Sannyuya Liu
Evaluating the Design Features of an Intelligent Tutoring System for Advanced Mathematics Learning
Dec 23, 2024Abstract:Xiaomai is an intelligent tutoring system (ITS) designed to help Chinese college students in learning advanced mathematics and preparing for the graduate school math entrance exam. This study investigates two distinctive features within Xiaomai: the incorporation of free-response questions with automatic feedback and the metacognitive element of reflecting on self-made errors.
Gradual Vigilance and Interval Communication: Enhancing Value Alignment in Multi-Agent Debates
Dec 18, 2024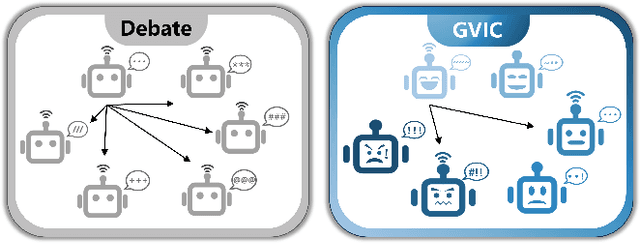
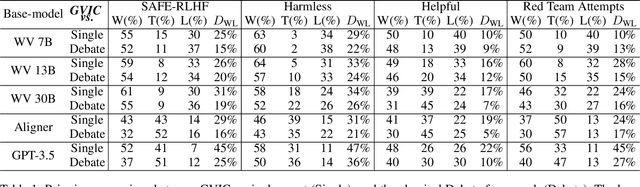
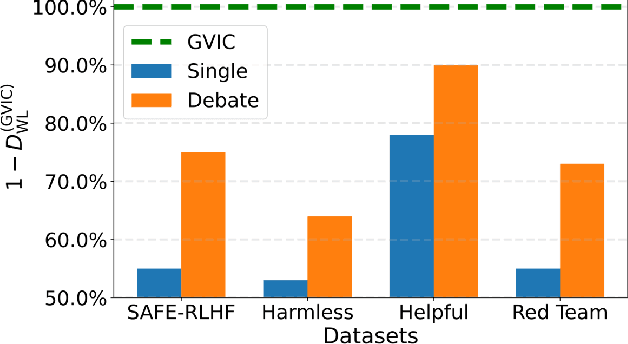
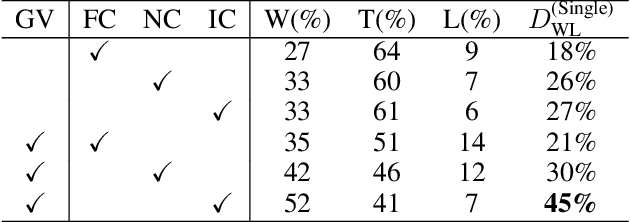
Abstract:In recent years, large language models have shown exceptional performance in fulfilling diverse human needs. However, their training data can introduce harmful content, underscoring the necessity for robust value alignment. Mainstream methods, which depend on feedback learning and supervised training, are resource-intensive and may constrain the full potential of the models. Multi-Agent Debate (MAD) offers a more efficient and innovative solution by enabling the generation of reliable answers through agent interactions. To apply MAD to value alignment, we examine the relationship between the helpfulness and harmlessness of debate outcomes and individual responses, and propose a MAD based framework Gradual Vigilance and Interval Communication (GVIC). GVIC allows agents to assess risks with varying levels of vigilance and to exchange diverse information through interval communication. We theoretically prove that GVIC optimizes debate efficiency while reducing communication overhead. Experimental results demonstrate that GVIC consistently outperforms baseline methods across various tasks and datasets, particularly excelling in harmfulness mitigation and fraud prevention. Additionally, GVIC exhibits strong adaptability across different base model sizes, including both unaligned and aligned models, and across various task types.
CLIP-SCGI: Synthesized Caption-Guided Inversion for Person Re-Identification
Oct 12, 2024Abstract:Person re-identification (ReID) has recently benefited from large pretrained vision-language models such as Contrastive Language-Image Pre-Training (CLIP). However, the absence of concrete descriptions necessitates the use of implicit text embeddings, which demand complicated and inefficient training strategies. To address this issue, we first propose one straightforward solution by leveraging existing image captioning models to generate pseudo captions for person images, and thereby boost person re-identification with large vision language models. Using models like the Large Language and Vision Assistant (LLAVA), we generate high-quality captions based on fixed templates that capture key semantic attributes such as gender, clothing, and age. By augmenting ReID training sets from uni-modality (image) to bi-modality (image and text), we introduce CLIP-SCGI, a simple yet effective framework that leverages synthesized captions to guide the learning of discriminative and robust representations. Built on CLIP, CLIP-SCGI fuses image and text embeddings through two modules to enhance the training process. To address quality issues in generated captions, we introduce a caption-guided inversion module that captures semantic attributes from images by converting relevant visual information into pseudo-word tokens based on the descriptions. This approach helps the model better capture key information and focus on relevant regions. The extracted features are then utilized in a cross-modal fusion module, guiding the model to focus on regions semantically consistent with the caption, thereby facilitating the optimization of the visual encoder to extract discriminative and robust representations. Extensive experiments on four popular ReID benchmarks demonstrate that CLIP-SCGI outperforms the state-of-the-art by a significant margin.
COMET: "Cone of experience" enhanced large multimodal model for mathematical problem generation
Jul 16, 2024Abstract:The automatic generation of high-quality mathematical problems is practically valuable in many educational scenarios. Large multimodal model provides a novel technical approach for the mathematical problem generation because of its wide success in cross-modal data scenarios. However, the traditional method of separating problem solving from problem generation and the mainstream fine-tuning framework of monotonous data structure with homogeneous training objectives limit the application of large multimodal model in mathematical problem generation. Addressing these challenges, this paper proposes COMET, a "Cone of Experience" enhanced large multimodal model for mathematical problem generation. Firstly, from the perspective of mutual ability promotion and application logic, we unify stem generation and problem solving into mathematical problem generation. Secondly, a three-stage fine-turning framework guided by the "Cone of Experience" is proposed. The framework divides the fine-tuning data into symbolic experience, iconic experience, and direct experience to draw parallels with experiences in the career growth of teachers. Several fine-grained data construction and injection methods are designed in this framework. Finally, we construct a Chinese multimodal mathematical problem dataset to fill the vacancy of Chinese multimodal data in this field. Combined with objective and subjective indicators, experiments on multiple datasets fully verify the effectiveness of the proposed framework and model.
Annotation Guidelines-Based Knowledge Augmentation: Towards Enhancing Large Language Models for Educational Text Classification
Jun 03, 2024



Abstract:Various machine learning approaches have gained significant popularity for the automated classification of educational text to identify indicators of learning engagement -- i.e. learning engagement classification (LEC). LEC can offer comprehensive insights into human learning processes, attracting significant interest from diverse research communities, including Natural Language Processing (NLP), Learning Analytics, and Educational Data Mining. Recently, Large Language Models (LLMs), such as ChatGPT, have demonstrated remarkable performance in various NLP tasks. However, their comprehensive evaluation and improvement approaches in LEC tasks have not been thoroughly investigated. In this study, we propose the Annotation Guidelines-based Knowledge Augmentation (AGKA) approach to improve LLMs. AGKA employs GPT 4.0 to retrieve label definition knowledge from annotation guidelines, and then applies the random under-sampler to select a few typical examples. Subsequently, we conduct a systematic evaluation benchmark of LEC, which includes six LEC datasets covering behavior classification (question and urgency level), emotion classification (binary and epistemic emotion), and cognition classification (opinion and cognitive presence). The study results demonstrate that AGKA can enhance non-fine-tuned LLMs, particularly GPT 4.0 and Llama 3 70B. GPT 4.0 with AGKA few-shot outperforms full-shot fine-tuned models such as BERT and RoBERTa on simple binary classification datasets. However, GPT 4.0 lags in multi-class tasks that require a deep understanding of complex semantic information. Notably, Llama 3 70B with AGKA is a promising combination based on open-source LLM, because its performance is on par with closed-source GPT 4.0 with AGKA. In addition, LLMs struggle to distinguish between labels with similar names in multi-class classification.
Automated discovery of symbolic laws governing skill acquisition from naturally occurring data
Apr 08, 2024



Abstract:Skill acquisition is a key area of research in cognitive psychology as it encompasses multiple psychological processes. The laws discovered under experimental paradigms are controversial and lack generalizability. This paper aims to unearth the laws of skill learning from large-scale training log data. A two-stage algorithm was developed to tackle the issues of unobservable cognitive states and algorithmic explosion in searching. Initially a deep learning model is employed to determine the learner's cognitive state and assess the feature importance. Subsequently, symbolic regression algorithms are utilized to parse the neural network model into algebraic equations. The experimental results of simulated data demonstrate that the proposed algorithm can accurately restore various preset laws within a certain range of noise, in continues feedback setting. Application of proposed method to Lumosity training data demonstrates superior performance compared to traditional and latest models in terms of fitness. The results indicate the discovery of two new forms of skill acquisition laws, while some previous findings have been reaffirmed.
Towards Detecting AI-Generated Text within Human-AI Collaborative Hybrid Texts
Mar 06, 2024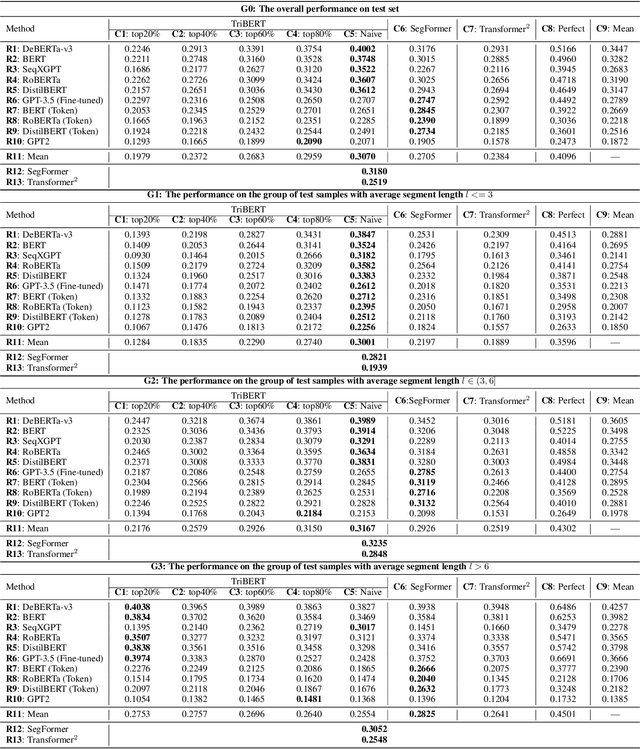
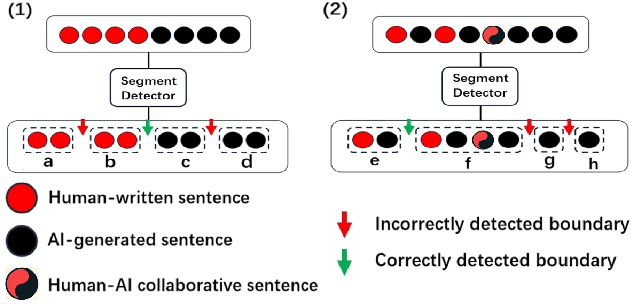
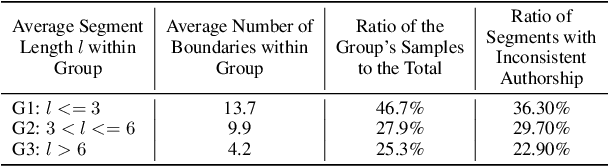
Abstract:This study explores the challenge of sentence-level AI-generated text detection within human-AI collaborative hybrid texts. Existing studies of AI-generated text detection for hybrid texts often rely on synthetic datasets. These typically involve hybrid texts with a limited number of boundaries. We contend that studies of detecting AI-generated content within hybrid texts should cover different types of hybrid texts generated in realistic settings to better inform real-world applications. Therefore, our study utilizes the CoAuthor dataset, which includes diverse, realistic hybrid texts generated through the collaboration between human writers and an intelligent writing system in multi-turn interactions. We adopt a two-step, segmentation-based pipeline: (i) detect segments within a given hybrid text where each segment contains sentences of consistent authorship, and (ii) classify the authorship of each identified segment. Our empirical findings highlight (1) detecting AI-generated sentences in hybrid texts is overall a challenging task because (1.1) human writers' selecting and even editing AI-generated sentences based on personal preferences adds difficulty in identifying the authorship of segments; (1.2) the frequent change of authorship between neighboring sentences within the hybrid text creates difficulties for segment detectors in identifying authorship-consistent segments; (1.3) the short length of text segments within hybrid texts provides limited stylistic cues for reliable authorship determination; (2) before embarking on the detection process, it is beneficial to assess the average length of segments within the hybrid text. This assessment aids in deciding whether (2.1) to employ a text segmentation-based strategy for hybrid texts with longer segments, or (2.2) to adopt a direct sentence-by-sentence classification strategy for those with shorter segments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge