Ning Cheng
Rethinking LLM-as-a-Judge: Representation-as-a-Judge with Small Language Models via Semantic Capacity Asymmetry
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are widely used as reference-free evaluators via prompting, but this "LLM-as-a-Judge" paradigm is costly, opaque, and sensitive to prompt design. In this work, we investigate whether smaller models can serve as efficient evaluators by leveraging internal representations instead of surface generation. We uncover a consistent empirical pattern: small LMs, despite with weak generative ability, encode rich evaluative signals in their hidden states. This motivates us to propose the Semantic Capacity Asymmetry Hypothesis: evaluation requires significantly less semantic capacity than generation and can be grounded in intermediate representations, suggesting that evaluation does not necessarily need to rely on large-scale generative models but can instead leverage latent features from smaller ones. Our findings motivate a paradigm shift from LLM-as-a-Judge to Representation-as-a-Judge, a decoding-free evaluation strategy that probes internal model structure rather than relying on prompted output. We instantiate this paradigm through INSPECTOR, a probing-based framework that predicts aspect-level evaluation scores from small model representations. Experiments on reasoning benchmarks (GSM8K, MATH, GPQA) show that INSPECTOR substantially outperforms prompting-based small LMs and closely approximates full LLM judges, while offering a more efficient, reliable, and interpretable alternative for scalable evaluation.
Sentinel: Attention Probing of Proxy Models for LLM Context Compression with an Understanding Perspective
May 29, 2025Abstract:Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) enhances large language models (LLMs) with external context, but retrieved passages are often lengthy, noisy, or exceed input limits. Existing compression methods typically require supervised training of dedicated compression models, increasing cost and reducing portability. We propose Sentinel, a lightweight sentence-level compression framework that reframes context filtering as an attention-based understanding task. Rather than training a compression model, Sentinel probes decoder attention from an off-the-shelf 0.5B proxy LLM using a lightweight classifier to identify sentence relevance. Empirically, we find that query-context relevance estimation is consistent across model scales, with 0.5B proxies closely matching the behaviors of larger models. On the LongBench benchmark, Sentinel achieves up to 5$\times$ compression while matching the QA performance of 7B-scale compression systems. Our results suggest that probing native attention signals enables fast, effective, and question-aware context compression. Code available at: https://github.com/yzhangchuck/Sentinel.
SToLa: Self-Adaptive Touch-Language Framework with Tactile Commonsense Reasoning in Open-Ended Scenarios
May 07, 2025Abstract:This paper explores the challenges of integrating tactile sensing into intelligent systems for multimodal reasoning, particularly in enabling commonsense reasoning about the open-ended physical world. We identify two key challenges: modality discrepancy, where existing large touch-language models often treat touch as a mere sub-modality of language, and open-ended tactile data scarcity, where current datasets lack the diversity, open-endness and complexity needed for reasoning. To overcome these challenges, we introduce SToLa, a Self-Adaptive Touch-Language framework. SToLa utilizes Mixture of Experts (MoE) to dynamically process, unify, and manage tactile and language modalities, capturing their unique characteristics. Crucially, we also present a comprehensive tactile commonsense reasoning dataset and benchmark featuring free-form questions and responses, 8 physical properties, 4 interactive characteristics, and diverse commonsense knowledge. Experiments show SToLa exhibits competitive performance compared to existing models on the PhysiCLeAR benchmark and self-constructed datasets, proving the effectiveness of the Mixture of Experts architecture in multimodal management and the performance advantages for open-scenario tactile commonsense reasoning tasks.
Self-Enhanced Reasoning Training: Activating Latent Reasoning in Small Models for Enhanced Reasoning Distillation
Feb 18, 2025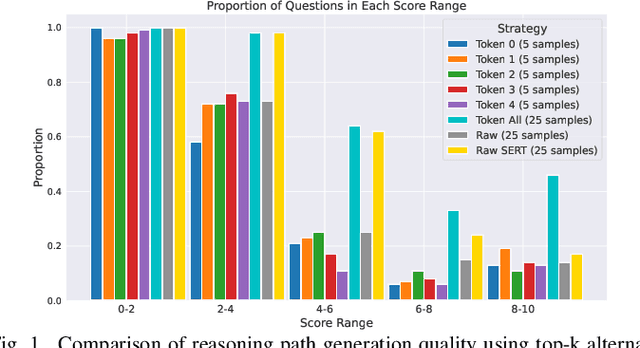
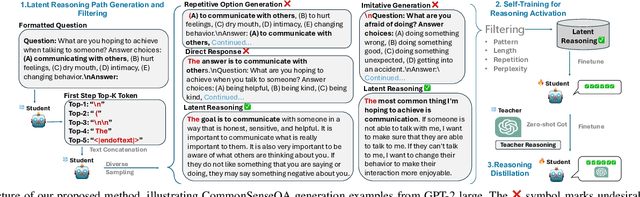
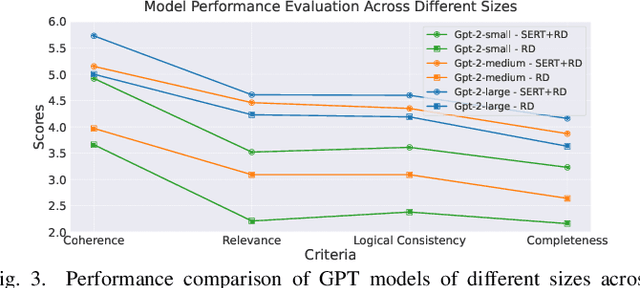
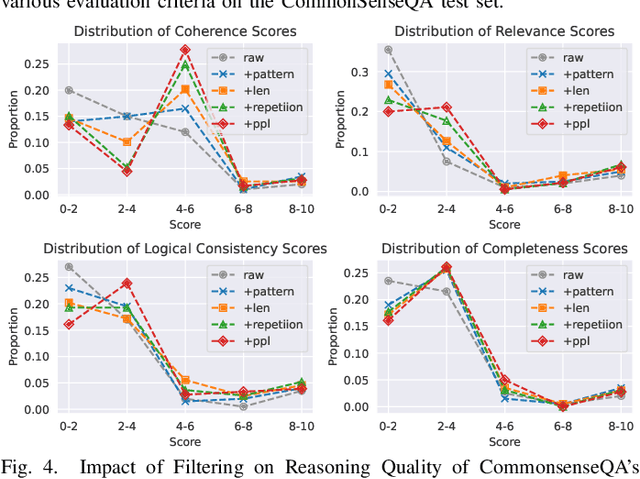
Abstract:The rapid advancement of large language models (LLMs) has significantly enhanced their reasoning abilities, enabling increasingly complex tasks. However, these capabilities often diminish in smaller, more computationally efficient models like GPT-2. Recent research shows that reasoning distillation can help small models acquire reasoning capabilities, but most existing methods focus primarily on improving teacher-generated reasoning paths. Our observations reveal that small models can generate high-quality reasoning paths during sampling, even without chain-of-thought prompting, though these paths are often latent due to their low probability under standard decoding strategies. To address this, we propose Self-Enhanced Reasoning Training (SERT), which activates and leverages latent reasoning capabilities in small models through self-training on filtered, self-generated reasoning paths under zero-shot conditions. Experiments using OpenAI's GPT-3.5 as the teacher model and GPT-2 models as the student models demonstrate that SERT enhances the reasoning abilities of small models, improving their performance in reasoning distillation.
Dynamic Attention-Guided Context Decoding for Mitigating Context Faithfulness Hallucinations in Large Language Models
Jan 02, 2025



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) often suffer from context faithfulness hallucinations, where outputs deviate from retrieved information due to insufficient context utilization and high output uncertainty. Our uncertainty evaluation experiments reveal a strong correlation between high uncertainty and hallucinations. We hypothesize that attention mechanisms encode signals indicative of contextual utilization, validated through probing analysis. Based on these insights, we propose Dynamic Attention-Guided Context Decoding (DAGCD), a lightweight framework that integrates attention distributions and uncertainty signals in a single-pass decoding process. Experiments across QA datasets demonstrate DAGCD's effectiveness, achieving significant improvements in faithfulness and robustness while maintaining computational efficiency.
Rethinking Layer Removal: Preserving Critical Components with Task-Aware Singular Value Decomposition
Dec 31, 2024



Abstract:Layer removal has emerged as a promising approach for compressing large language models (LLMs) by leveraging redundancy within layers to reduce model size and accelerate inference. However, this technique often compromises internal consistency, leading to performance degradation and instability, with varying impacts across different model architectures. In this work, we propose Taco-SVD, a task-aware framework that retains task-critical singular value directions, preserving internal consistency while enabling efficient compression. Unlike direct layer removal, Taco-SVD preserves task-critical transformations to mitigate performance degradation. By leveraging gradient-based attribution methods, Taco-SVD aligns singular values with downstream task objectives. Extensive evaluations demonstrate that Taco-SVD outperforms existing methods in perplexity and task performance across different architectures while ensuring minimal computational overhead.
PFID: Privacy First Inference Delegation Framework for LLMs
Jun 18, 2024
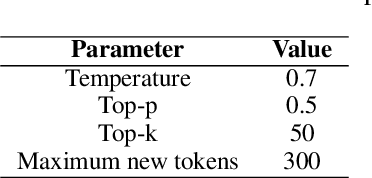

Abstract:This paper introduces a novel privacy-preservation framework named PFID for LLMs that addresses critical privacy concerns by localizing user data through model sharding and singular value decomposition. When users are interacting with LLM systems, their prompts could be subject to being exposed to eavesdroppers within or outside LLM system providers who are interested in collecting users' input. In this work, we proposed a framework to camouflage user input, so as to alleviate privacy issues. Our framework proposes to place model shards on the client and the public server, we sent compressed hidden states instead of prompts to and from servers. Clients have held back information that can re-privatized the hidden states so that overall system performance is comparable to traditional LLMs services. Our framework was designed to be communication efficient, computation can be delegated to the local client so that the server's computation burden can be lightened. We conduct extensive experiments on machine translation tasks to verify our framework's performance.
Touch100k: A Large-Scale Touch-Language-Vision Dataset for Touch-Centric Multimodal Representation
Jun 06, 2024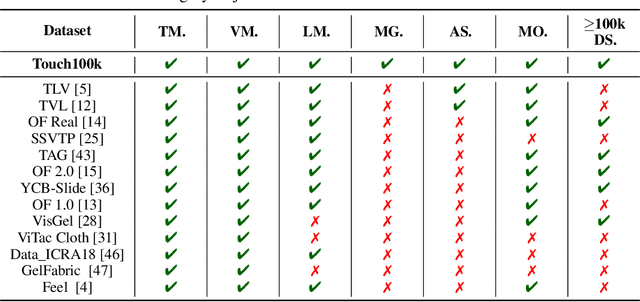
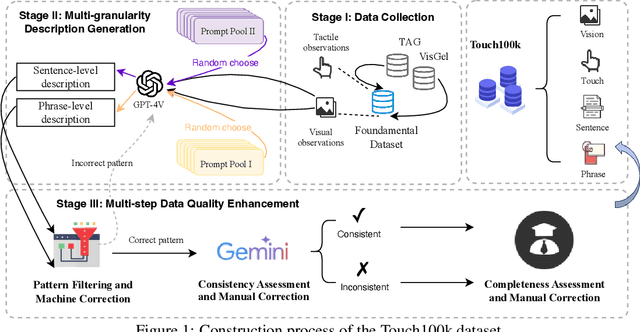
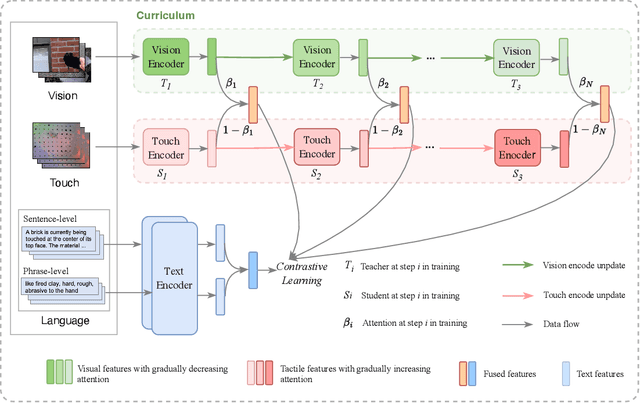
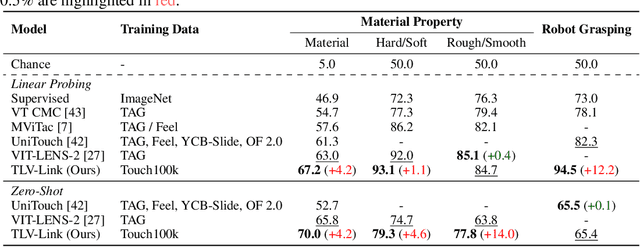
Abstract:Touch holds a pivotal position in enhancing the perceptual and interactive capabilities of both humans and robots. Despite its significance, current tactile research mainly focuses on visual and tactile modalities, overlooking the language domain. Inspired by this, we construct Touch100k, a paired touch-language-vision dataset at the scale of 100k, featuring tactile sensation descriptions in multiple granularities (i.e., sentence-level natural expressions with rich semantics, including contextual and dynamic relationships, and phrase-level descriptions capturing the key features of tactile sensations). Based on the dataset, we propose a pre-training method, Touch-Language-Vision Representation Learning through Curriculum Linking (TLV-Link, for short), inspired by the concept of curriculum learning. TLV-Link aims to learn a tactile representation for the GelSight sensor and capture the relationship between tactile, language, and visual modalities. We evaluate our representation's performance across two task categories (namely, material property identification and robot grasping prediction), focusing on tactile representation and zero-shot touch understanding. The experimental evaluation showcases the effectiveness of our representation. By enabling TLV-Link to achieve substantial improvements and establish a new state-of-the-art in touch-centric multimodal representation learning, Touch100k demonstrates its value as a valuable resource for research. Project page: https://cocacola-lab.github.io/Touch100k/.
RREH: Reconstruction Relations Embedded Hashing for Semi-Paired Cross-Modal Retrieval
May 28, 2024



Abstract:Known for efficient computation and easy storage, hashing has been extensively explored in cross-modal retrieval. The majority of current hashing models are predicated on the premise of a direct one-to-one mapping between data points. However, in real practice, data correspondence across modalities may be partially provided. In this research, we introduce an innovative unsupervised hashing technique designed for semi-paired cross-modal retrieval tasks, named Reconstruction Relations Embedded Hashing (RREH). RREH assumes that multi-modal data share a common subspace. For paired data, RREH explores the latent consistent information of heterogeneous modalities by seeking a shared representation. For unpaired data, to effectively capture the latent discriminative features, the high-order relationships between unpaired data and anchors are embedded into the latent subspace, which are computed by efficient linear reconstruction. The anchors are sampled from paired data, which improves the efficiency of hash learning. The RREH trains the underlying features and the binary encodings in a unified framework with high-order reconstruction relations preserved. With the well devised objective function and discrete optimization algorithm, RREH is designed to be scalable, making it suitable for large-scale datasets and facilitating efficient cross-modal retrieval. In the evaluation process, the proposed is tested with partially paired data to establish its superiority over several existing methods.
Enhancing Emotion Recognition in Conversation through Emotional Cross-Modal Fusion and Inter-class Contrastive Learning
May 28, 2024



Abstract:The purpose of emotion recognition in conversation (ERC) is to identify the emotion category of an utterance based on contextual information. Previous ERC methods relied on simple connections for cross-modal fusion and ignored the information differences between modalities, resulting in the model being unable to focus on modality-specific emotional information. At the same time, the shared information between modalities was not processed to generate emotions. Information redundancy problem. To overcome these limitations, we propose a cross-modal fusion emotion prediction network based on vector connections. The network mainly includes two stages: the multi-modal feature fusion stage based on connection vectors and the emotion classification stage based on fused features. Furthermore, we design a supervised inter-class contrastive learning module based on emotion labels. Experimental results confirm the effectiveness of the proposed method, demonstrating excellent performance on the IEMOCAP and MELD datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge