Raphael Shu
Controllable Conversational Theme Detection Track at DSTC 12
Aug 26, 2025Abstract:Conversational analytics has been on the forefront of transformation driven by the advances in Speech and Natural Language Processing techniques. Rapid adoption of Large Language Models (LLMs) in the analytics field has taken the problems that can be automated to a new level of complexity and scale. In this paper, we introduce Theme Detection as a critical task in conversational analytics, aimed at automatically identifying and categorizing topics within conversations. This process can significantly reduce the manual effort involved in analyzing expansive dialogs, particularly in domains like customer support or sales. Unlike traditional dialog intent detection, which often relies on a fixed set of intents for downstream system logic, themes are intended as a direct, user-facing summary of the conversation's core inquiry. This distinction allows for greater flexibility in theme surface forms and user-specific customizations. We pose Controllable Conversational Theme Detection problem as a public competition track at Dialog System Technology Challenge (DSTC) 12 -- it is framed as joint clustering and theme labeling of dialog utterances, with the distinctive aspect being controllability of the resulting theme clusters' granularity achieved via the provided user preference data. We give an overview of the problem, the associated dataset and the evaluation metrics, both automatic and human. Finally, we discuss the participant teams' submissions and provide insights from those. The track materials (data and code) are openly available in the GitHub repository.
Optimizing LLM-Based Multi-Agent System with Textual Feedback: A Case Study on Software Development
May 22, 2025Abstract:We have seen remarkable progress in large language models (LLMs) empowered multi-agent systems solving complex tasks necessitating cooperation among experts with diverse skills. However, optimizing LLM-based multi-agent systems remains challenging. In this work, we perform an empirical case study on group optimization of role-based multi-agent systems utilizing natural language feedback for challenging software development tasks under various evaluation dimensions. We propose a two-step agent prompts optimization pipeline: identifying underperforming agents with their failure explanations utilizing textual feedback and then optimizing system prompts of identified agents utilizing failure explanations. We then study the impact of various optimization settings on system performance with two comparison groups: online against offline optimization and individual against group optimization. For group optimization, we study two prompting strategies: one-pass and multi-pass prompting optimizations. Overall, we demonstrate the effectiveness of our optimization method for role-based multi-agent systems tackling software development tasks evaluated on diverse evaluation dimensions, and we investigate the impact of diverse optimization settings on group behaviors of the multi-agent systems to provide practical insights for future development.
Faithful, Unfaithful or Ambiguous? Multi-Agent Debate with Initial Stance for Summary Evaluation
Feb 12, 2025Abstract:Faithfulness evaluators based on large language models (LLMs) are often fooled by the fluency of the text and struggle with identifying errors in the summaries. We propose an approach to summary faithfulness evaluation in which multiple LLM-based agents are assigned initial stances (regardless of what their belief might be) and forced to come up with a reason to justify the imposed belief, thus engaging in a multi-round debate to reach an agreement. The uniformly distributed initial assignments result in a greater diversity of stances leading to more meaningful debates and ultimately more errors identified. Furthermore, by analyzing the recent faithfulness evaluation datasets, we observe that naturally, it is not always the case for a summary to be either faithful to the source document or not. We therefore introduce a new dimension, ambiguity, and a detailed taxonomy to identify such special cases. Experiments demonstrate our approach can help identify ambiguities, and have even a stronger performance on non-ambiguous summaries.
TReMu: Towards Neuro-Symbolic Temporal Reasoning for LLM-Agents with Memory in Multi-Session Dialogues
Feb 03, 2025
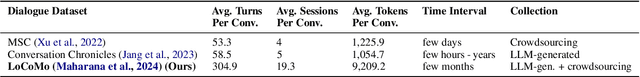
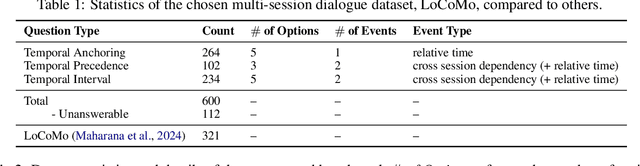
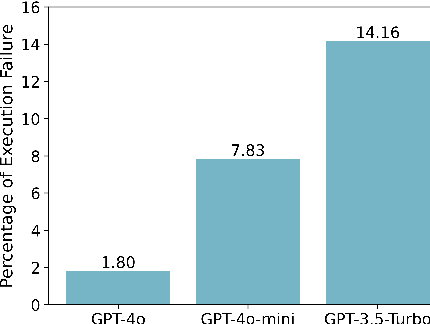
Abstract:Temporal reasoning in multi-session dialogues presents a significant challenge which has been under-studied in previous temporal reasoning benchmarks. To bridge this gap, we propose a new evaluation task for temporal reasoning in multi-session dialogues and introduce an approach to construct a new benchmark by augmenting dialogues from LoCoMo and creating multi-choice QAs. Furthermore, we present TReMu, a new framework aimed at enhancing the temporal reasoning capabilities of LLM-agents in this context. Specifically, the framework employs \textit{time-aware memorization} through timeline summarization, generating retrievable memory by summarizing events in each dialogue session with their inferred dates. Additionally, we integrate \textit{neuro-symbolic temporal reasoning}, where LLMs generate Python code to perform temporal calculations and select answers. Experimental evaluations on popular LLMs demonstrate that our benchmark is challenging, and the proposed framework significantly improves temporal reasoning performance compared to baseline methods, raising from 29.83 on GPT-4o via standard prompting to 77.67 via our approach and highlighting its effectiveness in addressing temporal reasoning in multi-session dialogues.
Towards Effective GenAI Multi-Agent Collaboration: Design and Evaluation for Enterprise Applications
Dec 06, 2024Abstract:AI agents powered by large language models (LLMs) have shown strong capabilities in problem solving. Through combining many intelligent agents, multi-agent collaboration has emerged as a promising approach to tackle complex, multi-faceted problems that exceed the capabilities of single AI agents. However, designing the collaboration protocols and evaluating the effectiveness of these systems remains a significant challenge, especially for enterprise applications. This report addresses these challenges by presenting a comprehensive evaluation of coordination and routing capabilities in a novel multi-agent collaboration framework. We evaluate two key operational modes: (1) a coordination mode enabling complex task completion through parallel communication and payload referencing, and (2) a routing mode for efficient message forwarding between agents. We benchmark on a set of handcrafted scenarios from three enterprise domains, which are publicly released with the report. For coordination capabilities, we demonstrate the effectiveness of inter-agent communication and payload referencing mechanisms, achieving end-to-end goal success rates of 90%. Our analysis yields several key findings: multi-agent collaboration enhances goal success rates by up to 70% compared to single-agent approaches in our benchmarks; payload referencing improves performance on code-intensive tasks by 23%; latency can be substantially reduced with a routing mechanism that selectively bypasses agent orchestration. These findings offer valuable guidance for enterprise deployments of multi-agent systems and advance the development of scalable, efficient multi-agent collaboration frameworks.
RoundTable: Investigating Group Decision-Making Mechanism in Multi-Agent Collaboration
Nov 11, 2024Abstract:This study investigates the efficacy of Multi-Agent Systems in eliciting cross-agent communication and enhancing collective intelligence through group decision-making in a decentralized setting. Unlike centralized mechanisms, where a fixed hierarchy governs social choice, decentralized group decision-making allows agents to engage in joint deliberation. Our research focuses on the dynamics of communication and decision-making within various social choice methods. By applying different voting rules in various environments, we find that moderate decision flexibility yields better outcomes. Additionally, exploring the linguistic features of agent-to-agent conversations reveals indicators of effective collaboration, offering insights into communication patterns that facilitate or hinder collaboration. Finally, we propose various methods for determining the optimal stopping point in multi-agent collaborations based on linguistic cues. Our findings contribute to a deeper understanding of how decentralized decision-making and group conversation shape multi-agent collaboration, with implications for the design of more effective MAS environments.
Structured List-Grounded Question Answering
Oct 04, 2024Abstract:Document-grounded dialogue systems aim to answer user queries by leveraging external information. Previous studies have mainly focused on handling free-form documents, often overlooking structured data such as lists, which can represent a range of nuanced semantic relations. Motivated by the observation that even advanced language models like GPT-3.5 often miss semantic cues from lists, this paper aims to enhance question answering (QA) systems for better interpretation and use of structured lists. To this end, we introduce the LIST2QA dataset, a novel benchmark to evaluate the ability of QA systems to respond effectively using list information. This dataset is created from unlabeled customer service documents using language models and model-based filtering processes to enhance data quality, and can be used to fine-tune and evaluate QA models. Apart from directly generating responses through fine-tuned models, we further explore the explicit use of Intermediate Steps for Lists (ISL), aligning list items with user backgrounds to better reflect how humans interpret list items before generating responses. Our experimental results demonstrate that models trained on LIST2QA with our ISL approach outperform baselines across various metrics. Specifically, our fine-tuned Flan-T5-XL model shows increases of 3.1% in ROUGE-L, 4.6% in correctness, 4.5% in faithfulness, and 20.6% in completeness compared to models without applying filtering and the proposed ISL method.
User Simulation with Large Language Models for Evaluating Task-Oriented Dialogue
Sep 23, 2023
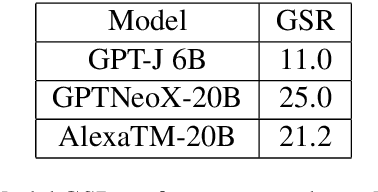
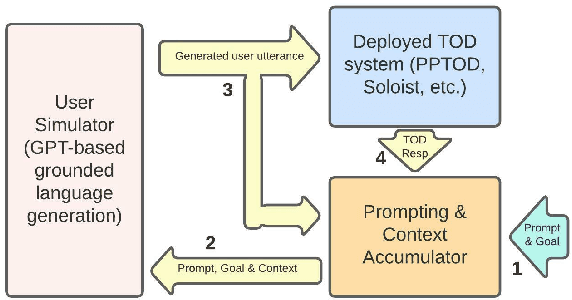
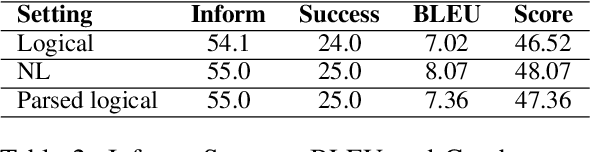
Abstract:One of the major impediments to the development of new task-oriented dialogue (TOD) systems is the need for human evaluation at multiple stages and iterations of the development process. In an effort to move toward automated evaluation of TOD, we propose a novel user simulator built using recently developed large pretrained language models (LLMs). In order to increase the linguistic diversity of our system relative to the related previous work, we do not fine-tune the LLMs used by our system on existing TOD datasets; rather we use in-context learning to prompt the LLMs to generate robust and linguistically diverse output with the goal of simulating the behavior of human interlocutors. Unlike previous work, which sought to maximize goal success rate (GSR) as the primary metric of simulator performance, our goal is a system which achieves a GSR similar to that observed in human interactions with TOD systems. Using this approach, our current simulator is effectively able to interact with several TOD systems, especially on single-intent conversational goals, while generating lexically and syntactically diverse output relative to previous simulators that rely upon fine-tuned models. Finally, we collect a Human2Bot dataset of humans interacting with the same TOD systems with which we experimented in order to better quantify these achievements.
DiactTOD: Learning Generalizable Latent Dialogue Acts for Controllable Task-Oriented Dialogue Systems
Aug 01, 2023Abstract:Dialogue act annotations are important to improve response generation quality in task-oriented dialogue systems. However, it can be challenging to use dialogue acts to control response generation in a generalizable way because different datasets and tasks may have incompatible annotations. While alternative methods that utilize latent action spaces or reinforcement learning do not require explicit annotations, they may lack interpretability or face difficulties defining task-specific rewards. In this work, we present a novel end-to-end latent dialogue act model (DiactTOD) that represents dialogue acts in a latent space. DiactTOD, when pre-trained on a large corpus, is able to predict and control dialogue acts to generate controllable responses using these latent representations in a zero-shot fashion. Our approach demonstrates state-of-the-art performance across a wide range of experimental settings on the MultiWOZ dataset, including zero-shot, few-shot, and full data fine-tuning with both end-to-end and policy optimization configurations.
Pre-training Intent-Aware Encoders for Zero- and Few-Shot Intent Classification
May 24, 2023Abstract:Intent classification (IC) plays an important role in task-oriented dialogue systems as it identifies user intents from given utterances. However, models trained on limited annotations for IC often suffer from a lack of generalization to unseen intent classes. We propose a novel pre-training method for text encoders that uses contrastive learning with intent psuedo-labels to produce embeddings that are well-suited for IC tasks. By applying this pre-training strategy, we also introduce the pre-trained intent-aware encoder (PIE). Specifically, we first train a tagger to identify key phrases within utterances that are crucial for interpreting intents. We then use these extracted phrases to create examples for pre-training a text encoder in a contrastive manner. As a result, our PIE model achieves up to 5.4% and 4.0% higher accuracy than the previous state-of-the-art pre-trained sentence encoder for the N-way zero- and one-shot settings on four IC datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge