Shichen Zhang
Multimodal 3D Genome Pre-training
Apr 12, 2025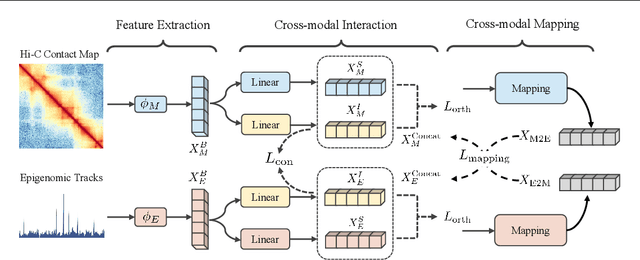
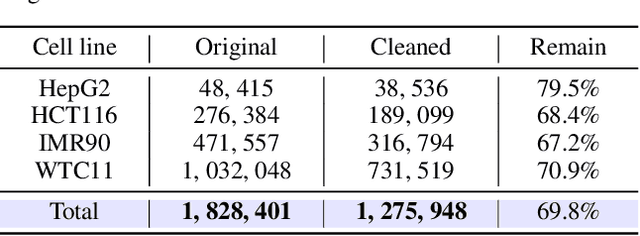
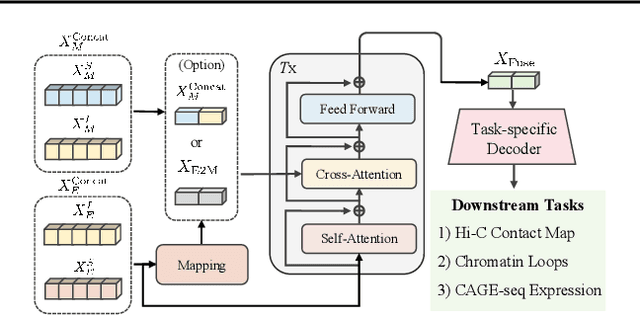
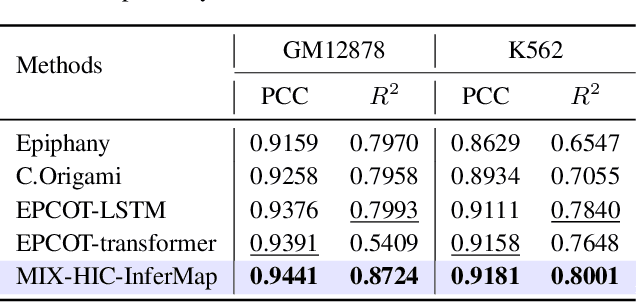
Abstract:Deep learning techniques have driven significant progress in various analytical tasks within 3D genomics in computational biology. However, a holistic understanding of 3D genomics knowledge remains underexplored. Here, we propose MIX-HIC, the first multimodal foundation model of 3D genome that integrates both 3D genome structure and epigenomic tracks, which obtains unified and comprehensive semantics. For accurate heterogeneous semantic fusion, we design the cross-modal interaction and mapping blocks for robust unified representation, yielding the accurate aggregation of 3D genome knowledge. Besides, we introduce the first large-scale dataset comprising over 1 million pairwise samples of Hi-C contact maps and epigenomic tracks for high-quality pre-training, enabling the exploration of functional implications in 3D genomics. Extensive experiments show that MIX-HIC can significantly surpass existing state-of-the-art methods in diverse downstream tasks. This work provides a valuable resource for advancing 3D genomics research.
Rene: A Pre-trained Multi-modal Architecture for Auscultation of Respiratory Diseases
May 13, 2024

Abstract:This study presents a novel methodology utilizing a pre-trained speech recognition model for processing respiratory sound data. By incorporating medical record information, we introduce an innovative multi-modal deep-learning architecture, named Rene, which addresses the challenges of poor interpretability and underperformance in real-time clinical diagnostic response observed in previous respiratory disease-focused models. The proposed Rene architecture demonstrated significant improvements of 10.24%, 16.15%, 15.29%, and 18.90% respectively, compared to the baseline across four tasks related to respiratory event detection and audio record classification on the SPRSound database. In patient disease prediction tests on the ICBHI database, the architecture exhibited improvements of 23% in the mean of average score and harmonic score compared to the baseline. Furthermore, we developed a real-time respiratory sound discrimination system based on the Rene architecture, featuring a dual-thread design and compressed model parameters for simultaneous microphone recording and real-time dynamic decoding. Employing state-of-the-art Edge AI technology, this system enables rapid and accurate responses for respiratory sound auscultation, facilitating deployment on wearable clinical detection devices to capture incremental data, which can be synergistically evolved with large-scale models deployed on cloud servers for downstream tasks.
Structured Reinforcement Learning for Delay-Optimal Data Transmission in Dense mmWave Networks
Apr 25, 2024Abstract:We study the data packet transmission problem (mmDPT) in dense cell-free millimeter wave (mmWave) networks, i.e., users sending data packet requests to access points (APs) via uplinks and APs transmitting requested data packets to users via downlinks. Our objective is to minimize the average delay in the system due to APs' limited service capacity and unreliable wireless channels between APs and users. This problem can be formulated as a restless multi-armed bandits problem with fairness constraint (RMAB-F). Since finding the optimal policy for RMAB-F is intractable, existing learning algorithms are computationally expensive and not suitable for practical dynamic dense mmWave networks. In this paper, we propose a structured reinforcement learning (RL) solution for mmDPT by exploiting the inherent structure encoded in RMAB-F. To achieve this, we first design a low-complexity and provably asymptotically optimal index policy for RMAB-F. Then, we leverage this structure information to develop a structured RL algorithm called mmDPT-TS, which provably achieves an \tilde{O}(\sqrt{T}) Bayesian regret. More importantly, mmDPT-TS is computation-efficient and thus amenable to practical implementation, as it fully exploits the structure of index policy for making decisions. Extensive emulation based on data collected in realistic mmWave networks demonstrate significant gains of mmDPT-TS over existing approaches.
ChatTracer: Large Language Model Powered Real-time Bluetooth Device Tracking System
Mar 28, 2024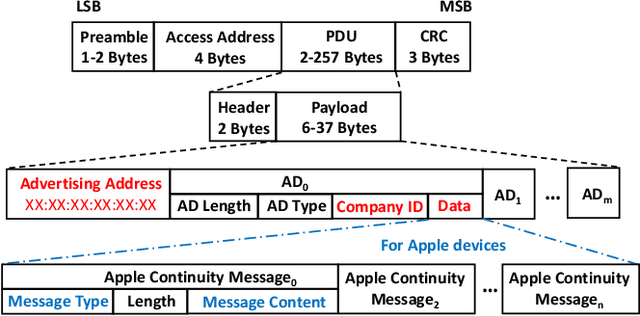
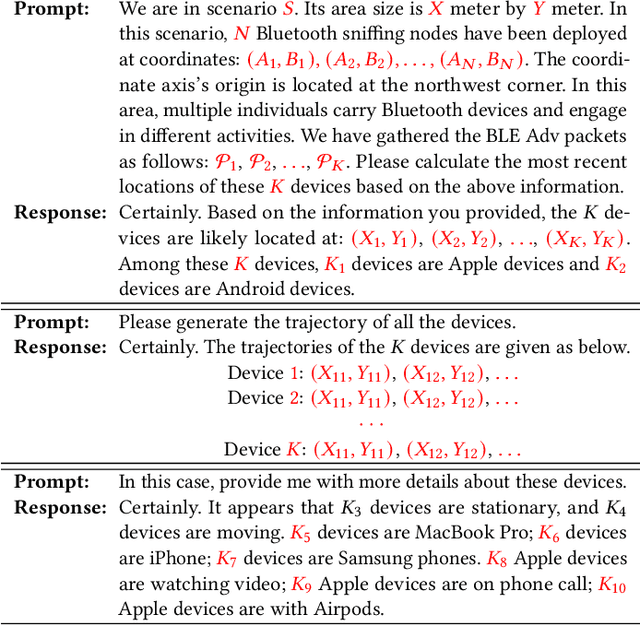
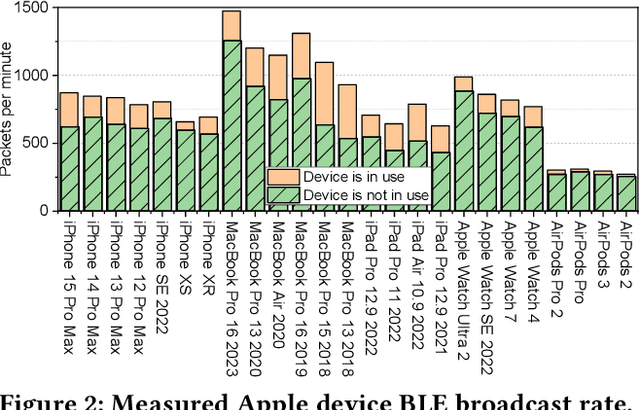

Abstract:Large language models (LLMs), exemplified by OpenAI ChatGPT and Google Bard, have transformed the way we interact with cyber technologies. In this paper, we study the possibility of connecting LLM with wireless sensor networks (WSN). A successful design will not only extend LLM's knowledge landscape to the physical world but also revolutionize human interaction with WSN. To the end, we present ChatTracer, an LLM-powered real-time Bluetooth device tracking system. ChatTracer comprises three key components: an array of Bluetooth sniffing nodes, a database, and a fine-tuned LLM. ChatTracer was designed based on our experimental observation that commercial Apple/Android devices always broadcast hundreds of BLE packets per minute even in their idle status. Its novelties lie in two aspects: i) a reliable and efficient BLE packet grouping algorithm; and ii) an LLM fine-tuning strategy that combines both supervised fine-tuning (SFT) and reinforcement learning with human feedback (RLHF). We have built a prototype of ChatTracer with four sniffing nodes. Experimental results show that ChatTracer not only outperforms existing localization approaches, but also provides an intelligent interface for user interaction.
Dual-Reference Source-Free Active Domain Adaptation for Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Tumor Segmentation across Multiple Hospitals
Sep 23, 2023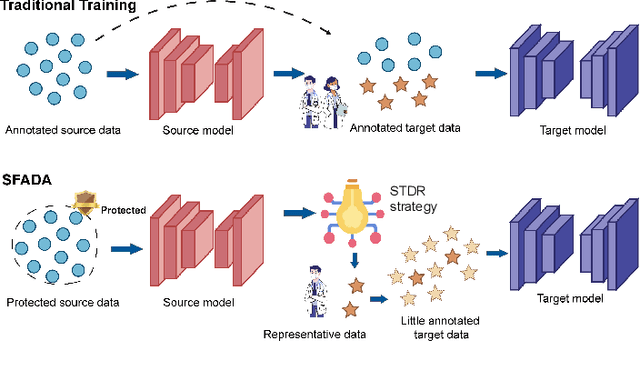
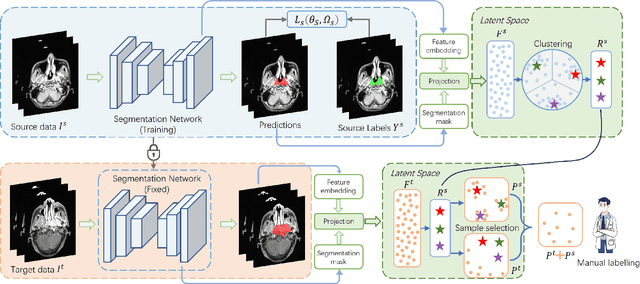
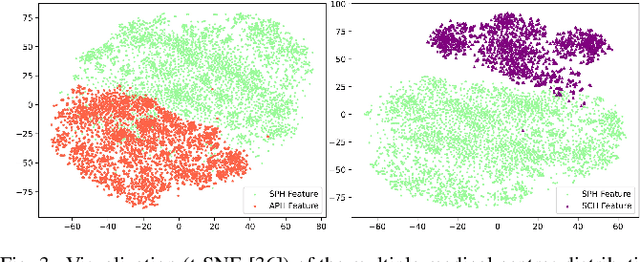
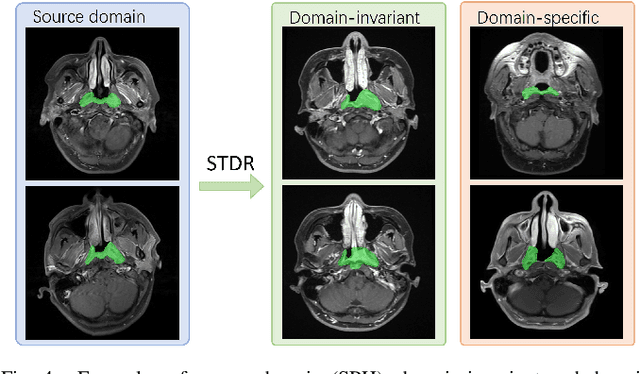
Abstract:Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is a prevalent and clinically significant malignancy that predominantly impacts the head and neck area. Precise delineation of the Gross Tumor Volume (GTV) plays a pivotal role in ensuring effective radiotherapy for NPC. Despite recent methods that have achieved promising results on GTV segmentation, they are still limited by lacking carefully-annotated data and hard-to-access data from multiple hospitals in clinical practice. Although some unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) has been proposed to alleviate this problem, unconditionally mapping the distribution distorts the underlying structural information, leading to inferior performance. To address this challenge, we devise a novel Sourece-Free Active Domain Adaptation (SFADA) framework to facilitate domain adaptation for the GTV segmentation task. Specifically, we design a dual reference strategy to select domain-invariant and domain-specific representative samples from a specific target domain for annotation and model fine-tuning without relying on source-domain data. Our approach not only ensures data privacy but also reduces the workload for oncologists as it just requires annotating a few representative samples from the target domain and does not need to access the source data. We collect a large-scale clinical dataset comprising 1057 NPC patients from five hospitals to validate our approach. Experimental results show that our method outperforms the UDA methods and achieves comparable results to the fully supervised upper bound, even with few annotations, highlighting the significant medical utility of our approach. In addition, there is no public dataset about multi-center NPC segmentation, we will release code and dataset for future research.
Video-Instrument Synergistic Network for Referring Video Instrument Segmentation in Robotic Surgery
Aug 18, 2023



Abstract:Robot-assisted surgery has made significant progress, with instrument segmentation being a critical factor in surgical intervention quality. It serves as the building block to facilitate surgical robot navigation and surgical education for the next generation of operating intelligence. Although existing methods have achieved accurate instrument segmentation results, they simultaneously generate segmentation masks for all instruments, without the capability to specify a target object and allow an interactive experience. This work explores a new task of Referring Surgical Video Instrument Segmentation (RSVIS), which aims to automatically identify and segment the corresponding surgical instruments based on the given language expression. To achieve this, we devise a novel Video-Instrument Synergistic Network (VIS-Net) to learn both video-level and instrument-level knowledge to boost performance, while previous work only used video-level information. Meanwhile, we design a Graph-based Relation-aware Module (GRM) to model the correlation between multi-modal information (i.e., textual description and video frame) to facilitate the extraction of instrument-level information. We are also the first to produce two RSVIS datasets to promote related research. Our method is verified on these datasets, and experimental results exhibit that the VIS-Net can significantly outperform existing state-of-the-art referring segmentation methods. Our code and our datasets will be released upon the publication of this work.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge