Yaohui Li
MoMa: A Modular Deep Learning Framework for Material Property Prediction
Feb 21, 2025



Abstract:Deep learning methods for material property prediction have been widely explored to advance materials discovery. However, the prevailing pre-train then fine-tune paradigm often fails to address the inherent diversity and disparity of material tasks. To overcome these challenges, we introduce MoMa, a Modular framework for Materials that first trains specialized modules across a wide range of tasks and then adaptively composes synergistic modules tailored to each downstream scenario. Evaluation across 17 datasets demonstrates the superiority of MoMa, with a substantial 14% average improvement over the strongest baseline. Few-shot and continual learning experiments further highlight MoMa's potential for real-world applications. Pioneering a new paradigm of modular material learning, MoMa will be open-sourced to foster broader community collaboration.
DeepSeek-V3 Technical Report
Dec 27, 2024



Abstract:We present DeepSeek-V3, a strong Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) language model with 671B total parameters with 37B activated for each token. To achieve efficient inference and cost-effective training, DeepSeek-V3 adopts Multi-head Latent Attention (MLA) and DeepSeekMoE architectures, which were thoroughly validated in DeepSeek-V2. Furthermore, DeepSeek-V3 pioneers an auxiliary-loss-free strategy for load balancing and sets a multi-token prediction training objective for stronger performance. We pre-train DeepSeek-V3 on 14.8 trillion diverse and high-quality tokens, followed by Supervised Fine-Tuning and Reinforcement Learning stages to fully harness its capabilities. Comprehensive evaluations reveal that DeepSeek-V3 outperforms other open-source models and achieves performance comparable to leading closed-source models. Despite its excellent performance, DeepSeek-V3 requires only 2.788M H800 GPU hours for its full training. In addition, its training process is remarkably stable. Throughout the entire training process, we did not experience any irrecoverable loss spikes or perform any rollbacks. The model checkpoints are available at https://github.com/deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-V3.
DeMamba: AI-Generated Video Detection on Million-Scale GenVideo Benchmark
May 30, 2024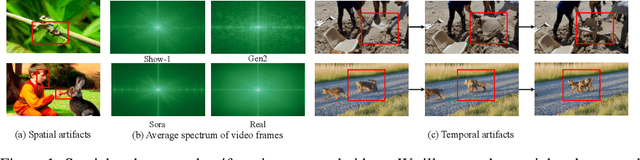
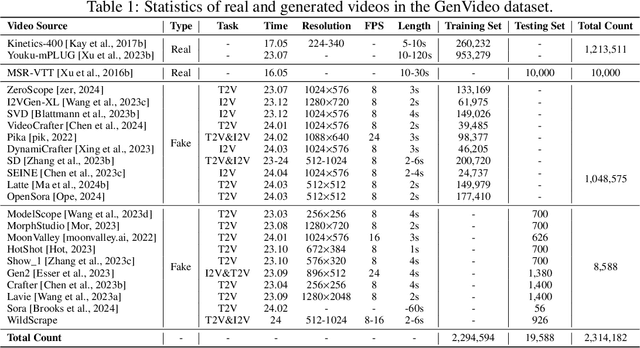
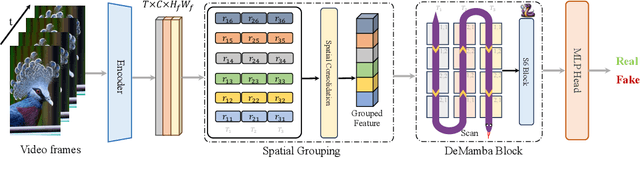
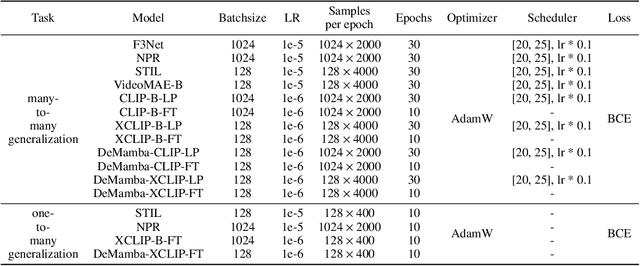
Abstract:Recently, video generation techniques have advanced rapidly. Given the popularity of video content on social media platforms, these models intensify concerns about the spread of fake information. Therefore, there is a growing demand for detectors capable of distinguishing between fake AI-generated videos and mitigating the potential harm caused by fake information. However, the lack of large-scale datasets from the most advanced video generators poses a barrier to the development of such detectors. To address this gap, we introduce the first AI-generated video detection dataset, GenVideo. It features the following characteristics: (1) a large volume of videos, including over one million AI-generated and real videos collected; (2) a rich diversity of generated content and methodologies, covering a broad spectrum of video categories and generation techniques. We conducted extensive studies of the dataset and proposed two evaluation methods tailored for real-world-like scenarios to assess the detectors' performance: the cross-generator video classification task assesses the generalizability of trained detectors on generators; the degraded video classification task evaluates the robustness of detectors to handle videos that have degraded in quality during dissemination. Moreover, we introduced a plug-and-play module, named Detail Mamba (DeMamba), designed to enhance the detectors by identifying AI-generated videos through the analysis of inconsistencies in temporal and spatial dimensions. Our extensive experiments demonstrate DeMamba's superior generalizability and robustness on GenVideo compared to existing detectors. We believe that the GenVideo dataset and the DeMamba module will significantly advance the field of AI-generated video detection. Our code and dataset will be aviliable at \url{https://github.com/chenhaoxing/DeMamba}.
Dual-Adapter: Training-free Dual Adaptation for Few-shot Out-of-Distribution Detection
May 25, 2024



Abstract:We study the problem of few-shot out-of-distribution (OOD) detection, which aims to detect OOD samples from unseen categories during inference time with only a few labeled in-domain (ID) samples. Existing methods mainly focus on training task-aware prompts for OOD detection. However, training on few-shot data may cause severe overfitting and textual prompts alone may not be enough for effective detection. To tackle these problems, we propose a prior-based Training-free Dual Adaptation method (Dual-Adapter) to detect OOD samples from both textual and visual perspectives. Specifically, Dual-Adapter first extracts the most significant channels as positive features and designates the remaining less relevant channels as negative features. Then, it constructs both a positive adapter and a negative adapter from a dual perspective, thereby better leveraging previously outlooked or interfering features in the training dataset. In this way, Dual-Adapter can inherit the advantages of CLIP not having to train, but also excels in distinguishing between ID and OOD samples. Extensive experimental results on four benchmark datasets demonstrate the superiority of Dual-Adapter.
The Devil is in the Few Shots: Iterative Visual Knowledge Completion for Few-shot Learning
Apr 19, 2024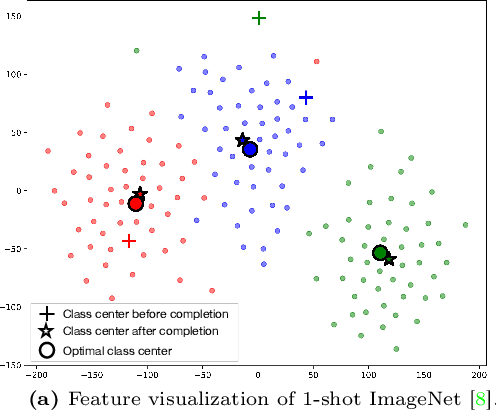
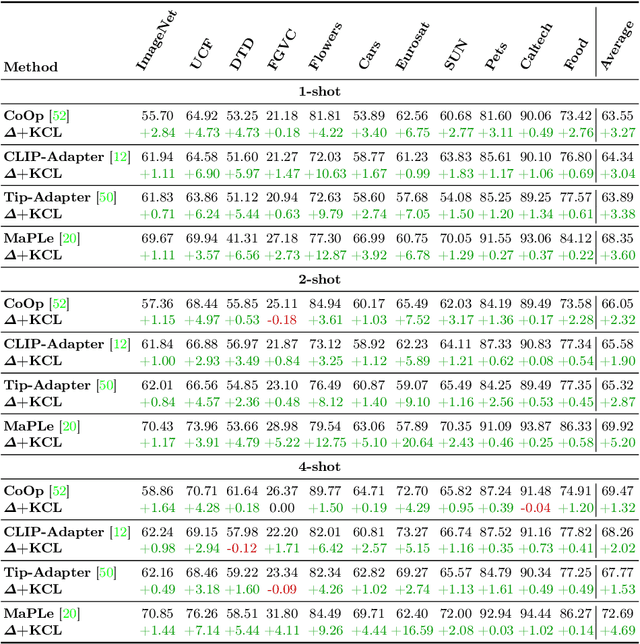
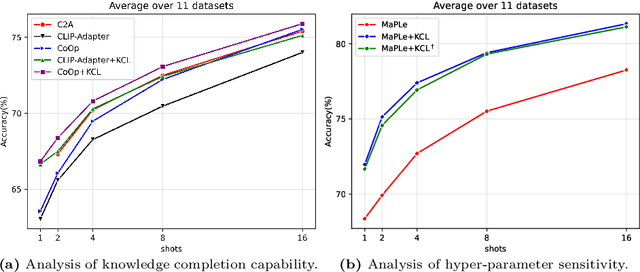
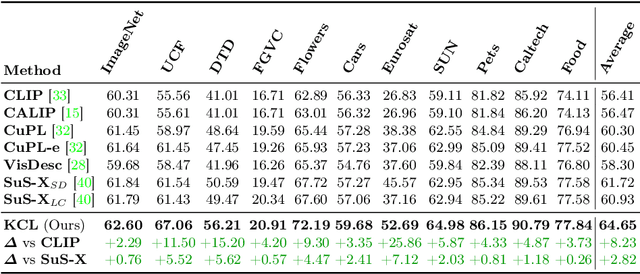
Abstract:Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training (CLIP) has shown powerful zero-shot learning performance. Few-shot learning aims to further enhance the transfer capability of CLIP by giving few images in each class, aka 'few shots'. Most existing methods either implicitly learn from the few shots by incorporating learnable prompts or adapters, or explicitly embed them in a cache model for inference. However, the narrow distribution of few shots often contains incomplete class information, leading to biased visual knowledge with high risk of misclassification. To tackle this problem, recent methods propose to supplement visual knowledge by generative models or extra databases, which can be costly and time-consuming. In this paper, we propose an Iterative Visual Knowledge CompLetion (KCL) method to complement visual knowledge by properly taking advantages of unlabeled samples without access to any auxiliary or synthetic data. Specifically, KCL first measures the similarities between unlabeled samples and each category. Then, the samples with top confidence to each category is selected and collected by a designed confidence criterion. Finally, the collected samples are treated as labeled ones and added to few shots to jointly re-estimate the remaining unlabeled ones. The above procedures will be repeated for a certain number of iterations with more and more samples being collected until convergence, ensuring a progressive and robust knowledge completion process. Extensive experiments on 11 benchmark datasets demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of KCL as a plug-and-play module under both few-shot and zero-shot learning settings. Code is available at https://github.com/Mark-Sky/KCL.
Conditional Prototype Rectification Prompt Learning
Apr 15, 2024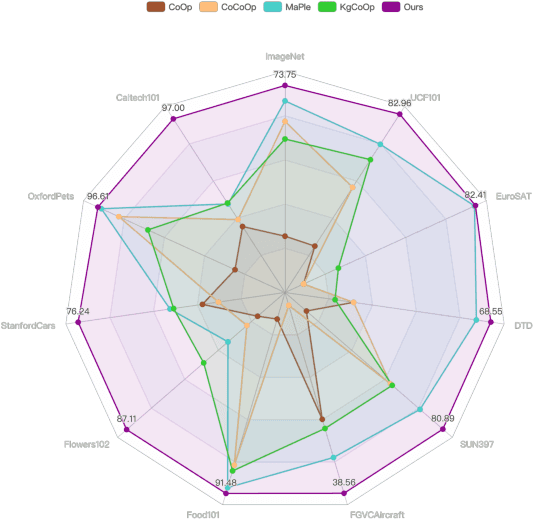

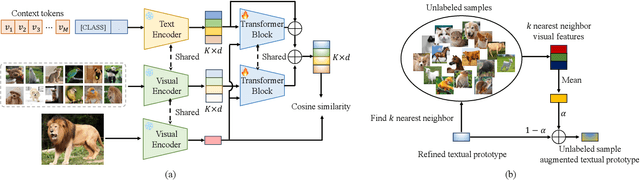

Abstract:Pre-trained large-scale vision-language models (VLMs) have acquired profound understanding of general visual concepts. Recent advancements in efficient transfer learning (ETL) have shown remarkable success in fine-tuning VLMs within the scenario of limited data, introducing only a few parameters to harness task-specific insights from VLMs. Despite significant progress, current leading ETL methods tend to overfit the narrow distributions of base classes seen during training and encounter two primary challenges: (i) only utilizing uni-modal information to modeling task-specific knowledge; and (ii) using costly and time-consuming methods to supplement knowledge. To address these issues, we propose a Conditional Prototype Rectification Prompt Learning (CPR) method to correct the bias of base examples and augment limited data in an effective way. Specifically, we alleviate overfitting on base classes from two aspects. First, each input image acquires knowledge from both textual and visual prototypes, and then generates sample-conditional text tokens. Second, we extract utilizable knowledge from unlabeled data to further refine the prototypes. These two strategies mitigate biases stemming from base classes, yielding a more effective classifier. Extensive experiments on 11 benchmark datasets show that our CPR achieves state-of-the-art performance on both few-shot classification and base-to-new generalization tasks. Our code is avaliable at \url{https://github.com/chenhaoxing/CPR}.
Segment Anything Model Meets Image Harmonization
Dec 20, 2023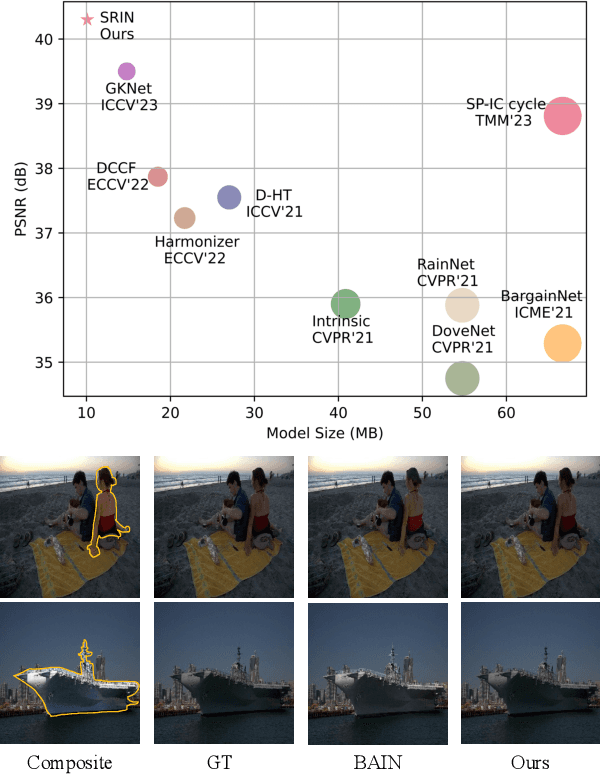
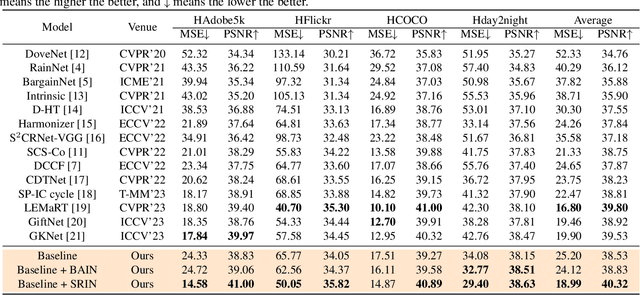
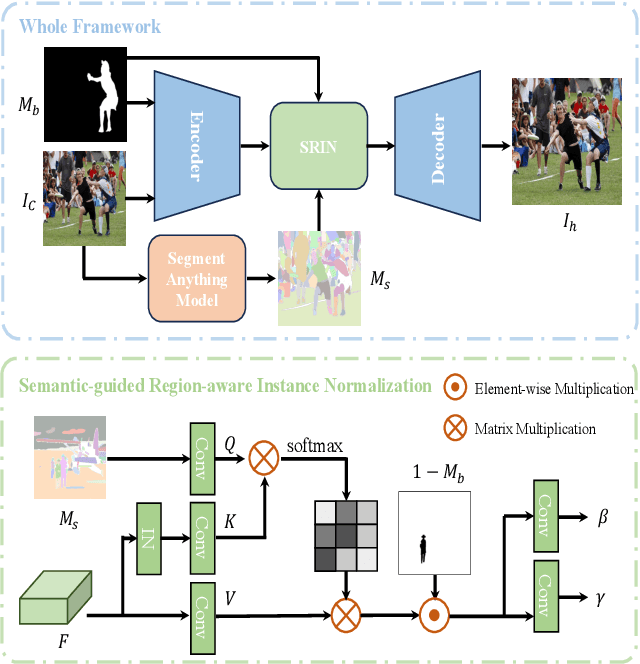
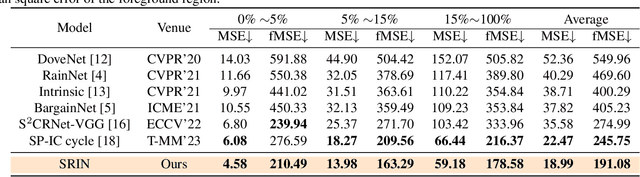
Abstract:Image harmonization is a crucial technique in image composition that aims to seamlessly match the background by adjusting the foreground of composite images. Current methods adopt either global-level or pixel-level feature matching. Global-level feature matching ignores the proximity prior, treating foreground and background as separate entities. On the other hand, pixel-level feature matching loses contextual information. Therefore, it is necessary to use the information from semantic maps that describe different objects to guide harmonization. In this paper, we propose Semantic-guided Region-aware Instance Normalization (SRIN) that can utilize the semantic segmentation maps output by a pre-trained Segment Anything Model (SAM) to guide the visual consistency learning of foreground and background features. Abundant experiments demonstrate the superiority of our method for image harmonization over state-of-the-art methods.
Boosting Audio-visual Zero-shot Learning with Large Language Models
Nov 21, 2023Abstract:Audio-visual zero-shot learning aims to recognize unseen categories based on paired audio-visual sequences. Recent methods mainly focus on learning aligned and discriminative multi-modal features to boost generalization towards unseen categories. However, these approaches ignore the obscure action concepts in category names and may inevitably introduce complex network structures with difficult training objectives. In this paper, we propose a simple yet effective framework named Knowledge-aware Distribution Adaptation (KDA) to help the model better grasp the novel action contents with an external knowledge base. Specifically, we first propose using large language models to generate rich descriptions from category names, which leads to a better understanding of unseen categories. Additionally, we propose a distribution alignment loss as well as a knowledge-aware adaptive margin loss to further improve the generalization ability towards unseen categories. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that our proposed KDA can outperform state-of-the-art methods on three popular audio-visual zero-shot learning datasets. Our code will be avaliable at \url{https://github.com/chenhaoxing/KDA}.
DiffUTE: Universal Text Editing Diffusion Model
May 19, 2023Abstract:Diffusion model based language-guided image editing has achieved great success recently. However, existing state-of-the-art diffusion models struggle with rendering correct text and text style during generation. To tackle this problem, we propose a universal self-supervised text editing diffusion model (DiffUTE), which aims to replace or modify words in the source image with another one while maintaining its realistic appearance. Specifically, we build our model on a diffusion model and carefully modify the network structure to enable the model for drawing multilingual characters with the help of glyph and position information. Moreover, we design a self-supervised learning framework to leverage large amounts of web data to improve the representation ability of the model. Experimental results show that our method achieves an impressive performance and enables controllable editing on in-the-wild images with high fidelity. Our code will be avaliable in \url{https://github.com/chenhaoxing/DiffUTE}.
Hierarchical Dynamic Image Harmonization
Nov 16, 2022Abstract:Image harmonization is a critical task in computer vision, which aims to adjust the fore-ground to make it compatible with the back-ground. Recent works mainly focus on using global transformation (i.e., normalization and color curve rendering) to achieve visual consistency. However, these model ignore local consistency and their model size limit their harmonization ability on edge devices. Inspired by the dynamic deep networks that adapt the model structures or parameters conditioned on the inputs, we propose a hierarchical dynamic network (HDNet) for efficient image harmonization to adapt the model parameters and features from local to global view for better feature transformation. Specifically, local dynamics (LD) and mask-aware global dynamics (MGD) are applied. LD enables features of different channels and positions to change adaptively and improve the representation ability of geometric transformation through structural information learning. MGD learns the representations of fore- and back-ground regions and correlations to global harmonization. Experiments show that the proposed HDNet reduces more than 80\% parameters compared with previous methods but still achieves the state-of-the-art performance on the popular iHarmony4 dataset. Our code is avaliable in https://github.com/chenhaoxing/HDNet.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge