Rajib Rana
UAT-LITE: Inference-Time Uncertainty-Aware Attention for Pretrained Transformers
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Neural NLP models are often miscalibrated, assigning high confidence to incorrect predictions, which undermines selective prediction and high-stakes deployment. Post-hoc calibration methods adjust output probabilities but leave internal computation unchanged, while ensemble and Bayesian approaches improve uncertainty at substantial training or storage cost. We propose UAT-LITE, an inference-time framework that makes self-attention uncertainty-aware using approximate Bayesian inference via Monte Carlo dropout in pretrained transformer classifiers. Token-level epistemic uncertainty is estimated from stochastic forward passes and used to modulate self-attention during contextualization, without modifying pretrained weights or training objectives. We additionally introduce a layerwise variance decomposition to diagnose how predictive uncertainty accumulates across transformer depth. Across the SQuAD 2.0 answerability, MNLI, and SST-2, UAT-LITE reduces Expected Calibration Error by approximately 20% on average relative to a fine-tuned BERT-base baseline while preserving task accuracy, and improves selective prediction and robustness under distribution shift.
FedMLAC: Mutual Learning Driven Heterogeneous Federated Audio Classification
Jun 11, 2025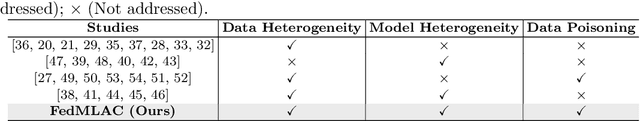
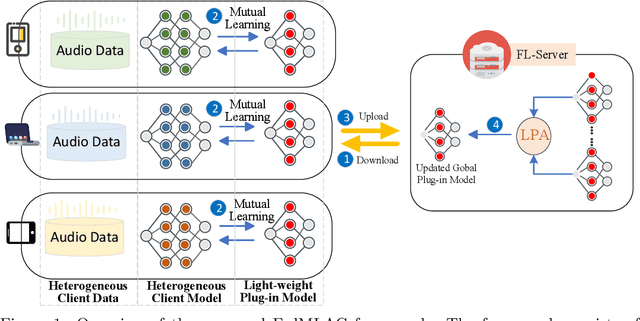

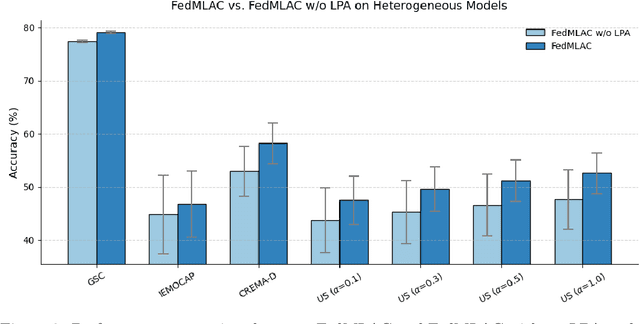
Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) provides a privacy-preserving paradigm for training audio classification (AC) models across distributed clients without sharing raw data. However, Federated Audio Classification (FedAC) faces three critical challenges that substantially hinder performance: data heterogeneity, model heterogeneity, and data poisoning. While prior works have attempted to address these issues, they are typically treated independently, lacking a unified and robust solution suited to real-world federated audio scenarios. To bridge this gap, we propose FedMLAC, a unified mutual learning framework designed to simultaneously tackle these challenges in FedAC. Specifically, FedMLAC introduces a dual-model architecture on each client, comprising a personalized local AC model and a lightweight, globally shared Plug-in model. Through bidirectional knowledge distillation, the Plug-in model enables global knowledge transfer while adapting to client-specific data distributions, thus supporting both generalization and personalization. To further enhance robustness against corrupted audio data, we develop a Layer-wise Pruning Aggregation (LPA) strategy that filters unreliable Plug-in model updates based on parameter deviations during server-side aggregation. Extensive experiments on four diverse audio classification benchmarks, spanning both speech and non-speech tasks, demonstrate that FedMLAC consistently outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods in terms of classification accuracy and robustness to noisy data.
Parameterised Quantum Circuits for Novel Representation Learning in Speech Emotion Recognition
Jan 21, 2025Abstract:Speech Emotion Recognition (SER) is a complex and challenging task in human-computer interaction due to the intricate dependencies of features and the overlapping nature of emotional expressions conveyed through speech. Although traditional deep learning methods have shown effectiveness, they often struggle to capture subtle emotional variations and overlapping states. This paper introduces a hybrid classical-quantum framework that integrates Parameterised Quantum Circuits (PQCs) with conventional Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) architectures. By leveraging quantum properties such as superposition and entanglement, the proposed model enhances feature representation and captures complex dependencies more effectively than classical methods. Experimental evaluations conducted on benchmark datasets, including IEMOCAP, RECOLA, and MSP-Improv, demonstrate that the hybrid model achieves higher accuracy in both binary and multi-class emotion classification while significantly reducing the number of trainable parameters. While a few existing studies have explored the feasibility of using Quantum Circuits to reduce model complexity, none have successfully shown how they can enhance accuracy. This study is the first to demonstrate that Quantum Circuits has the potential to improve the accuracy of SER. The findings highlight the promise of QML to transform SER, suggesting a promising direction for future research and practical applications in emotion-aware systems.
Raw Audio Classification with Cosine Convolutional Neural Network (CosCovNN)
Nov 30, 2024Abstract:This study explores the field of audio classification from raw waveform using Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), a method that eliminates the need for extracting specialised features in the pre-processing step. Unlike recent trends in literature, which often focuses on designing frontends or filters for only the initial layers of CNNs, our research introduces the Cosine Convolutional Neural Network (CosCovNN) replacing the traditional CNN filters with Cosine filters. The CosCovNN surpasses the accuracy of the equivalent CNN architectures with approximately $77\%$ less parameters. Our research further progresses with the development of an augmented CosCovNN named Vector Quantised Cosine Convolutional Neural Network with Memory (VQCCM), incorporating a memory and vector quantisation layer VQCCM achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance across five different datasets in comparison with existing literature. Our findings show that cosine filters can greatly improve the efficiency and accuracy of CNNs in raw audio classification.
Feasibility of Mental Health Triage Call Priority Prediction Using Machine Learning
Nov 25, 2024Abstract:Ensuring accurate call prioritisation is essential for optimising the efficiency and responsiveness of mental health helplines. Currently, call operators rely entirely on the caller's statements to determine the priority of the calls. It has been shown that entirely subjective assessment can lead to errors. Furthermore, it is a missed opportunity not to utilise the voice properties readily available during the call to aid in the evaluation. Incorrect prioritisation can result in delayed assistance for high-risk individuals, resource misallocation, increased mental health deterioration, loss of trust, and potential legal consequences. It is vital to address these risks to guarantee the reliability and effectiveness of mental health services. This study delves into the potential of using machine learning, a branch of Artificial Intelligence, to estimate call priority from the callers' voices for users of mental health phone helplines. After analysing 459 call records from a mental health helpline, we achieved a balanced accuracy of 92\%, showing promise in aiding the call operators' efficiency in call handling processes and improving customer satisfaction.
A Lightweight Attention-based Deep Network via Multi-Scale Feature Fusion for Multi-View Facial Expression Recognition
Mar 21, 2024Abstract:Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and their variations have shown effectiveness in facial expression recognition (FER). However, they face challenges when dealing with high computational complexity and multi-view head poses in real-world scenarios. We introduce a lightweight attentional network incorporating multi-scale feature fusion (LANMSFF) to tackle these issues. For the first challenge, we have carefully designed a lightweight fully convolutional network (FCN). We address the second challenge by presenting two novel components, namely mass attention (MassAtt) and point wise feature selection (PWFS) blocks. The MassAtt block simultaneously generates channel and spatial attention maps to recalibrate feature maps by emphasizing important features while suppressing irrelevant ones. On the other hand, the PWFS block employs a feature selection mechanism that discards less meaningful features prior to the fusion process. This mechanism distinguishes it from previous methods that directly fuse multi-scale features. Our proposed approach achieved results comparable to state-of-the-art methods in terms of parameter counts and robustness to pose variation, with accuracy rates of 90.77% on KDEF, 70.44% on FER-2013, and 86.96% on FERPlus datasets. The code for LANMSFF is available at https://github.com/AE-1129/LANMSFF.
emoDARTS: Joint Optimisation of CNN & Sequential Neural Network Architectures for Superior Speech Emotion Recognition
Mar 21, 2024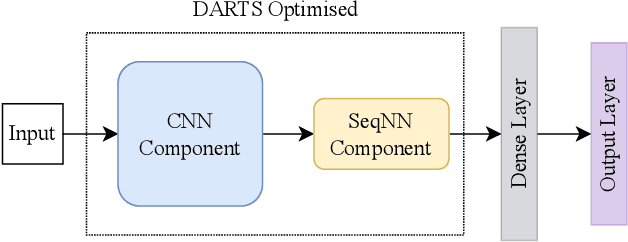
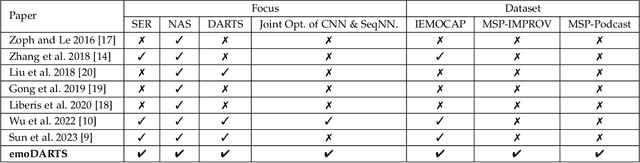
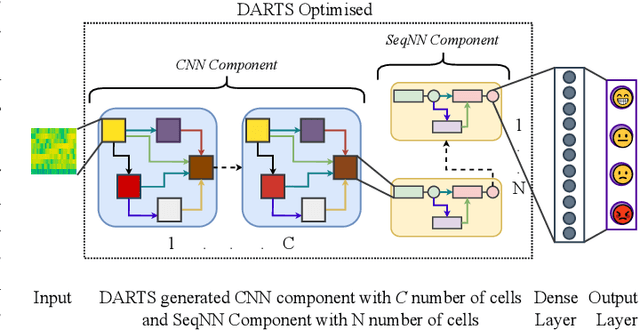

Abstract:Speech Emotion Recognition (SER) is crucial for enabling computers to understand the emotions conveyed in human communication. With recent advancements in Deep Learning (DL), the performance of SER models has significantly improved. However, designing an optimal DL architecture requires specialised knowledge and experimental assessments. Fortunately, Neural Architecture Search (NAS) provides a potential solution for automatically determining the best DL model. The Differentiable Architecture Search (DARTS) is a particularly efficient method for discovering optimal models. This study presents emoDARTS, a DARTS-optimised joint CNN and Sequential Neural Network (SeqNN: LSTM, RNN) architecture that enhances SER performance. The literature supports the selection of CNN and LSTM coupling to improve performance. While DARTS has previously been used to choose CNN and LSTM operations independently, our technique adds a novel mechanism for selecting CNN and SeqNN operations in conjunction using DARTS. Unlike earlier work, we do not impose limits on the layer order of the CNN. Instead, we let DARTS choose the best layer order inside the DARTS cell. We demonstrate that emoDARTS outperforms conventionally designed CNN-LSTM models and surpasses the best-reported SER results achieved through DARTS on CNN-LSTM by evaluating our approach on the IEMOCAP, MSP-IMPROV, and MSP-Podcast datasets.
Integrating Contrastive Learning into a Multitask Transformer Model for Effective Domain Adaptation
Oct 07, 2023



Abstract:While speech emotion recognition (SER) research has made significant progress, achieving generalization across various corpora continues to pose a problem. We propose a novel domain adaptation technique that embodies a multitask framework with SER as the primary task, and contrastive learning and information maximisation loss as auxiliary tasks, underpinned by fine-tuning of transformers pre-trained on large language models. Empirical results obtained through experiments on well-established datasets like IEMOCAP and MSP-IMPROV, illustrate that our proposed model achieves state-of-the-art performance in SER within cross-corpus scenarios.
Natural Language Processing in Electronic Health Records in Relation to Healthcare Decision-making: A Systematic Review
Jun 22, 2023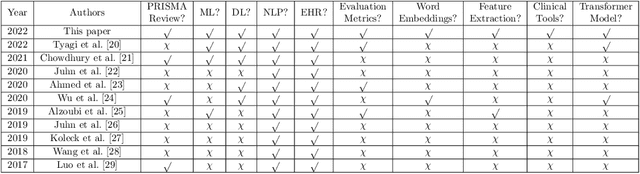
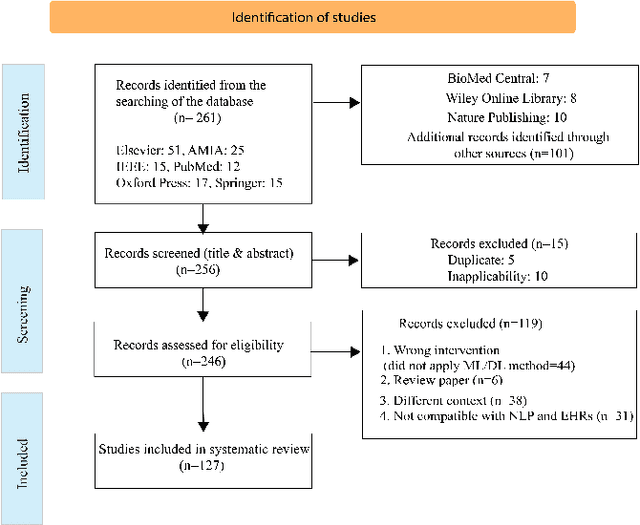
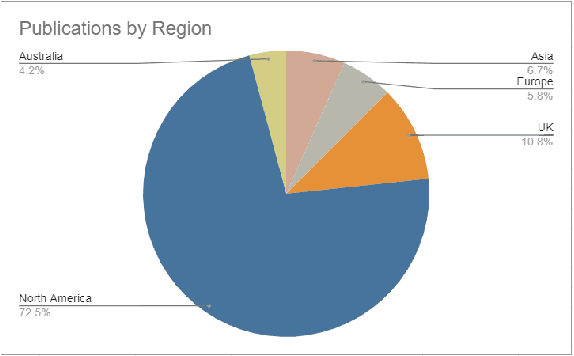
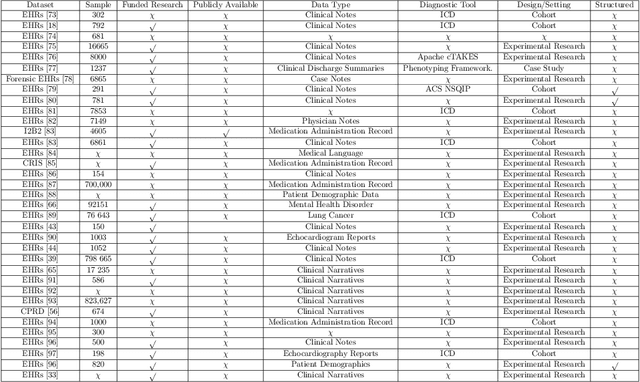
Abstract:Background: Natural Language Processing (NLP) is widely used to extract clinical insights from Electronic Health Records (EHRs). However, the lack of annotated data, automated tools, and other challenges hinder the full utilisation of NLP for EHRs. Various Machine Learning (ML), Deep Learning (DL) and NLP techniques are studied and compared to understand the limitations and opportunities in this space comprehensively. Methodology: After screening 261 articles from 11 databases, we included 127 papers for full-text review covering seven categories of articles: 1) medical note classification, 2) clinical entity recognition, 3) text summarisation, 4) deep learning (DL) and transfer learning architecture, 5) information extraction, 6) Medical language translation and 7) other NLP applications. This study follows the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines. Result and Discussion: EHR was the most commonly used data type among the selected articles, and the datasets were primarily unstructured. Various ML and DL methods were used, with prediction or classification being the most common application of ML or DL. The most common use cases were: the International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision (ICD-9) classification, clinical note analysis, and named entity recognition (NER) for clinical descriptions and research on psychiatric disorders. Conclusion: We find that the adopted ML models were not adequately assessed. In addition, the data imbalance problem is quite important, yet we must find techniques to address this underlining problem. Future studies should address key limitations in studies, primarily identifying Lupus Nephritis, Suicide Attempts, perinatal self-harmed and ICD-9 classification.
Improving Speech Emotion Recognition Performance using Differentiable Architecture Search
May 23, 2023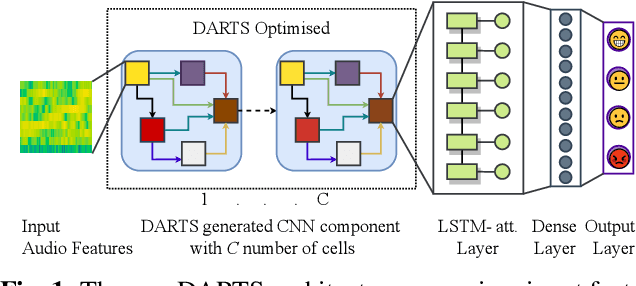
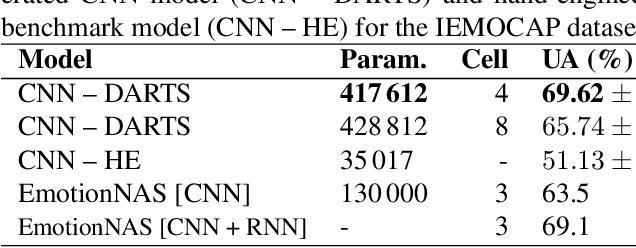
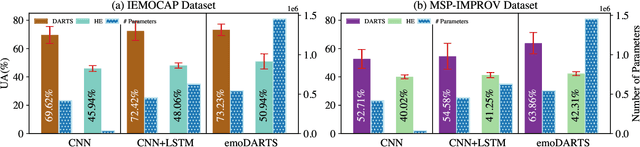
Abstract:Speech Emotion Recognition (SER) is a critical enabler of emotion-aware communication in human-computer interactions. Deep Learning (DL) has improved the performance of SER models by improving model complexity. However, designing DL architectures requires prior experience and experimental evaluations. Encouragingly, Neural Architecture Search (NAS) allows automatic search for an optimum DL model. In particular, Differentiable Architecture Search (DARTS) is an efficient method of using NAS to search for optimised models. In this paper, we propose DARTS for a joint CNN and LSTM architecture for improving SER performance. Our choice of the CNN LSTM coupling is inspired by results showing that similar models offer improved performance. While SER researchers have considered CNNs and RNNs separately, the viability of using DARTs jointly for CNN and LSTM still needs exploration. Experimenting with the IEMOCAP dataset, we demonstrate that our approach outperforms best-reported results using DARTS for SER.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge