Tanvi Dinkar
Can NLP Tackle Hate Speech in the Real World? Stakeholder-Informed Feedback and Survey on Counterspeech
Aug 06, 2025Abstract:Counterspeech, i.e. the practice of responding to online hate speech, has gained traction in NLP as a promising intervention. While early work emphasised collaboration with non-governmental organisation stakeholders, recent research trends have shifted toward automated pipelines that reuse a small set of legacy datasets, often without input from affected communities. This paper presents a systematic review of 74 NLP studies on counterspeech, analysing the extent to which stakeholder participation influences dataset creation, model development, and evaluation. To complement this analysis, we conducted a participatory case study with five NGOs specialising in online Gender-Based Violence (oGBV), identifying stakeholder-informed practices for counterspeech generation. Our findings reveal a growing disconnect between current NLP research and the needs of communities most impacted by toxic online content. We conclude with concrete recommendations for re-centring stakeholder expertise in counterspeech research.
Re-examining Sexism and Misogyny Classification with Annotator Attitudes
Oct 04, 2024



Abstract:Gender-Based Violence (GBV) is an increasing problem online, but existing datasets fail to capture the plurality of possible annotator perspectives or ensure the representation of affected groups. We revisit two important stages in the moderation pipeline for GBV: (1) manual data labelling; and (2) automated classification. For (1), we examine two datasets to investigate the relationship between annotator identities and attitudes and the responses they give to two GBV labelling tasks. To this end, we collect demographic and attitudinal information from crowd-sourced annotators using three validated surveys from Social Psychology. We find that higher Right Wing Authoritarianism scores are associated with a higher propensity to label text as sexist, while for Social Dominance Orientation and Neosexist Attitudes, higher scores are associated with a negative tendency to do so. For (2), we conduct classification experiments using Large Language Models and five prompting strategies, including infusing prompts with annotator information. We find: (i) annotator attitudes affect the ability of classifiers to predict their labels; (ii) including attitudinal information can boost performance when we use well-structured brief annotator descriptions; and (iii) models struggle to reflect the increased complexity and imbalanced classes of the new label sets.
NLP Verification: Towards a General Methodology for Certifying Robustness
Mar 15, 2024Abstract:Deep neural networks have exhibited substantial success in the field of Natural Language Processing (NLP) and ensuring their safety and reliability is crucial: there are safety critical contexts where such models must be robust to variability or attack, and give guarantees over their output. Unlike Computer Vision, NLP lacks a unified verification methodology and, despite recent advancements in literature, they are often light on the pragmatical issues of NLP verification. In this paper, we make an attempt to distil and evaluate general components of an NLP verification pipeline, that emerges from the progress in the field to date. Our contributions are two-fold. Firstly, we give a general characterisation of verifiable subspaces that result from embedding sentences into continuous spaces. We identify, and give an effective method to deal with, the technical challenge of semantic generalisability of verified subspaces; and propose it as a standard metric in the NLP verification pipelines (alongside with the standard metrics of model accuracy and model verifiability). Secondly, we propose a general methodology to analyse the effect of the embedding gap, a problem that refers to the discrepancy between verification of geometric subpspaces on the one hand, and semantic meaning of sentences which the geometric subspaces are supposed to represent, on the other hand. In extreme cases, poor choices in embedding of sentences may invalidate verification results. We propose a number of practical NLP methods that can help to identify the effects of the embedding gap; and in particular we propose the metric of falsifiability of semantic subpspaces as another fundamental metric to be reported as part of the NLP verification pipeline. We believe that together these general principles pave the way towards a more consolidated and effective development of this new domain.
FurNav: Development and Preliminary Study of a Robot Direction Giver
Sep 25, 2023
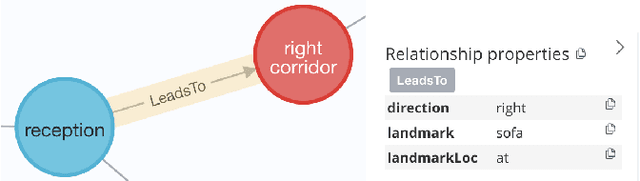
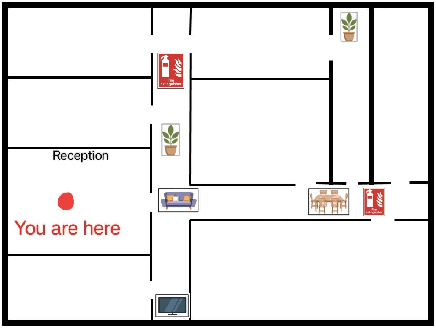
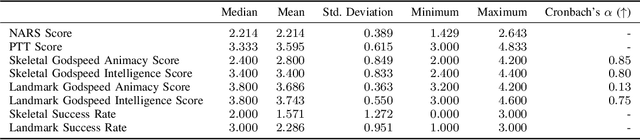
Abstract:When giving directions to a lost-looking tourist, would you first reference the street-names, cardinal directions, landmarks, or simply tell them to walk five hundred metres in one direction then turn left? Depending on the circumstances, one could reasonably make use of any of these direction giving styles. However, research on direction giving with a robot does not often look at how these different direction styles impact perceptions of the robots intelligence, nor does it take into account how users prior dispositions may impact ratings. In this work, we look at generating natural language for two navigation styles using a created system for a Furhat robot, before measuring perceived intelligence and animacy alongside users prior dispositions to robots in a small preliminary study (N=7). Our results confirm findings by previous work that prior negative attitudes towards robots correlates negatively with propensity to trust robots, and also suggests avenues for future research. For example, more data is needed to explore the link between perceived intelligence and direction style. We end by discussing our plan to run a larger scale experiment, and how to improve our existing study design.
FurChat: An Embodied Conversational Agent using LLMs, Combining Open and Closed-Domain Dialogue with Facial Expressions
Aug 30, 2023Abstract:We demonstrate an embodied conversational agent that can function as a receptionist and generate a mixture of open and closed-domain dialogue along with facial expressions, by using a large language model (LLM) to develop an engaging conversation. We deployed the system onto a Furhat robot, which is highly expressive and capable of using both verbal and nonverbal cues during interaction. The system was designed specifically for the National Robotarium to interact with visitors through natural conversations, providing them with information about the facilities, research, news, upcoming events, etc. The system utilises the state-of-the-art GPT-3.5 model to generate such information along with domain-general conversations and facial expressions based on prompt engineering.
Mirages: On Anthropomorphism in Dialogue Systems
May 16, 2023Abstract:Automated dialogue or conversational systems are anthropomorphised by developers and personified by users. While a degree of anthropomorphism is inevitable, conscious and unconscious design choices can guide users to personify them to varying degrees. Encouraging users to relate to automated systems as if they were human can lead to transparency and trust issues, and high risk scenarios caused by over-reliance on their outputs. As a result, natural language processing researchers have begun to investigate factors that induce personification and develop resources to mitigate such effects. However, these efforts are fragmented, and many aspects of anthropomorphism have yet to be considered. In this paper, we discuss the linguistic factors that contribute to the anthropomorphism of dialogue systems and the harms that can arise, arguing that it can reinforce stereotypes of gender roles and notions of acceptable language. We recommend that future efforts towards developing dialogue systems take particular care in their design, development, release, and description; and attend to the many linguistic cues that can elicit personification by users.
iLab at SemEval-2023 Task 11 Le-Wi-Di: Modelling Disagreement or Modelling Perspectives?
May 10, 2023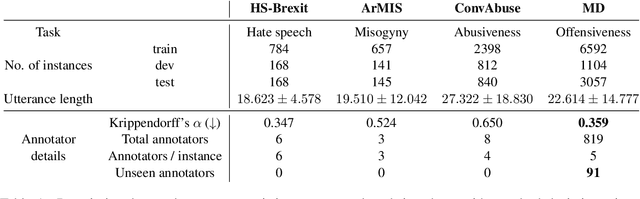
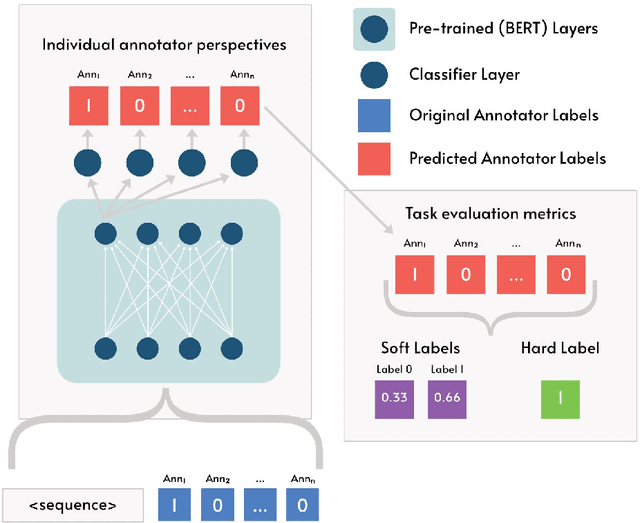
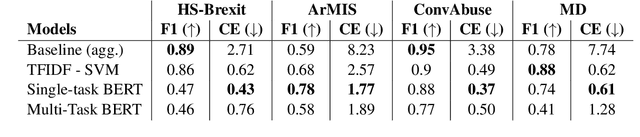
Abstract:There are two competing approaches for modelling annotator disagreement: distributional soft-labelling approaches (which aim to capture the level of disagreement) or modelling perspectives of individual annotators or groups thereof. We adapt a multi-task architecture -- which has previously shown success in modelling perspectives -- to evaluate its performance on the SEMEVAL Task 11. We do so by combining both approaches, i.e. predicting individual annotator perspectives as an interim step towards predicting annotator disagreement. Despite its previous success, we found that a multi-task approach performed poorly on datasets which contained distinct annotator opinions, suggesting that this approach may not always be suitable when modelling perspectives. Furthermore, our results explain that while strongly perspectivist approaches might not achieve state-of-the-art performance according to evaluation metrics used by distributional approaches, our approach allows for a more nuanced understanding of individual perspectives present in the data. We argue that perspectivist approaches are preferable because they enable decision makers to amplify minority views, and that it is important to re-evaluate metrics to reflect this goal.
ANTONIO: Towards a Systematic Method of Generating NLP Benchmarks for Verification
May 06, 2023



Abstract:Verification of machine learning models used in Natural Language Processing (NLP) is known to be a hard problem. In particular, many known neural network verification methods that work for computer vision and other numeric datasets do not work for NLP. Here, we study technical reasons that underlie this problem. Based on this analysis, we propose practical methods and heuristics for preparing NLP datasets and models in a way that renders them amenable to known verification methods based on abstract interpretation. We implement these methods as a Python library called ANTONIO that links to the neural network verifiers ERAN and Marabou. We perform evaluation of the tool using an NLP dataset R-U-A-Robot suggested as a benchmark for verifying legally critical NLP applications. We hope that, thanks to its general applicability, this work will open novel possibilities for including NLP verification problems into neural network verification competitions, and will popularise NLP problems within this community.
Missing Information, Unresponsive Authors, Experimental Flaws: The Impossibility of Assessing the Reproducibility of Previous Human Evaluations in NLP
May 02, 2023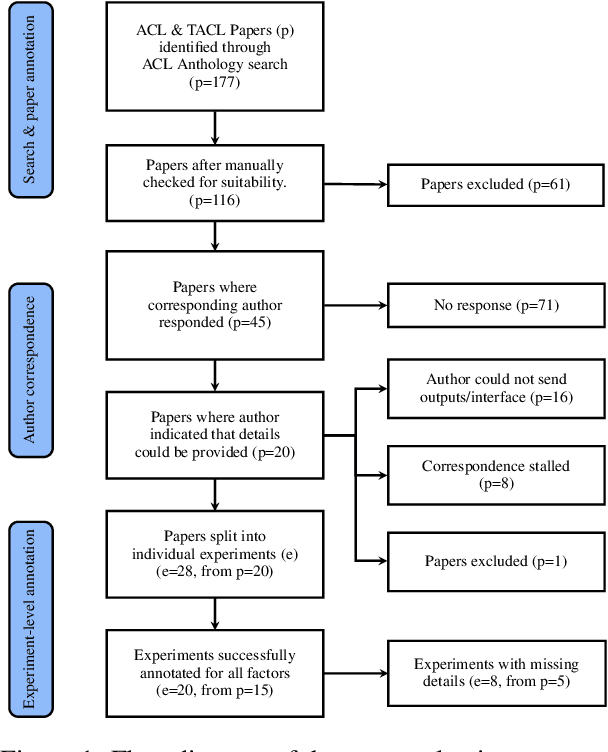
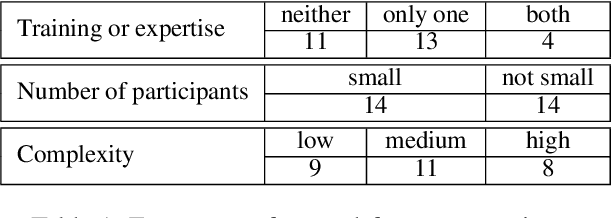
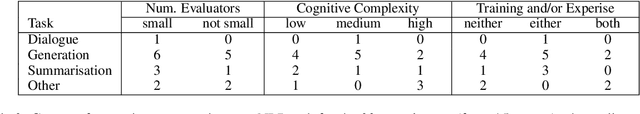

Abstract:We report our efforts in identifying a set of previous human evaluations in NLP that would be suitable for a coordinated study examining what makes human evaluations in NLP more/less reproducible. We present our results and findings, which include that just 13\% of papers had (i) sufficiently low barriers to reproduction, and (ii) enough obtainable information, to be considered for reproduction, and that all but one of the experiments we selected for reproduction was discovered to have flaws that made the meaningfulness of conducting a reproduction questionable. As a result, we had to change our coordinated study design from a reproduce approach to a standardise-then-reproduce-twice approach. Our overall (negative) finding that the great majority of human evaluations in NLP is not repeatable and/or not reproducible and/or too flawed to justify reproduction, paints a dire picture, but presents an opportunity for a rethink about how to design and report human evaluations in NLP.
Fillers in Spoken Language Understanding: Computational and Psycholinguistic Perspectives
Jan 25, 2023Abstract:Disfluencies (i.e. interruptions in the regular flow of speech), are ubiquitous to spoken discourse. Fillers ("uh", "um") are disfluencies that occur the most frequently compared to other kinds of disfluencies. Yet, to the best of our knowledge, there isn't a resource that brings together the research perspectives influencing Spoken Language Understanding (SLU) on these speech events. This aim of this article is to synthesise a breadth of perspectives in a holistic way; i.e. from considering underlying (psycho)linguistic theory, to their annotation and consideration in Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) and SLU systems, to lastly, their study from a generation standpoint. This article aims to present the perspectives in an approachable way to the SLU and Conversational AI community, and discuss moving forward, what we believe are the trends and challenges in each area.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge