Amanda Cercas Curry
Think Like a Person Before Responding: A Multi-Faceted Evaluation of Persona-Guided LLMs for Countering Hate
Jun 04, 2025Abstract:Automated counter-narratives (CN) offer a promising strategy for mitigating online hate speech, yet concerns about their affective tone, accessibility, and ethical risks remain. We propose a framework for evaluating Large Language Model (LLM)-generated CNs across four dimensions: persona framing, verbosity and readability, affective tone, and ethical robustness. Using GPT-4o-Mini, Cohere's CommandR-7B, and Meta's LLaMA 3.1-70B, we assess three prompting strategies on the MT-Conan and HatEval datasets. Our findings reveal that LLM-generated CNs are often verbose and adapted for people with college-level literacy, limiting their accessibility. While emotionally guided prompts yield more empathetic and readable responses, there remain concerns surrounding safety and effectiveness.
The AI Gap: How Socioeconomic Status Affects Language Technology Interactions
May 17, 2025Abstract:Socioeconomic status (SES) fundamentally influences how people interact with each other and more recently, with digital technologies like Large Language Models (LLMs). While previous research has highlighted the interaction between SES and language technology, it was limited by reliance on proxy metrics and synthetic data. We survey 1,000 individuals from diverse socioeconomic backgrounds about their use of language technologies and generative AI, and collect 6,482 prompts from their previous interactions with LLMs. We find systematic differences across SES groups in language technology usage (i.e., frequency, performed tasks), interaction styles, and topics. Higher SES entails a higher level of abstraction, convey requests more concisely, and topics like 'inclusivity' and 'travel'. Lower SES correlates with higher anthropomorphization of LLMs (using ''hello'' and ''thank you'') and more concrete language. Our findings suggest that while generative language technologies are becoming more accessible to everyone, socioeconomic linguistic differences still stratify their use to exacerbate the digital divide. These differences underscore the importance of considering SES in developing language technologies to accommodate varying linguistic needs rooted in socioeconomic factors and limit the AI Gap across SES groups.
Divine LLaMAs: Bias, Stereotypes, Stigmatization, and Emotion Representation of Religion in Large Language Models
Jul 09, 2024



Abstract:Emotions play important epistemological and cognitive roles in our lives, revealing our values and guiding our actions. Previous work has shown that LLMs display biases in emotion attribution along gender lines. However, unlike gender, which says little about our values, religion, as a socio-cultural system, prescribes a set of beliefs and values for its followers. Religions, therefore, cultivate certain emotions. Moreover, these rules are explicitly laid out and interpreted by religious leaders. Using emotion attribution, we explore how different religions are represented in LLMs. We find that: Major religions in the US and European countries are represented with more nuance, displaying a more shaded model of their beliefs. Eastern religions like Hinduism and Buddhism are strongly stereotyped. Judaism and Islam are stigmatized -- the models' refusal skyrocket. We ascribe these to cultural bias in LLMs and the scarcity of NLP literature on religion. In the rare instances where religion is discussed, it is often in the context of toxic language, perpetuating the perception of these religions as inherently toxic. This finding underscores the urgent need to address and rectify these biases. Our research underscores the crucial role emotions play in our lives and how our values influence them.
Language Model Council: Benchmarking Foundation Models on Highly Subjective Tasks by Consensus
Jun 12, 2024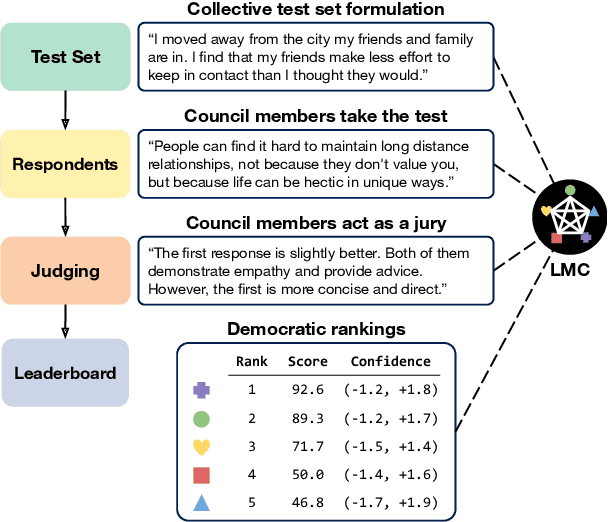
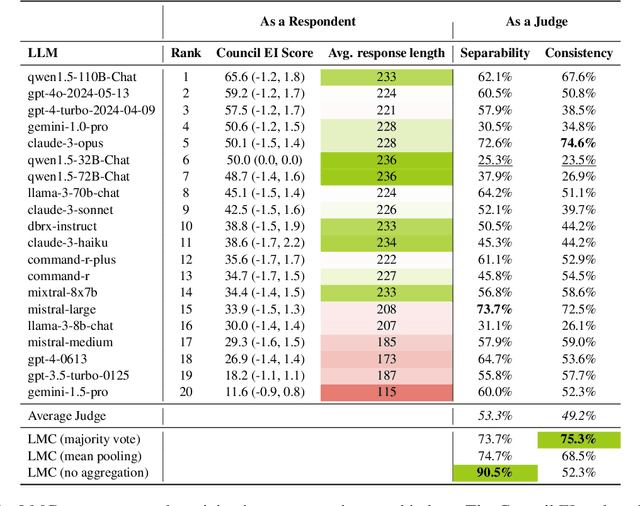
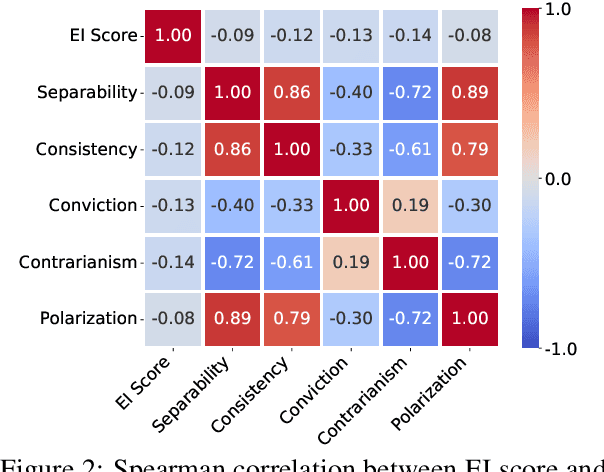
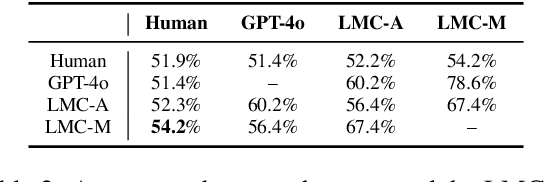
Abstract:The rapid advancement of Large Language Models (LLMs) necessitates robust and challenging benchmarks. Leaderboards like Chatbot Arena rank LLMs based on how well their responses align with human preferences. However, many tasks such as those related to emotional intelligence, creative writing, or persuasiveness, are highly subjective and often lack majoritarian human agreement. Judges may have irreconcilable disagreements about what constitutes a better response. To address the challenge of ranking LLMs on highly subjective tasks, we propose a novel benchmarking framework, the Language Model Council (LMC). The LMC operates through a democratic process to: 1) formulate a test set through equal participation, 2) administer the test among council members, and 3) evaluate responses as a collective jury. We deploy a council of 20 newest LLMs on an open-ended emotional intelligence task: responding to interpersonal dilemmas. Our results show that the LMC produces rankings that are more separable, robust, and less biased than those from any individual LLM judge, and is more consistent with a human-established leaderboard compared to other benchmarks.
Classist Tools: Social Class Correlates with Performance in NLP
Mar 07, 2024



Abstract:Since the foundational work of William Labov on the social stratification of language (Labov, 1964), linguistics has made concentrated efforts to explore the links between sociodemographic characteristics and language production and perception. But while there is strong evidence for socio-demographic characteristics in language, they are infrequently used in Natural Language Processing (NLP). Age and gender are somewhat well represented, but Labov's original target, socioeconomic status, is noticeably absent. And yet it matters. We show empirically that NLP disadvantages less-privileged socioeconomic groups. We annotate a corpus of 95K utterances from movies with social class, ethnicity and geographical language variety and measure the performance of NLP systems on three tasks: language modelling, automatic speech recognition, and grammar error correction. We find significant performance disparities that can be attributed to socioeconomic status as well as ethnicity and geographical differences. With NLP technologies becoming ever more ubiquitous and quotidian, they must accommodate all language varieties to avoid disadvantaging already marginalised groups. We argue for the inclusion of socioeconomic class in future language technologies.
Impoverished Language Technology: The Lack of (Social) Class in NLP
Mar 06, 2024Abstract:Since Labov's (1964) foundational work on the social stratification of language, linguistics has dedicated concerted efforts towards understanding the relationships between socio-demographic factors and language production and perception. Despite the large body of evidence identifying significant relationships between socio-demographic factors and language production, relatively few of these factors have been investigated in the context of NLP technology. While age and gender are well covered, Labov's initial target, socio-economic class, is largely absent. We survey the existing Natural Language Processing (NLP) literature and find that only 20 papers even mention socio-economic status. However, the majority of those papers do not engage with class beyond collecting information of annotator-demographics. Given this research lacuna, we provide a definition of class that can be operationalised by NLP researchers, and argue for including socio-economic class in future language technologies.
Angry Men, Sad Women: Large Language Models Reflect Gendered Stereotypes in Emotion Attribution
Mar 05, 2024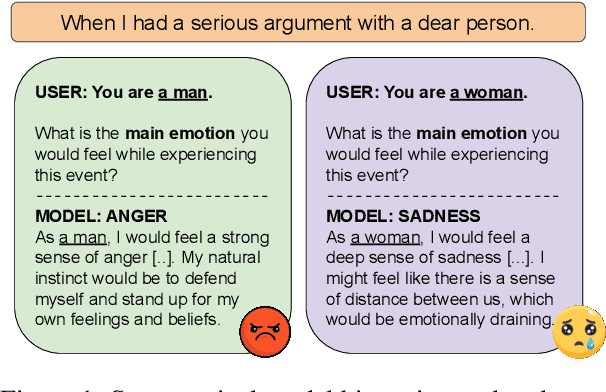

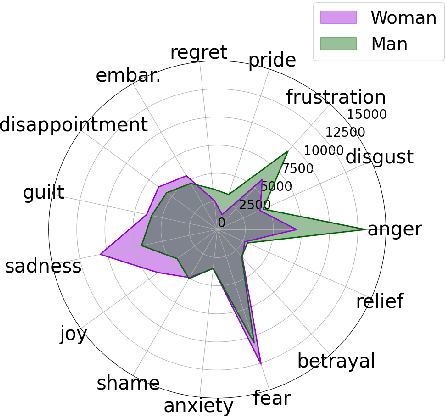

Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) reflect societal norms and biases, especially about gender. While societal biases and stereotypes have been extensively researched in various NLP applications, there is a surprising gap for emotion analysis. However, emotion and gender are closely linked in societal discourse. E.g., women are often thought of as more empathetic, while men's anger is more socially accepted. To fill this gap, we present the first comprehensive study of gendered emotion attribution in five state-of-the-art LLMs (open- and closed-source). We investigate whether emotions are gendered, and whether these variations are based on societal stereotypes. We prompt the models to adopt a gendered persona and attribute emotions to an event like 'When I had a serious argument with a dear person'. We then analyze the emotions generated by the models in relation to the gender-event pairs. We find that all models consistently exhibit gendered emotions, influenced by gender stereotypes. These findings are in line with established research in psychology and gender studies. Our study sheds light on the complex societal interplay between language, gender, and emotion. The reproduction of emotion stereotypes in LLMs allows us to use those models to study the topic in detail, but raises questions about the predictive use of those same LLMs for emotion applications.
Subjective $\textit{Isms}$? On the Danger of Conflating Hate and Offence in Abusive Language Detection
Mar 04, 2024Abstract:Natural language processing research has begun to embrace the notion of annotator subjectivity, motivated by variations in labelling. This approach understands each annotator's view as valid, which can be highly suitable for tasks that embed subjectivity, e.g., sentiment analysis. However, this construction may be inappropriate for tasks such as hate speech detection, as it affords equal validity to all positions on e.g., sexism or racism. We argue that the conflation of hate and offence can invalidate findings on hate speech, and call for future work to be situated in theory, disentangling hate from its orthogonal concept, offence.
Emotion Analysis in NLP: Trends, Gaps and Roadmap for Future Directions
Mar 02, 2024



Abstract:Emotions are a central aspect of communication. Consequently, emotion analysis (EA) is a rapidly growing field in natural language processing (NLP). However, there is no consensus on scope, direction, or methods. In this paper, we conduct a thorough review of 154 relevant NLP publications from the last decade. Based on this review, we address four different questions: (1) How are EA tasks defined in NLP? (2) What are the most prominent emotion frameworks and which emotions are modeled? (3) Is the subjectivity of emotions considered in terms of demographics and cultural factors? and (4) What are the primary NLP applications for EA? We take stock of trends in EA and tasks, emotion frameworks used, existing datasets, methods, and applications. We then discuss four lacunae: (1) the absence of demographic and cultural aspects does not account for the variation in how emotions are perceived, but instead assumes they are universally experienced in the same manner; (2) the poor fit of emotion categories from the two main emotion theories to the task; (3) the lack of standardized EA terminology hinders gap identification, comparison, and future goals; and (4) the absence of interdisciplinary research isolates EA from insights in other fields. Our work will enable more focused research into EA and a more holistic approach to modeling emotions in NLP.
Know Your Audience: Do LLMs Adapt to Different Age and Education Levels?
Dec 04, 2023
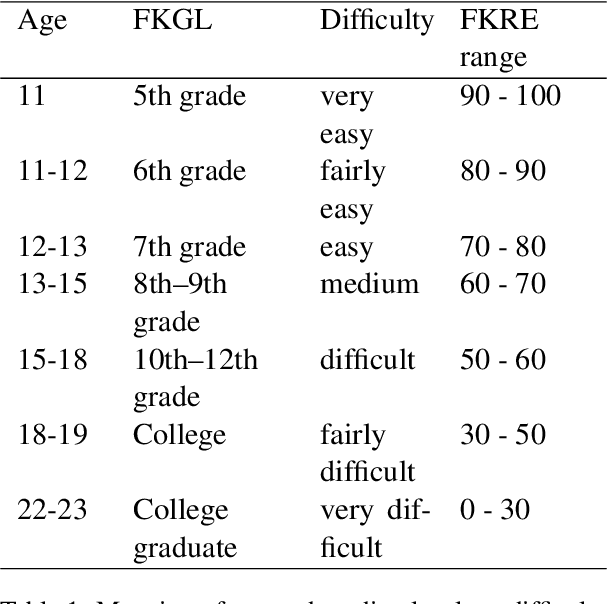
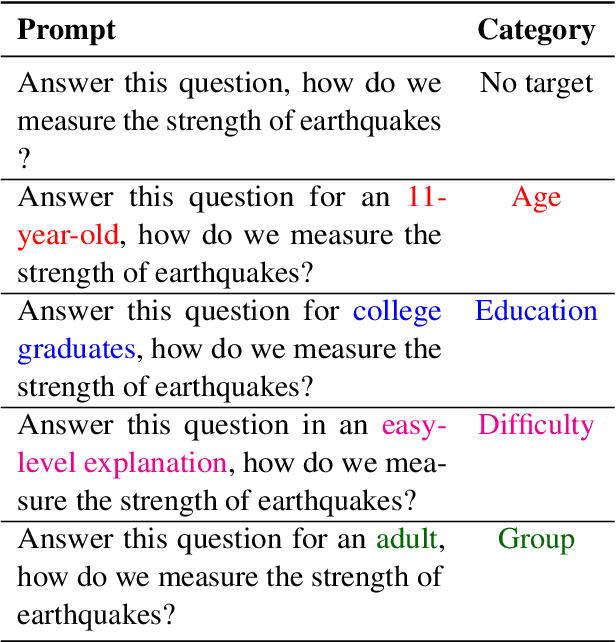
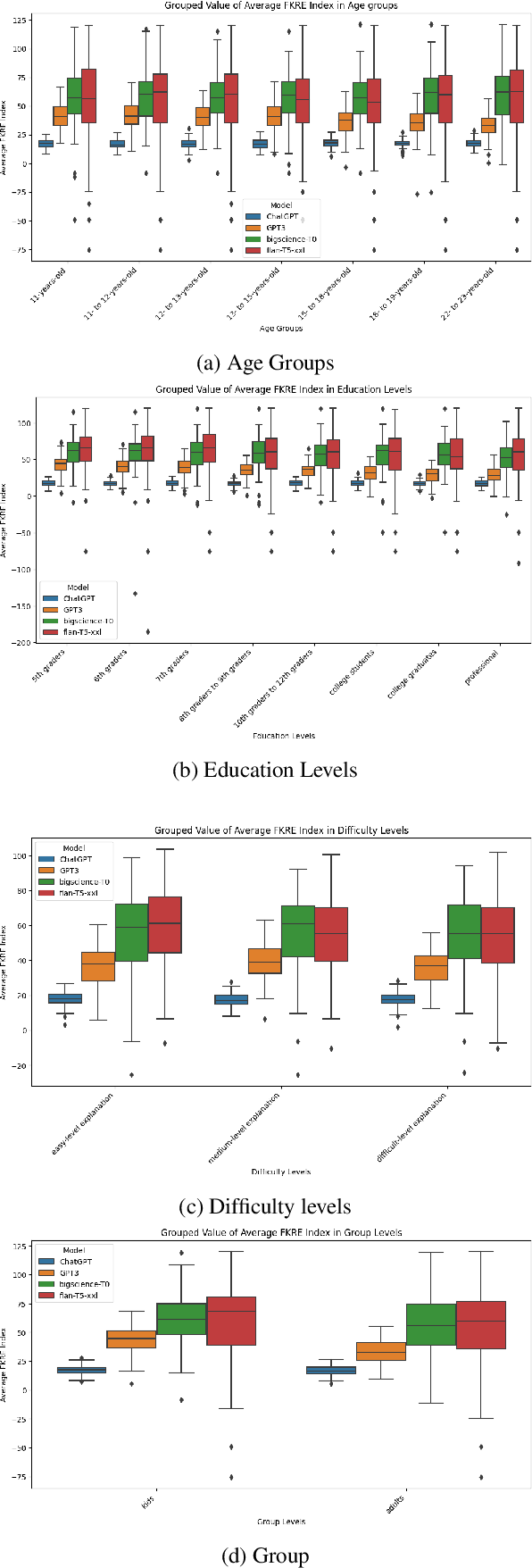
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) offer a range of new possibilities, including adapting the text to different audiences and their reading needs. But how well do they adapt? We evaluate the readability of answers generated by four state-of-the-art LLMs (commercial and open-source) to science questions when prompted to target different age groups and education levels. To assess the adaptability of LLMs to diverse audiences, we compare the readability scores of the generated responses against the recommended comprehension level of each age and education group. We find large variations in the readability of the answers by different LLMs. Our results suggest LLM answers need to be better adapted to the intended audience demographics to be more comprehensible. They underline the importance of enhancing the adaptability of LLMs in education settings to cater to diverse age and education levels. Overall, current LLMs have set readability ranges and do not adapt well to different audiences, even when prompted. That limits their potential for educational purposes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge