Tosin Adewumi
From the Rock Floor to the Cloud: A Systematic Survey of State-of-the-Art NLP in Battery Life Cycle
Oct 31, 2025



Abstract:We present a comprehensive systematic survey of the application of natural language processing (NLP) along the entire battery life cycle, instead of one stage or method, and introduce a novel technical language processing (TLP) framework for the EU's proposed digital battery passport (DBP) and other general battery predictions. We follow the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) method and employ three reputable databases or search engines, including Google Scholar, Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Xplore (IEEE Xplore), and Scopus. Consequently, we assessed 274 scientific papers before the critical review of the final 66 relevant papers. We publicly provide artifacts of the review for validation and reproducibility. The findings show that new NLP tasks are emerging in the battery domain, which facilitate materials discovery and other stages of the life cycle. Notwithstanding, challenges remain, such as the lack of standard benchmarks. Our proposed TLP framework, which incorporates agentic AI and optimized prompts, will be apt for tackling some of the challenges.
Findings of MEGA: Maths Explanation with LLMs using the Socratic Method for Active Learning
Jul 16, 2025Abstract:This paper presents an intervention study on the effects of the combined methods of (1) the Socratic method, (2) Chain of Thought (CoT) reasoning, (3) simplified gamification and (4) formative feedback on university students' Maths learning driven by large language models (LLMs). We call our approach Mathematics Explanations through Games by AI LLMs (MEGA). Some students struggle with Maths and as a result avoid Math-related discipline or subjects despite the importance of Maths across many fields, including signal processing. Oftentimes, students' Maths difficulties stem from suboptimal pedagogy. We compared the MEGA method to the traditional step-by-step (CoT) method to ascertain which is better by using a within-group design after randomly assigning questions for the participants, who are university students. Samples (n=60) were randomly drawn from each of the two test sets of the Grade School Math 8K (GSM8K) and Mathematics Aptitude Test of Heuristics (MATH) datasets, based on the error margin of 11%, the confidence level of 90%, and a manageable number of samples for the student evaluators. These samples were used to evaluate two capable LLMs at length (Generative Pretrained Transformer 4o (GPT4o) and Claude 3.5 Sonnet) out of the initial six that were tested for capability. The results showed that students agree in more instances that the MEGA method is experienced as better for learning for both datasets. It is even much better than the CoT (47.5% compared to 26.67%) in the more difficult MATH dataset, indicating that MEGA is better at explaining difficult Maths problems.
Trends and Challenges in Authorship Analysis: A Review of ML, DL, and LLM Approaches
May 21, 2025



Abstract:Authorship analysis plays an important role in diverse domains, including forensic linguistics, academia, cybersecurity, and digital content authentication. This paper presents a systematic literature review on two key sub-tasks of authorship analysis; Author Attribution and Author Verification. The review explores SOTA methodologies, ranging from traditional ML approaches to DL models and LLMs, highlighting their evolution, strengths, and limitations, based on studies conducted from 2015 to 2024. Key contributions include a comprehensive analysis of methods, techniques, their corresponding feature extraction techniques, datasets used, and emerging challenges in authorship analysis. The study highlights critical research gaps, particularly in low-resource language processing, multilingual adaptation, cross-domain generalization, and AI-generated text detection. This review aims to help researchers by giving an overview of the latest trends and challenges in authorship analysis. It also points out possible areas for future study. The goal is to support the development of better, more reliable, and accurate authorship analysis system in diverse textual domain.
Fairness and Bias in Multimodal AI: A Survey
Jun 27, 2024Abstract:The importance of addressing fairness and bias in artificial intelligence (AI) systems cannot be over-emphasized. Mainstream media has been awashed with news of incidents around stereotypes and bias in many of these systems in recent years. In this survey, we fill a gap with regards to the minimal study of fairness and bias in Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) compared to Large Language Models (LLMs), providing 50 examples of datasets and models along with the challenges affecting them; we identify a new category of quantifying bias (preuse), in addition to the two well-known ones in the literature: intrinsic and extrinsic; we critically discuss the various ways researchers are addressing these challenges. Our method involved two slightly different search queries on Google Scholar, which revealed that 33,400 and 538,000 links are the results for the terms "Fairness and bias in Large Multimodal Models" and "Fairness and bias in Large Language Models", respectively. We believe this work contributes to filling this gap and providing insight to researchers and other stakeholders on ways to address the challenge of fairness and bias in multimodal A!.
1000 African Voices: Advancing inclusive multi-speaker multi-accent speech synthesis
Jun 17, 2024Abstract:Recent advances in speech synthesis have enabled many useful applications like audio directions in Google Maps, screen readers, and automated content generation on platforms like TikTok. However, these systems are mostly dominated by voices sourced from data-rich geographies with personas representative of their source data. Although 3000 of the world's languages are domiciled in Africa, African voices and personas are under-represented in these systems. As speech synthesis becomes increasingly democratized, it is desirable to increase the representation of African English accents. We present Afro-TTS, the first pan-African accented English speech synthesis system able to generate speech in 86 African accents, with 1000 personas representing the rich phonological diversity across the continent for downstream application in Education, Public Health, and Automated Content Creation. Speaker interpolation retains naturalness and accentedness, enabling the creation of new voices.
Data Bias According to Bipol: Men are Naturally Right and It is the Role of Women to Follow Their Lead
Apr 07, 2024



Abstract:We introduce new large labeled datasets on bias in 3 languages and show in experiments that bias exists in all 10 datasets of 5 languages evaluated, including benchmark datasets on the English GLUE/SuperGLUE leaderboards. The 3 new languages give a total of almost 6 million labeled samples and we benchmark on these datasets using SotA multilingual pretrained models: mT5 and mBERT. The challenge of social bias, based on prejudice, is ubiquitous, as recent events with AI and large language models (LLMs) have shown. Motivated by this challenge, we set out to estimate bias in multiple datasets. We compare some recent bias metrics and use bipol, which has explainability in the metric. We also confirm the unverified assumption that bias exists in toxic comments by randomly sampling 200 samples from a toxic dataset population using the confidence level of 95% and error margin of 7%. Thirty gold samples were randomly distributed in the 200 samples to secure the quality of the annotation. Our findings confirm that many of the datasets have male bias (prejudice against women), besides other types of bias. We publicly release our new datasets, lexica, models, and codes.
On the Limitations of Large Language Models : False Attribution
Apr 06, 2024



Abstract:In this work, we provide insight into one important limitation of large language models (LLMs), i.e. false attribution, and introduce a new hallucination metric - Simple Hallucination Index (SHI). The task of automatic author attribution for relatively small chunks of text is an important NLP task but can be challenging. We empirically evaluate the power of 3 open SotA LLMs in zero-shot setting (LLaMA-2-13B, Mixtral 8x7B, and Gemma-7B), especially as human annotation can be costly. We collected the top 10 most popular books, according to Project Gutenberg, divided each one into equal chunks of 400 words, and asked each LLM to predict the author. We then randomly sampled 162 chunks for human evaluation from each of the annotated books, based on the error margin of 7% and a confidence level of 95% for the book with the most chunks (Great Expectations by Charles Dickens, having 922 chunks). The average results show that Mixtral 8x7B has the highest prediction accuracy, the lowest SHI, and a Pearson's correlation (r) of 0.737, 0.249, and -0.9996, respectively, followed by LLaMA-2-13B and Gemma-7B. However, Mixtral 8x7B suffers from high hallucinations for 3 books, rising as high as an SHI of 0.87 (in the range 0-1, where 1 is the worst). The strong negative correlation of accuracy and SHI, given by r, demonstrates the fidelity of the new hallucination metric, which is generalizable to other tasks. We publicly release the annotated chunks of data and our codes to aid the reproducibility and evaluation of other models.
Generative AI and Teachers -- For Us or Against Us? A Case Study
Apr 04, 2024



Abstract:We present insightful results of a survey on the adoption of generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) by university teachers in their teaching activities. The transformation of education by GenAI, particularly large language models (LLMs), has been presenting both opportunities and challenges, including cheating by students. We prepared the online survey according to best practices and the questions were created by the authors, who have pedagogy experience. The survey contained 12 questions and a pilot study was first conducted. The survey was then sent to all teachers in multiple departments across different campuses of the university of interest in Sweden: Lule{\aa} University of Technology. The survey was available in both Swedish and English. The results show that 35 teachers (more than half) use GenAI out of 67 respondents. Preparation is the teaching activity with the most frequency that GenAI is used for and ChatGPT is the most commonly used GenAI. 59% say it has impacted their teaching, however, 55% say there should be legislation around the use of GenAI, especially as inaccuracies and cheating are the biggest concerns.
Aurora-M: The First Open Source Multilingual Language Model Red-teamed according to the U.S. Executive Order
Mar 30, 2024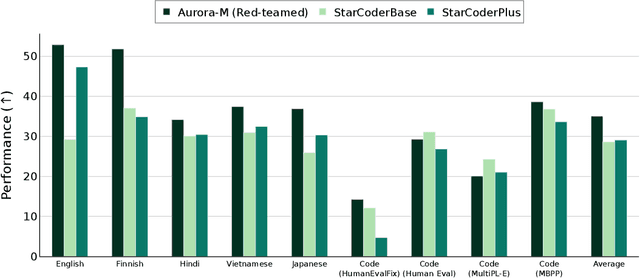
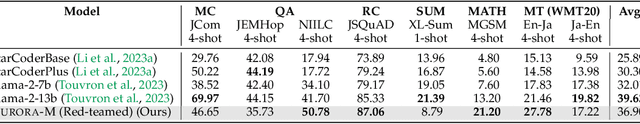
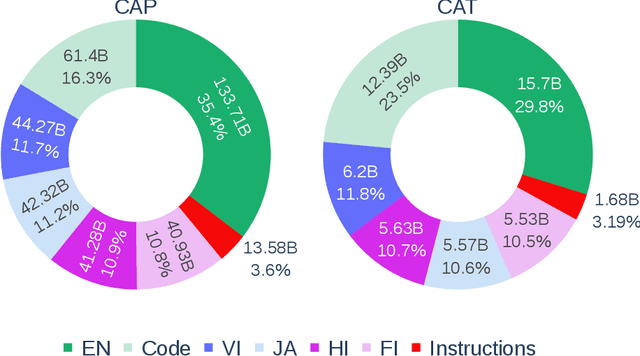
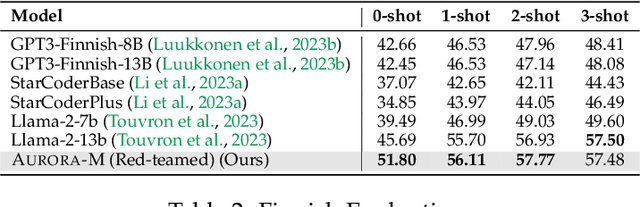
Abstract:Pretrained language models underpin several AI applications, but their high computational cost for training limits accessibility. Initiatives such as BLOOM and StarCoder aim to democratize access to pretrained models for collaborative community development. However, such existing models face challenges: limited multilingual capabilities, continual pretraining causing catastrophic forgetting, whereas pretraining from scratch is computationally expensive, and compliance with AI safety and development laws. This paper presents Aurora-M, a 15B parameter multilingual open-source model trained on English, Finnish, Hindi, Japanese, Vietnamese, and code. Continually pretrained from StarCoderPlus on 435 billion additional tokens, Aurora-M surpasses 2 trillion tokens in total training token count. It is the first open-source multilingual model fine-tuned on human-reviewed safety instructions, thus aligning its development not only with conventional red-teaming considerations, but also with the specific concerns articulated in the Biden-Harris Executive Order on the Safe, Secure, and Trustworthy Development and Use of Artificial Intelligence. Aurora-M is rigorously evaluated across various tasks and languages, demonstrating robustness against catastrophic forgetting and outperforming alternatives in multilingual settings, particularly in safety evaluations. To promote responsible open-source LLM development, Aurora-M and its variants are released at https://huggingface.co/collections/aurora-m/aurora-m-models-65fdfdff62471e09812f5407 .
Instruction Makes a Difference
Feb 01, 2024Abstract:We introduce Instruction Document Visual Question Answering (iDocVQA) dataset and Large Language Document (LLaDoc) model, for training Language-Vision (LV) models for document analysis and predictions on document images, respectively. Usually, deep neural networks for the DocVQA task are trained on datasets lacking instructions. We show that using instruction-following datasets improves performance. We compare performance across document-related datasets using the recent state-of-the-art (SotA) Large Language and Vision Assistant (LLaVA)1.5 as the base model. We also evaluate the performance of the derived models for object hallucination using the Polling-based Object Probing Evaluation (POPE) dataset. The results show that instruction-tuning performance ranges from 11X to 32X of zero-shot performance and from 0.1% to 4.2% over non-instruction (traditional task) finetuning. Despite the gains, these still fall short of human performance (94.36%), implying there's much room for improvement.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge