Yuanpeng Tu
PlayerOne: Egocentric World Simulator
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:We introduce PlayerOne, the first egocentric realistic world simulator, facilitating immersive and unrestricted exploration within vividly dynamic environments. Given an egocentric scene image from the user, PlayerOne can accurately construct the corresponding world and generate egocentric videos that are strictly aligned with the real scene human motion of the user captured by an exocentric camera. PlayerOne is trained in a coarse-to-fine pipeline that first performs pretraining on large-scale egocentric text-video pairs for coarse-level egocentric understanding, followed by finetuning on synchronous motion-video data extracted from egocentric-exocentric video datasets with our automatic construction pipeline. Besides, considering the varying importance of different components, we design a part-disentangled motion injection scheme, enabling precise control of part-level movements. In addition, we devise a joint reconstruction framework that progressively models both the 4D scene and video frames, ensuring scene consistency in the long-form video generation. Experimental results demonstrate its great generalization ability in precise control of varying human movements and worldconsistent modeling of diverse scenarios. It marks the first endeavor into egocentric real-world simulation and can pave the way for the community to delve into fresh frontiers of world modeling and its diverse applications.
LayerFlow: A Unified Model for Layer-aware Video Generation
Jun 04, 2025Abstract:We present LayerFlow, a unified solution for layer-aware video generation. Given per-layer prompts, LayerFlow generates videos for the transparent foreground, clean background, and blended scene. It also supports versatile variants like decomposing a blended video or generating the background for the given foreground and vice versa. Starting from a text-to-video diffusion transformer, we organize the videos for different layers as sub-clips, and leverage layer embeddings to distinguish each clip and the corresponding layer-wise prompts. In this way, we seamlessly support the aforementioned variants in one unified framework. For the lack of high-quality layer-wise training videos, we design a multi-stage training strategy to accommodate static images with high-quality layer annotations. Specifically, we first train the model with low-quality video data. Then, we tune a motion LoRA to make the model compatible with static frames. Afterward, we train the content LoRA on the mixture of image data with high-quality layered images along with copy-pasted video data. During inference, we remove the motion LoRA thus generating smooth videos with desired layers.
Unleashing Diffusion Transformers for Visual Correspondence by Modulating Massive Activations
May 24, 2025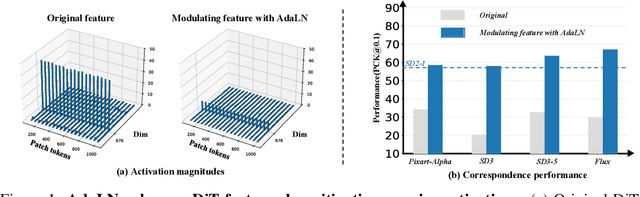
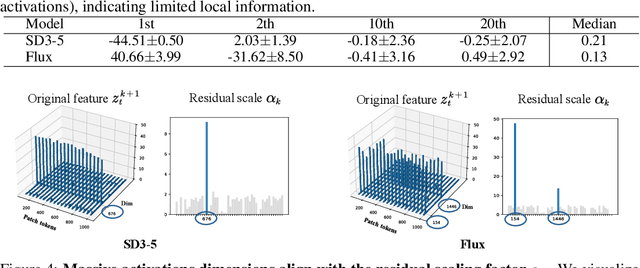
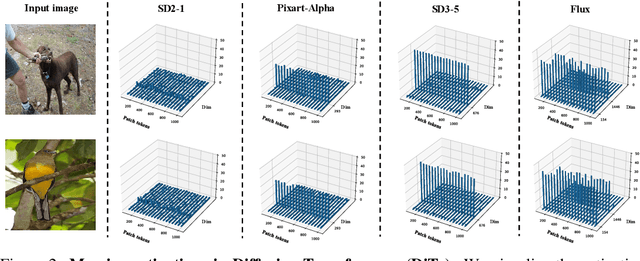
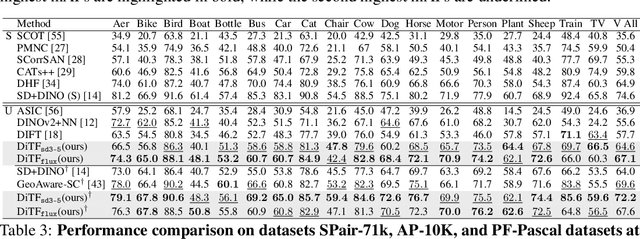
Abstract:Pre-trained stable diffusion models (SD) have shown great advances in visual correspondence. In this paper, we investigate the capabilities of Diffusion Transformers (DiTs) for accurate dense correspondence. Distinct from SD, DiTs exhibit a critical phenomenon in which very few feature activations exhibit significantly larger values than others, known as \textit{massive activations}, leading to uninformative representations and significant performance degradation for DiTs. The massive activations consistently concentrate at very few fixed dimensions across all image patch tokens, holding little local information. We trace these dimension-concentrated massive activations and find that such concentration can be effectively localized by the zero-initialized Adaptive Layer Norm (AdaLN-zero). Building on these findings, we propose Diffusion Transformer Feature (DiTF), a training-free framework designed to extract semantic-discriminative features from DiTs. Specifically, DiTF employs AdaLN to adaptively localize and normalize massive activations with channel-wise modulation. In addition, we develop a channel discard strategy to further eliminate the negative impacts from massive activations. Experimental results demonstrate that our DiTF outperforms both DINO and SD-based models and establishes a new state-of-the-art performance for DiTs in different visual correspondence tasks (\eg, with +9.4\% on Spair-71k and +4.4\% on AP-10K-C.S.).
VideoAnydoor: High-fidelity Video Object Insertion with Precise Motion Control
Jan 07, 2025



Abstract:Despite significant advancements in video generation, inserting a given object into videos remains a challenging task. The difficulty lies in preserving the appearance details of the reference object and accurately modeling coherent motions at the same time. In this paper, we propose VideoAnydoor, a zero-shot video object insertion framework with high-fidelity detail preservation and precise motion control. Starting from a text-to-video model, we utilize an ID extractor to inject the global identity and leverage a box sequence to control the overall motion. To preserve the detailed appearance and meanwhile support fine-grained motion control, we design a pixel warper. It takes the reference image with arbitrary key-points and the corresponding key-point trajectories as inputs. It warps the pixel details according to the trajectories and fuses the warped features with the diffusion U-Net, thus improving detail preservation and supporting users in manipulating the motion trajectories. In addition, we propose a training strategy involving both videos and static images with a weighted loss to enhance insertion quality. VideoAnydoor demonstrates significant superiority over existing methods and naturally supports various downstream applications (e.g., talking head generation, video virtual try-on, multi-region editing) without task-specific fine-tuning.
DreamMask: Boosting Open-vocabulary Panoptic Segmentation with Synthetic Data
Jan 03, 2025Abstract:Open-vocabulary panoptic segmentation has received significant attention due to its applicability in the real world. Despite claims of robust generalization, we find that the advancements of previous works are attributed mainly on trained categories, exposing a lack of generalization to novel classes. In this paper, we explore boosting existing models from a data-centric perspective. We propose DreamMask, which systematically explores how to generate training data in the open-vocabulary setting, and how to train the model with both real and synthetic data. For the first part, we propose an automatic data generation pipeline with off-the-shelf models. We propose crucial designs for vocabulary expansion, layout arrangement, data filtering, etc. Equipped with these techniques, our generated data could significantly outperform the manually collected web data. To train the model with generated data, a synthetic-real alignment loss is designed to bridge the representation gap, bringing noticeable improvements across multiple benchmarks. In general, DreamMask significantly simplifies the collection of large-scale training data, serving as a plug-and-play enhancement for existing methods. For instance, when trained on COCO and tested on ADE20K, the model equipped with DreamMask outperforms the previous state-of-the-art by a substantial margin of 2.1% mIoU.
DAC: 2D-3D Retrieval with Noisy Labels via Divide-and-Conquer Alignment and Correction
Jul 25, 2024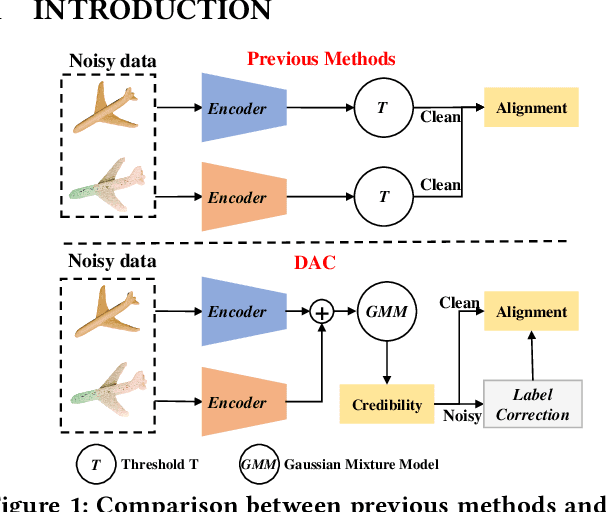

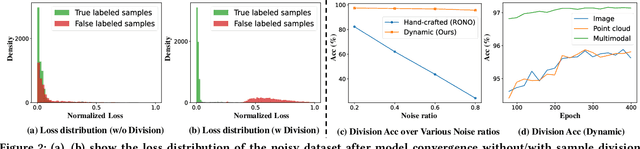

Abstract:With the recent burst of 2D and 3D data, cross-modal retrieval has attracted increasing attention recently. However, manual labeling by non-experts will inevitably introduce corrupted annotations given ambiguous 2D/3D content. Though previous works have addressed this issue by designing a naive division strategy with hand-crafted thresholds, their performance generally exhibits great sensitivity to the threshold value. Besides, they fail to fully utilize the valuable supervisory signals within each divided subset. To tackle this problem, we propose a Divide-and-conquer 2D-3D cross-modal Alignment and Correction framework (DAC), which comprises Multimodal Dynamic Division (MDD) and Adaptive Alignment and Correction (AAC). Specifically, the former performs accurate sample division by adaptive credibility modeling for each sample based on the compensation information within multimodal loss distribution. Then in AAC, samples in distinct subsets are exploited with different alignment strategies to fully enhance the semantic compactness and meanwhile alleviate over-fitting to noisy labels, where a self-correction strategy is introduced to improve the quality of representation. Moreover. To evaluate the effectiveness in real-world scenarios, we introduce a challenging noisy benchmark, namely Objaverse-N200, which comprises 200k-level samples annotated with 1156 realistic noisy labels. Extensive experiments on both traditional and the newly proposed benchmarks demonstrate the generality and superiority of our DAC, where DAC outperforms state-of-the-art models by a large margin. (i.e., with +5.9% gain on ModelNet40 and +5.8% on Objaverse-N200).
Memory Consistency Guided Divide-and-Conquer Learning for Generalized Category Discovery
Feb 01, 2024Abstract:Generalized category discovery (GCD) aims at addressing a more realistic and challenging setting of semi-supervised learning, where only part of the category labels are assigned to certain training samples. Previous methods generally employ naive contrastive learning or unsupervised clustering scheme for all the samples. Nevertheless, they usually ignore the inherent critical information within the historical predictions of the model being trained. Specifically, we empirically reveal that a significant number of salient unlabeled samples yield consistent historical predictions corresponding to their ground truth category. From this observation, we propose a Memory Consistency guided Divide-and-conquer Learning framework (MCDL). In this framework, we introduce two memory banks to record historical prediction of unlabeled data, which are exploited to measure the credibility of each sample in terms of its prediction consistency. With the guidance of credibility, we can design a divide-and-conquer learning strategy to fully utilize the discriminative information of unlabeled data while alleviating the negative influence of noisy labels. Extensive experimental results on multiple benchmarks demonstrate the generality and superiority of our method, where our method outperforms state-of-the-art models by a large margin on both seen and unseen classes of the generic image recognition and challenging semantic shift settings (i.e.,with +8.4% gain on CUB and +8.1% on Standford Cars).
DROP: Decouple Re-Identification and Human Parsing with Task-specific Features for Occluded Person Re-identification
Jan 31, 2024Abstract:The paper introduces the Decouple Re-identificatiOn and human Parsing (DROP) method for occluded person re-identification (ReID). Unlike mainstream approaches using global features for simultaneous multi-task learning of ReID and human parsing, or relying on semantic information for attention guidance, DROP argues that the inferior performance of the former is due to distinct granularity requirements for ReID and human parsing features. ReID focuses on instance part-level differences between pedestrian parts, while human parsing centers on semantic spatial context, reflecting the internal structure of the human body. To address this, DROP decouples features for ReID and human parsing, proposing detail-preserving upsampling to combine varying resolution feature maps. Parsing-specific features for human parsing are decoupled, and human position information is exclusively added to the human parsing branch. In the ReID branch, a part-aware compactness loss is introduced to enhance instance-level part differences. Experimental results highlight the efficacy of DROP, especially achieving a Rank-1 accuracy of 76.8% on Occluded-Duke, surpassing two mainstream methods. The codebase is accessible at https://github.com/shuguang-52/DROP.
Self-supervised Feature Adaptation for 3D Industrial Anomaly Detection
Jan 17, 2024



Abstract:Industrial anomaly detection is generally addressed as an unsupervised task that aims at locating defects with only normal training samples. Recently, numerous 2D anomaly detection methods have been proposed and have achieved promising results, however, using only the 2D RGB data as input is not sufficient to identify imperceptible geometric surface anomalies. Hence, in this work, we focus on multi-modal anomaly detection. Specifically, we investigate early multi-modal approaches that attempted to utilize models pre-trained on large-scale visual datasets, i.e., ImageNet, to construct feature databases. And we empirically find that directly using these pre-trained models is not optimal, it can either fail to detect subtle defects or mistake abnormal features as normal ones. This may be attributed to the domain gap between target industrial data and source data.Towards this problem, we propose a Local-to-global Self-supervised Feature Adaptation (LSFA) method to finetune the adaptors and learn task-oriented representation toward anomaly detection.Both intra-modal adaptation and cross-modal alignment are optimized from a local-to-global perspective in LSFA to ensure the representation quality and consistency in the inference stage.Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method not only brings a significant performance boost to feature embedding based approaches, but also outperforms previous State-of-The-Art (SoTA) methods prominently on both MVTec-3D AD and Eyecandies datasets, e.g., LSFA achieves 97.1% I-AUROC on MVTec-3D, surpass previous SoTA by +3.4%.
Learning from Noisy Labels with Decoupled Meta Label Purifier
Feb 17, 2023



Abstract:Training deep neural networks(DNN) with noisy labels is challenging since DNN can easily memorize inaccurate labels, leading to poor generalization ability. Recently, the meta-learning based label correction strategy is widely adopted to tackle this problem via identifying and correcting potential noisy labels with the help of a small set of clean validation data. Although training with purified labels can effectively improve performance, solving the meta-learning problem inevitably involves a nested loop of bi-level optimization between model weights and hyper-parameters (i.e., label distribution). As compromise, previous methods resort to a coupled learning process with alternating update. In this paper, we empirically find such simultaneous optimization over both model weights and label distribution can not achieve an optimal routine, consequently limiting the representation ability of backbone and accuracy of corrected labels. From this observation, a novel multi-stage label purifier named DMLP is proposed. DMLP decouples the label correction process into label-free representation learning and a simple meta label purifier. In this way, DMLP can focus on extracting discriminative feature and label correction in two distinctive stages. DMLP is a plug-and-play label purifier, the purified labels can be directly reused in naive end-to-end network retraining or other robust learning methods, where state-of-the-art results are obtained on several synthetic and real-world noisy datasets, especially under high noise levels.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge