Morgan R. Frank
AI-exposed jobs deteriorated before ChatGPT
Jan 05, 2026Abstract:Public debate links worsening job prospects for AI-exposed occupations to the release of ChatGPT in late 2022. Using monthly U.S. unemployment insurance records, we measure occupation- and location-specific unemployment risk and find that risk rose in AI-exposed occupations beginning in early 2022, months before ChatGPT. Analyzing millions of LinkedIn profiles, we show that graduate cohorts from 2021 onward entered AI-exposed jobs at lower rates than earlier cohorts, with gaps opening before late 2022. Finally, from millions of university syllabi, we find that graduates taking more AI-exposed curricula had higher first-job pay and shorter job searches after ChatGPT. Together, these results point to forces pre-dating generative AI and to the ongoing value of LLM-relevant education.
A national longitudinal dataset of skills taught in U.S. higher education curricula
Apr 19, 2024Abstract:Higher education plays a critical role in driving an innovative economy by equipping students with knowledge and skills demanded by the workforce. While researchers and practitioners have developed data systems to track detailed occupational skills, such as those established by the U.S. Department of Labor (DOL), much less effort has been made to document skill development in higher education at a similar granularity. Here, we fill this gap by presenting a longitudinal dataset of skills inferred from over three million course syllabi taught at nearly three thousand U.S. higher education institutions. To construct this dataset, we apply natural language processing to extract from course descriptions detailed workplace activities (DWAs) used by the DOL to describe occupations. We then aggregate these DWAs to create skill profiles for institutions and academic majors. Our dataset offers a large-scale representation of college-educated workers and their role in the economy. To showcase the utility of this dataset, we use it to 1) compare the similarity of skills taught and skills in the workforce according to the US Bureau of Labor Statistics, 2) estimate gender differences in acquired skills based on enrollment data, 3) depict temporal trends in the skills taught in social science curricula, and 4) connect college majors' skill distinctiveness to salary differences of graduates. Overall, this dataset can enable new research on the source of skills in the context of workforce development and provide actionable insights for shaping the future of higher education to meet evolving labor demands especially in the face of new technologies.
Brief for the Canada House of Commons Study on the Implications of Artificial Intelligence Technologies for the Canadian Labor Force: Generative Artificial Intelligence Shatters Models of AI and Labor
Nov 06, 2023Abstract:Exciting advances in generative artificial intelligence (AI) have sparked concern for jobs, education, productivity, and the future of work. As with past technologies, generative AI may not lead to mass unemployment. But, unlike past technologies, generative AI is creative, cognitive, and potentially ubiquitous which makes the usual assumptions of automation predictions ill-suited for today. Existing projections suggest that generative AI will impact workers in occupations that were previously considered immune to automation. As AI's full set of capabilities and applications emerge, policy makers should promote workers' career adaptability. This goal requires improved data on job separations and unemployment by locality and job titles in order to identify early-indicators for the workers facing labor disruption. Further, prudent policy should incentivize education programs to accommodate learning with AI as a tool while preparing students for the demands of the future of work.
The Resume Paradox: Greater Language Differences, Smaller Pay Gaps
Jul 17, 2023



Abstract:Over the past decade, the gender pay gap has remained steady with women earning 84 cents for every dollar earned by men on average. Many studies explain this gap through demand-side bias in the labor market represented through employers' job postings. However, few studies analyze potential bias from the worker supply-side. Here, we analyze the language in millions of US workers' resumes to investigate how differences in workers' self-representation by gender compare to differences in earnings. Across US occupations, language differences between male and female resumes correspond to 11% of the variation in gender pay gap. This suggests that females' resumes that are semantically similar to males' resumes may have greater wage parity. However, surprisingly, occupations with greater language differences between male and female resumes have lower gender pay gaps. A doubling of the language difference between female and male resumes results in an annual wage increase of $2,797 for the average female worker. This result holds with controls for gender-biases of resume text and we find that per-word bias poorly describes the variance in wage gap. The results demonstrate that textual data and self-representation are valuable factors for improving worker representations and understanding employment inequities.
Art and the science of generative AI: A deeper dive
Jun 07, 2023Abstract:A new class of tools, colloquially called generative AI, can produce high-quality artistic media for visual arts, concept art, music, fiction, literature, video, and animation. The generative capabilities of these tools are likely to fundamentally alter the creative processes by which creators formulate ideas and put them into production. As creativity is reimagined, so too may be many sectors of society. Understanding the impact of generative AI - and making policy decisions around it - requires new interdisciplinary scientific inquiry into culture, economics, law, algorithms, and the interaction of technology and creativity. We argue that generative AI is not the harbinger of art's demise, but rather is a new medium with its own distinct affordances. In this vein, we consider the impacts of this new medium on creators across four themes: aesthetics and culture, legal questions of ownership and credit, the future of creative work, and impacts on the contemporary media ecosystem. Across these themes, we highlight key research questions and directions to inform policy and beneficial uses of the technology.
Exposure of occupations to technologies of the fourth industrial revolution
Oct 25, 2021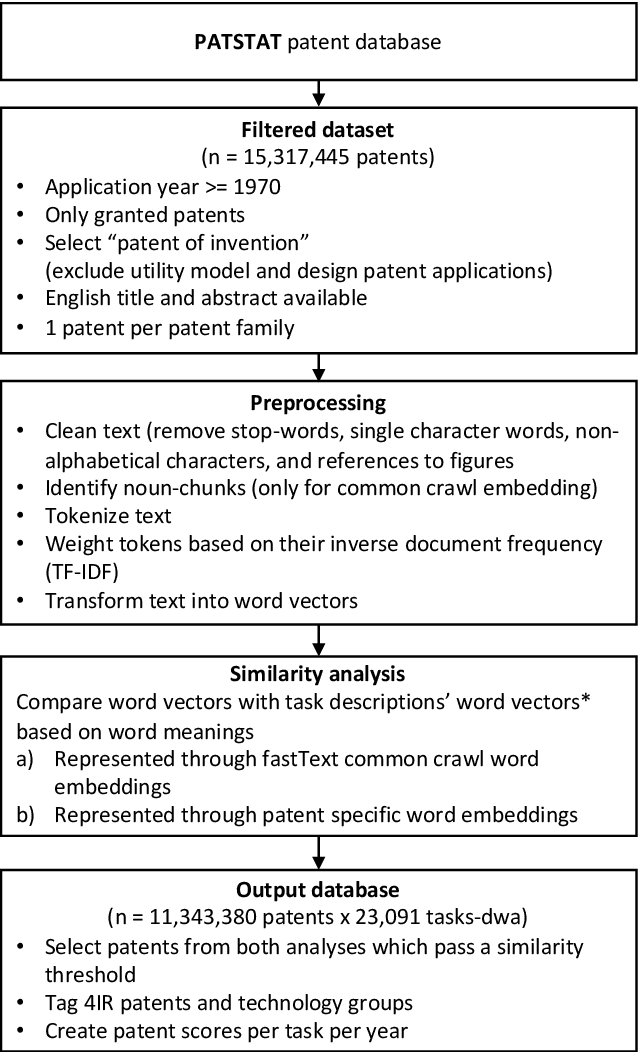
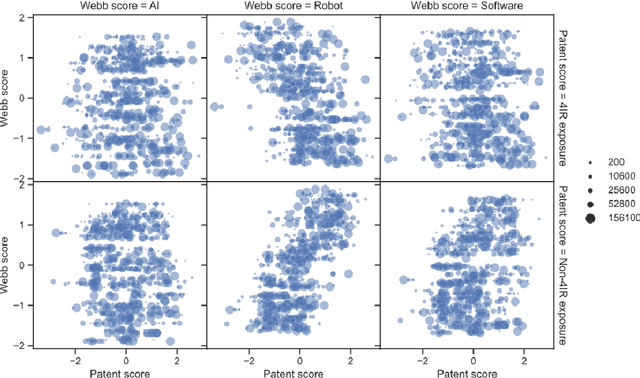
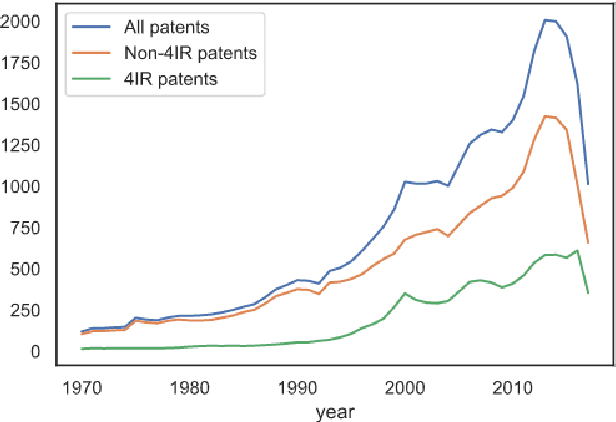

Abstract:The fourth industrial revolution (4IR) is likely to have a substantial impact on the economy. Companies need to build up capabilities to implement new technologies, and automation may make some occupations obsolete. However, where, when, and how the change will happen remain to be determined. Robust empirical indicators of technological progress linked to occupations can help to illuminate this change. With this aim, we provide such an indicator based on patent data. Using natural language processing, we calculate patent exposure scores for more than 900 occupations, which represent the technological progress related to them. To provide a lens on the impact of the 4IR, we differentiate between traditional and 4IR patent exposure. Our method differs from previous approaches in that it both accounts for the diversity of task-level patent exposures within an occupation and reflects work activities more accurately. We find that exposure to 4IR patents differs from traditional patent exposure. Manual tasks, and accordingly occupations such as construction and production, are exposed mainly to traditional (non-4IR) patents but have low exposure to 4IR patents. The analysis suggests that 4IR technologies may have a negative impact on job growth; this impact appears 10 to 20 years after patent filing. Further, we compared the 4IR exposure to other automation and AI exposure scores. Whereas many measures refer to theoretical automation potential, our patent-based indicator reflects actual technology diffusion. Our work not only allows analyses of the impact of 4IR technologies as a whole, but also provides exposure scores for more than 300 technology fields, such as AI and smart office technologies. Finally, the work provides a general mapping of patents to tasks and occupations, which enables future researchers to construct individual exposure measures.
Industrial Topics in Urban Labor System
Sep 18, 2020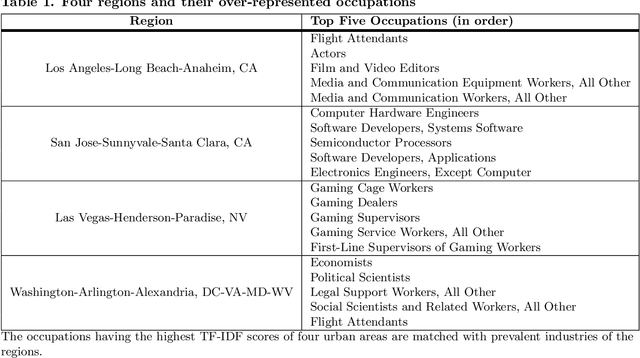
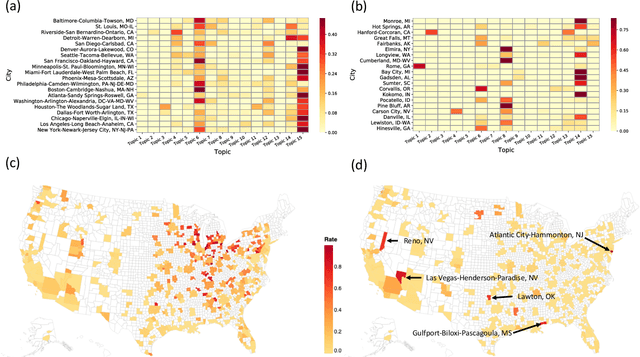
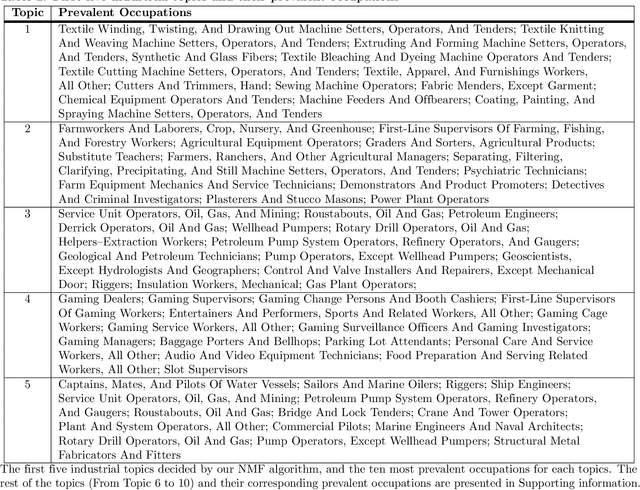
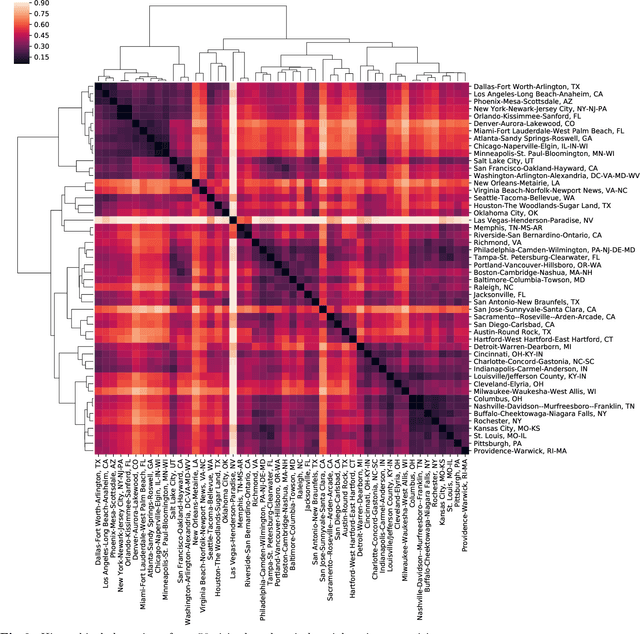
Abstract:Categorization is an essential component for us to understand the world for ourselves and to communicate it collectively. It is therefore important to recognize that classification system are not necessarily static, especially for economic systems, and even more so in urban areas where most innovation takes place and is implemented. Out-of-date classification systems would potentially limit further understanding of the current economy because things constantly change. Here, we develop an occupation-based classification system for the US labor economy, called industrial topics, that satisfy adaptability and representability. By leveraging the distributions of occupations across the US urban areas, we identify industrial topics - clusters of occupations based on their co-existence pattern. Industrial topics indicate the mechanisms under the systematic allocation of different occupations. Considering the densely connected occupations as an industrial topic, our approach characterizes regional economies by their topical composition. Unlike the existing survey-based top-down approach, our method provides timely information about the underlying structure of the regional economy, which is critical for policymakers and business leaders, especially in our fast-changing economy.
Generalized Word Shift Graphs: A Method for Visualizing and Explaining Pairwise Comparisons Between Texts
Aug 05, 2020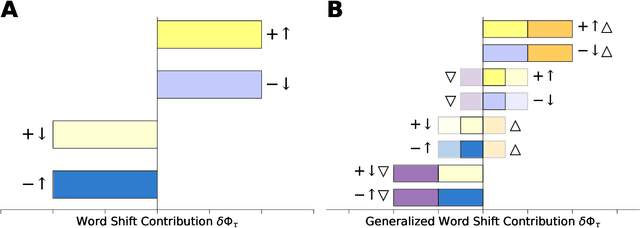
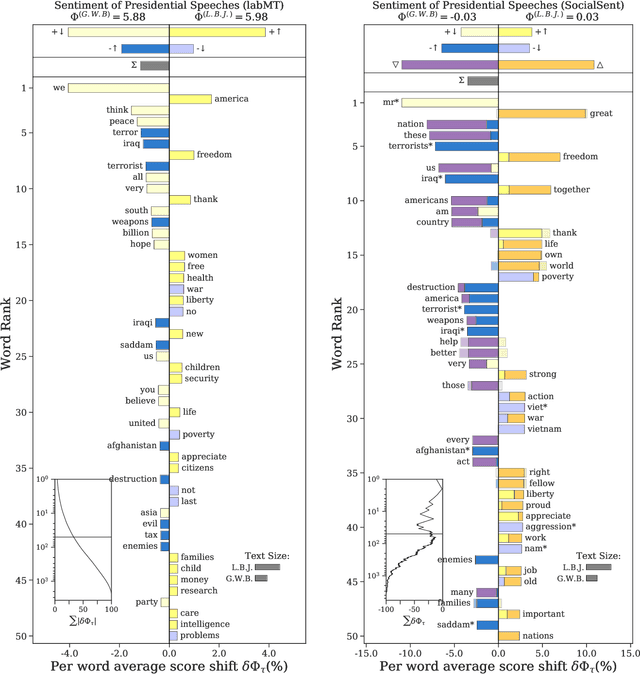
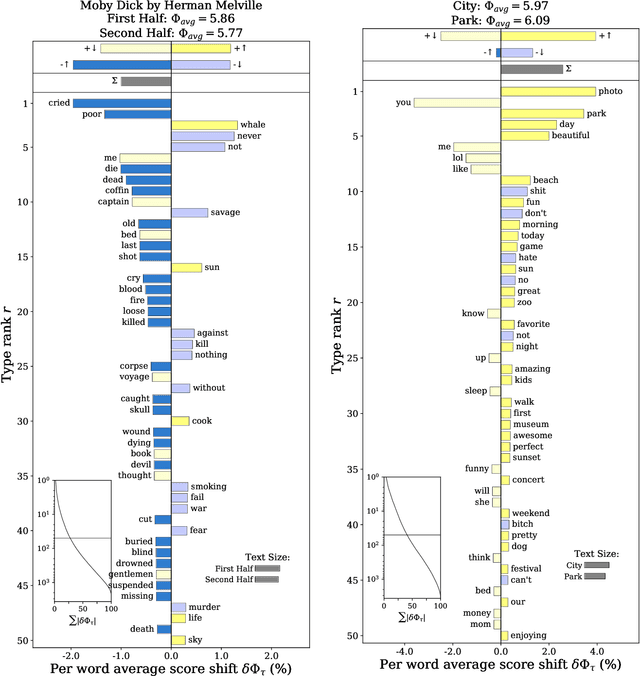
Abstract:A common task in computational text analyses is to quantify how two corpora differ according to a measurement like word frequency, sentiment, or information content. However, collapsing the texts' rich stories into a single number is often conceptually perilous, and it is difficult to confidently interpret interesting or unexpected textual patterns without looming concerns about data artifacts or measurement validity. To better capture fine-grained differences between texts, we introduce generalized word shift graphs, visualizations which yield a meaningful and interpretable summary of how individual words contribute to the variation between two texts for any measure that can be formulated as a weighted average. We show that this framework naturally encompasses many of the most commonly used approaches for comparing texts, including relative frequencies, dictionary scores, and entropy-based measures like the Kullback-Leibler and Jensen-Shannon divergences. Through several case studies, we demonstrate how generalized word shift graphs can be flexibly applied across domains for diagnostic investigation, hypothesis generation, and substantive interpretation. By providing a detailed lens into textual shifts between corpora, generalized word shift graphs help computational social scientists, digital humanists, and other text analysis practitioners fashion more robust scientific narratives.
Human language reveals a universal positivity bias
Jun 15, 2014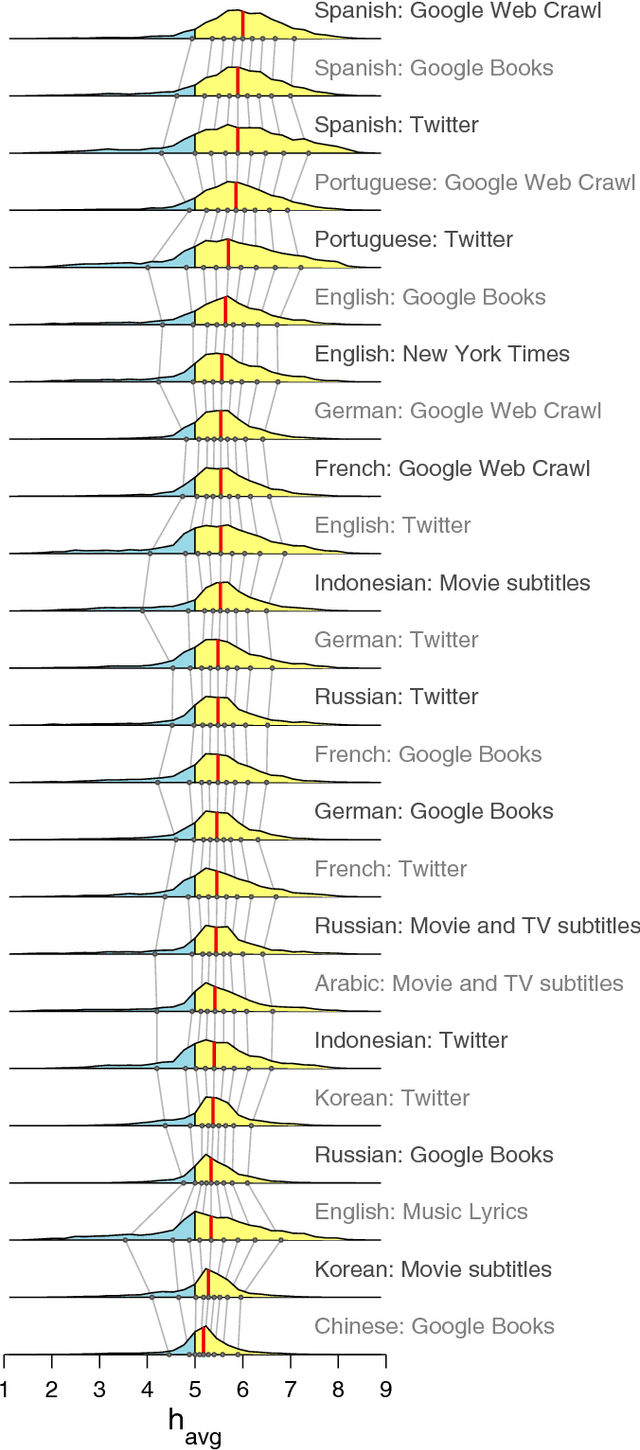
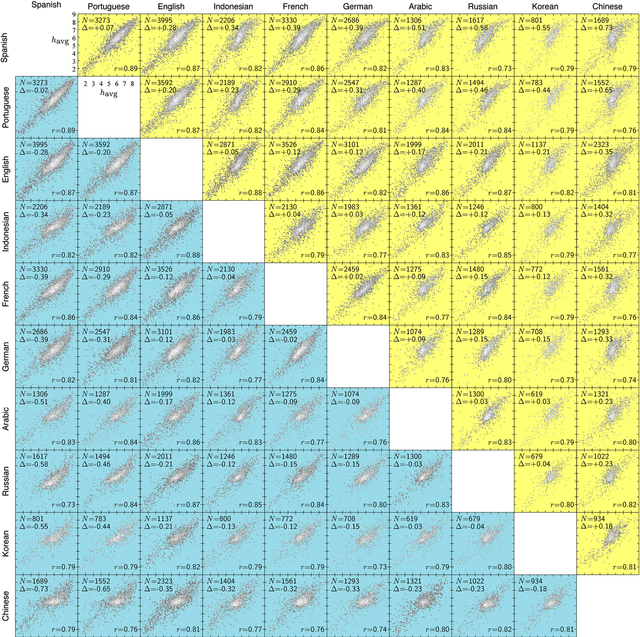
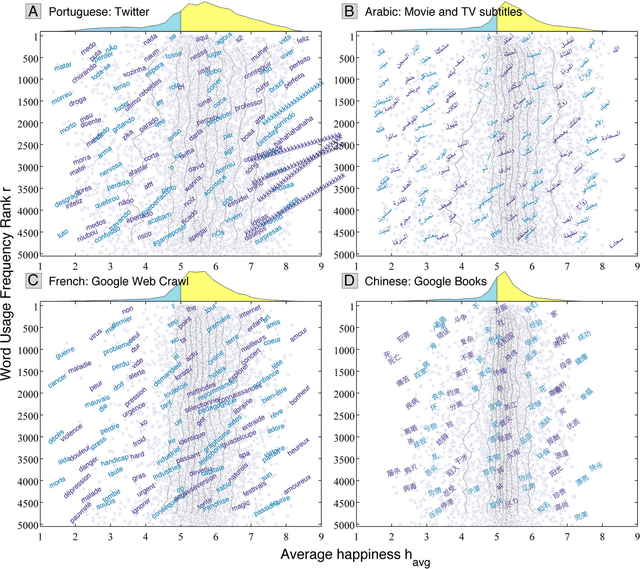
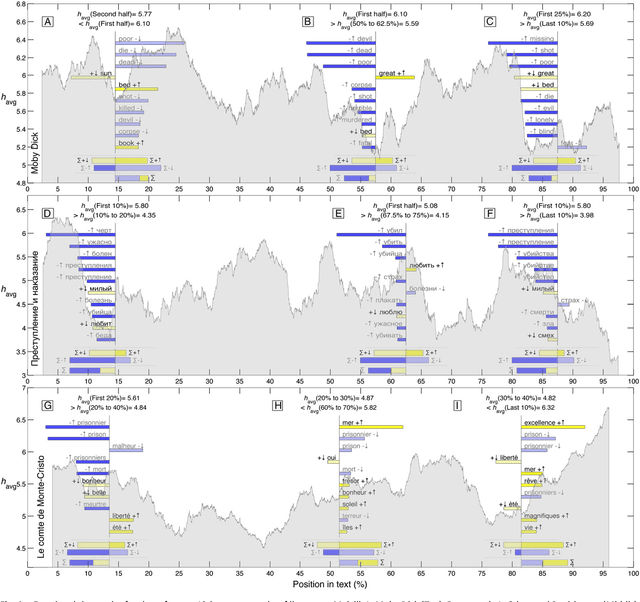
Abstract:Using human evaluation of 100,000 words spread across 24 corpora in 10 languages diverse in origin and culture, we present evidence of a deep imprint of human sociality in language, observing that (1) the words of natural human language possess a universal positivity bias; (2) the estimated emotional content of words is consistent between languages under translation; and (3) this positivity bias is strongly independent of frequency of word usage. Alongside these general regularities, we describe inter-language variations in the emotional spectrum of languages which allow us to rank corpora. We also show how our word evaluations can be used to construct physical-like instruments for both real-time and offline measurement of the emotional content of large-scale texts.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge