveness of DRL algorithms in autonomous driving. In this study, we evaluated the safety performance of three baseline DRL models (DQN, A2C, and PPO) and proposed a self-awareness module from an attention mechanism for DRL to improve the safety evaluation for an anomalous vehicle in a complex road traffic junction environment, such as intersection and roundabout scenarios, based on four metrics: collision rate, success rate, freezing rate, and total reward. Our two experimental results in the training and testing phases revealed the baseline DRL with poor safety performance, while our proposed self-awareness attention-DQN can significantly improve the safety performance in intersection and roundabout scenarios.
Retrieving Event-related Human Brain Dynamics from Natural Sentence Reading
Mar 29, 2021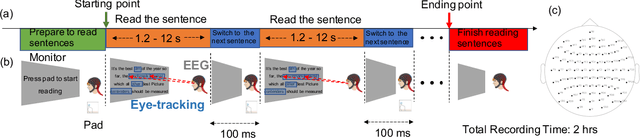
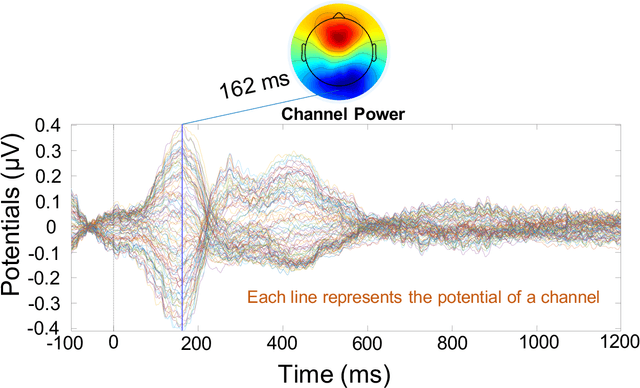
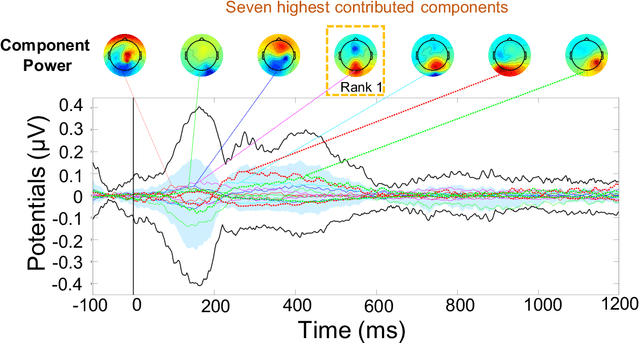
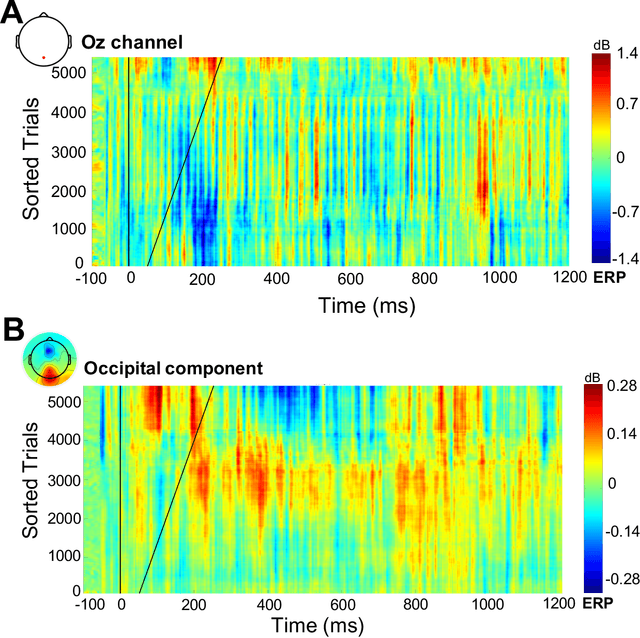
Abstract:Electroencephalography (EEG) signals recordings when people reading natural languages are commonly used as a cognitive method to interpret human language understanding in neuroscience and psycholinguistics. Previous studies have demonstrated that the human fixation and activation in word reading associated with some brain regions, but it is not clear when and how to measure the brain dynamics across time and frequency domains. In this study, we propose the first analysis of event-related brain potentials (ERPs), and event-related spectral perturbations (ERSPs) on benchmark datasets which consist of sentence-level simultaneous EEG and related eye-tracking recorded from human natural reading experiment tasks. Our results showed peaks evoked at around 162 ms after the stimulus (starting to read each sentence) in the occipital area, indicating the brain retriving lexical and semantic visual information processing approaching 200 ms from the sentence onset. Furthermore, the occipital ERP around 200ms presents negative power and positive power in short and long reaction times. In addition, the occipital ERSP around 200ms demonstrated increased high gamma and decreased low beta and low gamma power, relative to the baseline. Our results implied that most of the semantic-perception responses occurred around the 200ms in alpha, beta and gamma bands of EEG signals. Our findings also provide potential impacts on promoting cognitive natural language processing models evaluation from EEG dynamics.
Identification of EEG Dynamics During Freezing of Gait and Voluntary Stopping in Patients with Parkinson's Disease
Feb 06, 2021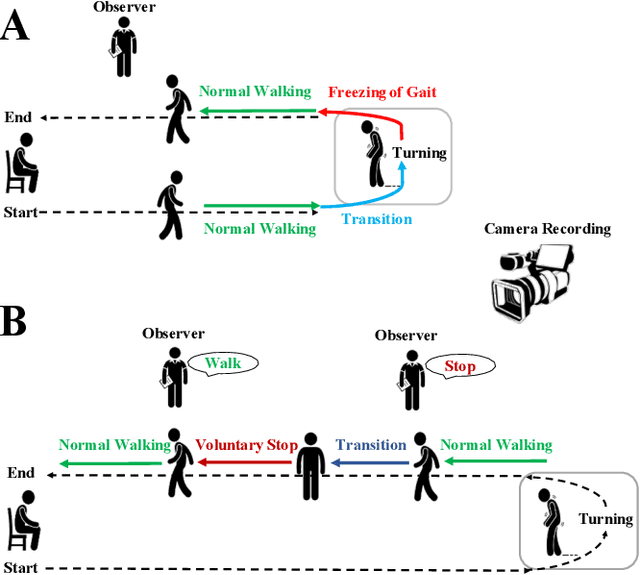
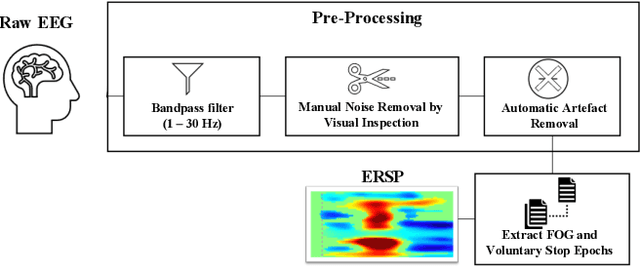
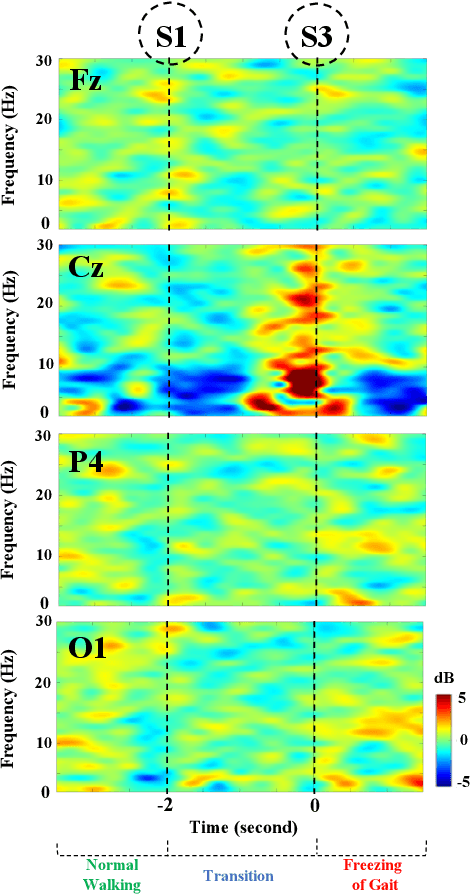
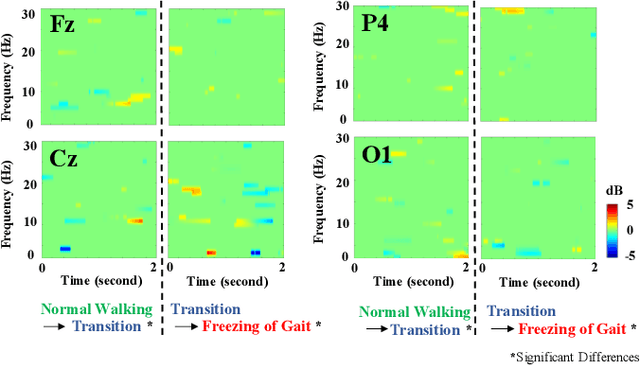
Abstract:Mobility is severely impacted in patients with Parkinson's disease (PD), especially when they experience involuntary stopping from the freezing of gait (FOG). Understanding the neurophysiological difference between "voluntary stopping" and "involuntary stopping" caused by FOG is vital for the detection and potential intervention of FOG in the daily lives of patients. This study characterised the electroencephalographic (EEG) signature associated with FOG in contrast to voluntary stopping. The protocol consisted of a timed up-and-go (TUG) task and an additional TUG task with a voluntary stopping component, where participants reacted to verbal "stop" and "walk" instructions by voluntarily stopping or walking. Event-related spectral perturbation (ERSP) analysis was used to study the dynamics of the EEG spectra induced by different walking phases, which included normal walking, voluntary stopping and episodes of involuntary stopping (FOG), as well as the transition windows between normal walking and voluntary stopping or FOG. These results demonstrate for the first time that the EEG signal during the transition from walking to voluntary stopping is distinguishable from that of the transition to involuntary stopping caused by FOG. The EEG signature of voluntary stopping exhibits a significantly decreased power spectrum compared to that of FOG episodes, with distinctly different patterns in the delta and low-beta power in the central area. These findings suggest the possibility of a practical EEG-based treatment strategy that can accurately predict FOG episodes, excluding the potential confound of voluntary stopping.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge