Wenqing Zheng
Explain What You Mean: Intent Augmented Knowledge Graph Recommender Built With LLM
May 16, 2025Abstract:Interaction sparsity is the primary obstacle for recommendation systems. Sparsity manifests in environments with disproportional cardinality of groupings of entities, such as users and products in an online marketplace. It also is found for newly introduced entities, described as the cold-start problem. Recent efforts to mitigate this sparsity issue shifts the performance bottleneck to other areas in the computational pipeline. Those that focus on enriching sparse representations with connectivity data from other external sources propose methods that are resource demanding and require careful domain expert aided addition of this newly introduced data. Others that turn to Large Language Model (LLM) based recommenders will quickly encounter limitations surrounding data quality and availability. In this work, we propose LLM-based Intent Knowledge Graph Recommender (IKGR), a novel framework that leverages retrieval-augmented generation and an encoding approach to construct and densify a knowledge graph. IKGR learns latent user-item affinities from an interaction knowledge graph and further densifies it through mutual intent connectivity. This addresses sparsity issues and allows the model to make intent-grounded recommendations with an interpretable embedding translation layer. Through extensive experiments on real-world datasets, we demonstrate that IKGR overcomes knowledge gaps and achieves substantial gains over state-of-the-art baselines on both publicly available and our internal recommendation datasets.
Revisiting Zeroth-Order Optimization for Memory-Efficient LLM Fine-Tuning: A Benchmark
Feb 26, 2024
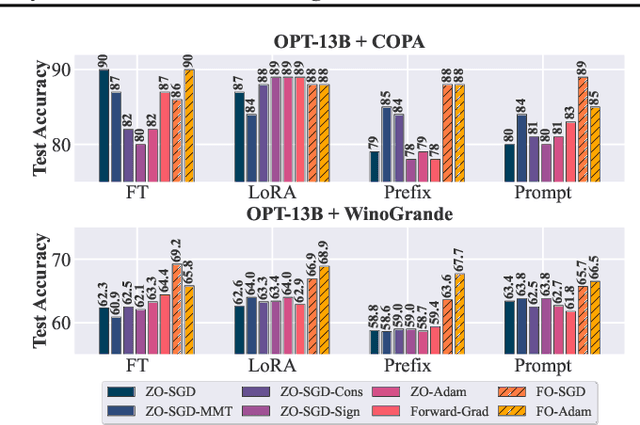


Abstract:In the evolving landscape of natural language processing (NLP), fine-tuning pre-trained Large Language Models (LLMs) with first-order (FO) optimizers like SGD and Adam has become standard. Yet, as LLMs grow {in size}, the substantial memory overhead from back-propagation (BP) for FO gradient computation presents a significant challenge. Addressing this issue is crucial, especially for applications like on-device training where memory efficiency is paramount. This paper proposes a shift towards BP-free, zeroth-order (ZO) optimization as a solution for reducing memory costs during LLM fine-tuning, building on the initial concept introduced by MeZO. Unlike traditional ZO-SGD methods, our work expands the exploration to a wider array of ZO optimization techniques, through a comprehensive, first-of-its-kind benchmarking study across five LLM families (Roberta, OPT, LLaMA, Vicuna, Mistral), three task complexities, and five fine-tuning schemes. Our study unveils previously overlooked optimization principles, highlighting the importance of task alignment, the role of the forward gradient method, and the balance between algorithm complexity and fine-tuning performance. We further introduce novel enhancements to ZO optimization, including block-wise descent, hybrid training, and gradient sparsity. Our study offers a promising direction for achieving further memory-efficient LLM fine-tuning. Codes to reproduce all our experiments are at https://github.com/ZO-Bench/ZO-LLM .
Outline, Then Details: Syntactically Guided Coarse-To-Fine Code Generation
May 08, 2023



Abstract:For a complicated algorithm, its implementation by a human programmer usually starts with outlining a rough control flow followed by iterative enrichments, eventually yielding carefully generated syntactic structures and variables in a hierarchy. However, state-of-the-art large language models generate codes in a single pass, without intermediate warm-ups to reflect the structured thought process of "outline-then-detail". Inspired by the recent success of chain-of-thought prompting, we propose ChainCoder, a program synthesis language model that generates Python code progressively, i.e. from coarse to fine in multiple passes. We first decompose source code into layout frame components and accessory components via abstract syntax tree parsing to construct a hierarchical representation. We then reform our prediction target into a multi-pass objective, each pass generates a subsequence, which is concatenated in the hierarchy. Finally, a tailored transformer architecture is leveraged to jointly encode the natural language descriptions and syntactically aligned I/O data samples. Extensive evaluations show that ChainCoder outperforms state-of-the-arts, demonstrating that our progressive generation eases the reasoning procedure and guides the language model to generate higher-quality solutions. Our codes are available at: https://github.com/VITA-Group/ChainCoder.
You Only Transfer What You Share: Intersection-Induced Graph Transfer Learning for Link Prediction
Feb 27, 2023



Abstract:Link prediction is central to many real-world applications, but its performance may be hampered when the graph of interest is sparse. To alleviate issues caused by sparsity, we investigate a previously overlooked phenomenon: in many cases, a densely connected, complementary graph can be found for the original graph. The denser graph may share nodes with the original graph, which offers a natural bridge for transferring meaningful knowledge. We identify this setting as Graph Intersection-induced Transfer Learning (GITL), which is motivated by practical applications in e-commerce or academic co-authorship predictions. We develop a framework to effectively leverage the structural prior in this setting. We first create an intersection subgraph using the shared nodes between the two graphs, then transfer knowledge from the source-enriched intersection subgraph to the full target graph. In the second step, we consider two approaches: a modified label propagation, and a multi-layer perceptron (MLP) model in a teacher-student regime. Experimental results on proprietary e-commerce datasets and open-source citation graphs show that the proposed workflow outperforms existing transfer learning baselines that do not explicitly utilize the intersection structure.
Symbolic Visual Reinforcement Learning: A Scalable Framework with Object-Level Abstraction and Differentiable Expression Search
Dec 30, 2022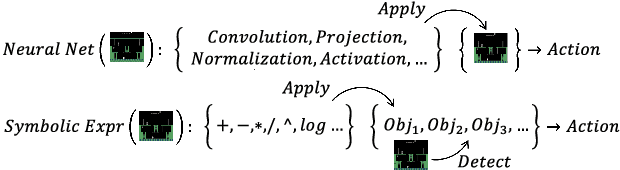
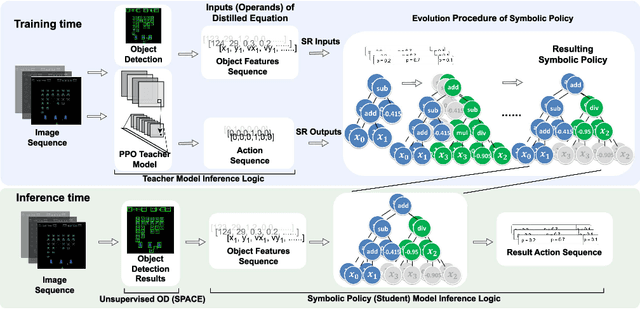
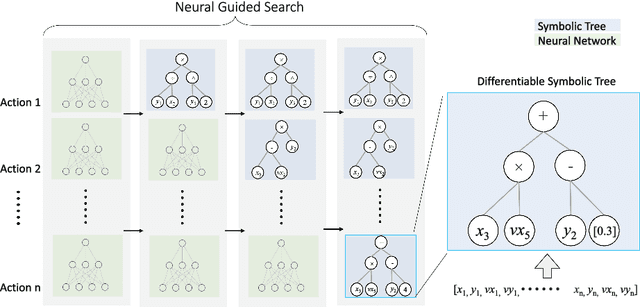
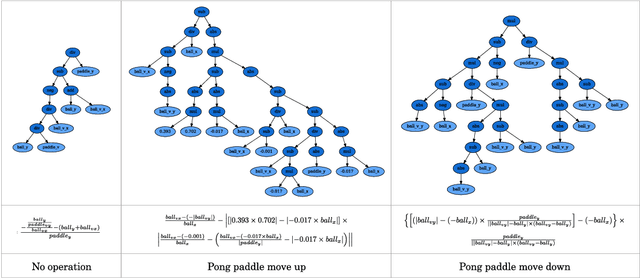
Abstract:Learning efficient and interpretable policies has been a challenging task in reinforcement learning (RL), particularly in the visual RL setting with complex scenes. While neural networks have achieved competitive performance, the resulting policies are often over-parameterized black boxes that are difficult to interpret and deploy efficiently. More recent symbolic RL frameworks have shown that high-level domain-specific programming logic can be designed to handle both policy learning and symbolic planning. However, these approaches rely on coded primitives with little feature learning, and when applied to high-dimensional visual scenes, they can suffer from scalability issues and perform poorly when images have complex object interactions. To address these challenges, we propose \textit{Differentiable Symbolic Expression Search} (DiffSES), a novel symbolic learning approach that discovers discrete symbolic policies using partially differentiable optimization. By using object-level abstractions instead of raw pixel-level inputs, DiffSES is able to leverage the simplicity and scalability advantages of symbolic expressions, while also incorporating the strengths of neural networks for feature learning and optimization. Our experiments demonstrate that DiffSES is able to generate symbolic policies that are simpler and more and scalable than state-of-the-art symbolic RL methods, with a reduced amount of symbolic prior knowledge.
Search Behavior Prediction: A Hypergraph Perspective
Nov 29, 2022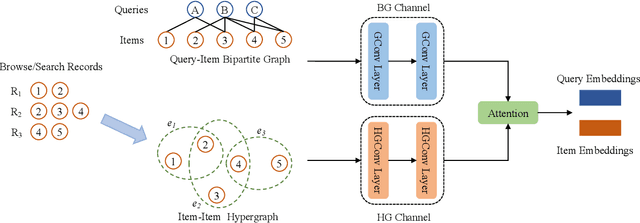
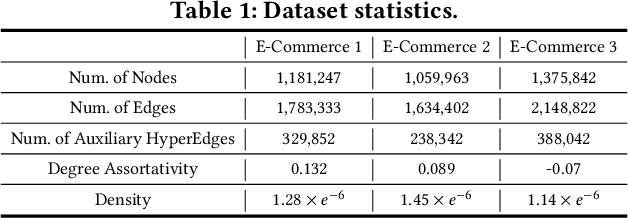
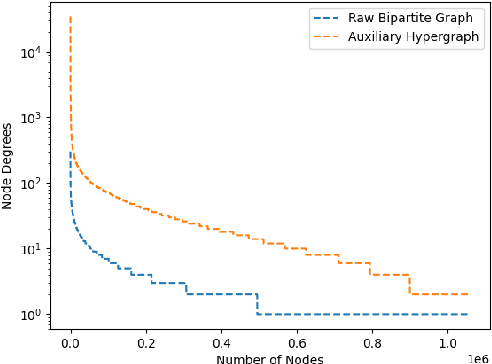
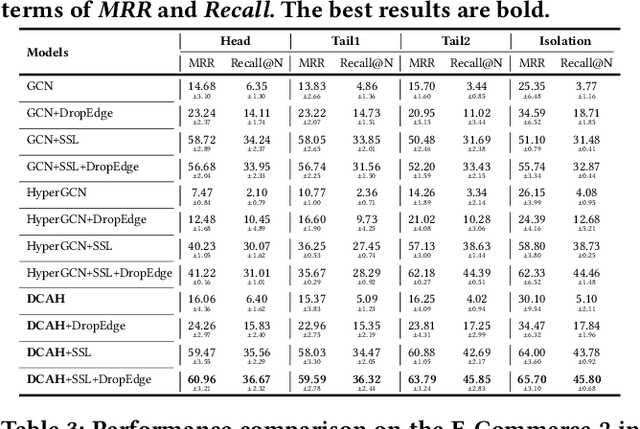
Abstract:Although the bipartite shopping graphs are straightforward to model search behavior, they suffer from two challenges: 1) The majority of items are sporadically searched and hence have noisy/sparse query associations, leading to a \textit{long-tail} distribution. 2) Infrequent queries are more likely to link to popular items, leading to another hurdle known as \textit{disassortative mixing}. To address these two challenges, we go beyond the bipartite graph to take a hypergraph perspective, introducing a new paradigm that leverages \underline{auxiliary} information from anonymized customer engagement sessions to assist the \underline{main task} of query-item link prediction. This auxiliary information is available at web scale in the form of search logs. We treat all items appearing in the same customer session as a single hyperedge. The hypothesis is that items in a customer session are unified by a common shopping interest. With these hyperedges, we augment the original bipartite graph into a new \textit{hypergraph}. We develop a \textit{\textbf{D}ual-\textbf{C}hannel \textbf{A}ttention-Based \textbf{H}ypergraph Neural Network} (\textbf{DCAH}), which synergizes information from two potentially noisy sources (original query-item edges and item-item hyperedges). In this way, items on the tail are better connected due to the extra hyperedges, thereby enhancing their link prediction performance. We further integrate DCAH with self-supervised graph pre-training and/or DropEdge training, both of which effectively alleviate disassortative mixing. Extensive experiments on three proprietary E-Commerce datasets show that DCAH yields significant improvements of up to \textbf{24.6\% in mean reciprocal rank (MRR)} and \textbf{48.3\% in recall} compared to GNN-based baselines. Our source code is available at \url{https://github.com/amazon-science/dual-channel-hypergraph-neural-network}.
Symbolic Distillation for Learned TCP Congestion Control
Oct 24, 2022Abstract:Recent advances in TCP congestion control (CC) have achieved tremendous success with deep reinforcement learning (RL) approaches, which use feedforward neural networks (NN) to learn complex environment conditions and make better decisions. However, such "black-box" policies lack interpretability and reliability, and often, they need to operate outside the traditional TCP datapath due to the use of complex NNs. This paper proposes a novel two-stage solution to achieve the best of both worlds: first to train a deep RL agent, then distill its (over-)parameterized NN policy into white-box, light-weight rules in the form of symbolic expressions that are much easier to understand and to implement in constrained environments. At the core of our proposal is a novel symbolic branching algorithm that enables the rule to be aware of the context in terms of various network conditions, eventually converting the NN policy into a symbolic tree. The distilled symbolic rules preserve and often improve performance over state-of-the-art NN policies while being faster and simpler than a standard neural network. We validate the performance of our distilled symbolic rules on both simulation and emulation environments. Our code is available at https://github.com/VITA-Group/SymbolicPCC.
A Comprehensive Study on Large-Scale Graph Training: Benchmarking and Rethinking
Oct 14, 2022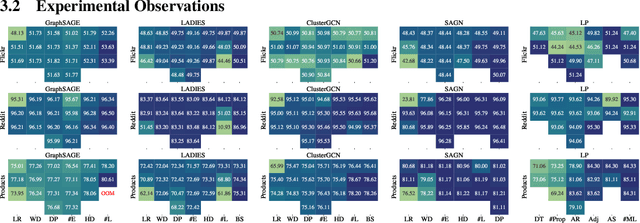
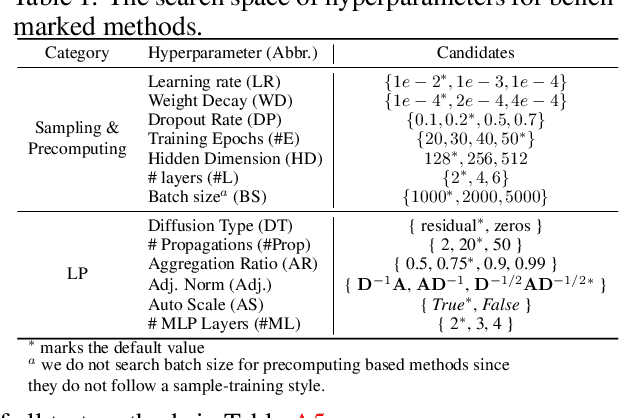

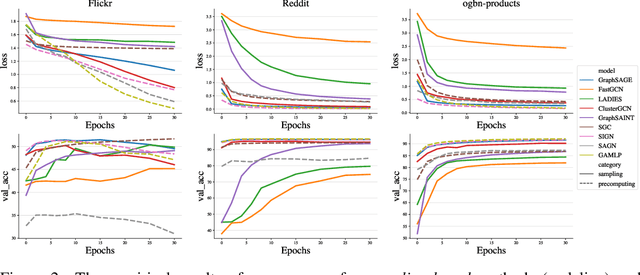
Abstract:Large-scale graph training is a notoriously challenging problem for graph neural networks (GNNs). Due to the nature of evolving graph structures into the training process, vanilla GNNs usually fail to scale up, limited by the GPU memory space. Up to now, though numerous scalable GNN architectures have been proposed, we still lack a comprehensive survey and fair benchmark of this reservoir to find the rationale for designing scalable GNNs. To this end, we first systematically formulate the representative methods of large-scale graph training into several branches and further establish a fair and consistent benchmark for them by a greedy hyperparameter searching. In addition, regarding efficiency, we theoretically evaluate the time and space complexity of various branches and empirically compare them w.r.t GPU memory usage, throughput, and convergence. Furthermore, We analyze the pros and cons for various branches of scalable GNNs and then present a new ensembling training manner, named EnGCN, to address the existing issues. Remarkably, our proposed method has achieved new state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance on large-scale datasets. Our code is available at https://github.com/VITA-Group/Large_Scale_GCN_Benchmarking.
Symbolic Learning to Optimize: Towards Interpretability and Scalability
Apr 02, 2022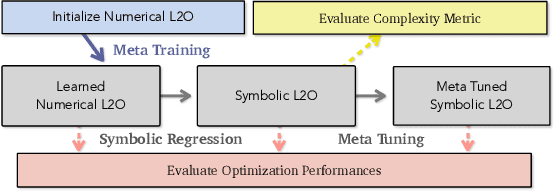

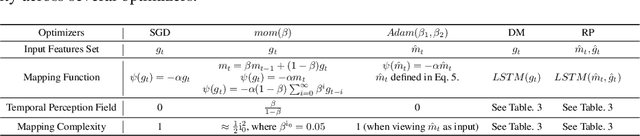
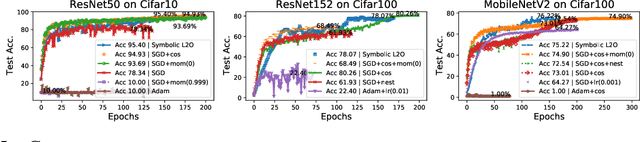
Abstract:Recent studies on Learning to Optimize (L2O) suggest a promising path to automating and accelerating the optimization procedure for complicated tasks. Existing L2O models parameterize optimization rules by neural networks, and learn those numerical rules via meta-training. However, they face two common pitfalls: (1) scalability: the numerical rules represented by neural networks create extra memory overhead for applying L2O models, and limit their applicability to optimizing larger tasks; (2) interpretability: it is unclear what an L2O model has learned in its black-box optimization rule, nor is it straightforward to compare different L2O models in an explainable way. To avoid both pitfalls, this paper proves the concept that we can "kill two birds by one stone", by introducing the powerful tool of symbolic regression to L2O. In this paper, we establish a holistic symbolic representation and analysis framework for L2O, which yields a series of insights for learnable optimizers. Leveraging our findings, we further propose a lightweight L2O model that can be meta-trained on large-scale problems and outperformed human-designed and tuned optimizers. Our work is set to supply a brand-new perspective to L2O research. Codes are available at: https://github.com/VITA-Group/Symbolic-Learning-To-Optimize.
Anti-Oversmoothing in Deep Vision Transformers via the Fourier Domain Analysis: From Theory to Practice
Mar 09, 2022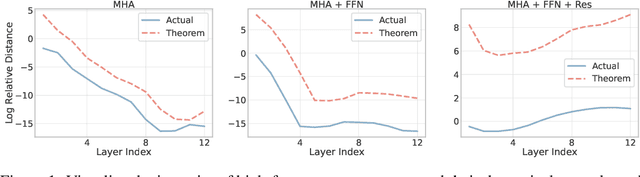
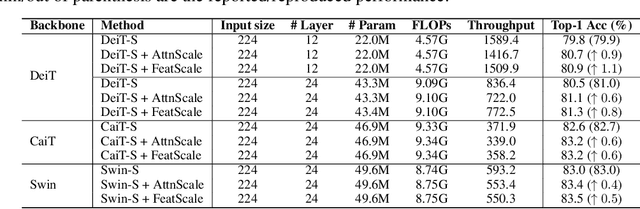
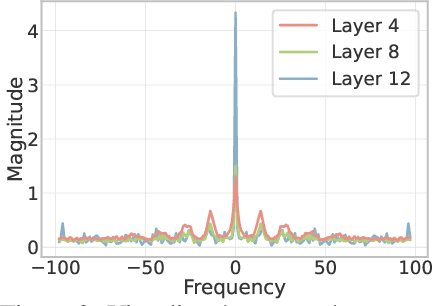
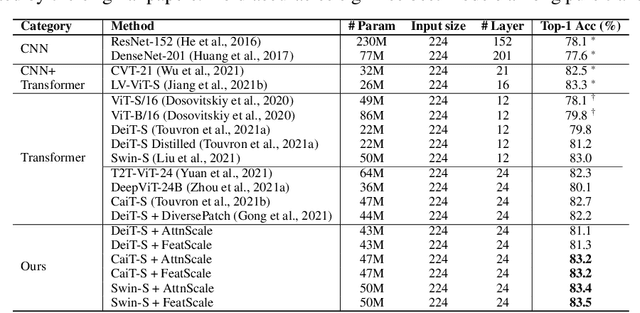
Abstract:Vision Transformer (ViT) has recently demonstrated promise in computer vision problems. However, unlike Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN), it is known that the performance of ViT saturates quickly with depth increasing, due to the observed attention collapse or patch uniformity. Despite a couple of empirical solutions, a rigorous framework studying on this scalability issue remains elusive. In this paper, we first establish a rigorous theory framework to analyze ViT features from the Fourier spectrum domain. We show that the self-attention mechanism inherently amounts to a low-pass filter, which indicates when ViT scales up its depth, excessive low-pass filtering will cause feature maps to only preserve their Direct-Current (DC) component. We then propose two straightforward yet effective techniques to mitigate the undesirable low-pass limitation. The first technique, termed AttnScale, decomposes a self-attention block into low-pass and high-pass components, then rescales and combines these two filters to produce an all-pass self-attention matrix. The second technique, termed FeatScale, re-weights feature maps on separate frequency bands to amplify the high-frequency signals. Both techniques are efficient and hyperparameter-free, while effectively overcoming relevant ViT training artifacts such as attention collapse and patch uniformity. By seamlessly plugging in our techniques to multiple ViT variants, we demonstrate that they consistently help ViTs benefit from deeper architectures, bringing up to 1.1% performance gains "for free" (e.g., with little parameter overhead). We publicly release our codes and pre-trained models at https://github.com/VITA-Group/ViT-Anti-Oversmoothing.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge