Lele Sha
Annotation Guidelines-Based Knowledge Augmentation: Towards Enhancing Large Language Models for Educational Text Classification
Jun 03, 2024



Abstract:Various machine learning approaches have gained significant popularity for the automated classification of educational text to identify indicators of learning engagement -- i.e. learning engagement classification (LEC). LEC can offer comprehensive insights into human learning processes, attracting significant interest from diverse research communities, including Natural Language Processing (NLP), Learning Analytics, and Educational Data Mining. Recently, Large Language Models (LLMs), such as ChatGPT, have demonstrated remarkable performance in various NLP tasks. However, their comprehensive evaluation and improvement approaches in LEC tasks have not been thoroughly investigated. In this study, we propose the Annotation Guidelines-based Knowledge Augmentation (AGKA) approach to improve LLMs. AGKA employs GPT 4.0 to retrieve label definition knowledge from annotation guidelines, and then applies the random under-sampler to select a few typical examples. Subsequently, we conduct a systematic evaluation benchmark of LEC, which includes six LEC datasets covering behavior classification (question and urgency level), emotion classification (binary and epistemic emotion), and cognition classification (opinion and cognitive presence). The study results demonstrate that AGKA can enhance non-fine-tuned LLMs, particularly GPT 4.0 and Llama 3 70B. GPT 4.0 with AGKA few-shot outperforms full-shot fine-tuned models such as BERT and RoBERTa on simple binary classification datasets. However, GPT 4.0 lags in multi-class tasks that require a deep understanding of complex semantic information. Notably, Llama 3 70B with AGKA is a promising combination based on open-source LLM, because its performance is on par with closed-source GPT 4.0 with AGKA. In addition, LLMs struggle to distinguish between labels with similar names in multi-class classification.
Towards Detecting AI-Generated Text within Human-AI Collaborative Hybrid Texts
Mar 06, 2024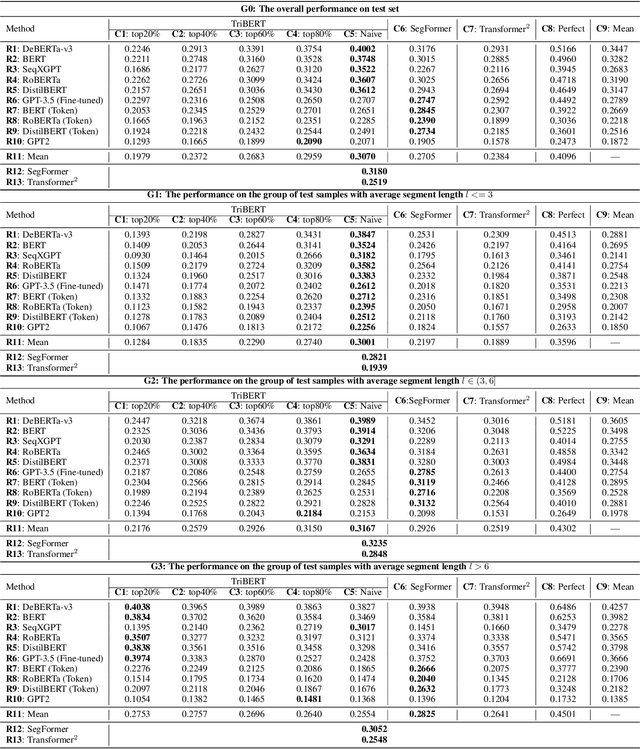
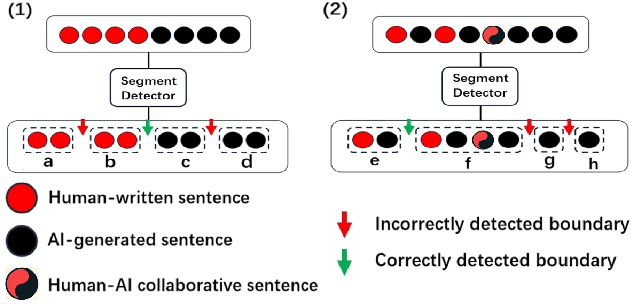
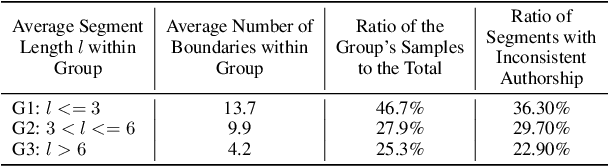
Abstract:This study explores the challenge of sentence-level AI-generated text detection within human-AI collaborative hybrid texts. Existing studies of AI-generated text detection for hybrid texts often rely on synthetic datasets. These typically involve hybrid texts with a limited number of boundaries. We contend that studies of detecting AI-generated content within hybrid texts should cover different types of hybrid texts generated in realistic settings to better inform real-world applications. Therefore, our study utilizes the CoAuthor dataset, which includes diverse, realistic hybrid texts generated through the collaboration between human writers and an intelligent writing system in multi-turn interactions. We adopt a two-step, segmentation-based pipeline: (i) detect segments within a given hybrid text where each segment contains sentences of consistent authorship, and (ii) classify the authorship of each identified segment. Our empirical findings highlight (1) detecting AI-generated sentences in hybrid texts is overall a challenging task because (1.1) human writers' selecting and even editing AI-generated sentences based on personal preferences adds difficulty in identifying the authorship of segments; (1.2) the frequent change of authorship between neighboring sentences within the hybrid text creates difficulties for segment detectors in identifying authorship-consistent segments; (1.3) the short length of text segments within hybrid texts provides limited stylistic cues for reliable authorship determination; (2) before embarking on the detection process, it is beneficial to assess the average length of segments within the hybrid text. This assessment aids in deciding whether (2.1) to employ a text segmentation-based strategy for hybrid texts with longer segments, or (2.2) to adopt a direct sentence-by-sentence classification strategy for those with shorter segments.
Towards Automatic Boundary Detection for Human-AI Collaborative Hybrid Essay in Education
Aug 16, 2023



Abstract:The recent large language models (LLMs), e.g., ChatGPT, have been able to generate human-like and fluent responses when provided with specific instructions. While admitting the convenience brought by technological advancement, educators also have concerns that students might leverage LLMs to complete their writing assignments and pass them off as their original work. Although many AI content detection studies have been conducted as a result of such concerns, most of these prior studies modeled AI content detection as a classification problem, assuming that a text is either entirely human-written or entirely AI-generated. In this study, we investigated AI content detection in a rarely explored yet realistic setting where the text to be detected is collaboratively written by human and generative LLMs (i.e., hybrid text). We first formalized the detection task as identifying the transition points between human-written content and AI-generated content from a given hybrid text (boundary detection). Then we proposed a two-step approach where we (1) separated AI-generated content from human-written content during the encoder training process; and (2) calculated the distances between every two adjacent prototypes and assumed that the boundaries exist between the two adjacent prototypes that have the furthest distance from each other. Through extensive experiments, we observed the following main findings: (1) the proposed approach consistently outperformed the baseline methods across different experiment settings; (2) the encoder training process can significantly boost the performance of the proposed approach; (3) when detecting boundaries for single-boundary hybrid essays, the proposed approach could be enhanced by adopting a relatively large prototype size, leading to a 22% improvement in the In-Domain evaluation and an 18% improvement in the Out-of-Domain evaluation.
Practical and Ethical Challenges of Large Language Models in Education: A Systematic Literature Review
Mar 17, 2023
Abstract:Educational technology innovations that have been developed based on large language models (LLMs) have shown the potential to automate the laborious process of generating and analysing textual content. While various innovations have been developed to automate a range of educational tasks (e.g., question generation, feedback provision, and essay grading), there are concerns regarding the practicality and ethicality of these innovations. Such concerns may hinder future research and the adoption of LLMs-based innovations in authentic educational contexts. To address this, we conducted a systematic literature review of 118 peer-reviewed papers published since 2017 to pinpoint the current state of research on using LLMs to automate and support educational tasks. The practical and ethical challenges of LLMs-based innovations were also identified by assessing their technological readiness, model performance, replicability, system transparency, privacy, equality, and beneficence. The findings were summarised into three recommendations for future studies, including updating existing innovations with state-of-the-art models (e.g., GPT-3), embracing the initiative of open-sourcing models/systems, and adopting a human-centred approach throughout the developmental process. These recommendations could support future research to develop practical and ethical innovations for supporting diverse educational tasks and benefiting students, teachers, and institutions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge