Chaofan Gan
VidLaDA: Bidirectional Diffusion Large Language Models for Efficient Video Understanding
Jan 25, 2026Abstract:Standard Autoregressive Video LLMs inevitably suffer from causal masking biases that hinder global spatiotemporal modeling, leading to suboptimal understanding efficiency. We propose VidLaDA, a Video LLM based on Diffusion Language Model utilizing bidirectional attention to capture bidirectional dependencies. To further tackle the inference bottleneck of diffusion decoding on massive video tokens, we introduce MARS-Cache. This framework accelerates inference by combining asynchronous visual cache refreshing with frame-wise chunk attention, effectively pruning redundancy while preserving global connectivity via anchor tokens. Extensive experiments show VidLaDA outperforms diffusion baselines and rivals state-of-the-art autoregressive models (e.g., Qwen2.5-VL and LLaVA-Video), with MARS-Cache delivering over 12x speedup without compromising reasoning accuracy. Code and checkpoints are open-sourced at https://github.com/ziHoHe/VidLaDA.
Enhancing Video Large Language Models with Structured Multi-Video Collaborative Reasoning (early version)
Sep 16, 2025Abstract:Despite the prosperity of the video language model, the current pursuit of comprehensive video reasoning is thwarted by the inherent spatio-temporal incompleteness within individual videos, resulting in hallucinations and inaccuracies. A promising solution is to augment the reasoning performance with multiple related videos. However, video tokens are numerous and contain redundant information, so directly feeding the relevant video data into a large language model to enhance responses could be counterproductive. To address this challenge, we propose a multi-video collaborative framework for video language models. For efficient and flexible video representation, we establish a Video Structuring Module to represent the video's knowledge as a spatio-temporal graph. Based on the structured video representation, we design the Graph Fusion Module to fuse the structured knowledge and valuable information from related videos into the augmented graph node tokens. Finally, we construct an elaborate multi-video structured prompt to integrate the graph, visual, and textual tokens as the input to the large language model. Extensive experiments substantiate the effectiveness of our framework, showcasing its potential as a promising avenue for advancing video language models.
MCA: 2D-3D Retrieval with Noisy Labels via Multi-level Adaptive Correction and Alignment
Aug 08, 2025Abstract:With the increasing availability of 2D and 3D data, significant advancements have been made in the field of cross-modal retrieval. Nevertheless, the existence of imperfect annotations presents considerable challenges, demanding robust solutions for 2D-3D cross-modal retrieval in the presence of noisy label conditions. Existing methods generally address the issue of noise by dividing samples independently within each modality, making them susceptible to overfitting on corrupted labels. To address these issues, we propose a robust 2D-3D \textbf{M}ulti-level cross-modal adaptive \textbf{C}orrection and \textbf{A}lignment framework (MCA). Specifically, we introduce a Multimodal Joint label Correction (MJC) mechanism that leverages multimodal historical self-predictions to jointly model the modality prediction consistency, enabling reliable label refinement. Additionally, we propose a Multi-level Adaptive Alignment (MAA) strategy to effectively enhance cross-modal feature semantics and discrimination across different levels. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of our method, MCA, which achieves state-of-the-art performance on both conventional and realistic noisy 3D benchmarks, highlighting its generality and effectiveness.
Looking Beyond Visible Cues: Implicit Video Question Answering via Dual-Clue Reasoning
Jun 09, 2025



Abstract:Video Question Answering (VideoQA) aims to answer natural language questions based on the given video, with prior work primarily focusing on identifying the duration of relevant segments, referred to as explicit visual evidence. However, explicit visual evidence is not always directly available, particularly when questions target symbolic meanings or deeper intentions, leading to significant performance degradation. To fill this gap, we introduce a novel task and dataset, $\textbf{I}$mplicit $\textbf{V}$ideo $\textbf{Q}$uestion $\textbf{A}$nswering (I-VQA), which focuses on answering questions in scenarios where explicit visual evidence is inaccessible. Given an implicit question and its corresponding video, I-VQA requires answering based on the contextual visual cues present within the video. To tackle I-VQA, we propose a novel reasoning framework, IRM (Implicit Reasoning Model), incorporating dual-stream modeling of contextual actions and intent clues as implicit reasoning chains. IRM comprises the Action-Intent Module (AIM) and the Visual Enhancement Module (VEM). AIM deduces and preserves question-related dual clues by generating clue candidates and performing relation deduction. VEM enhances contextual visual representation by leveraging key contextual clues. Extensive experiments validate the effectiveness of our IRM in I-VQA tasks, outperforming GPT-4o, OpenAI-o3, and fine-tuned VideoChat2 by $0.76\%$, $1.37\%$, and $4.87\%$, respectively. Additionally, IRM performs SOTA on similar implicit advertisement understanding and future prediction in traffic-VQA. Datasets and codes are available for double-blind review in anonymous repo: https://github.com/tychen-SJTU/Implicit-VideoQA.
Unleashing Diffusion Transformers for Visual Correspondence by Modulating Massive Activations
May 24, 2025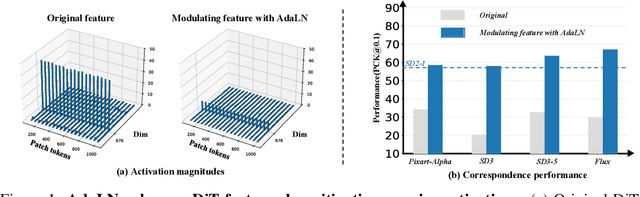
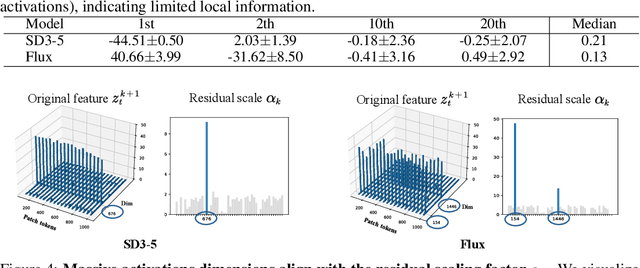
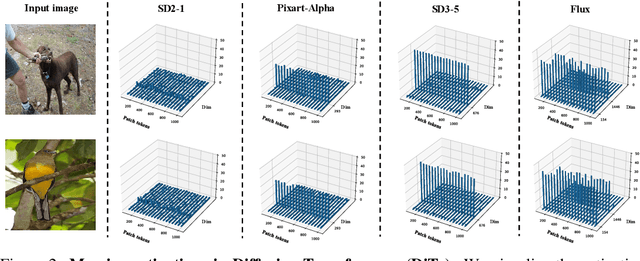
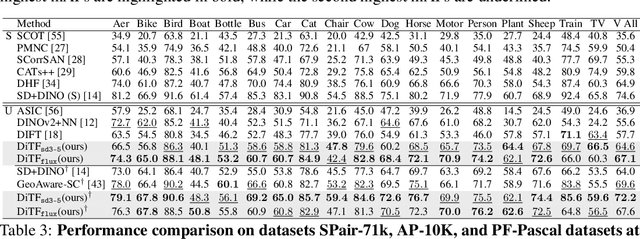
Abstract:Pre-trained stable diffusion models (SD) have shown great advances in visual correspondence. In this paper, we investigate the capabilities of Diffusion Transformers (DiTs) for accurate dense correspondence. Distinct from SD, DiTs exhibit a critical phenomenon in which very few feature activations exhibit significantly larger values than others, known as \textit{massive activations}, leading to uninformative representations and significant performance degradation for DiTs. The massive activations consistently concentrate at very few fixed dimensions across all image patch tokens, holding little local information. We trace these dimension-concentrated massive activations and find that such concentration can be effectively localized by the zero-initialized Adaptive Layer Norm (AdaLN-zero). Building on these findings, we propose Diffusion Transformer Feature (DiTF), a training-free framework designed to extract semantic-discriminative features from DiTs. Specifically, DiTF employs AdaLN to adaptively localize and normalize massive activations with channel-wise modulation. In addition, we develop a channel discard strategy to further eliminate the negative impacts from massive activations. Experimental results demonstrate that our DiTF outperforms both DINO and SD-based models and establishes a new state-of-the-art performance for DiTs in different visual correspondence tasks (\eg, with +9.4\% on Spair-71k and +4.4\% on AP-10K-C.S.).
MECD+: Unlocking Event-Level Causal Graph Discovery for Video Reasoning
Jan 16, 2025



Abstract:Video causal reasoning aims to achieve a high-level understanding of videos from a causal perspective. However, it exhibits limitations in its scope, primarily executed in a question-answering paradigm and focusing on brief video segments containing isolated events and basic causal relations, lacking comprehensive and structured causality analysis for videos with multiple interconnected events. To fill this gap, we introduce a new task and dataset, Multi-Event Causal Discovery (MECD). It aims to uncover the causal relations between events distributed chronologically across long videos. Given visual segments and textual descriptions of events, MECD identifies the causal associations between these events to derive a comprehensive and structured event-level video causal graph explaining why and how the result event occurred. To address the challenges of MECD, we devise a novel framework inspired by the Granger Causality method, incorporating an efficient mask-based event prediction model to perform an Event Granger Test. It estimates causality by comparing the predicted result event when premise events are masked versus unmasked. Furthermore, we integrate causal inference techniques such as front-door adjustment and counterfactual inference to mitigate challenges in MECD like causality confounding and illusory causality. Additionally, context chain reasoning is introduced to conduct more robust and generalized reasoning. Experiments validate the effectiveness of our framework in reasoning complete causal relations, outperforming GPT-4o and VideoChat2 by 5.77% and 2.70%, respectively. Further experiments demonstrate that causal relation graphs can also contribute to downstream video understanding tasks such as video question answering and video event prediction.
MECD: Unlocking Multi-Event Causal Discovery in Video Reasoning
Sep 26, 2024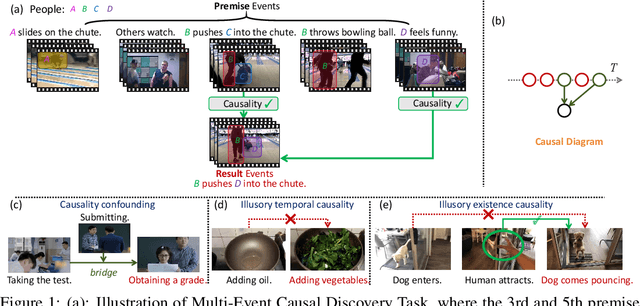
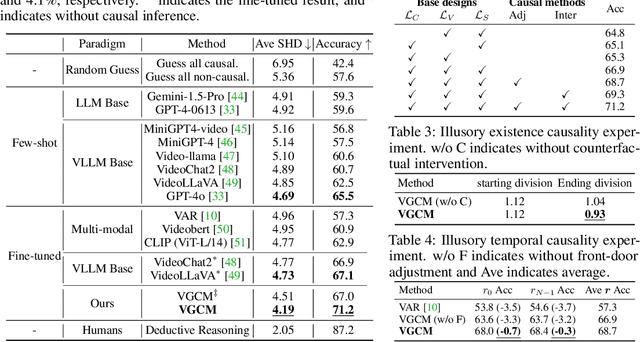
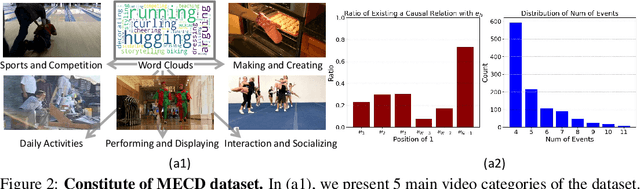
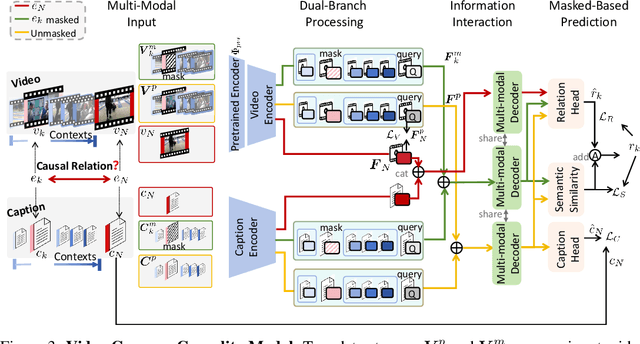
Abstract:Video causal reasoning aims to achieve a high-level understanding of video content from a causal perspective. However, current video reasoning tasks are limited in scope, primarily executed in a question-answering paradigm and focusing on short videos containing only a single event and simple causal relationships, lacking comprehensive and structured causality analysis for videos with multiple events. To fill this gap, we introduce a new task and dataset, Multi-Event Causal Discovery (MECD). It aims to uncover the causal relationships between events distributed chronologically across long videos. Given visual segments and textual descriptions of events, MECD requires identifying the causal associations between these events to derive a comprehensive, structured event-level video causal diagram explaining why and how the final result event occurred. To address MECD, we devise a novel framework inspired by the Granger Causality method, using an efficient mask-based event prediction model to perform an Event Granger Test, which estimates causality by comparing the predicted result event when premise events are masked versus unmasked. Furthermore, we integrate causal inference techniques such as front-door adjustment and counterfactual inference to address challenges in MECD like causality confounding and illusory causality. Experiments validate the effectiveness of our framework in providing causal relationships in multi-event videos, outperforming GPT-4o and VideoLLaVA by 5.7% and 4.1%, respectively.
DAC: 2D-3D Retrieval with Noisy Labels via Divide-and-Conquer Alignment and Correction
Jul 25, 2024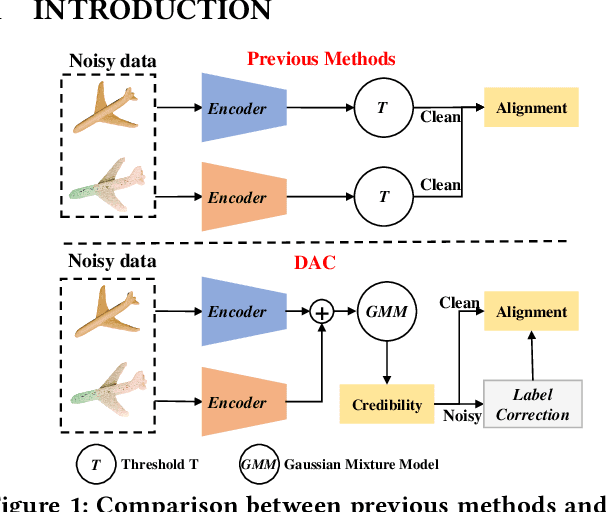

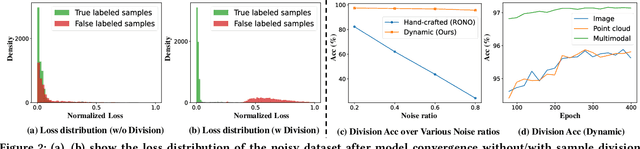

Abstract:With the recent burst of 2D and 3D data, cross-modal retrieval has attracted increasing attention recently. However, manual labeling by non-experts will inevitably introduce corrupted annotations given ambiguous 2D/3D content. Though previous works have addressed this issue by designing a naive division strategy with hand-crafted thresholds, their performance generally exhibits great sensitivity to the threshold value. Besides, they fail to fully utilize the valuable supervisory signals within each divided subset. To tackle this problem, we propose a Divide-and-conquer 2D-3D cross-modal Alignment and Correction framework (DAC), which comprises Multimodal Dynamic Division (MDD) and Adaptive Alignment and Correction (AAC). Specifically, the former performs accurate sample division by adaptive credibility modeling for each sample based on the compensation information within multimodal loss distribution. Then in AAC, samples in distinct subsets are exploited with different alignment strategies to fully enhance the semantic compactness and meanwhile alleviate over-fitting to noisy labels, where a self-correction strategy is introduced to improve the quality of representation. Moreover. To evaluate the effectiveness in real-world scenarios, we introduce a challenging noisy benchmark, namely Objaverse-N200, which comprises 200k-level samples annotated with 1156 realistic noisy labels. Extensive experiments on both traditional and the newly proposed benchmarks demonstrate the generality and superiority of our DAC, where DAC outperforms state-of-the-art models by a large margin. (i.e., with +5.9% gain on ModelNet40 and +5.8% on Objaverse-N200).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge