Yiyang Wang
MASCOT: Towards Multi-Agent Socio-Collaborative Companion Systems
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Multi-agent systems (MAS) have recently emerged as promising socio-collaborative companions for emotional and cognitive support. However, these systems frequently suffer from persona collapse--where agents revert to generic, homogenized assistant behaviors--and social sycophancy, which produces redundant, non-constructive dialogue. We propose MASCOT, a generalizable framework for multi-perspective socio-collaborative companions. MASCOT introduces a novel bi-level optimization strategy to harmonize individual and collective behaviors: 1) Persona-Aware Behavioral Alignment, an RLAIF-driven pipeline that finetunes individual agents for strict persona fidelity to prevent identity loss; and 2) Collaborative Dialogue Optimization, a meta-policy guided by group-level rewards to ensure diverse and productive discourse. Extensive evaluations across psychological support and workplace domains demonstrate that MASCOT significantly outperforms state-of-the-art baselines, achieving improvements of up to +14.1 in Persona Consistency and +10.6 in Social Contribution. Our framework provides a practical roadmap for engineering the next generation of socially intelligent multi-agent systems.
GDRO: Group-level Reward Post-training Suitable for Diffusion Models
Jan 05, 2026Abstract:Recent advancements adopt online reinforcement learning (RL) from LLMs to text-to-image rectified flow diffusion models for reward alignment. The use of group-level rewards successfully aligns the model with the targeted reward. However, it faces challenges including low efficiency, dependency on stochastic samplers, and reward hacking. The problem is that rectified flow models are fundamentally different from LLMs: 1) For efficiency, online image sampling takes much more time and dominates the time of training. 2) For stochasticity, rectified flow is deterministic once the initial noise is fixed. Aiming at these problems and inspired by the effects of group-level rewards from LLMs, we design Group-level Direct Reward Optimization (GDRO). GDRO is a new post-training paradigm for group-level reward alignment that combines the characteristics of rectified flow models. Through rigorous theoretical analysis, we point out that GDRO supports full offline training that saves the large time cost for image rollout sampling. Also, it is diffusion-sampler-independent, which eliminates the need for the ODE-to-SDE approximation to obtain stochasticity. We also empirically study the reward hacking trap that may mislead the evaluation, and involve this factor in the evaluation using a corrected score that not only considers the original evaluation reward but also the trend of reward hacking. Extensive experiments demonstrate that GDRO effectively and efficiently improves the reward score of the diffusion model through group-wise offline optimization across the OCR and GenEval tasks, while demonstrating strong stability and robustness in mitigating reward hacking.
CompanionCast: A Multi-Agent Conversational AI Framework with Spatial Audio for Social Co-Viewing Experiences
Dec 11, 2025Abstract:Social presence is central to the enjoyment of watching content together, yet modern media consumption is increasingly solitary. We investigate whether multi-agent conversational AI systems can recreate the dynamics of shared viewing experiences across diverse content types. We present CompanionCast, a general framework for orchestrating multiple role-specialized AI agents that respond to video content using multimodal inputs, speech synthesis, and spatial audio. Distinctly, CompanionCast integrates an LLM-as-a-Judge module that iteratively scores and refines conversations across five dimensions (relevance, authenticity, engagement, diversity, personality consistency). We validate this framework through sports viewing, a domain with rich dynamics and strong social traditions, where a pilot study with soccer fans suggests that multi-agent interaction improves perceived social presence compared to solo viewing. We contribute: (1) a generalizable framework for orchestrating multi-agent conversations around multimodal video content, (2) a novel evaluator-agent pipeline for conversation quality control, and (3) exploratory evidence of increased social presence in AI-mediated co-viewing. We discuss challenges and future directions for applying this approach to diverse viewing contexts including entertainment, education, and collaborative watching experiences.
DiffCamera: Arbitrary Refocusing on Images
Sep 30, 2025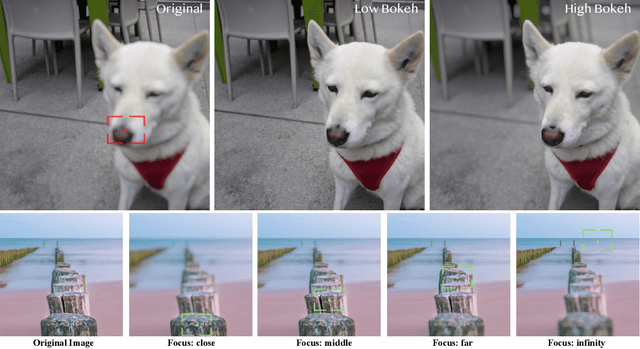
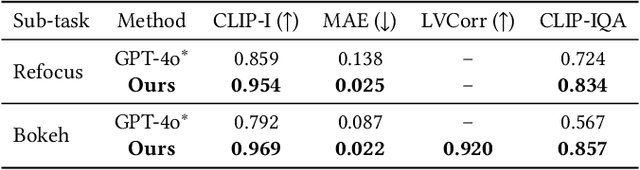
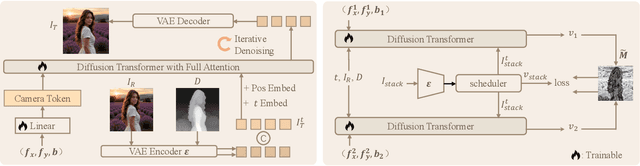
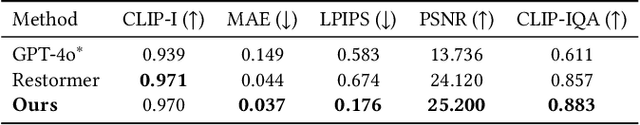
Abstract:The depth-of-field (DoF) effect, which introduces aesthetically pleasing blur, enhances photographic quality but is fixed and difficult to modify once the image has been created. This becomes problematic when the applied blur is undesirable~(e.g., the subject is out of focus). To address this, we propose DiffCamera, a model that enables flexible refocusing of a created image conditioned on an arbitrary new focus point and a blur level. Specifically, we design a diffusion transformer framework for refocusing learning. However, the training requires pairs of data with different focus planes and bokeh levels in the same scene, which are hard to acquire. To overcome this limitation, we develop a simulation-based pipeline to generate large-scale image pairs with varying focus planes and bokeh levels. With the simulated data, we find that training with only a vanilla diffusion objective often leads to incorrect DoF behaviors due to the complexity of the task. This requires a stronger constraint during training. Inspired by the photographic principle that photos of different focus planes can be linearly blended into a multi-focus image, we propose a stacking constraint during training to enforce precise DoF manipulation. This constraint enhances model training by imposing physically grounded refocusing behavior that the focusing results should be faithfully aligned with the scene structure and the camera conditions so that they can be combined into the correct multi-focus image. We also construct a benchmark to evaluate the effectiveness of our refocusing model. Extensive experiments demonstrate that DiffCamera supports stable refocusing across a wide range of scenes, providing unprecedented control over DoF adjustments for photography and generative AI applications.
LayerFlow: A Unified Model for Layer-aware Video Generation
Jun 04, 2025Abstract:We present LayerFlow, a unified solution for layer-aware video generation. Given per-layer prompts, LayerFlow generates videos for the transparent foreground, clean background, and blended scene. It also supports versatile variants like decomposing a blended video or generating the background for the given foreground and vice versa. Starting from a text-to-video diffusion transformer, we organize the videos for different layers as sub-clips, and leverage layer embeddings to distinguish each clip and the corresponding layer-wise prompts. In this way, we seamlessly support the aforementioned variants in one unified framework. For the lack of high-quality layer-wise training videos, we design a multi-stage training strategy to accommodate static images with high-quality layer annotations. Specifically, we first train the model with low-quality video data. Then, we tune a motion LoRA to make the model compatible with static frames. Afterward, we train the content LoRA on the mixture of image data with high-quality layered images along with copy-pasted video data. During inference, we remove the motion LoRA thus generating smooth videos with desired layers.
DiffDoctor: Diagnosing Image Diffusion Models Before Treating
Jan 21, 2025



Abstract:In spite of the recent progress, image diffusion models still produce artifacts. A common solution is to refine an established model with a quality assessment system, which generally rates an image in its entirety. In this work, we believe problem-solving starts with identification, yielding the request that the model should be aware of not just the presence of defects in an image, but their specific locations. Motivated by this, we propose DiffDoctor, a two-stage pipeline to assist image diffusion models in generating fewer artifacts. Concretely, the first stage targets developing a robust artifact detector, for which we collect a dataset of over 1M flawed synthesized images and set up an efficient human-in-the-loop annotation process, incorporating a carefully designed class-balance strategy. The learned artifact detector is then involved in the second stage to tune the diffusion model through assigning a per-pixel confidence map for each synthesis. Extensive experiments on text-to-image diffusion models demonstrate the effectiveness of our artifact detector as well as the soundness of our diagnose-then-treat design.
FashionComposer: Compositional Fashion Image Generation
Dec 19, 2024Abstract:We present FashionComposer for compositional fashion image generation. Unlike previous methods, FashionComposer is highly flexible. It takes multi-modal input (i.e., text prompt, parametric human model, garment image, and face image) and supports personalizing the appearance, pose, and figure of the human and assigning multiple garments in one pass. To achieve this, we first develop a universal framework capable of handling diverse input modalities. We construct scaled training data to enhance the model's robust compositional capabilities. To accommodate multiple reference images (garments and faces) seamlessly, we organize these references in a single image as an "asset library" and employ a reference UNet to extract appearance features. To inject the appearance features into the correct pixels in the generated result, we propose subject-binding attention. It binds the appearance features from different "assets" with the corresponding text features. In this way, the model could understand each asset according to their semantics, supporting arbitrary numbers and types of reference images. As a comprehensive solution, FashionComposer also supports many other applications like human album generation, diverse virtual try-on tasks, etc.
Scito2M: A 2 Million, 30-Year Cross-disciplinary Dataset for Temporal Scientometric Analysis
Oct 12, 2024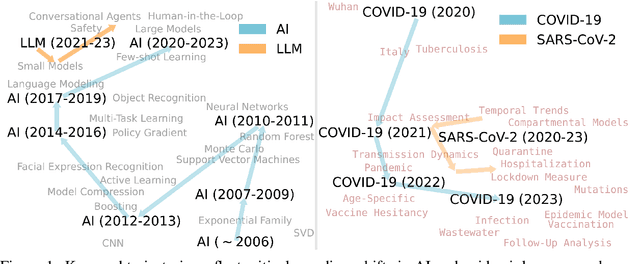
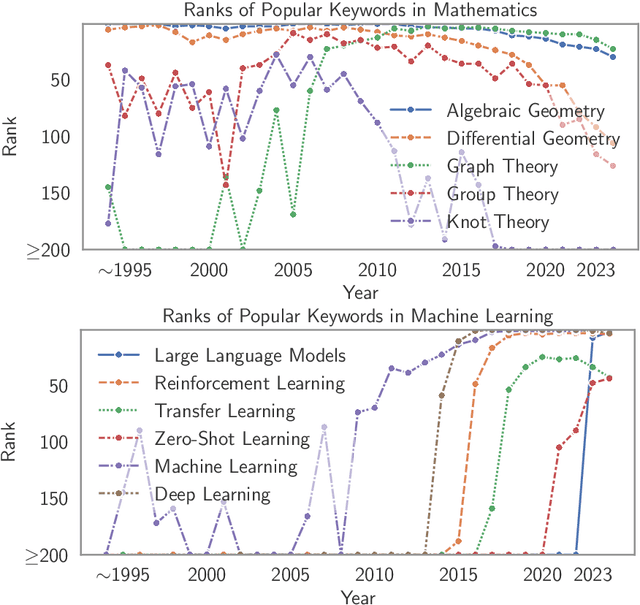

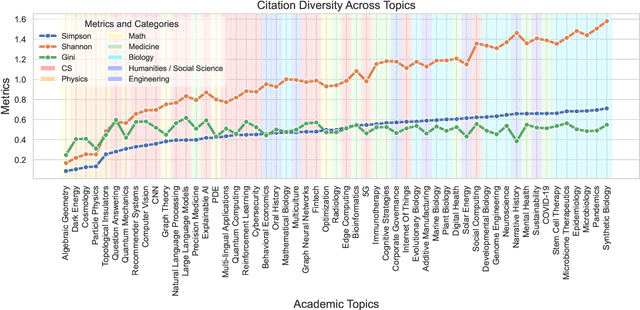
Abstract:Understanding the creation, evolution, and dissemination of scientific knowledge is crucial for bridging diverse subject areas and addressing complex global challenges such as pandemics, climate change, and ethical AI. Scientometrics, the quantitative and qualitative study of scientific literature, provides valuable insights into these processes. We introduce Scito2M, a longitudinal scientometric dataset with over two million academic publications, providing comprehensive contents information and citation graphs to support cross-disciplinary analyses. Using Scito2M, we conduct a temporal study spanning over 30 years to explore key questions in scientometrics: the evolution of academic terminology, citation patterns, and interdisciplinary knowledge exchange. Our findings reveal critical insights, such as disparities in epistemic cultures, knowledge production modes, and citation practices. For example, rapidly developing, application-driven fields like LLMs exhibit significantly shorter citation age (2.48 years) compared to traditional theoretical disciplines like oral history (9.71 years).
KUNPENG: An Embodied Large Model for Intelligent Maritime
Jul 12, 2024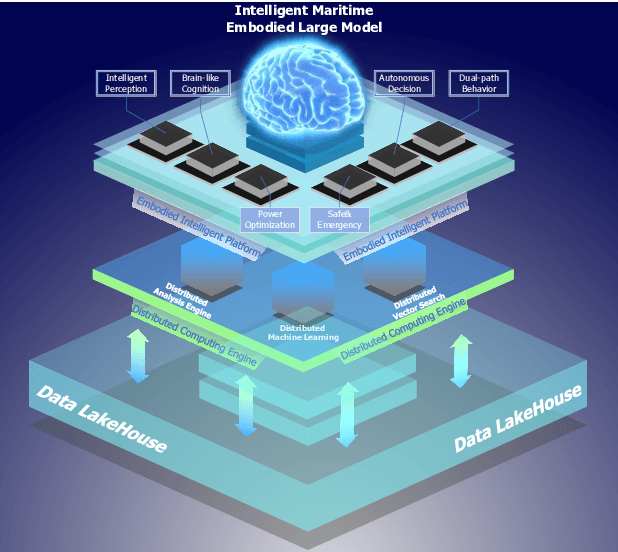
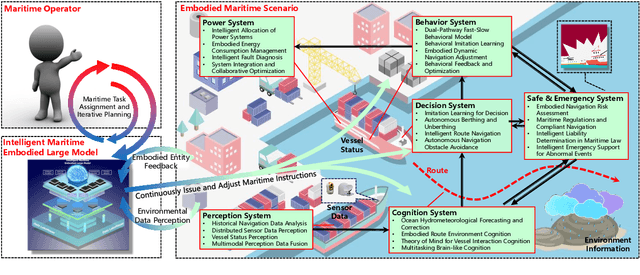
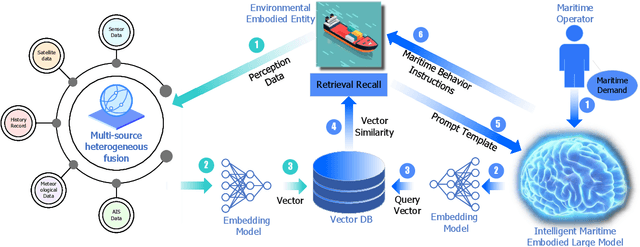
Abstract:Intelligent maritime, as an essential component of smart ocean construction, deeply integrates advanced artificial intelligence technology and data analysis methods, which covers multiple aspects such as smart vessels, route optimization, safe navigation, aiming to enhance the efficiency of ocean resource utilization and the intelligence of transportation networks. However, the complex and dynamic maritime environment, along with diverse and heterogeneous large-scale data sources, present challenges for real-time decision-making in intelligent maritime. In this paper, We propose KUNPENG, the first-ever embodied large model for intelligent maritime in the smart ocean construction, which consists of six systems. The model perceives multi-source heterogeneous data for the cognition of environmental interaction and make autonomous decision strategies, which are used for intelligent vessels to perform navigation behaviors under safety and emergency guarantees and continuously optimize power to achieve embodied intelligence in maritime. In comprehensive maritime task evaluations, KUNPENG has demonstrated excellent performance.
AgentReview: Exploring Peer Review Dynamics with LLM Agents
Jun 18, 2024



Abstract:Peer review is fundamental to the integrity and advancement of scientific publication. Traditional methods of peer review analyses often rely on exploration and statistics of existing peer review data, which do not adequately address the multivariate nature of the process, account for the latent variables, and are further constrained by privacy concerns due to the sensitive nature of the data. We introduce AgentReview, the first large language model (LLM) based peer review simulation framework, which effectively disentangles the impacts of multiple latent factors and addresses the privacy issue. Our study reveals significant insights, including a notable 37.1% variation in paper decisions due to reviewers' biases, supported by sociological theories such as the social influence theory, altruism fatigue, and authority bias. We believe that this study could offer valuable insights to improve the design of peer review mechanisms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge