Dragan Gasevic
PromptDSI: Prompt-based Rehearsal-free Instance-wise Incremental Learning for Document Retrieval
Jun 18, 2024
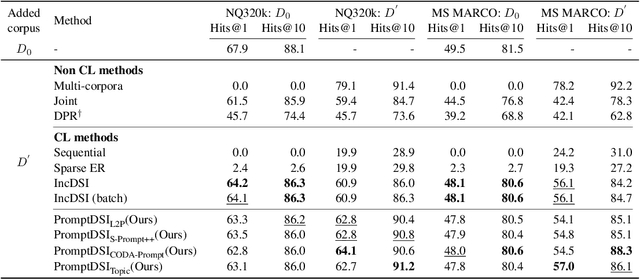
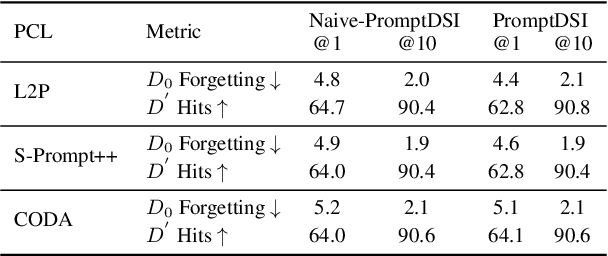
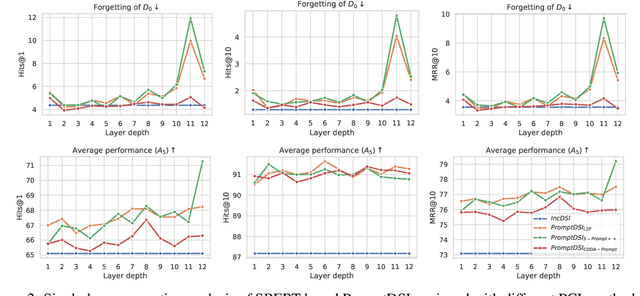
Abstract:Differentiable Search Index (DSI) utilizes Pre-trained Language Models (PLMs) for efficient document retrieval without relying on external indexes. However, DSIs need full re-training to handle updates in dynamic corpora, causing significant computational inefficiencies. We introduce PromptDSI, a rehearsal-free, prompt-based approach for instance-wise incremental learning in document retrieval. PromptDSI attaches prompts to the frozen PLM's encoder of DSI, leveraging its powerful representation to efficiently index new corpora while maintaining a balance between stability and plasticity. We eliminate the initial forward pass of prompt-based continual learning methods that doubles training and inference time. Moreover, we propose a topic-aware prompt pool that employs neural topic embeddings as fixed keys. This strategy ensures diverse and effective prompt usage, addressing the challenge of parameter underutilization caused by the collapse of the query-key matching mechanism. Our empirical evaluations demonstrate that PromptDSI matches IncDSI in managing forgetting while significantly enhancing recall by over 4% on new corpora.
Annotation Guidelines-Based Knowledge Augmentation: Towards Enhancing Large Language Models for Educational Text Classification
Jun 03, 2024



Abstract:Various machine learning approaches have gained significant popularity for the automated classification of educational text to identify indicators of learning engagement -- i.e. learning engagement classification (LEC). LEC can offer comprehensive insights into human learning processes, attracting significant interest from diverse research communities, including Natural Language Processing (NLP), Learning Analytics, and Educational Data Mining. Recently, Large Language Models (LLMs), such as ChatGPT, have demonstrated remarkable performance in various NLP tasks. However, their comprehensive evaluation and improvement approaches in LEC tasks have not been thoroughly investigated. In this study, we propose the Annotation Guidelines-based Knowledge Augmentation (AGKA) approach to improve LLMs. AGKA employs GPT 4.0 to retrieve label definition knowledge from annotation guidelines, and then applies the random under-sampler to select a few typical examples. Subsequently, we conduct a systematic evaluation benchmark of LEC, which includes six LEC datasets covering behavior classification (question and urgency level), emotion classification (binary and epistemic emotion), and cognition classification (opinion and cognitive presence). The study results demonstrate that AGKA can enhance non-fine-tuned LLMs, particularly GPT 4.0 and Llama 3 70B. GPT 4.0 with AGKA few-shot outperforms full-shot fine-tuned models such as BERT and RoBERTa on simple binary classification datasets. However, GPT 4.0 lags in multi-class tasks that require a deep understanding of complex semantic information. Notably, Llama 3 70B with AGKA is a promising combination based on open-source LLM, because its performance is on par with closed-source GPT 4.0 with AGKA. In addition, LLMs struggle to distinguish between labels with similar names in multi-class classification.
Large Language Models Meet User Interfaces: The Case of Provisioning Feedback
Apr 17, 2024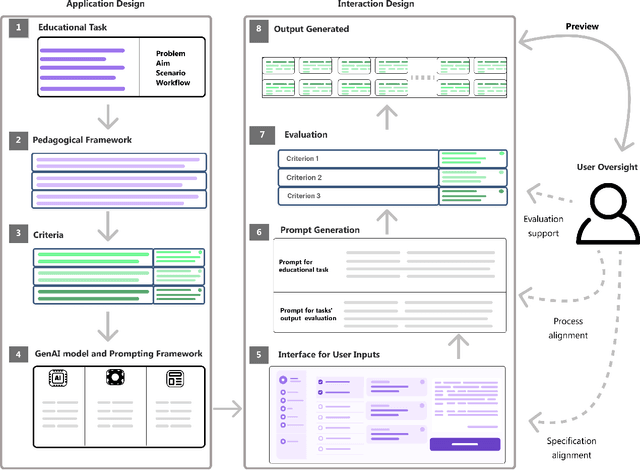

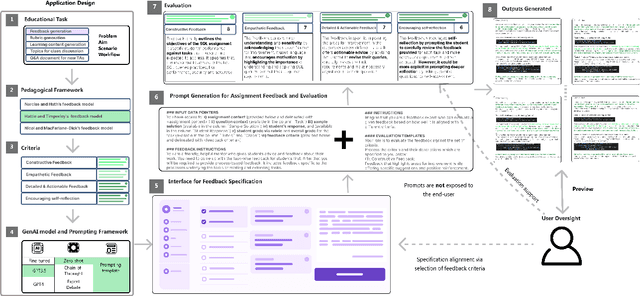

Abstract:Incorporating Generative AI (GenAI) and Large Language Models (LLMs) in education can enhance teaching efficiency and enrich student learning. Current LLM usage involves conversational user interfaces (CUIs) for tasks like generating materials or providing feedback. However, this presents challenges including the need for educator expertise in AI and CUIs, ethical concerns with high-stakes decisions, and privacy risks. CUIs also struggle with complex tasks. To address these, we propose transitioning from CUIs to user-friendly applications leveraging LLMs via API calls. We present a framework for ethically incorporating GenAI into educational tools and demonstrate its application in our tool, Feedback Copilot, which provides personalized feedback on student assignments. Our evaluation shows the effectiveness of this approach, with implications for GenAI researchers, educators, and technologists. This work charts a course for the future of GenAI in education.
Robust Educational Dialogue Act Classifiers with Low-Resource and Imbalanced Datasets
Apr 15, 2023
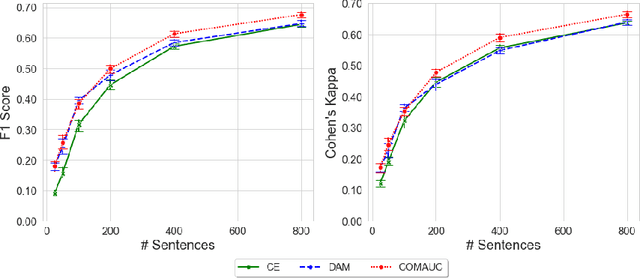
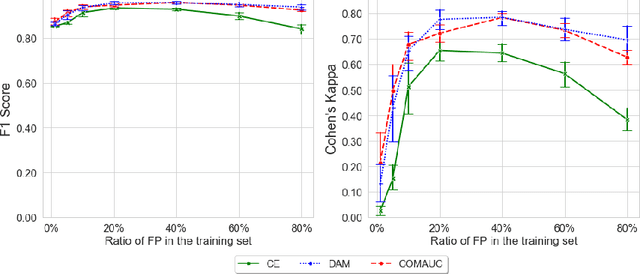
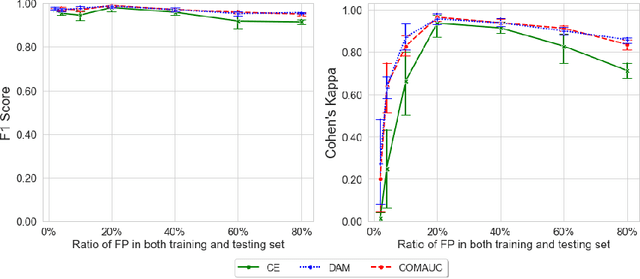
Abstract:Dialogue acts (DAs) can represent conversational actions of tutors or students that take place during tutoring dialogues. Automating the identification of DAs in tutoring dialogues is significant to the design of dialogue-based intelligent tutoring systems. Many prior studies employ machine learning models to classify DAs in tutoring dialogues and invest much effort to optimize the classification accuracy by using limited amounts of training data (i.e., low-resource data scenario). However, beyond the classification accuracy, the robustness of the classifier is also important, which can reflect the capability of the classifier on learning the patterns from different class distributions. We note that many prior studies on classifying educational DAs employ cross entropy (CE) loss to optimize DA classifiers on low-resource data with imbalanced DA distribution. The DA classifiers in these studies tend to prioritize accuracy on the majority class at the expense of the minority class which might not be robust to the data with imbalanced ratios of different DA classes. To optimize the robustness of classifiers on imbalanced class distributions, we propose to optimize the performance of the DA classifier by maximizing the area under the ROC curve (AUC) score (i.e., AUC maximization). Through extensive experiments, our study provides evidence that (i) by maximizing AUC in the training process, the DA classifier achieves significant performance improvement compared to the CE approach under low-resource data, and (ii) AUC maximization approaches can improve the robustness of the DA classifier under different class imbalance ratios.
Does Informativeness Matter? Active Learning for Educational Dialogue Act Classification
Apr 12, 2023



Abstract:Dialogue Acts (DAs) can be used to explain what expert tutors do and what students know during the tutoring process. Most empirical studies adopt the random sampling method to obtain sentence samples for manual annotation of DAs, which are then used to train DA classifiers. However, these studies have paid little attention to sample informativeness, which can reflect the information quantity of the selected samples and inform the extent to which a classifier can learn patterns. Notably, the informativeness level may vary among the samples and the classifier might only need a small amount of low informative samples to learn the patterns. Random sampling may overlook sample informativeness, which consumes human labelling costs and contributes less to training the classifiers. As an alternative, researchers suggest employing statistical sampling methods of Active Learning (AL) to identify the informative samples for training the classifiers. However, the use of AL methods in educational DA classification tasks is under-explored. In this paper, we examine the informativeness of annotated sentence samples. Then, the study investigates how the AL methods can select informative samples to support DA classifiers in the AL sampling process. The results reveal that most annotated sentences present low informativeness in the training dataset and the patterns of these sentences can be easily captured by the DA classifier. We also demonstrate how AL methods can reduce the cost of manual annotation in the AL sampling process.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge