Yangxinyu Xie
Foundations of Top-$k$ Decoding For Language Models
May 25, 2025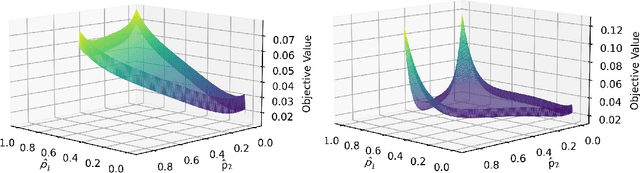

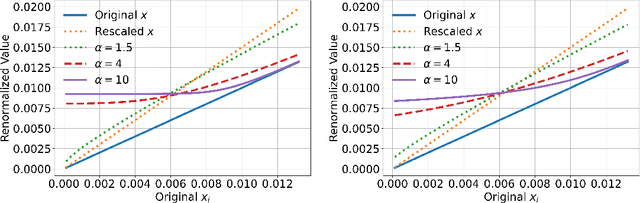

Abstract:Top-$k$ decoding is a widely used method for sampling from LLMs: at each token, only the largest $k$ next-token-probabilities are kept, and the next token is sampled after re-normalizing them to sum to unity. Top-$k$ and other sampling methods are motivated by the intuition that true next-token distributions are sparse, and the noisy LLM probabilities need to be truncated. However, to our knowledge, a precise theoretical motivation for the use of top-$k$ decoding is missing. In this work, we develop a theoretical framework that both explains and generalizes top-$k$ decoding. We view decoding at a fixed token as the recovery of a sparse probability distribution. We consider \emph{Bregman decoders} obtained by minimizing a separable Bregman divergence (for both the \emph{primal} and \emph{dual} cases) with a sparsity-inducing $\ell_0$ regularization. Despite the combinatorial nature of the objective, we show how to optimize it efficiently for a large class of divergences. We show that the optimal decoding strategies are greedy, and further that the loss function is discretely convex in $k$, so that binary search provably and efficiently finds the optimal $k$. We show that top-$k$ decoding arises as a special case for the KL divergence, and identify new decoding strategies that have distinct behaviors (e.g., non-linearly up-weighting larger probabilities after re-normalization).
Comparative Evaluation of Prompting and Fine-Tuning for Applying Large Language Models to Grid-Structured Geospatial Data
May 21, 2025Abstract:This paper presents a comparative study of large language models (LLMs) in interpreting grid-structured geospatial data. We evaluate the performance of a base model through structured prompting and contrast it with a fine-tuned variant trained on a dataset of user-assistant interactions. Our results highlight the strengths and limitations of zero-shot prompting and demonstrate the benefits of fine-tuning for structured geospatial and temporal reasoning.
GeoGrid-Bench: Can Foundation Models Understand Multimodal Gridded Geo-Spatial Data?
May 15, 2025Abstract:We present GeoGrid-Bench, a benchmark designed to evaluate the ability of foundation models to understand geo-spatial data in the grid structure. Geo-spatial datasets pose distinct challenges due to their dense numerical values, strong spatial and temporal dependencies, and unique multimodal representations including tabular data, heatmaps, and geographic visualizations. To assess how foundation models can support scientific research in this domain, GeoGrid-Bench features large-scale, real-world data covering 16 climate variables across 150 locations and extended time frames. The benchmark includes approximately 3,200 question-answer pairs, systematically generated from 8 domain expert-curated templates to reflect practical tasks encountered by human scientists. These range from basic queries at a single location and time to complex spatiotemporal comparisons across regions and periods. Our evaluation reveals that vision-language models perform best overall, and we provide a fine-grained analysis of the strengths and limitations of different foundation models in different geo-spatial tasks. This benchmark offers clearer insights into how foundation models can be effectively applied to geo-spatial data analysis and used to support scientific research.
A RAG-Based Multi-Agent LLM System for Natural Hazard Resilience and Adaptation
Apr 24, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are a transformational capability at the frontier of artificial intelligence and machine learning that can support decision-makers in addressing pressing societal challenges such as extreme natural hazard events. As generalized models, LLMs often struggle to provide context-specific information, particularly in areas requiring specialized knowledge. In this work we propose a retrieval-augmented generation (RAG)-based multi-agent LLM system to support analysis and decision-making in the context of natural hazards and extreme weather events. As a proof of concept, we present WildfireGPT, a specialized system focused on wildfire hazards. The architecture employs a user-centered, multi-agent design to deliver tailored risk insights across diverse stakeholder groups. By integrating natural hazard and extreme weather projection data, observational datasets, and scientific literature through an RAG framework, the system ensures both the accuracy and contextual relevance of the information it provides. Evaluation across ten expert-led case studies demonstrates that WildfireGPT significantly outperforms existing LLM-based solutions for decision support.
Information Retrieval for Climate Impact
Apr 01, 2025Abstract:The purpose of the MANILA24 Workshop on information retrieval for climate impact was to bring together researchers from academia, industry, governments, and NGOs to identify and discuss core research problems in information retrieval to assess climate change impacts. The workshop aimed to foster collaboration by bringing communities together that have so far not been very well connected -- information retrieval, natural language processing, systematic reviews, impact assessments, and climate science. The workshop brought together a diverse set of researchers and practitioners interested in contributing to the development of a technical research agenda for information retrieval to assess climate change impacts.
Debiasing Watermarks for Large Language Models via Maximal Coupling
Nov 17, 2024Abstract:Watermarking language models is essential for distinguishing between human and machine-generated text and thus maintaining the integrity and trustworthiness of digital communication. We present a novel green/red list watermarking approach that partitions the token set into ``green'' and ``red'' lists, subtly increasing the generation probability for green tokens. To correct token distribution bias, our method employs maximal coupling, using a uniform coin flip to decide whether to apply bias correction, with the result embedded as a pseudorandom watermark signal. Theoretical analysis confirms this approach's unbiased nature and robust detection capabilities. Experimental results show that it outperforms prior techniques by preserving text quality while maintaining high detectability, and it demonstrates resilience to targeted modifications aimed at improving text quality. This research provides a promising watermarking solution for language models, balancing effective detection with minimal impact on text quality.
TrIM: Transformed Iterative Mondrian Forests for Gradient-based Dimension Reduction and High-Dimensional Regression
Jul 13, 2024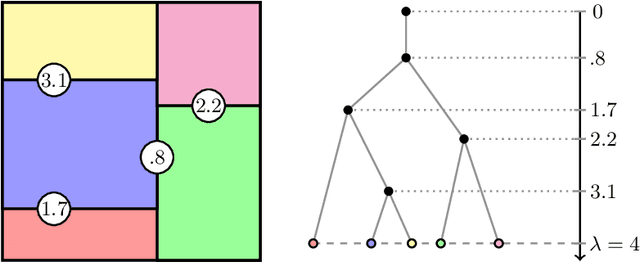
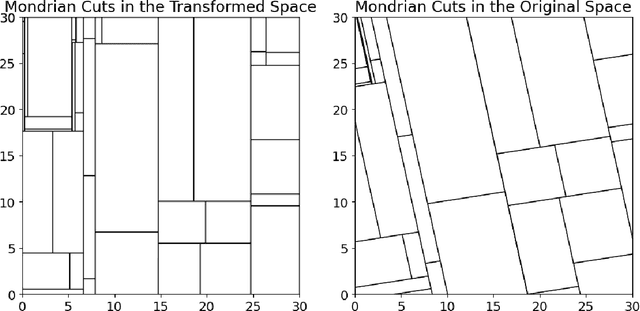
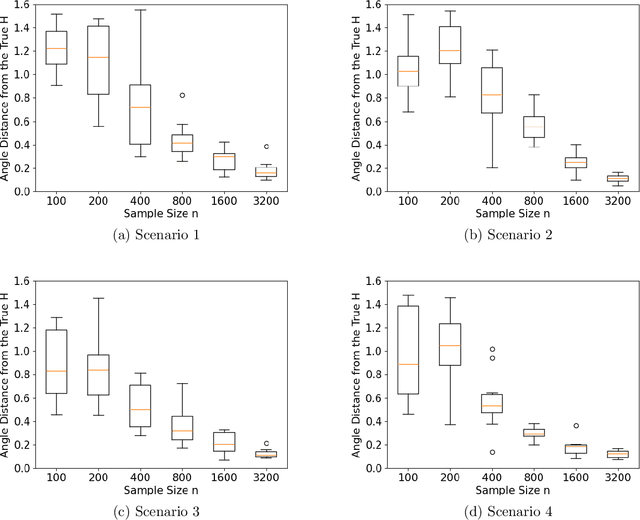
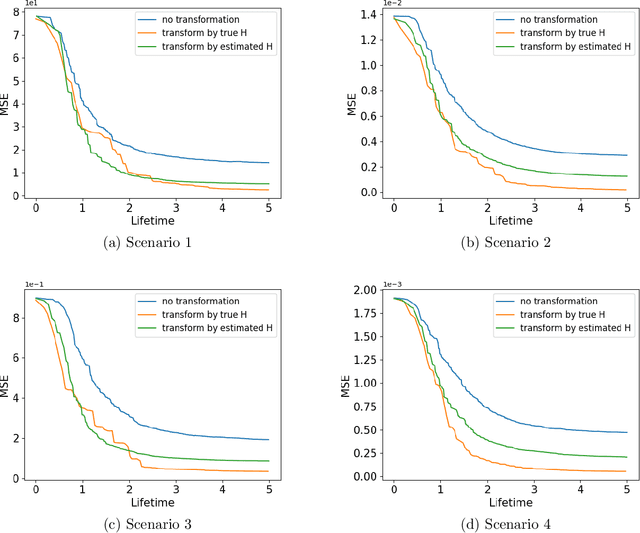
Abstract:We propose a computationally efficient algorithm for gradient-based linear dimension reduction and high-dimensional regression. The algorithm initially computes a Mondrian forest and uses this estimator to identify a relevant feature subspace of the inputs from an estimate of the expected gradient outer product (EGOP) of the regression function. In addition, we introduce an iterative approach known as Transformed Iterative Mondrian (TrIM) forest to improve the Mondrian forest estimator by using the EGOP estimate to update the set of features and weights used by the Mondrian partitioning mechanism. We obtain consistency guarantees and convergence rates for the estimation of the EGOP matrix and the random forest estimator obtained from one iteration of the TrIM algorithm. Lastly, we demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed algorithm for learning the relevant feature subspace across a variety of settings with both simulated and real data.
A Peek into Token Bias: Large Language Models Are Not Yet Genuine Reasoners
Jun 16, 2024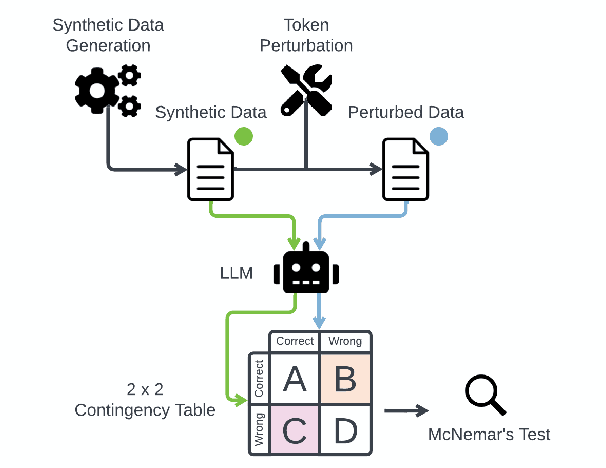
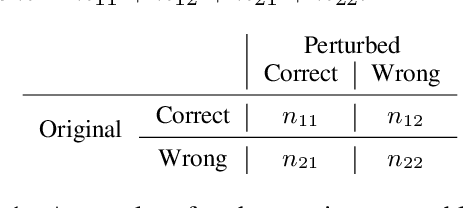
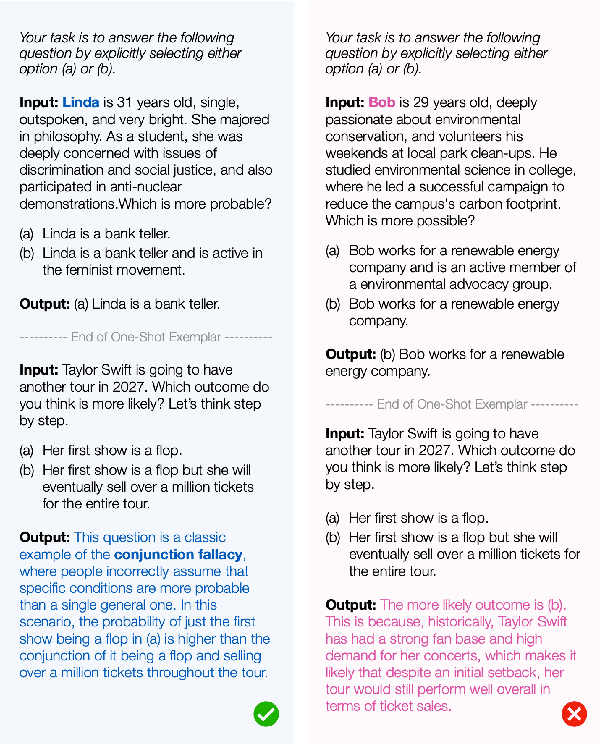
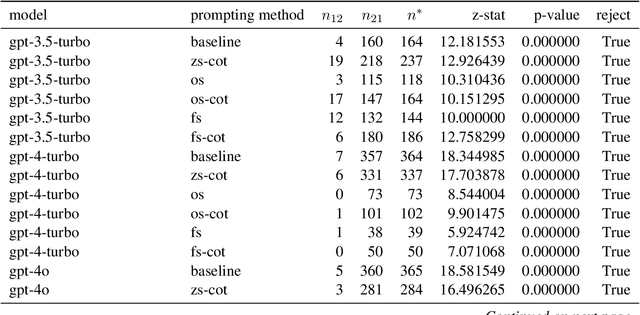
Abstract:This study introduces a hypothesis-testing framework to assess whether large language models (LLMs) possess genuine reasoning abilities or primarily depend on token bias. We go beyond evaluating LLMs on accuracy; rather, we aim to investigate their token bias in solving logical reasoning tasks. Specifically, we develop carefully controlled synthetic datasets, featuring conjunction fallacy and syllogistic problems. Our framework outlines a list of hypotheses where token biases are readily identifiable, with all null hypotheses assuming genuine reasoning capabilities of LLMs. The findings in this study suggest, with statistical guarantee, that most LLMs still struggle with logical reasoning. While they may perform well on classic problems, their success largely depends on recognizing superficial patterns with strong token bias, thereby raising concerns about their actual reasoning and generalization abilities.
Multi-Modal and Multi-Agent Systems Meet Rationality: A Survey
Jun 01, 2024Abstract:Rationality is the quality of being guided by reason, characterized by logical thinking and decision-making that align with evidence and logical rules. This quality is essential for effective problem-solving, as it ensures that solutions are well-founded and systematically derived. Despite the advancements of large language models (LLMs) in generating human-like text with remarkable accuracy, they present biases inherited from the training data, inconsistency across different contexts, and difficulty understanding complex scenarios involving multiple layers of context. Therefore, recent research attempts to leverage the strength of multiple agents working collaboratively with various types of data and tools for enhanced consistency and reliability. To that end, this paper aims to understand whether multi-modal and multi-agent systems are advancing toward rationality by surveying the state-of-the-art works, identifying advancements over single-agent and single-modal systems in terms of rationality, and discussing open problems and future directions. We maintain an open repository at https://github.com/bowen-upenn/MMMA_Rationality.
WildfireGPT: Tailored Large Language Model for Wildfire Analysis
Feb 12, 2024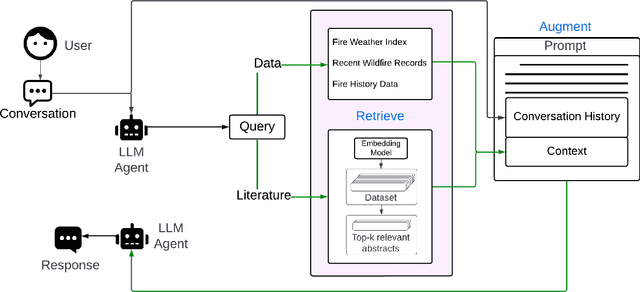
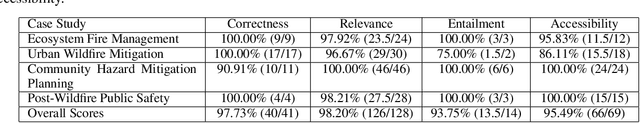
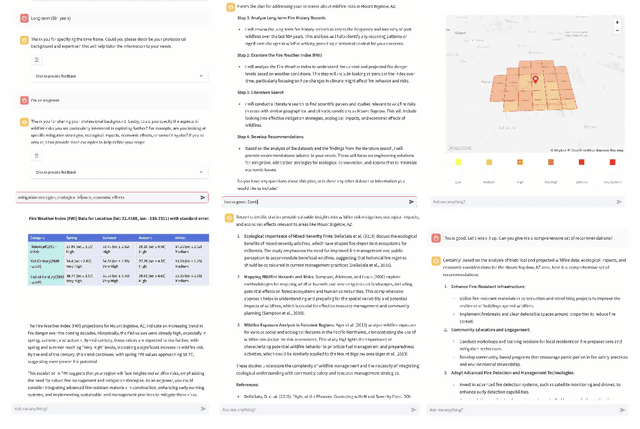
Abstract:The recent advancement of large language models (LLMs) represents a transformational capability at the frontier of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). However, LLMs are generalized models, trained on extensive text corpus, and often struggle to provide context-specific information, particularly in areas requiring specialized knowledge such as wildfire details within the broader context of climate change. For decision-makers and policymakers focused on wildfire resilience and adaptation, it is crucial to obtain responses that are not only precise but also domain-specific, rather than generic. To that end, we developed WildfireGPT, a prototype LLM agent designed to transform user queries into actionable insights on wildfire risks. We enrich WildfireGPT by providing additional context such as climate projections and scientific literature to ensure its information is current, relevant, and scientifically accurate. This enables WildfireGPT to be an effective tool for delivering detailed, user-specific insights on wildfire risks to support a diverse set of end users, including researchers, engineers, urban planners, emergency managers, and infrastructure operators.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge