David Lang
Robust Educational Dialogue Act Classifiers with Low-Resource and Imbalanced Datasets
Apr 15, 2023
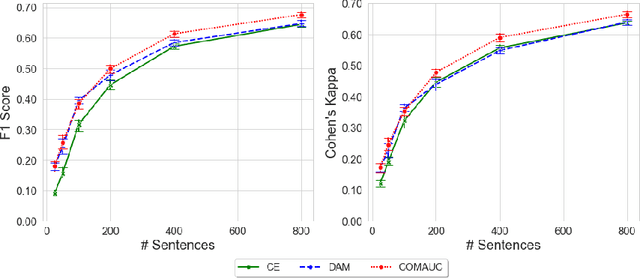
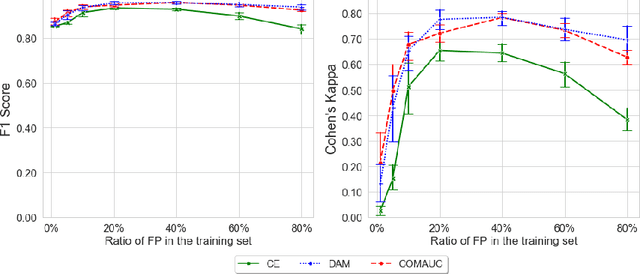
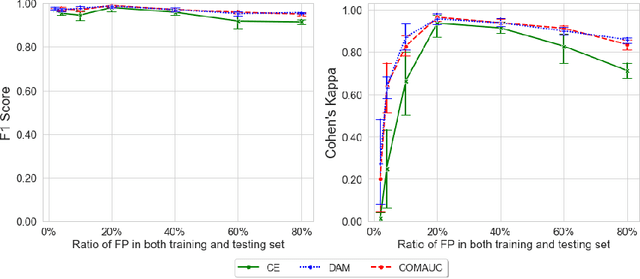
Abstract:Dialogue acts (DAs) can represent conversational actions of tutors or students that take place during tutoring dialogues. Automating the identification of DAs in tutoring dialogues is significant to the design of dialogue-based intelligent tutoring systems. Many prior studies employ machine learning models to classify DAs in tutoring dialogues and invest much effort to optimize the classification accuracy by using limited amounts of training data (i.e., low-resource data scenario). However, beyond the classification accuracy, the robustness of the classifier is also important, which can reflect the capability of the classifier on learning the patterns from different class distributions. We note that many prior studies on classifying educational DAs employ cross entropy (CE) loss to optimize DA classifiers on low-resource data with imbalanced DA distribution. The DA classifiers in these studies tend to prioritize accuracy on the majority class at the expense of the minority class which might not be robust to the data with imbalanced ratios of different DA classes. To optimize the robustness of classifiers on imbalanced class distributions, we propose to optimize the performance of the DA classifier by maximizing the area under the ROC curve (AUC) score (i.e., AUC maximization). Through extensive experiments, our study provides evidence that (i) by maximizing AUC in the training process, the DA classifier achieves significant performance improvement compared to the CE approach under low-resource data, and (ii) AUC maximization approaches can improve the robustness of the DA classifier under different class imbalance ratios.
Does Informativeness Matter? Active Learning for Educational Dialogue Act Classification
Apr 12, 2023



Abstract:Dialogue Acts (DAs) can be used to explain what expert tutors do and what students know during the tutoring process. Most empirical studies adopt the random sampling method to obtain sentence samples for manual annotation of DAs, which are then used to train DA classifiers. However, these studies have paid little attention to sample informativeness, which can reflect the information quantity of the selected samples and inform the extent to which a classifier can learn patterns. Notably, the informativeness level may vary among the samples and the classifier might only need a small amount of low informative samples to learn the patterns. Random sampling may overlook sample informativeness, which consumes human labelling costs and contributes less to training the classifiers. As an alternative, researchers suggest employing statistical sampling methods of Active Learning (AL) to identify the informative samples for training the classifiers. However, the use of AL methods in educational DA classification tasks is under-explored. In this paper, we examine the informativeness of annotated sentence samples. Then, the study investigates how the AL methods can select informative samples to support DA classifiers in the AL sampling process. The results reveal that most annotated sentences present low informativeness in the training dataset and the patterns of these sentences can be easily captured by the DA classifier. We also demonstrate how AL methods can reduce the cost of manual annotation in the AL sampling process.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge