Search Behavior Prediction: A Hypergraph Perspective
Paper and Code
Nov 29, 2022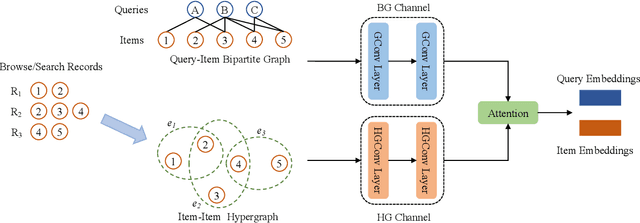
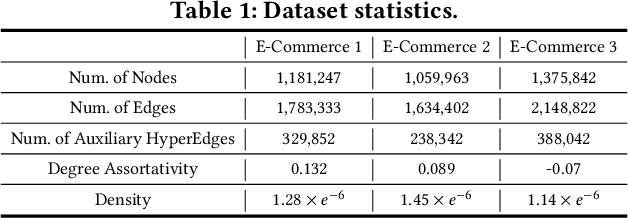
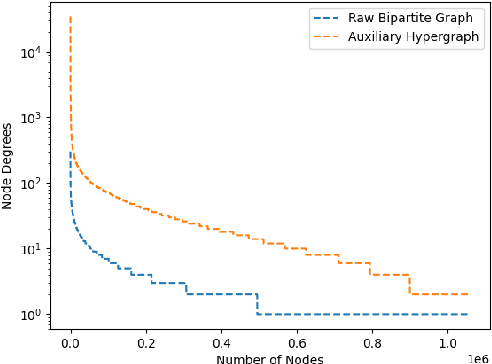
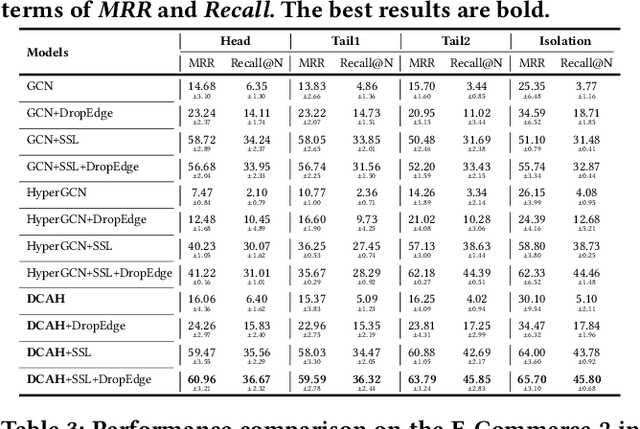
Although the bipartite shopping graphs are straightforward to model search behavior, they suffer from two challenges: 1) The majority of items are sporadically searched and hence have noisy/sparse query associations, leading to a \textit{long-tail} distribution. 2) Infrequent queries are more likely to link to popular items, leading to another hurdle known as \textit{disassortative mixing}. To address these two challenges, we go beyond the bipartite graph to take a hypergraph perspective, introducing a new paradigm that leverages \underline{auxiliary} information from anonymized customer engagement sessions to assist the \underline{main task} of query-item link prediction. This auxiliary information is available at web scale in the form of search logs. We treat all items appearing in the same customer session as a single hyperedge. The hypothesis is that items in a customer session are unified by a common shopping interest. With these hyperedges, we augment the original bipartite graph into a new \textit{hypergraph}. We develop a \textit{\textbf{D}ual-\textbf{C}hannel \textbf{A}ttention-Based \textbf{H}ypergraph Neural Network} (\textbf{DCAH}), which synergizes information from two potentially noisy sources (original query-item edges and item-item hyperedges). In this way, items on the tail are better connected due to the extra hyperedges, thereby enhancing their link prediction performance. We further integrate DCAH with self-supervised graph pre-training and/or DropEdge training, both of which effectively alleviate disassortative mixing. Extensive experiments on three proprietary E-Commerce datasets show that DCAH yields significant improvements of up to \textbf{24.6\% in mean reciprocal rank (MRR)} and \textbf{48.3\% in recall} compared to GNN-based baselines. Our source code is available at \url{https://github.com/amazon-science/dual-channel-hypergraph-neural-network}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge