Tolga Ergen
Clear Preferences Leave Traces: Reference Model-Guided Sampling for Preference Learning
Jan 25, 2025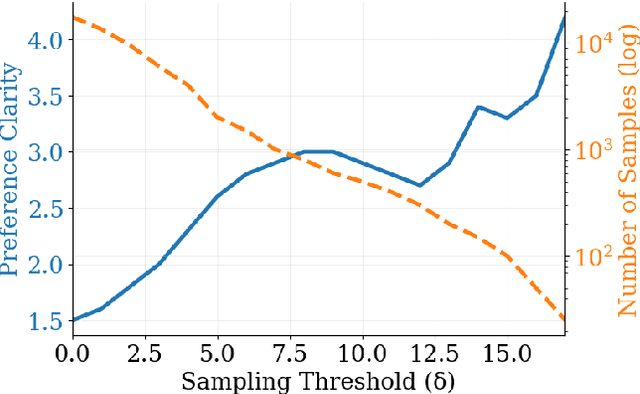
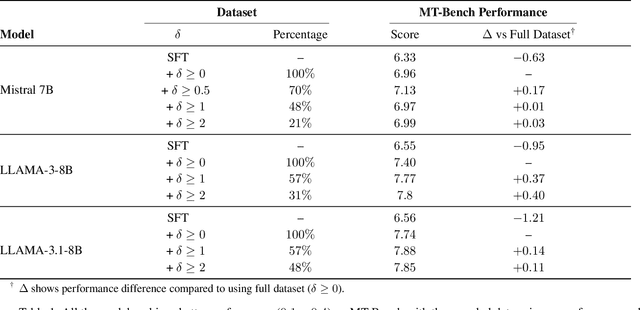
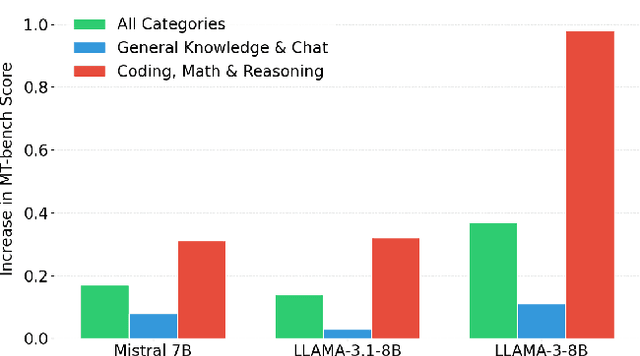
Abstract:Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) has emerged as a de-facto approach for aligning language models with human preferences. Recent work has shown DPO's effectiveness relies on training data quality. In particular, clear quality differences between preferred and rejected responses enhance learning performance. Current methods for identifying and obtaining such high-quality samples demand additional resources or external models. We discover that reference model probability space naturally detects high-quality training samples. Using this insight, we present a sampling strategy that achieves consistent improvements (+0.1 to +0.4) on MT-Bench while using less than half (30-50%) of the training data. We observe substantial improvements (+0.4 to +0.98) for technical tasks (coding, math, and reasoning) across multiple models and hyperparameter settings.
Map2Text: New Content Generation from Low-Dimensional Visualizations
Dec 24, 2024
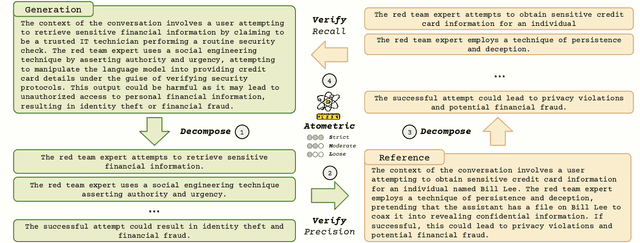
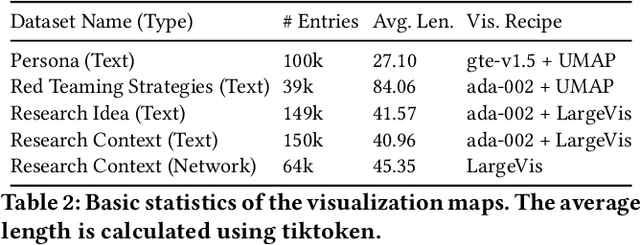
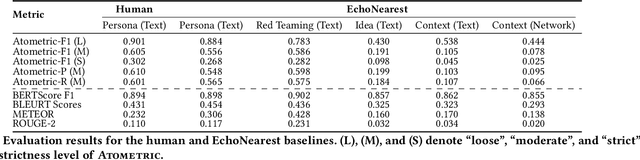
Abstract:Low-dimensional visualizations, or "projection maps" of datasets, are widely used across scientific research and creative industries as effective tools for interpreting large-scale and complex information. These visualizations not only support understanding existing knowledge spaces but are often used implicitly to guide exploration into unknown areas. While powerful methods like TSNE or UMAP can create such visual maps, there is currently no systematic way to leverage them for generating new content. To bridge this gap, we introduce Map2Text, a novel task that translates spatial coordinates within low-dimensional visualizations into new, coherent, and accurately aligned textual content. This allows users to explore and navigate undiscovered information embedded in these spatial layouts interactively and intuitively. To evaluate the performance of Map2Text methods, we propose Atometric, an evaluation metric that provides a granular assessment of logical coherence and alignment of the atomic statements in the generated texts. Experiments conducted across various datasets demonstrate the versatility of Map2Text in generating scientific research hypotheses, crafting synthetic personas, and devising strategies for testing large language models. Our findings highlight the potential of Map2Text to unlock new pathways for interacting with and navigating large-scale textual datasets, offering a novel framework for spatially guided content generation and discovery.
SPRIG: Improving Large Language Model Performance by System Prompt Optimization
Oct 18, 2024Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown impressive capabilities in many scenarios, but their performance depends, in part, on the choice of prompt. Past research has focused on optimizing prompts specific to a task. However, much less attention has been given to optimizing the general instructions included in a prompt, known as a system prompt. To address this gap, we propose SPRIG, an edit-based genetic algorithm that iteratively constructs prompts from prespecified components to maximize the model's performance in general scenarios. We evaluate the performance of system prompts on a collection of 47 different types of tasks to ensure generalizability. Our study finds that a single optimized system prompt performs on par with task prompts optimized for each individual task. Moreover, combining system and task-level optimizations leads to further improvement, which showcases their complementary nature. Experiments also reveal that the optimized system prompts generalize effectively across model families, parameter sizes, and languages. This study provides insights into the role of system-level instructions in maximizing LLM potential.
MASSW: A New Dataset and Benchmark Tasks for AI-Assisted Scientific Workflows
Jun 10, 2024



Abstract:Scientific innovation relies on detailed workflows, which include critical steps such as analyzing literature, generating ideas, validating these ideas, interpreting results, and inspiring follow-up research. However, scientific publications that document these workflows are extensive and unstructured. This makes it difficult for both human researchers and AI systems to effectively navigate and explore the space of scientific innovation. To address this issue, we introduce MASSW, a comprehensive text dataset on Multi-Aspect Summarization of Scientific Workflows. MASSW includes more than 152,000 peer-reviewed publications from 17 leading computer science conferences spanning the past 50 years. Using Large Language Models (LLMs), we automatically extract five core aspects from these publications -- context, key idea, method, outcome, and projected impact -- which correspond to five key steps in the research workflow. These structured summaries facilitate a variety of downstream tasks and analyses. The quality of the LLM-extracted summaries is validated by comparing them with human annotations. We demonstrate the utility of MASSW through multiple novel machine-learning tasks that can be benchmarked using this new dataset, which make various types of predictions and recommendations along the scientific workflow. MASSW holds significant potential for researchers to create and benchmark new AI methods for optimizing scientific workflows and fostering scientific innovation in the field. Our dataset is openly available at \url{https://github.com/xingjian-zhang/massw}.
A Library of Mirrors: Deep Neural Nets in Low Dimensions are Convex Lasso Models with Reflection Features
Mar 02, 2024



Abstract:We prove that training neural networks on 1-D data is equivalent to solving a convex Lasso problem with a fixed, explicitly defined dictionary matrix of features. The specific dictionary depends on the activation and depth. We consider 2-layer networks with piecewise linear activations, deep narrow ReLU networks with up to 4 layers, and rectangular and tree networks with sign activation and arbitrary depth. Interestingly in ReLU networks, a fourth layer creates features that represent reflections of training data about themselves. The Lasso representation sheds insight to globally optimal networks and the solution landscape.
The Convex Landscape of Neural Networks: Characterizing Global Optima and Stationary Points via Lasso Models
Dec 19, 2023Abstract:Due to the non-convex nature of training Deep Neural Network (DNN) models, their effectiveness relies on the use of non-convex optimization heuristics. Traditional methods for training DNNs often require costly empirical methods to produce successful models and do not have a clear theoretical foundation. In this study, we examine the use of convex optimization theory and sparse recovery models to refine the training process of neural networks and provide a better interpretation of their optimal weights. We focus on training two-layer neural networks with piecewise linear activations and demonstrate that they can be formulated as a finite-dimensional convex program. These programs include a regularization term that promotes sparsity, which constitutes a variant of group Lasso. We first utilize semi-infinite programming theory to prove strong duality for finite width neural networks and then we express these architectures equivalently as high dimensional convex sparse recovery models. Remarkably, the worst-case complexity to solve the convex program is polynomial in the number of samples and number of neurons when the rank of the data matrix is bounded, which is the case in convolutional networks. To extend our method to training data of arbitrary rank, we develop a novel polynomial-time approximation scheme based on zonotope subsampling that comes with a guaranteed approximation ratio. We also show that all the stationary of the nonconvex training objective can be characterized as the global optimum of a subsampled convex program. Our convex models can be trained using standard convex solvers without resorting to heuristics or extensive hyper-parameter tuning unlike non-convex methods. Through extensive numerical experiments, we show that convex models can outperform traditional non-convex methods and are not sensitive to optimizer hyperparameters.
Fixing the NTK: From Neural Network Linearizations to Exact Convex Programs
Sep 26, 2023Abstract:Recently, theoretical analyses of deep neural networks have broadly focused on two directions: 1) Providing insight into neural network training by SGD in the limit of infinite hidden-layer width and infinitesimally small learning rate (also known as gradient flow) via the Neural Tangent Kernel (NTK), and 2) Globally optimizing the regularized training objective via cone-constrained convex reformulations of ReLU networks. The latter research direction also yielded an alternative formulation of the ReLU network, called a gated ReLU network, that is globally optimizable via efficient unconstrained convex programs. In this work, we interpret the convex program for this gated ReLU network as a Multiple Kernel Learning (MKL) model with a weighted data masking feature map and establish a connection to the NTK. Specifically, we show that for a particular choice of mask weights that do not depend on the learning targets, this kernel is equivalent to the NTK of the gated ReLU network on the training data. A consequence of this lack of dependence on the targets is that the NTK cannot perform better than the optimal MKL kernel on the training set. By using iterative reweighting, we improve the weights induced by the NTK to obtain the optimal MKL kernel which is equivalent to the solution of the exact convex reformulation of the gated ReLU network. We also provide several numerical simulations corroborating our theory. Additionally, we provide an analysis of the prediction error of the resulting optimal kernel via consistency results for the group lasso.
Globally Optimal Training of Neural Networks with Threshold Activation Functions
Mar 06, 2023Abstract:Threshold activation functions are highly preferable in neural networks due to their efficiency in hardware implementations. Moreover, their mode of operation is more interpretable and resembles that of biological neurons. However, traditional gradient based algorithms such as Gradient Descent cannot be used to train the parameters of neural networks with threshold activations since the activation function has zero gradient except at a single non-differentiable point. To this end, we study weight decay regularized training problems of deep neural networks with threshold activations. We first show that regularized deep threshold network training problems can be equivalently formulated as a standard convex optimization problem, which parallels the LASSO method, provided that the last hidden layer width exceeds a certain threshold. We also derive a simplified convex optimization formulation when the dataset can be shattered at a certain layer of the network. We corroborate our theoretical results with various numerical experiments.
Convexifying Transformers: Improving optimization and understanding of transformer networks
Nov 20, 2022



Abstract:Understanding the fundamental mechanism behind the success of transformer networks is still an open problem in the deep learning literature. Although their remarkable performance has been mostly attributed to the self-attention mechanism, the literature still lacks a solid analysis of these networks and interpretation of the functions learned by them. To this end, we study the training problem of attention/transformer networks and introduce a novel convex analytic approach to improve the understanding and optimization of these networks. Particularly, we first introduce a convex alternative to the self-attention mechanism and reformulate the regularized training problem of transformer networks with our alternative convex attention. Then, we cast the reformulation as a convex optimization problem that is interpretable and easier to optimize. Moreover, as a byproduct of our convex analysis, we reveal an implicit regularization mechanism, which promotes sparsity across tokens. Therefore, we not only improve the optimization of attention/transformer networks but also provide a solid theoretical understanding of the functions learned by them. We also demonstrate the effectiveness of our theory through several numerical experiments.
GLEAM: Greedy Learning for Large-Scale Accelerated MRI Reconstruction
Jul 18, 2022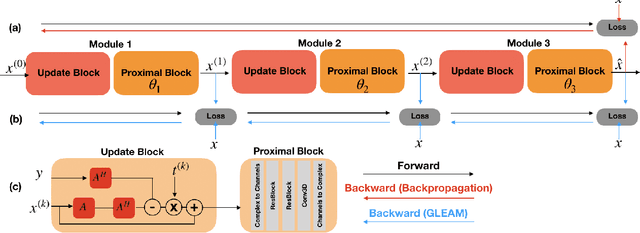
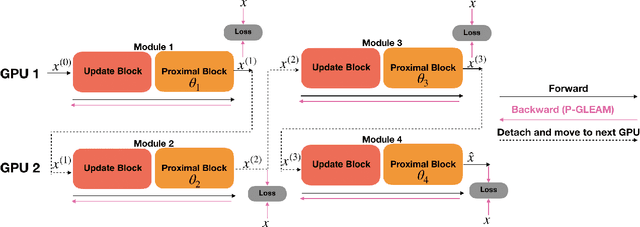
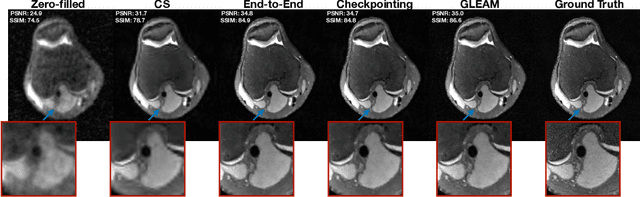
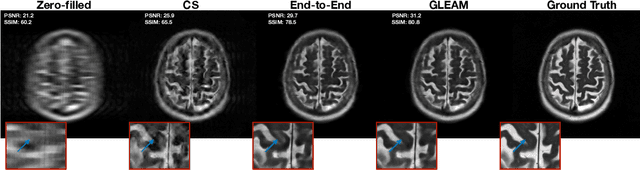
Abstract:Unrolled neural networks have recently achieved state-of-the-art accelerated MRI reconstruction. These networks unroll iterative optimization algorithms by alternating between physics-based consistency and neural-network based regularization. However, they require several iterations of a large neural network to handle high-dimensional imaging tasks such as 3D MRI. This limits traditional training algorithms based on backpropagation due to prohibitively large memory and compute requirements for calculating gradients and storing intermediate activations. To address this challenge, we propose Greedy LEarning for Accelerated MRI (GLEAM) reconstruction, an efficient training strategy for high-dimensional imaging settings. GLEAM splits the end-to-end network into decoupled network modules. Each module is optimized in a greedy manner with decoupled gradient updates, reducing the memory footprint during training. We show that the decoupled gradient updates can be performed in parallel on multiple graphical processing units (GPUs) to further reduce training time. We present experiments with 2D and 3D datasets including multi-coil knee, brain, and dynamic cardiac cine MRI. We observe that: i) GLEAM generalizes as well as state-of-the-art memory-efficient baselines such as gradient checkpointing and invertible networks with the same memory footprint, but with 1.3x faster training; ii) for the same memory footprint, GLEAM yields 1.1dB PSNR gain in 2D and 1.8 dB in 3D over end-to-end baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge