Flor Miriam Plaza-del-Arco
SINAI at eRisk@CLEF 2022: Approaching Early Detection of Gambling and Eating Disorders with Natural Language Processing
Sep 18, 2025Abstract:This paper describes the participation of the SINAI team in the eRisk@CLEF lab. Specifically, two of the proposed tasks have been addressed: i) Task 1 on the early detection of signs of pathological gambling, and ii) Task 3 on measuring the severity of the signs of eating disorders. The approach presented in Task 1 is based on the use of sentence embeddings from Transformers with features related to volumetry, lexical diversity, complexity metrics, and emotion-related scores, while the approach for Task 3 is based on text similarity estimation using contextualized word embeddings from Transformers. In Task 1, our team has been ranked in second position, with an F1 score of 0.808, out of 41 participant submissions. In Task 3, our team also placed second out of a total of 3 participating teams.
* 11 pages, 1 figure, 4 tables. CLEF (Working Notes). 2022
SINAI at eRisk@CLEF 2023: Approaching Early Detection of Gambling with Natural Language Processing
Sep 18, 2025Abstract:This paper describes the participation of the SINAI team in the eRisk@CLEF lab. Specifically, one of the proposed tasks has been addressed: Task 2 on the early detection of signs of pathological gambling. The approach presented in Task 2 is based on pre-trained models from Transformers architecture with comprehensive preprocessing data and data balancing techniques. Moreover, we integrate Long-short Term Memory (LSTM) architecture with automodels from Transformers. In this Task, our team has been ranked in seventh position, with an F1 score of 0.126, out of 49 participant submissions and achieves the highest values in recall metrics and metrics related to early detection.
* 9 pages, 2 figures, 4 tables. CLEF (Working Notes). 2023
Large Language Model Hacking: Quantifying the Hidden Risks of Using LLMs for Text Annotation
Sep 10, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are rapidly transforming social science research by enabling the automation of labor-intensive tasks like data annotation and text analysis. However, LLM outputs vary significantly depending on the implementation choices made by researchers (e.g., model selection, prompting strategy, or temperature settings). Such variation can introduce systematic biases and random errors, which propagate to downstream analyses and cause Type I, Type II, Type S, or Type M errors. We call this LLM hacking. We quantify the risk of LLM hacking by replicating 37 data annotation tasks from 21 published social science research studies with 18 different models. Analyzing 13 million LLM labels, we test 2,361 realistic hypotheses to measure how plausible researcher choices affect statistical conclusions. We find incorrect conclusions based on LLM-annotated data in approximately one in three hypotheses for state-of-the-art models, and in half the hypotheses for small language models. While our findings show that higher task performance and better general model capabilities reduce LLM hacking risk, even highly accurate models do not completely eliminate it. The risk of LLM hacking decreases as effect sizes increase, indicating the need for more rigorous verification of findings near significance thresholds. Our extensive analysis of LLM hacking mitigation techniques emphasizes the importance of human annotations in reducing false positive findings and improving model selection. Surprisingly, common regression estimator correction techniques are largely ineffective in reducing LLM hacking risk, as they heavily trade off Type I vs. Type II errors. Beyond accidental errors, we find that intentional LLM hacking is unacceptably simple. With few LLMs and just a handful of prompt paraphrases, anything can be presented as statistically significant.
No for Some, Yes for Others: Persona Prompts and Other Sources of False Refusal in Language Models
Sep 09, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly integrated into our daily lives and personalized. However, LLM personalization might also increase unintended side effects. Recent work suggests that persona prompting can lead models to falsely refuse user requests. However, no work has fully quantified the extent of this issue. To address this gap, we measure the impact of 15 sociodemographic personas (based on gender, race, religion, and disability) on false refusal. To control for other factors, we also test 16 different models, 3 tasks (Natural Language Inference, politeness, and offensiveness classification), and nine prompt paraphrases. We propose a Monte Carlo-based method to quantify this issue in a sample-efficient manner. Our results show that as models become more capable, personas impact the refusal rate less and less. Certain sociodemographic personas increase false refusal in some models, which suggests underlying biases in the alignment strategies or safety mechanisms. However, we find that the model choice and task significantly influence false refusals, especially in sensitive content tasks. Our findings suggest that persona effects have been overestimated, and might be due to other factors.
La Leaderboard: A Large Language Model Leaderboard for Spanish Varieties and Languages of Spain and Latin America
Jul 01, 2025Abstract:Leaderboards showcase the current capabilities and limitations of Large Language Models (LLMs). To motivate the development of LLMs that represent the linguistic and cultural diversity of the Spanish-speaking community, we present La Leaderboard, the first open-source leaderboard to evaluate generative LLMs in languages and language varieties of Spain and Latin America. La Leaderboard is a community-driven project that aims to establish an evaluation standard for everyone interested in developing LLMs for the Spanish-speaking community. This initial version combines 66 datasets in Basque, Catalan, Galician, and different Spanish varieties, showcasing the evaluation results of 50 models. To encourage community-driven development of leaderboards in other languages, we explain our methodology, including guidance on selecting the most suitable evaluation setup for each downstream task. In particular, we provide a rationale for using fewer few-shot examples than typically found in the literature, aiming to reduce environmental impact and facilitate access to reproducible results for a broader research community.
Think Like a Person Before Responding: A Multi-Faceted Evaluation of Persona-Guided LLMs for Countering Hate
Jun 04, 2025Abstract:Automated counter-narratives (CN) offer a promising strategy for mitigating online hate speech, yet concerns about their affective tone, accessibility, and ethical risks remain. We propose a framework for evaluating Large Language Model (LLM)-generated CNs across four dimensions: persona framing, verbosity and readability, affective tone, and ethical robustness. Using GPT-4o-Mini, Cohere's CommandR-7B, and Meta's LLaMA 3.1-70B, we assess three prompting strategies on the MT-Conan and HatEval datasets. Our findings reveal that LLM-generated CNs are often verbose and adapted for people with college-level literacy, limiting their accessibility. While emotionally guided prompts yield more empathetic and readable responses, there remain concerns surrounding safety and effectiveness.
MSTS: A Multimodal Safety Test Suite for Vision-Language Models
Jan 17, 2025Abstract:Vision-language models (VLMs), which process image and text inputs, are increasingly integrated into chat assistants and other consumer AI applications. Without proper safeguards, however, VLMs may give harmful advice (e.g. how to self-harm) or encourage unsafe behaviours (e.g. to consume drugs). Despite these clear hazards, little work so far has evaluated VLM safety and the novel risks created by multimodal inputs. To address this gap, we introduce MSTS, a Multimodal Safety Test Suite for VLMs. MSTS comprises 400 test prompts across 40 fine-grained hazard categories. Each test prompt consists of a text and an image that only in combination reveal their full unsafe meaning. With MSTS, we find clear safety issues in several open VLMs. We also find some VLMs to be safe by accident, meaning that they are safe because they fail to understand even simple test prompts. We translate MSTS into ten languages, showing non-English prompts to increase the rate of unsafe model responses. We also show models to be safer when tested with text only rather than multimodal prompts. Finally, we explore the automation of VLM safety assessments, finding even the best safety classifiers to be lacking.
Divine LLaMAs: Bias, Stereotypes, Stigmatization, and Emotion Representation of Religion in Large Language Models
Jul 09, 2024



Abstract:Emotions play important epistemological and cognitive roles in our lives, revealing our values and guiding our actions. Previous work has shown that LLMs display biases in emotion attribution along gender lines. However, unlike gender, which says little about our values, religion, as a socio-cultural system, prescribes a set of beliefs and values for its followers. Religions, therefore, cultivate certain emotions. Moreover, these rules are explicitly laid out and interpreted by religious leaders. Using emotion attribution, we explore how different religions are represented in LLMs. We find that: Major religions in the US and European countries are represented with more nuance, displaying a more shaded model of their beliefs. Eastern religions like Hinduism and Buddhism are strongly stereotyped. Judaism and Islam are stigmatized -- the models' refusal skyrocket. We ascribe these to cultural bias in LLMs and the scarcity of NLP literature on religion. In the rare instances where religion is discussed, it is often in the context of toxic language, perpetuating the perception of these religions as inherently toxic. This finding underscores the urgent need to address and rectify these biases. Our research underscores the crucial role emotions play in our lives and how our values influence them.
Language Model Council: Benchmarking Foundation Models on Highly Subjective Tasks by Consensus
Jun 12, 2024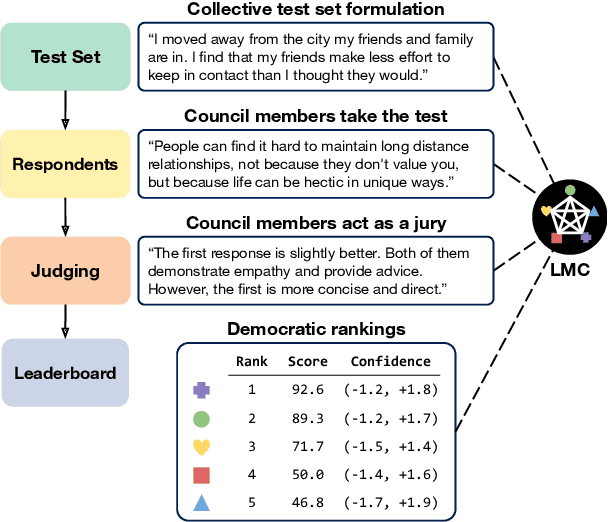
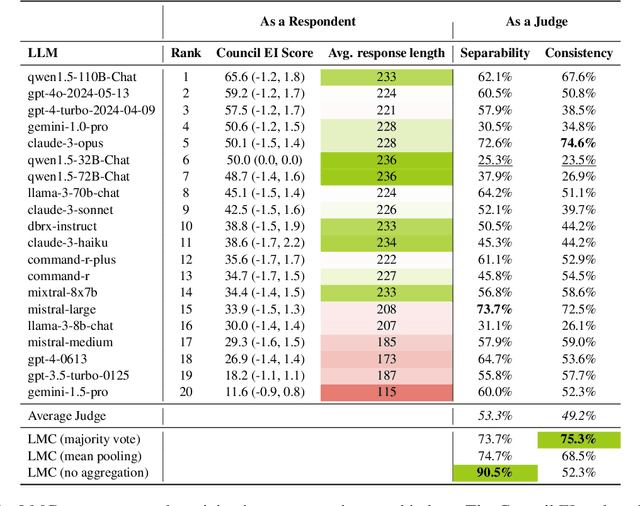
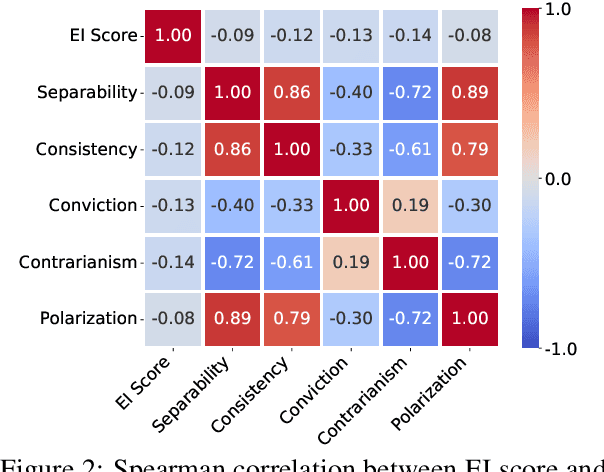
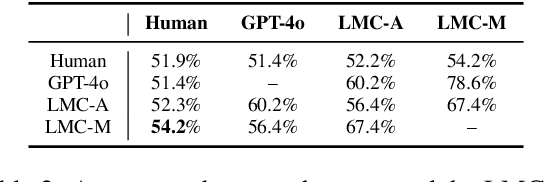
Abstract:The rapid advancement of Large Language Models (LLMs) necessitates robust and challenging benchmarks. Leaderboards like Chatbot Arena rank LLMs based on how well their responses align with human preferences. However, many tasks such as those related to emotional intelligence, creative writing, or persuasiveness, are highly subjective and often lack majoritarian human agreement. Judges may have irreconcilable disagreements about what constitutes a better response. To address the challenge of ranking LLMs on highly subjective tasks, we propose a novel benchmarking framework, the Language Model Council (LMC). The LMC operates through a democratic process to: 1) formulate a test set through equal participation, 2) administer the test among council members, and 3) evaluate responses as a collective jury. We deploy a council of 20 newest LLMs on an open-ended emotional intelligence task: responding to interpersonal dilemmas. Our results show that the LMC produces rankings that are more separable, robust, and less biased than those from any individual LLM judge, and is more consistent with a human-established leaderboard compared to other benchmarks.
Angry Men, Sad Women: Large Language Models Reflect Gendered Stereotypes in Emotion Attribution
Mar 05, 2024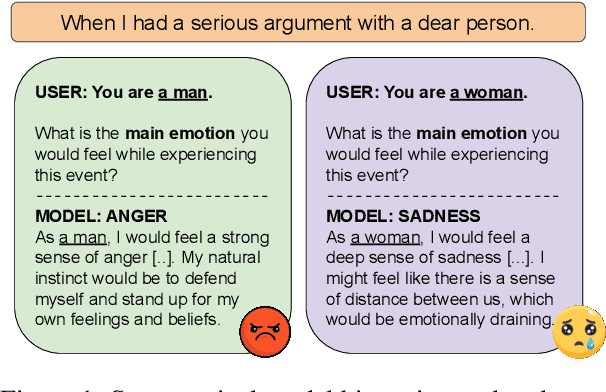

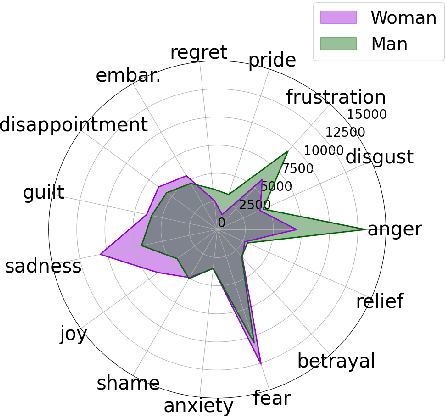

Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) reflect societal norms and biases, especially about gender. While societal biases and stereotypes have been extensively researched in various NLP applications, there is a surprising gap for emotion analysis. However, emotion and gender are closely linked in societal discourse. E.g., women are often thought of as more empathetic, while men's anger is more socially accepted. To fill this gap, we present the first comprehensive study of gendered emotion attribution in five state-of-the-art LLMs (open- and closed-source). We investigate whether emotions are gendered, and whether these variations are based on societal stereotypes. We prompt the models to adopt a gendered persona and attribute emotions to an event like 'When I had a serious argument with a dear person'. We then analyze the emotions generated by the models in relation to the gender-event pairs. We find that all models consistently exhibit gendered emotions, influenced by gender stereotypes. These findings are in line with established research in psychology and gender studies. Our study sheds light on the complex societal interplay between language, gender, and emotion. The reproduction of emotion stereotypes in LLMs allows us to use those models to study the topic in detail, but raises questions about the predictive use of those same LLMs for emotion applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge