Haoxiang Shi
Time-Layer Adaptive Alignment for Speaker Similarity in Flow-Matching Based Zero-Shot TTS
Nov 13, 2025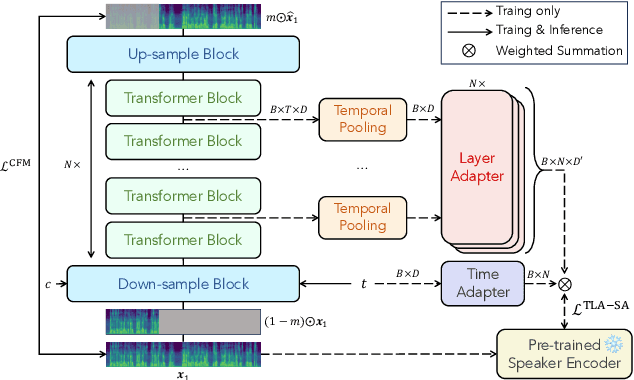
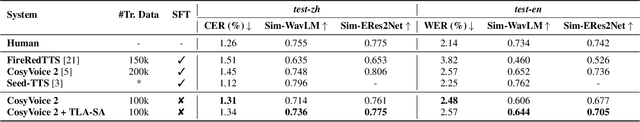
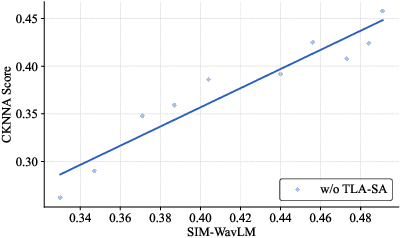
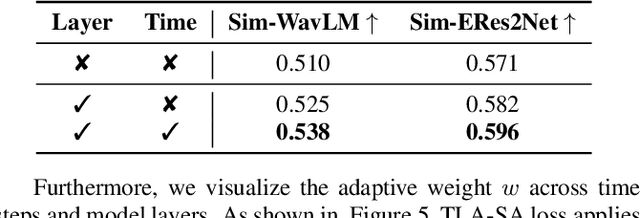
Abstract:Flow-Matching (FM)-based zero-shot text-to-speech (TTS) systems exhibit high-quality speech synthesis and robust generalization capabilities. However, the speaker representation ability of such systems remains underexplored, primarily due to the lack of explicit speaker-specific supervision in the FM framework. To this end, we conduct an empirical analysis of speaker information distribution and reveal its non-uniform allocation across time steps and network layers, underscoring the need for adaptive speaker alignment. Accordingly, we propose Time-Layer Adaptive Speaker Alignment (TLA-SA), a loss that enhances speaker consistency by jointly leveraging temporal and hierarchical variations in speaker information. Experimental results show that TLA-SA significantly improves speaker similarity compared to baseline systems on both research- and industrial-scale datasets and generalizes effectively across diverse model architectures, including decoder-only language models (LM) and FM-based TTS systems free of LM.
Visual-CoG: Stage-Aware Reinforcement Learning with Chain of Guidance for Text-to-Image Generation
Aug 25, 2025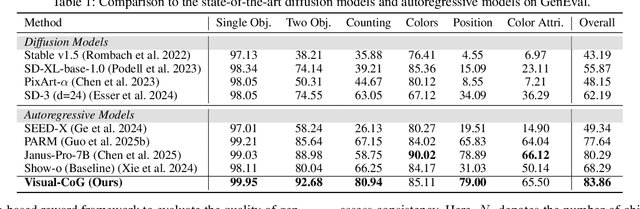
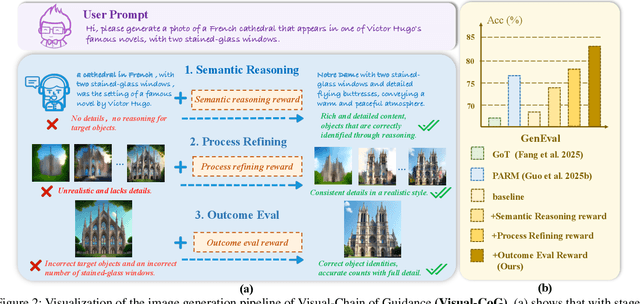
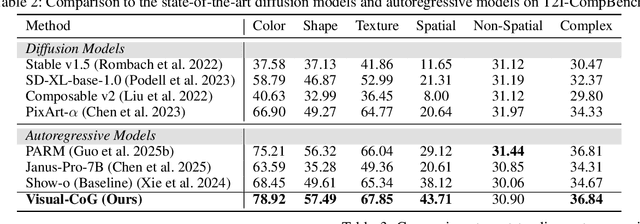
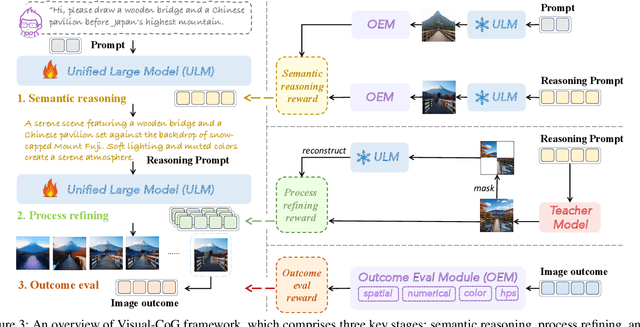
Abstract:Despite the promising progress of recent autoregressive models in text-to-image (T2I) generation, their ability to handle multi-attribute and ambiguous prompts remains limited. To address these limitations, existing works have applied chain-of-thought (CoT) to enable stage-aware visual synthesis and employed reinforcement learning (RL) to improve reasoning capabilities. However, most models provide reward signals only at the end of the generation stage. This monolithic final-only guidance makes it difficult to identify which stages contribute positively to the final outcome and may lead to suboptimal policies. To tackle this issue, we propose a Visual-Chain of Guidance (Visual-CoG) paradigm consisting of three stages: semantic reasoning, process refining, and outcome evaluation, with stage-aware rewards providing immediate guidance throughout the image generation pipeline. We further construct a visual cognition benchmark, VisCog-Bench, which comprises four subtasks to evaluate the effectiveness of semantic reasoning. Comprehensive evaluations on GenEval, T2I-CompBench, and the proposed VisCog-Bench show improvements of 15%, 5%, and 19%, respectively, demonstrating the superior performance of the proposed Visual-CoG. We will release all the resources soon.
An Empirical Study of Many-to-Many Summarization with Large Language Models
May 19, 2025
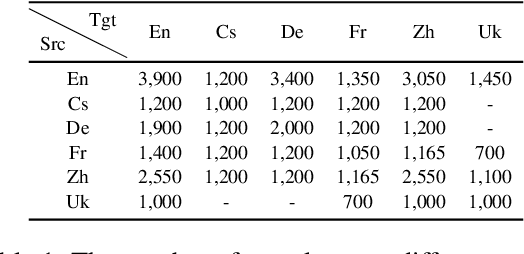
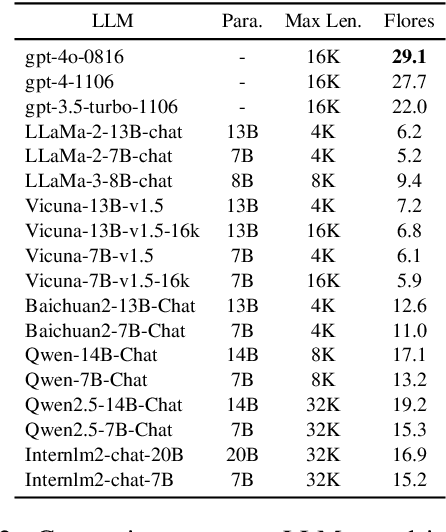
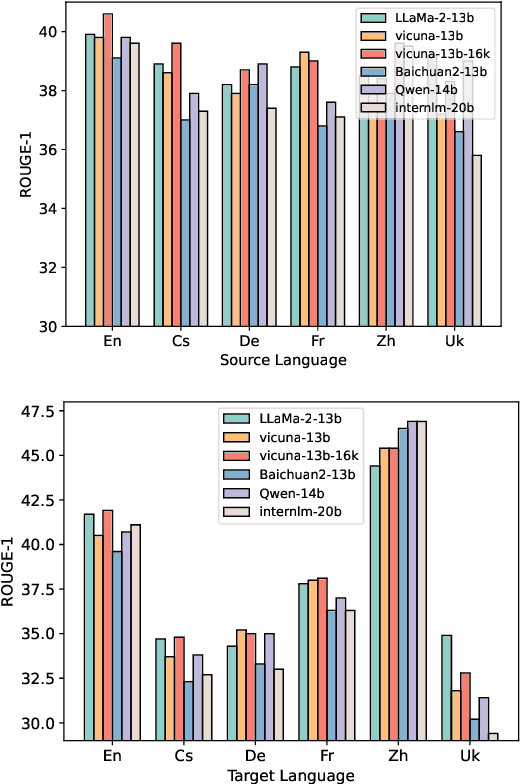
Abstract:Many-to-many summarization (M2MS) aims to process documents in any language and generate the corresponding summaries also in any language. Recently, large language models (LLMs) have shown strong multi-lingual abilities, giving them the potential to perform M2MS in real applications. This work presents a systematic empirical study on LLMs' M2MS ability. Specifically, we first reorganize M2MS data based on eight previous domain-specific datasets. The reorganized data contains 47.8K samples spanning five domains and six languages, which could be used to train and evaluate LLMs. Then, we benchmark 18 LLMs in a zero-shot manner and an instruction-tuning manner. Fine-tuned traditional models (e.g., mBART) are also conducted for comparisons. Our experiments reveal that, zero-shot LLMs achieve competitive results with fine-tuned traditional models. After instruct-tuning, open-source LLMs can significantly improve their M2MS ability, and outperform zero-shot LLMs (including GPT-4) in terms of automatic evaluations. In addition, we demonstrate that this task-specific improvement does not sacrifice the LLMs' general task-solving abilities. However, as revealed by our human evaluation, LLMs still face the factuality issue, and the instruction tuning might intensify the issue. Thus, how to control factual errors becomes the key when building LLM summarizers in real applications, and is worth noting in future research.
ESARM: 3D Emotional Speech-to-Animation via Reward Model from Automatically-Ranked Demonstrations
Nov 20, 2024Abstract:This paper proposes a novel 3D speech-to-animation (STA) generation framework designed to address the shortcomings of existing models in producing diverse and emotionally resonant animations. Current STA models often generate animations that lack emotional depth and variety, failing to align with human expectations. To overcome these limitations, we introduce a novel STA model coupled with a reward model. This combination enables the decoupling of emotion and content under audio conditions through a cross-coupling training approach. Additionally, we develop a training methodology that leverages automatic quality evaluation of generated facial animations to guide the reinforcement learning process. This methodology encourages the STA model to explore a broader range of possibilities, resulting in the generation of diverse and emotionally expressive facial animations of superior quality. We conduct extensive empirical experiments on a benchmark dataset, and the results validate the effectiveness of our proposed framework in generating high-quality, emotionally rich 3D animations that are better aligned with human preferences.
AlignCap: Aligning Speech Emotion Captioning to Human Preferences
Oct 24, 2024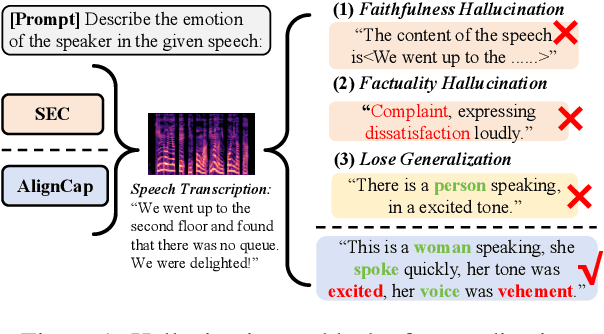

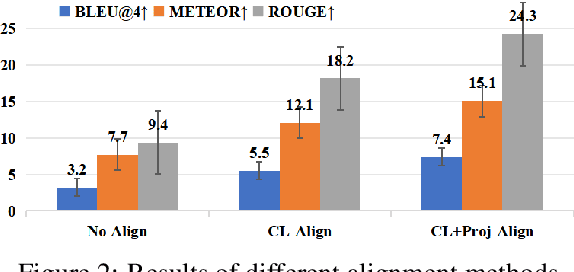
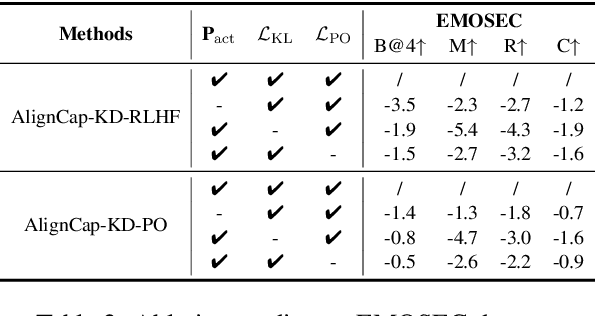
Abstract:Speech Emotion Captioning (SEC) has gradually become an active research task. The emotional content conveyed through human speech are often complex, and classifying them into fixed categories may not be enough to fully capture speech emotions. Describing speech emotions through natural language may be a more effective approach. However, existing SEC methods often produce hallucinations and lose generalization on unseen speech. To overcome these problems, we propose AlignCap, which Aligning Speech Emotion Captioning to Human Preferences based on large language model (LLM) with two properties: 1) Speech-Text Alignment, which minimizing the divergence between the LLM's response prediction distributions for speech and text inputs using knowledge distillation (KD) Regularization. 2) Human Preference Alignment, where we design Preference Optimization (PO) Regularization to eliminate factuality and faithfulness hallucinations. We also extract emotional clues as a prompt for enriching fine-grained information under KD-Regularization. Experiments demonstrate that AlignCap presents stronger performance to other state-of-the-art methods on Zero-shot SEC task.
Enhancing Emotion Recognition in Conversation through Emotional Cross-Modal Fusion and Inter-class Contrastive Learning
May 28, 2024



Abstract:The purpose of emotion recognition in conversation (ERC) is to identify the emotion category of an utterance based on contextual information. Previous ERC methods relied on simple connections for cross-modal fusion and ignored the information differences between modalities, resulting in the model being unable to focus on modality-specific emotional information. At the same time, the shared information between modalities was not processed to generate emotions. Information redundancy problem. To overcome these limitations, we propose a cross-modal fusion emotion prediction network based on vector connections. The network mainly includes two stages: the multi-modal feature fusion stage based on connection vectors and the emotion classification stage based on fused features. Furthermore, we design a supervised inter-class contrastive learning module based on emotion labels. Experimental results confirm the effectiveness of the proposed method, demonstrating excellent performance on the IEMOCAP and MELD datasets.
RREH: Reconstruction Relations Embedded Hashing for Semi-Paired Cross-Modal Retrieval
May 28, 2024



Abstract:Known for efficient computation and easy storage, hashing has been extensively explored in cross-modal retrieval. The majority of current hashing models are predicated on the premise of a direct one-to-one mapping between data points. However, in real practice, data correspondence across modalities may be partially provided. In this research, we introduce an innovative unsupervised hashing technique designed for semi-paired cross-modal retrieval tasks, named Reconstruction Relations Embedded Hashing (RREH). RREH assumes that multi-modal data share a common subspace. For paired data, RREH explores the latent consistent information of heterogeneous modalities by seeking a shared representation. For unpaired data, to effectively capture the latent discriminative features, the high-order relationships between unpaired data and anchors are embedded into the latent subspace, which are computed by efficient linear reconstruction. The anchors are sampled from paired data, which improves the efficiency of hash learning. The RREH trains the underlying features and the binary encodings in a unified framework with high-order reconstruction relations preserved. With the well devised objective function and discrete optimization algorithm, RREH is designed to be scalable, making it suitable for large-scale datasets and facilitating efficient cross-modal retrieval. In the evaluation process, the proposed is tested with partially paired data to establish its superiority over several existing methods.
RSET: Remapping-based Sorting Method for Emotion Transfer Speech Synthesis
May 27, 2024



Abstract:Although current Text-To-Speech (TTS) models are able to generate high-quality speech samples, there are still challenges in developing emotion intensity controllable TTS. Most existing TTS models achieve emotion intensity control by extracting intensity information from reference speeches. Unfortunately, limited by the lack of modeling for intra-class emotion intensity and the model's information decoupling capability, the generated speech cannot achieve fine-grained emotion intensity control and suffers from information leakage issues. In this paper, we propose an emotion transfer TTS model, which defines a remapping-based sorting method to model intra-class relative intensity information, combined with Mutual Information (MI) to decouple speaker and emotion information, and synthesizes expressive speeches with perceptible intensity differences. Experiments show that our model achieves fine-grained emotion control while preserving speaker information.
CT-Eval: Benchmarking Chinese Text-to-Table Performance in Large Language Models
May 20, 2024Abstract:Text-to-Table aims to generate structured tables to convey the key information from unstructured documents. Existing text-to-table datasets are typically oriented English, limiting the research in non-English languages. Meanwhile, the emergence of large language models (LLMs) has shown great success as general task solvers in multi-lingual settings (e.g., ChatGPT), theoretically enabling text-to-table in other languages. In this paper, we propose a Chinese text-to-table dataset, CT-Eval, to benchmark LLMs on this task. Our preliminary analysis of English text-to-table datasets highlights two key factors for dataset construction: data diversity and data hallucination. Inspired by this, the CT-Eval dataset selects a popular Chinese multidisciplinary online encyclopedia as the source and covers 28 domains to ensure data diversity. To minimize data hallucination, we first train an LLM to judge and filter out the task samples with hallucination, then employ human annotators to clean the hallucinations in the validation and testing sets. After this process, CT-Eval contains 88.6K task samples. Using CT-Eval, we evaluate the performance of open-source and closed-source LLMs. Our results reveal that zero-shot LLMs (including GPT-4) still have a significant performance gap compared with human judgment. Furthermore, after fine-tuning, open-source LLMs can significantly improve their text-to-table ability, outperforming GPT-4 by a large margin. In short, CT-Eval not only helps researchers evaluate and quickly understand the Chinese text-to-table ability of existing LLMs but also serves as a valuable resource to significantly improve the text-to-table performance of LLMs.
EM-TTS: Efficiently Trained Low-Resource Mongolian Lightweight Text-to-Speech
Mar 17, 2024



Abstract:Recently, deep learning-based Text-to-Speech (TTS) systems have achieved high-quality speech synthesis results. Recurrent neural networks have become a standard modeling technique for sequential data in TTS systems and are widely used. However, training a TTS model which includes RNN components requires powerful GPU performance and takes a long time. In contrast, CNN-based sequence synthesis techniques can significantly reduce the parameters and training time of a TTS model while guaranteeing a certain performance due to their high parallelism, which alleviate these economic costs of training. In this paper, we propose a lightweight TTS system based on deep convolutional neural networks, which is a two-stage training end-to-end TTS model and does not employ any recurrent units. Our model consists of two stages: Text2Spectrum and SSRN. The former is used to encode phonemes into a coarse mel spectrogram and the latter is used to synthesize the complete spectrum from the coarse mel spectrogram. Meanwhile, we improve the robustness of our model by a series of data augmentations, such as noise suppression, time warping, frequency masking and time masking, for solving the low resource mongolian problem. Experiments show that our model can reduce the training time and parameters while ensuring the quality and naturalness of the synthesized speech compared to using mainstream TTS models. Our method uses NCMMSC2022-MTTSC Challenge dataset for validation, which significantly reduces training time while maintaining a certain accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge