Ying Fang
LL-GaussianMap: Zero-shot Low-Light Image Enhancement via 2D Gaussian Splatting Guided Gain Maps
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Significant progress has been made in low-light image enhancement with respect to visual quality. However, most existing methods primarily operate in the pixel domain or rely on implicit feature representations. As a result, the intrinsic geometric structural priors of images are often neglected. 2D Gaussian Splatting (2DGS) has emerged as a prominent explicit scene representation technique characterized by superior structural fitting capabilities and high rendering efficiency. Despite these advantages, the utilization of 2DGS in low-level vision tasks remains unexplored. To bridge this gap, LL-GaussianMap is proposed as the first unsupervised framework incorporating 2DGS into low-light image enhancement. Distinct from conventional methodologies, the enhancement task is formulated as a gain map generation process guided by 2DGS primitives. The proposed method comprises two primary stages. First, high-fidelity structural reconstruction is executed utilizing 2DGS. Then, data-driven enhancement dictionary coefficients are rendered via the rasterization mechanism of Gaussian splatting through an innovative unified enhancement module. This design effectively incorporates the structural perception capabilities of 2DGS into gain map generation, thereby preserving edges and suppressing artifacts during enhancement. Additionally, the reliance on paired data is circumvented through unsupervised learning. Experimental results demonstrate that LL-GaussianMap achieves superior enhancement performance with an extremely low storage footprint, highlighting the effectiveness of explicit Gaussian representations for image enhancement.
LL-GaussianImage: Efficient Image Representation for Zero-shot Low-Light Enhancement with 2D Gaussian Splatting
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:2D Gaussian Splatting (2DGS) is an emerging explicit scene representation method with significant potential for image compression due to high fidelity and high compression ratios. However, existing low-light enhancement algorithms operate predominantly within the pixel domain. Processing 2DGS-compressed images necessitates a cumbersome decompression-enhancement-recompression pipeline, which compromises efficiency and introduces secondary degradation. To address these limitations, we propose LL-GaussianImage, the first zero-shot unsupervised framework designed for low-light enhancement directly within the 2DGS compressed representation domain. Three primary advantages are offered by this framework. First, a semantic-guided Mixture-of-Experts enhancement framework is designed. Dynamic adaptive transformations are applied to the sparse attribute space of 2DGS using rendered images as guidance to enable compression-as-enhancement without full decompression to a pixel grid. Second, a multi-objective collaborative loss function system is established to strictly constrain smoothness and fidelity during enhancement, suppressing artifacts while improving visual quality. Third, a two-stage optimization process is utilized to achieve reconstruction-as-enhancement. The accuracy of the base representation is ensured through single-scale reconstruction and network robustness is enhanced. High-quality enhancement of low-light images is achieved while high compression ratios are maintained. The feasibility and superiority of the paradigm for direct processing within the compressed representation domain are validated through experimental results.
UMA-Split: unimodal aggregation for both English and Mandarin non-autoregressive speech recognition
Sep 18, 2025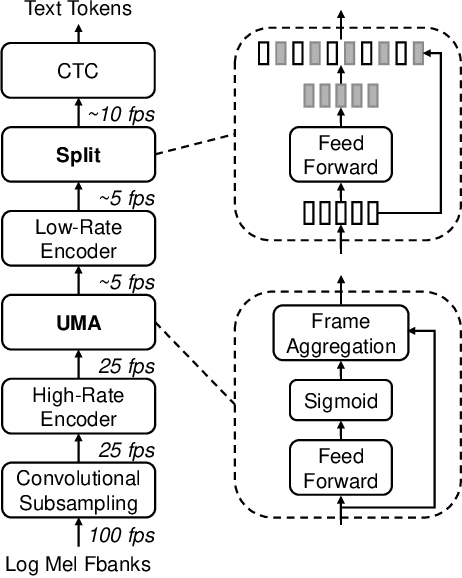
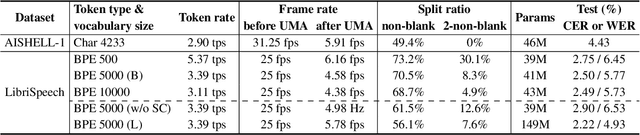
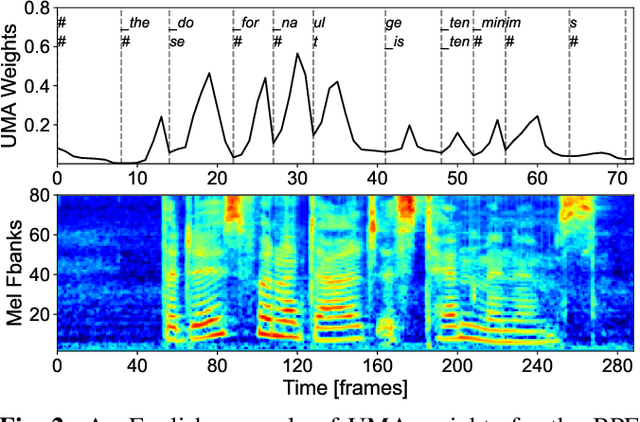
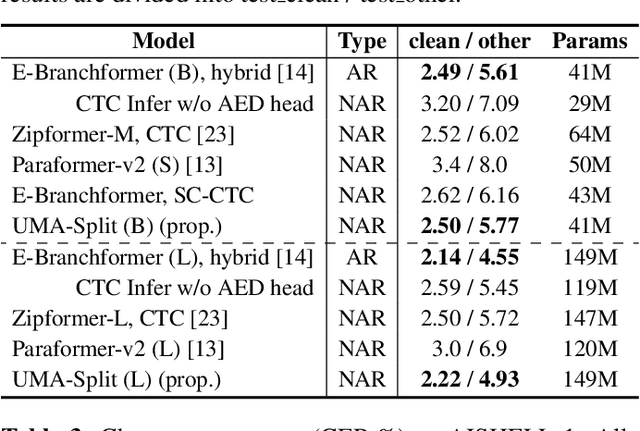
Abstract:This paper proposes a unimodal aggregation (UMA) based nonautoregressive model for both English and Mandarin speech recognition. The original UMA explicitly segments and aggregates acoustic frames (with unimodal weights that first monotonically increase and then decrease) of the same text token to learn better representations than regular connectionist temporal classification (CTC). However, it only works well in Mandarin. It struggles with other languages, such as English, for which a single syllable may be tokenized into multiple fine-grained tokens, or a token spans fewer than 3 acoustic frames and fails to form unimodal weights. To address this problem, we propose allowing each UMA-aggregated frame map to multiple tokens, via a simple split module that generates two tokens from each aggregated frame before computing the CTC loss.
Reshaping MOFs Text Mining with a Dynamic Multi-Agent Framework of Large Language Agents
Apr 26, 2025Abstract:The mining of synthesis conditions for metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) is a significant focus in materials science. However, identifying the precise synthesis conditions for specific MOFs within the vast array of possibilities presents a considerable challenge. Large Language Models (LLMs) offer a promising solution to this problem. We leveraged the capabilities of LLMs, specifically gpt-4o-mini, as core agents to integrate various MOF-related agents, including synthesis, attribute, and chemical information agents. This integration culminated in the development of MOFh6, an LLM tool designed to streamline the MOF synthesis process. MOFh6 allows users to query in multiple formats, such as submitting scientific literature, or inquiring about specific MOF codes or structural properties. The tool analyzes these queries to provide optimal synthesis conditions and generates model files for density functional theory pre modeling. We believe MOFh6 will enhance efficiency in the MOF synthesis of all researchers.
CleanMel: Mel-Spectrogram Enhancement for Improving Both Speech Quality and ASR
Feb 27, 2025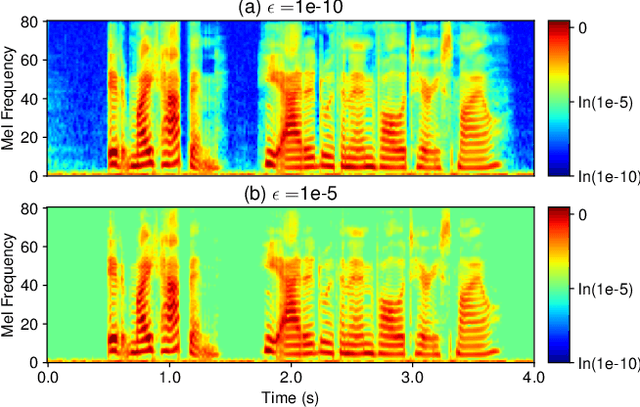
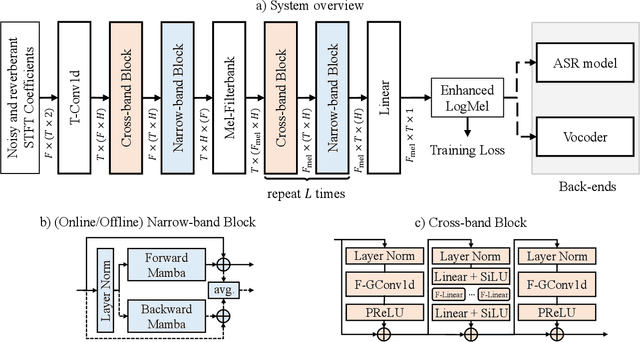
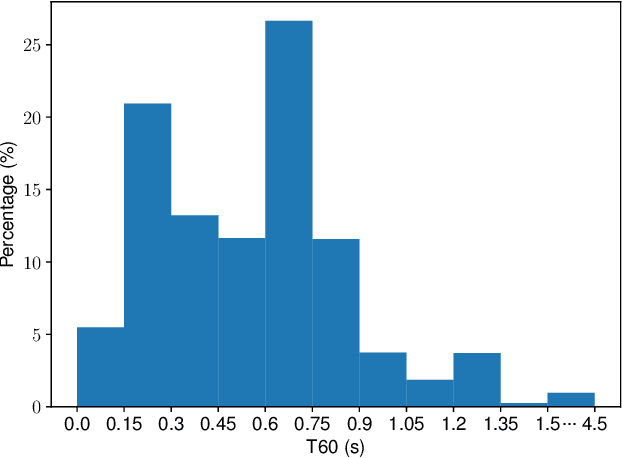
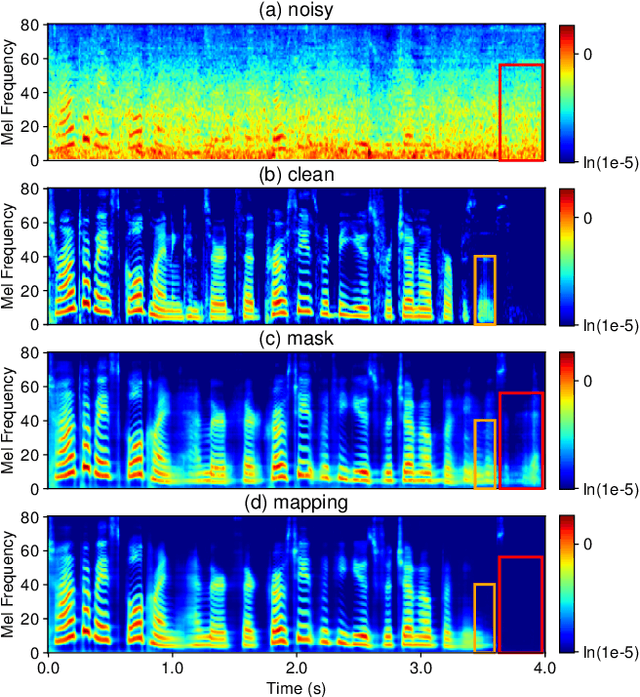
Abstract:In this work, we propose CleanMel, a single-channel Mel-spectrogram denoising and dereverberation network for improving both speech quality and automatic speech recognition (ASR) performance. The proposed network takes as input the noisy and reverberant microphone recording and predicts the corresponding clean Mel-spectrogram. The enhanced Mel-spectrogram can be either transformed to speech waveform with a neural vocoder or directly used for ASR. The proposed network is composed of interleaved cross-band and narrow-band processing in the Mel-frequency domain, for learning the full-band spectral pattern and the narrow-band properties of signals, respectively. Compared to linear-frequency domain or time-domain speech enhancement, the key advantage of Mel-spectrogram enhancement is that Mel-frequency presents speech in a more compact way and thus is easier to learn, which will benefit both speech quality and ASR. Experimental results on four English and one Chinese datasets demonstrate a significant improvement in both speech quality and ASR performance achieved by the proposed model. Code and audio examples of our model are available online in https://audio.westlake.edu.cn/Research/CleanMel.html.
VINP: Variational Bayesian Inference with Neural Speech Prior for Joint ASR-Effective Speech Dereverberation and Blind RIR Identification
Feb 11, 2025Abstract:Reverberant speech, denoting the speech signal degraded by the process of reverberation, contains crucial knowledge of both anechoic source speech and room impulse response (RIR). This work proposes a variational Bayesian inference (VBI) framework with neural speech prior (VINP) for joint speech dereverberation and blind RIR identification. In VINP, a probabilistic signal model is constructed in the time-frequency (T-F) domain based on convolution transfer function (CTF) approximation. For the first time, we propose using an arbitrary discriminative dereverberation deep neural network (DNN) to predict the prior distribution of anechoic speech within a probabilistic model. By integrating both reverberant speech and the anechoic speech prior, VINP yields the maximum a posteriori (MAP) and maximum likelihood (ML) estimations of the anechoic speech spectrum and CTF filter, respectively. After simple transformations, the waveforms of anechoic speech and RIR are estimated. Moreover, VINP is effective for automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems, which sets it apart from most deep learning (DL)-based single-channel dereverberation approaches. Experiments on single-channel speech dereverberation demonstrate that VINP reaches an advanced level in most metrics related to human perception and displays unquestionable state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance in ASR-related metrics. For blind RIR identification, experiments indicate that VINP attains the SOTA level in blind estimation of reverberation time at 60 dB (RT60) and direct-to-reverberation ratio (DRR). Codes and audio samples are available online.
Evaluating the Design Features of an Intelligent Tutoring System for Advanced Mathematics Learning
Dec 23, 2024Abstract:Xiaomai is an intelligent tutoring system (ITS) designed to help Chinese college students in learning advanced mathematics and preparing for the graduate school math entrance exam. This study investigates two distinctive features within Xiaomai: the incorporation of free-response questions with automatic feedback and the metacognitive element of reflecting on self-made errors.
RealMAN: A Real-Recorded and Annotated Microphone Array Dataset for Dynamic Speech Enhancement and Localization
Jun 28, 2024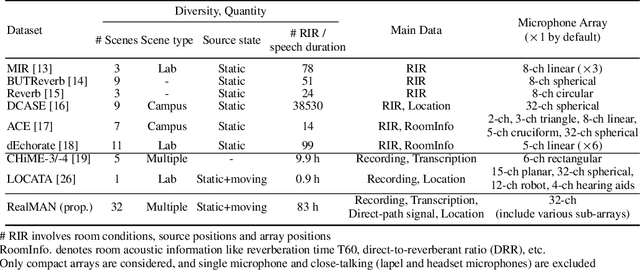
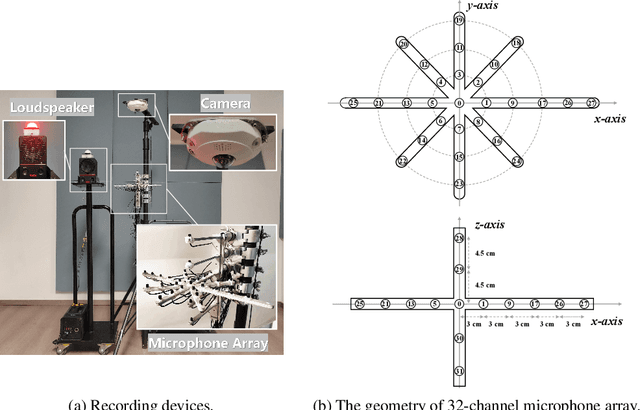


Abstract:The training of deep learning-based multichannel speech enhancement and source localization systems relies heavily on the simulation of room impulse response and multichannel diffuse noise, due to the lack of large-scale real-recorded datasets. However, the acoustic mismatch between simulated and real-world data could degrade the model performance when applying in real-world scenarios. To bridge this simulation-to-real gap, this paper presents a new relatively large-scale Real-recorded and annotated Microphone Array speech&Noise (RealMAN) dataset. The proposed dataset is valuable in two aspects: 1) benchmarking speech enhancement and localization algorithms in real scenarios; 2) offering a substantial amount of real-world training data for potentially improving the performance of real-world applications. Specifically, a 32-channel array with high-fidelity microphones is used for recording. A loudspeaker is used for playing source speech signals. A total of 83-hour speech signals (48 hours for static speaker and 35 hours for moving speaker) are recorded in 32 different scenes, and 144 hours of background noise are recorded in 31 different scenes. Both speech and noise recording scenes cover various common indoor, outdoor, semi-outdoor and transportation environments, which enables the training of general-purpose speech enhancement and source localization networks. To obtain the task-specific annotations, the azimuth angle of the loudspeaker is annotated with an omni-direction fisheye camera by automatically detecting the loudspeaker. The direct-path signal is set as the target clean speech for speech enhancement, which is obtained by filtering the source speech signal with an estimated direct-path propagation filter.
Converting High-Performance and Low-Latency SNNs through Explicit Modelling of Residual Error in ANNs
Apr 26, 2024



Abstract:Spiking neural networks (SNNs) have garnered interest due to their energy efficiency and superior effectiveness on neuromorphic chips compared with traditional artificial neural networks (ANNs). One of the mainstream approaches to implementing deep SNNs is the ANN-SNN conversion, which integrates the efficient training strategy of ANNs with the energy-saving potential and fast inference capability of SNNs. However, under extreme low-latency conditions, the existing conversion theory suggests that the problem of misrepresentation of residual membrane potentials in SNNs, i.e., the inability of IF neurons with a reset-by-subtraction mechanism to respond to residual membrane potentials beyond the range from resting potential to threshold, leads to a performance gap in the converted SNNs compared to the original ANNs. This severely limits the possibility of practical application of SNNs on delay-sensitive edge devices. Existing conversion methods addressing this problem usually involve modifying the state of the conversion spiking neurons. However, these methods do not consider their adaptability and compatibility with neuromorphic chips. We propose a new approach based on explicit modeling of residual errors as additive noise. The noise is incorporated into the activation function of the source ANN, which effectively reduces the residual error. Our experiments on the CIFAR10/100 dataset verify that our approach exceeds the prevailing ANN-SNN conversion methods and directly trained SNNs concerning accuracy and the required time steps. Overall, our method provides new ideas for improving SNN performance under ultra-low-latency conditions and is expected to promote practical neuromorphic hardware applications for further development.
Mel-FullSubNet: Mel-Spectrogram Enhancement for Improving Both Speech Quality and ASR
Feb 22, 2024



Abstract:In this work, we propose Mel-FullSubNet, a single-channel Mel-spectrogram denoising and dereverberation network for improving both speech quality and automatic speech recognition (ASR) performance. Mel-FullSubNet takes as input the noisy and reverberant Mel-spectrogram and predicts the corresponding clean Mel-spectrogram. The enhanced Mel-spectrogram can be either transformed to speech waveform with a neural vocoder or directly used for ASR. Mel-FullSubNet encapsulates interleaved full-band and sub-band networks, for learning the full-band spectral pattern of signals and the sub-band/narrow-band properties of signals, respectively. Compared to linear-frequency domain or time-domain speech enhancement, the major advantage of Mel-spectrogram enhancement is that Mel-frequency presents speech in a more compact way and thus is easier to learn, which will benefit both speech quality and ASR. Experimental results demonstrate a significant improvement in both speech quality and ASR performance achieved by the proposed model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge