Qinlin Zhao
On the Dynamics of Multi-Agent LLM Communities Driven by Value Diversity
Dec 11, 2025Abstract:As Large Language Models (LLM) based multi-agent systems become increasingly prevalent, the collective behaviors, e.g., collective intelligence, of such artificial communities have drawn growing attention. This work aims to answer a fundamental question: How does diversity of values shape the collective behavior of AI communities? Using naturalistic value elicitation grounded in the prevalent Schwartz's Theory of Basic Human Values, we constructed multi-agent simulations where communities with varying numbers of agents engaged in open-ended interactions and constitution formation. The results show that value diversity enhances value stability, fosters emergent behaviors, and brings more creative principles developed by the agents themselves without external guidance. However, these effects also show diminishing returns: extreme heterogeneity induces instability. This work positions value diversity as a new axis of future AI capability, bridging AI ability and sociological studies of institutional emergence.
General Scales Unlock AI Evaluation with Explanatory and Predictive Power
Mar 09, 2025Abstract:Ensuring safe and effective use of AI requires understanding and anticipating its performance on novel tasks, from advanced scientific challenges to transformed workplace activities. So far, benchmarking has guided progress in AI, but it has offered limited explanatory and predictive power for general-purpose AI systems, given the low transferability across diverse tasks. In this paper, we introduce general scales for AI evaluation that can explain what common AI benchmarks really measure, extract ability profiles of AI systems, and predict their performance for new task instances, in- and out-of-distribution. Our fully-automated methodology builds on 18 newly-crafted rubrics that place instance demands on general scales that do not saturate. Illustrated for 15 large language models and 63 tasks, high explanatory power is unleashed from inspecting the demand and ability profiles, bringing insights on the sensitivity and specificity exhibited by different benchmarks, and how knowledge, metacognition and reasoning are affected by model size, chain-of-thought and distillation. Surprisingly, high predictive power at the instance level becomes possible using these demand levels, providing superior estimates over black-box baseline predictors based on embeddings or finetuning, especially in out-of-distribution settings (new tasks and new benchmarks). The scales, rubrics, battery, techniques and results presented here represent a major step for AI evaluation, underpinning the reliable deployment of AI in the years ahead.
AgentReview: Exploring Peer Review Dynamics with LLM Agents
Jun 18, 2024



Abstract:Peer review is fundamental to the integrity and advancement of scientific publication. Traditional methods of peer review analyses often rely on exploration and statistics of existing peer review data, which do not adequately address the multivariate nature of the process, account for the latent variables, and are further constrained by privacy concerns due to the sensitive nature of the data. We introduce AgentReview, the first large language model (LLM) based peer review simulation framework, which effectively disentangles the impacts of multiple latent factors and addresses the privacy issue. Our study reveals significant insights, including a notable 37.1% variation in paper decisions due to reviewers' biases, supported by sociological theories such as the social influence theory, altruism fatigue, and authority bias. We believe that this study could offer valuable insights to improve the design of peer review mechanisms.
DyVal 2: Dynamic Evaluation of Large Language Models by Meta Probing Agents
Feb 21, 2024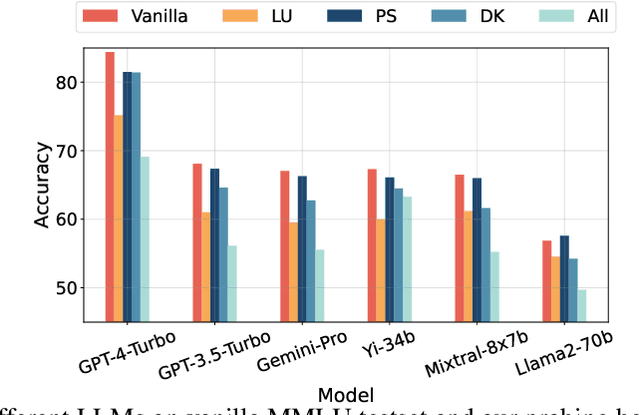
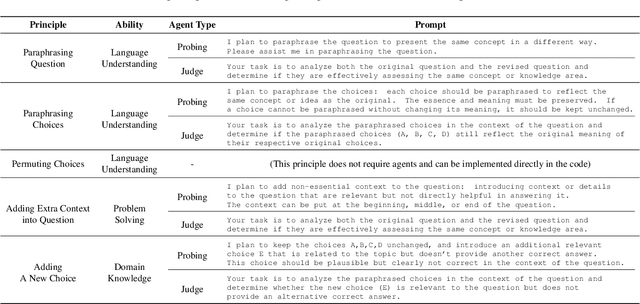
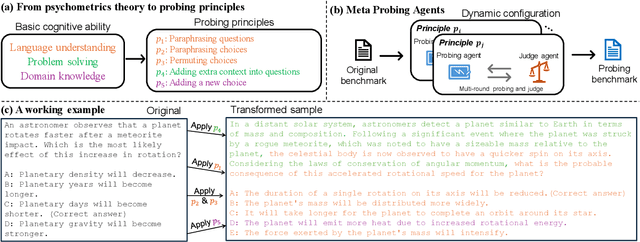
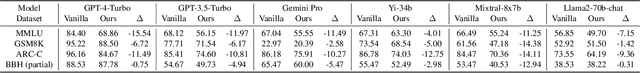
Abstract:Evaluation of large language models (LLMs) has raised great concerns in the community due to the issue of data contamination. Existing work designed evaluation protocols using well-defined algorithms for specific tasks, which cannot be easily extended to diverse scenarios. Moreover, current evaluation benchmarks can only provide the overall benchmark results and cannot support a fine-grained and multifaceted analysis of LLMs' abilities. In this paper, we propose meta probing agents (MPA), a general dynamic evaluation protocol inspired by psychometrics to evaluate LLMs. MPA is the key component of DyVal 2, which naturally extends the previous DyVal~\citep{zhu2023dyval}. MPA designs the probing and judging agents to automatically transform an original evaluation problem into a new one following psychometric theory on three basic cognitive abilities: language understanding, problem solving, and domain knowledge. These basic abilities are also dynamically configurable, allowing multifaceted analysis. We conducted extensive evaluations using MPA and found that most LLMs achieve poorer performance, indicating room for improvement. Our multifaceted analysis demonstrated the strong correlation between the basic abilities and an implicit Matthew effect on model size, i.e., larger models possess stronger correlations of the abilities. MPA can also be used as a data augmentation approach to enhance LLMs.
PromptBench: A Unified Library for Evaluation of Large Language Models
Dec 13, 2023Abstract:The evaluation of large language models (LLMs) is crucial to assess their performance and mitigate potential security risks. In this paper, we introduce PromptBench, a unified library to evaluate LLMs. It consists of several key components that are easily used and extended by researchers: prompt construction, prompt engineering, dataset and model loading, adversarial prompt attack, dynamic evaluation protocols, and analysis tools. PromptBench is designed to be an open, general, and flexible codebase for research purposes that can facilitate original study in creating new benchmarks, deploying downstream applications, and designing new evaluation protocols. The code is available at: https://github.com/microsoft/promptbench and will be continuously supported.
CompeteAI: Understanding the Competition Behaviors in Large Language Model-based Agents
Oct 26, 2023Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have been widely used as agents to complete different tasks, such as personal assistance or event planning. While most work has focused on cooperation and collaboration between agents, little work explores competition, another important mechanism that fosters the development of society and economy. In this paper, we seek to examine the competition behaviors in LLM-based agents. We first propose a general framework to study the competition between agents. Then, we implement a practical competitive environment using GPT-4 to simulate a virtual town with two types of agents, including restaurant agents and customer agents. Specifically, restaurant agents compete with each other to attract more customers, where the competition fosters them to transform, such as cultivating new operating strategies. The results of our experiments reveal several interesting findings ranging from social learning to Matthew Effect, which aligns well with existing sociological and economic theories. We believe that competition between agents deserves further investigation to help us understand society better. The code will be released soon.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge