Qifeng Zhou
Leveraging Gait Patterns as Biomarkers: An attention-guided Deep Multiple Instance Learning Network for Scoliosis Classification
Apr 04, 2025Abstract:Scoliosis is a spinal curvature disorder that is difficult to detect early and can compress the chest cavity, impacting respiratory function and cardiac health. Especially for adolescents, delayed detection and treatment result in worsening compression. Traditional scoliosis detection methods heavily rely on clinical expertise, and X-ray imaging poses radiation risks, limiting large-scale early screening. We propose an Attention-Guided Deep Multi-Instance Learning method (Gait-MIL) to effectively capture discriminative features from gait patterns, which is inspired by ScoNet-MT's pioneering use of gait patterns for scoliosis detection. We evaluate our method on the first large-scale dataset based on gait patterns for scoliosis classification. The results demonstrate that our study improves the performance of using gait as a biomarker for scoliosis detection, significantly enhances detection accuracy for the particularly challenging Neutral cases, where subtle indicators are often overlooked. Our Gait-MIL also performs robustly in imbalanced scenarios, making it a promising tool for large-scale scoliosis screening.
SS4Rec: Continuous-Time Sequential Recommendation with State Space Models
Feb 12, 2025Abstract:Sequential recommendation is a key area in the field of recommendation systems aiming to model user interest based on historical interaction sequences with irregular intervals. While previous recurrent neural network-based and attention-based approaches have achieved significant results, they have limitations in capturing system continuity due to the discrete characteristics. In the context of continuous-time modeling, state space model (SSM) offers a potential solution, as it can effectively capture the dynamic evolution of user interest over time. However, existing SSM-based approaches ignore the impact of irregular time intervals within historical user interactions, making it difficult to model complexed user-item transitions in sequences. To address this issue, we propose a hybrid SSM-based model called SS4Rec for continuous-time sequential recommendation. SS4Rec integrates a time-aware SSM to handle irregular time intervals and a relation-aware SSM to model contextual dependencies, enabling it to infer user interest from both temporal and sequential perspectives. In the training process, the time-aware SSM and the relation-aware SSM are discretized by variable stepsizes according to user interaction time intervals and input data, respectively. This helps capture the continuous dependency from irregular time intervals and provides time-specific personalized recommendations. Experimental studies on five benchmark datasets demonstrate the superiority and effectiveness of SS4Rec.
MLLM4PUE: Toward Universal Embeddings in Computational Pathology through Multimodal LLMs
Feb 11, 2025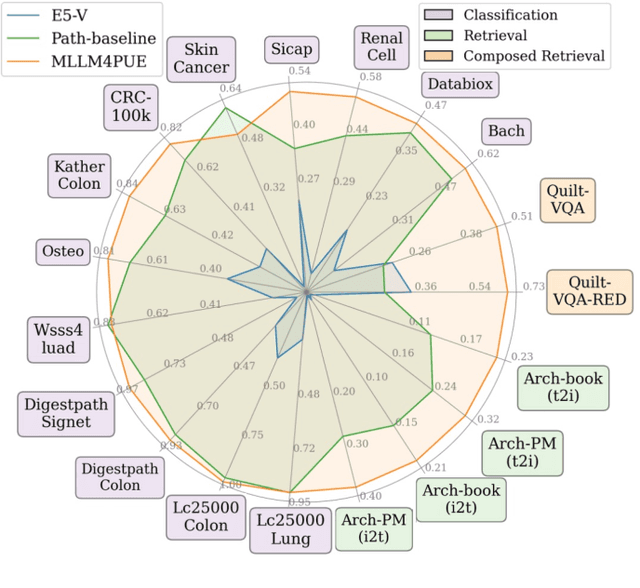
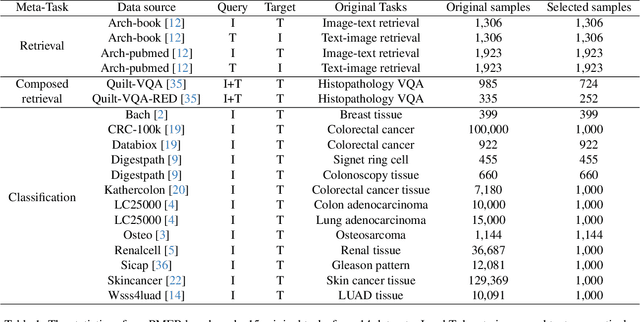
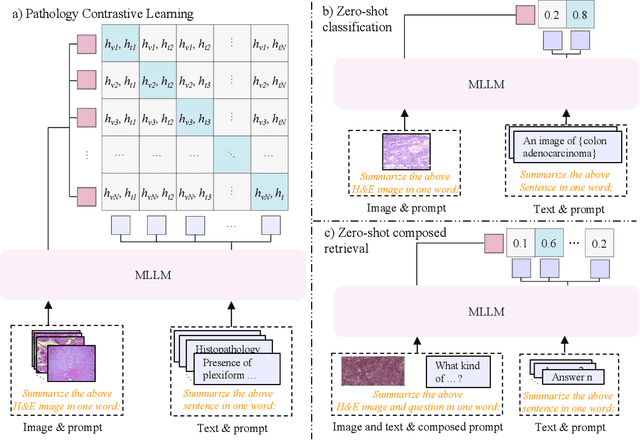
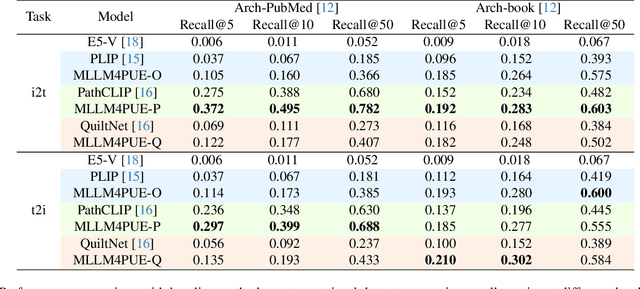
Abstract:Pathology plays a critical role in diagnosing a wide range of diseases, yet existing approaches often rely heavily on task-specific models trained on extensive, well-labeled datasets. These methods face sustainability challenges due to the diversity of pathologies and the labor-intensive nature of data collection. To address these limitations, we highlight the need for universal multimodal embeddings that can support multiple downstream tasks. Previous approaches often involve fine-tuning CLIP-based models, which handle images and text separately, limiting their ability to capture complex multimodal relationships. Additionally, these models are evaluated across diverse datasets without a unified benchmark for assessing multimodal embeddings in pathology. To address these challenges, we propose MLLM4PUE, a novel framework that leverages Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) to generate Pathology Universal Embeddings. The MLLM4PUE framework not only facilitates robust integration of images and text but also enhances understanding and fusion capabilities across various tasks. We further introduce the Pathology Multimodal Embedding Benchmark (PMEB), a comprehensive benchmark designed to assess the quality of pathology multimodal embeddings. PMEB comprises 15 original tasks drawn from 14 datasets, organized into three meta-tasks: retrieval, classification, and composed retrieval. Experimental results demonstrate the superiority of MLLM4PUE, illustrating MLLM-based models can effectively support a wide range of downstream tasks and unify the research direction for foundation models in pathology.
The Devil is in the Few Shots: Iterative Visual Knowledge Completion for Few-shot Learning
Apr 19, 2024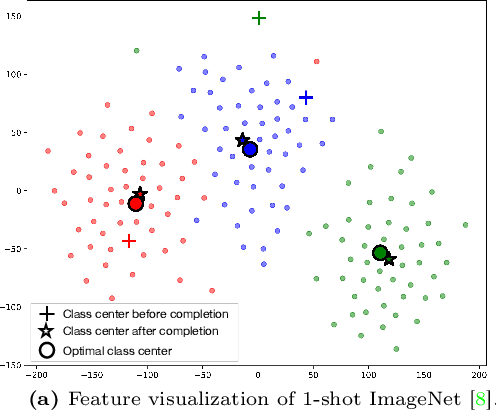
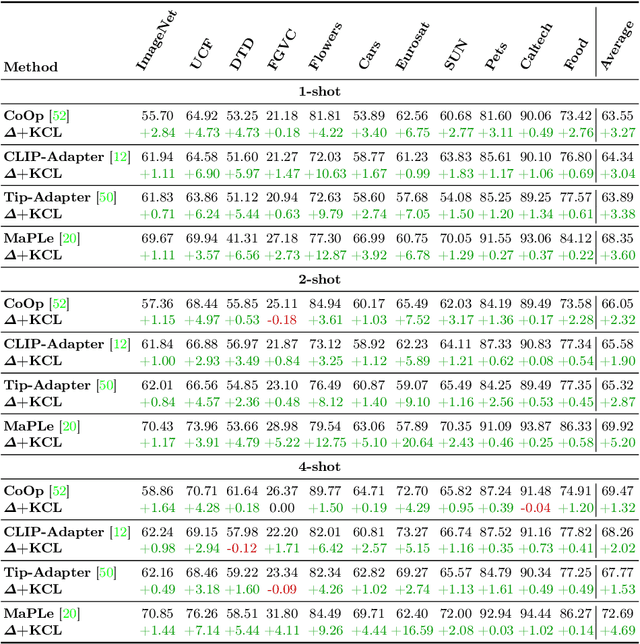
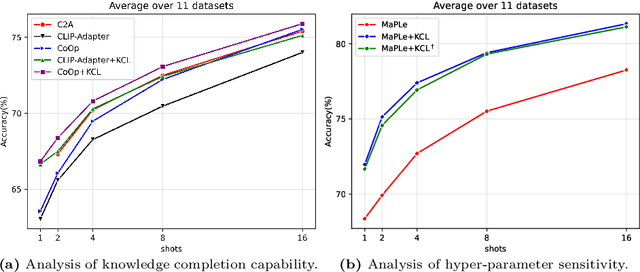
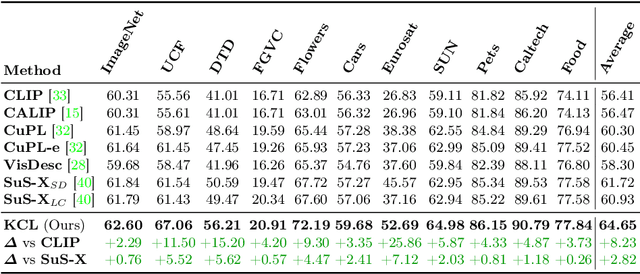
Abstract:Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training (CLIP) has shown powerful zero-shot learning performance. Few-shot learning aims to further enhance the transfer capability of CLIP by giving few images in each class, aka 'few shots'. Most existing methods either implicitly learn from the few shots by incorporating learnable prompts or adapters, or explicitly embed them in a cache model for inference. However, the narrow distribution of few shots often contains incomplete class information, leading to biased visual knowledge with high risk of misclassification. To tackle this problem, recent methods propose to supplement visual knowledge by generative models or extra databases, which can be costly and time-consuming. In this paper, we propose an Iterative Visual Knowledge CompLetion (KCL) method to complement visual knowledge by properly taking advantages of unlabeled samples without access to any auxiliary or synthetic data. Specifically, KCL first measures the similarities between unlabeled samples and each category. Then, the samples with top confidence to each category is selected and collected by a designed confidence criterion. Finally, the collected samples are treated as labeled ones and added to few shots to jointly re-estimate the remaining unlabeled ones. The above procedures will be repeated for a certain number of iterations with more and more samples being collected until convergence, ensuring a progressive and robust knowledge completion process. Extensive experiments on 11 benchmark datasets demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of KCL as a plug-and-play module under both few-shot and zero-shot learning settings. Code is available at https://github.com/Mark-Sky/KCL.
PathM3: A Multimodal Multi-Task Multiple Instance Learning Framework for Whole Slide Image Classification and Captioning
Mar 13, 2024Abstract:In the field of computational histopathology, both whole slide images (WSIs) and diagnostic captions provide valuable insights for making diagnostic decisions. However, aligning WSIs with diagnostic captions presents a significant challenge. This difficulty arises from two main factors: 1) Gigapixel WSIs are unsuitable for direct input into deep learning models, and the redundancy and correlation among the patches demand more attention; and 2) Authentic WSI diagnostic captions are extremely limited, making it difficult to train an effective model. To overcome these obstacles, we present PathM3, a multimodal, multi-task, multiple instance learning (MIL) framework for WSI classification and captioning. PathM3 adapts a query-based transformer to effectively align WSIs with diagnostic captions. Given that histopathology visual patterns are redundantly distributed across WSIs, we aggregate each patch feature with MIL method that considers the correlations among instances. Furthermore, our PathM3 overcomes data scarcity in WSI-level captions by leveraging limited WSI diagnostic caption data in the manner of multi-task joint learning. Extensive experiments with improved classification accuracy and caption generation demonstrate the effectiveness of our method on both WSI classification and captioning task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge