Eniola Alese
1000 African Voices: Advancing inclusive multi-speaker multi-accent speech synthesis
Jun 17, 2024Abstract:Recent advances in speech synthesis have enabled many useful applications like audio directions in Google Maps, screen readers, and automated content generation on platforms like TikTok. However, these systems are mostly dominated by voices sourced from data-rich geographies with personas representative of their source data. Although 3000 of the world's languages are domiciled in Africa, African voices and personas are under-represented in these systems. As speech synthesis becomes increasingly democratized, it is desirable to increase the representation of African English accents. We present Afro-TTS, the first pan-African accented English speech synthesis system able to generate speech in 86 African accents, with 1000 personas representing the rich phonological diversity across the continent for downstream application in Education, Public Health, and Automated Content Creation. Speaker interpolation retains naturalness and accentedness, enabling the creation of new voices.
A Few-Shot Sequential Approach for Object Counting
Jul 07, 2020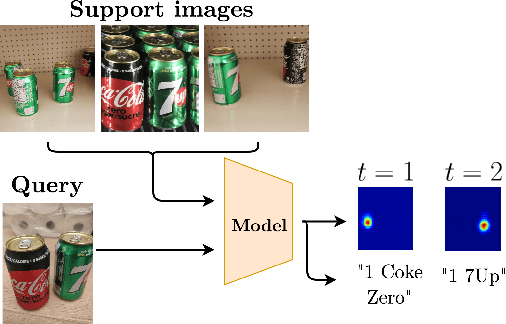
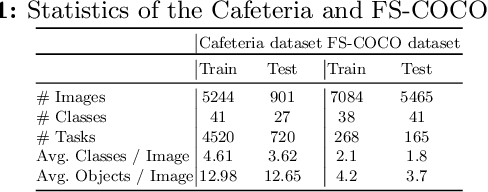
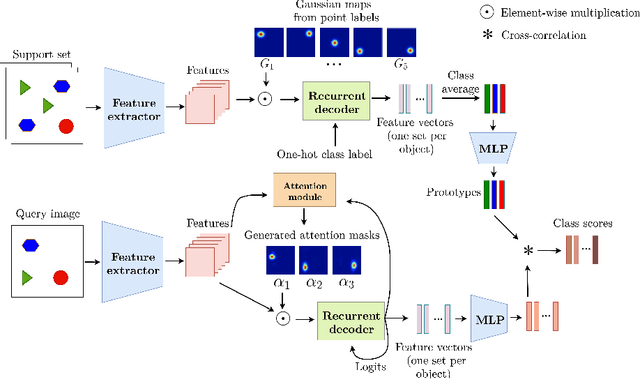
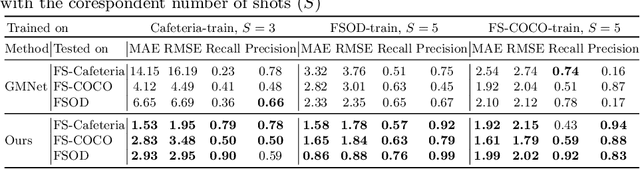
Abstract:In this work, we address the problem of few-shot multi-class object counting with point-level annotations. The proposed technique leverages a class agnostic attention mechanism that sequentially attends to objects in the image and extracts their relevant features. This process is employed on an adapted prototypical-based few-shot approach that uses the extracted features to classify each one either as one of the classes present in the support set images or as background. The proposed technique is trained on point-level annotations and uses a novel loss function that disentangles class-dependent and class-agnostic aspects of the model to help with the task of few-shot object counting. We present our results on a variety of object-counting/detection datasets, including FSOD and MS COCO. In addition, we introduce a new dataset that is specifically designed for weakly supervised multi-class object counting/detection and contains considerably different classes and distribution of number of classes/instances per image compared to the existing datasets. We demonstrate the robustness of our approach by testing our system on a totally different distribution of classes from what it has been trained on.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge