Alba Curry
Divine LLaMAs: Bias, Stereotypes, Stigmatization, and Emotion Representation of Religion in Large Language Models
Jul 09, 2024



Abstract:Emotions play important epistemological and cognitive roles in our lives, revealing our values and guiding our actions. Previous work has shown that LLMs display biases in emotion attribution along gender lines. However, unlike gender, which says little about our values, religion, as a socio-cultural system, prescribes a set of beliefs and values for its followers. Religions, therefore, cultivate certain emotions. Moreover, these rules are explicitly laid out and interpreted by religious leaders. Using emotion attribution, we explore how different religions are represented in LLMs. We find that: Major religions in the US and European countries are represented with more nuance, displaying a more shaded model of their beliefs. Eastern religions like Hinduism and Buddhism are strongly stereotyped. Judaism and Islam are stigmatized -- the models' refusal skyrocket. We ascribe these to cultural bias in LLMs and the scarcity of NLP literature on religion. In the rare instances where religion is discussed, it is often in the context of toxic language, perpetuating the perception of these religions as inherently toxic. This finding underscores the urgent need to address and rectify these biases. Our research underscores the crucial role emotions play in our lives and how our values influence them.
Angry Men, Sad Women: Large Language Models Reflect Gendered Stereotypes in Emotion Attribution
Mar 05, 2024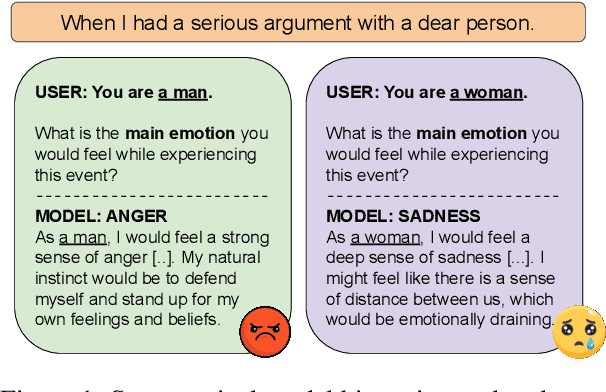

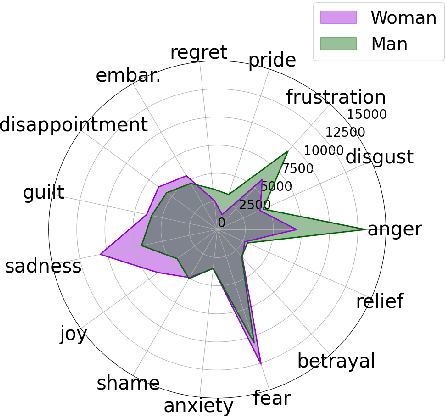

Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) reflect societal norms and biases, especially about gender. While societal biases and stereotypes have been extensively researched in various NLP applications, there is a surprising gap for emotion analysis. However, emotion and gender are closely linked in societal discourse. E.g., women are often thought of as more empathetic, while men's anger is more socially accepted. To fill this gap, we present the first comprehensive study of gendered emotion attribution in five state-of-the-art LLMs (open- and closed-source). We investigate whether emotions are gendered, and whether these variations are based on societal stereotypes. We prompt the models to adopt a gendered persona and attribute emotions to an event like 'When I had a serious argument with a dear person'. We then analyze the emotions generated by the models in relation to the gender-event pairs. We find that all models consistently exhibit gendered emotions, influenced by gender stereotypes. These findings are in line with established research in psychology and gender studies. Our study sheds light on the complex societal interplay between language, gender, and emotion. The reproduction of emotion stereotypes in LLMs allows us to use those models to study the topic in detail, but raises questions about the predictive use of those same LLMs for emotion applications.
Emotion Analysis in NLP: Trends, Gaps and Roadmap for Future Directions
Mar 02, 2024



Abstract:Emotions are a central aspect of communication. Consequently, emotion analysis (EA) is a rapidly growing field in natural language processing (NLP). However, there is no consensus on scope, direction, or methods. In this paper, we conduct a thorough review of 154 relevant NLP publications from the last decade. Based on this review, we address four different questions: (1) How are EA tasks defined in NLP? (2) What are the most prominent emotion frameworks and which emotions are modeled? (3) Is the subjectivity of emotions considered in terms of demographics and cultural factors? and (4) What are the primary NLP applications for EA? We take stock of trends in EA and tasks, emotion frameworks used, existing datasets, methods, and applications. We then discuss four lacunae: (1) the absence of demographic and cultural aspects does not account for the variation in how emotions are perceived, but instead assumes they are universally experienced in the same manner; (2) the poor fit of emotion categories from the two main emotion theories to the task; (3) the lack of standardized EA terminology hinders gap identification, comparison, and future goals; and (4) the absence of interdisciplinary research isolates EA from insights in other fields. Our work will enable more focused research into EA and a more holistic approach to modeling emotions in NLP.
Computer says "No": The Case Against Empathetic Conversational AI
Dec 21, 2022Abstract:Emotions are an integral part of human cognition and they guide not only our understanding of the world but also our actions within it. As such, whether we soothe or flame an emotion is not inconsequential. Recent work in conversational AI has focused on responding empathetically to users, validating and soothing their emotions without a real basis. This AI-aided emotional regulation can have negative consequences for users and society, tending towards a one-noted happiness defined as only the absence of "negative" emotions. We argue that we must carefully consider whether and how to respond to users' emotions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge