Matthew Groh
A Global Atlas of Digital Dermatology to Map Innovation and Disparities
Dec 27, 2025Abstract:The adoption of artificial intelligence in dermatology promises democratized access to healthcare, but model reliability depends on the quality and comprehensiveness of the data fueling these models. Despite rapid growth in publicly available dermatology images, the field lacks quantitative key performance indicators to measure whether new datasets expand clinical coverage or merely replicate what is already known. Here we present SkinMap, a multi-modal framework for the first comprehensive audit of the field's entire data basis. We unify the publicly available dermatology datasets into a single, queryable semantic atlas comprising more than 1.1 million images of skin conditions and quantify (i) informational novelty over time, (ii) dataset redundancy, and (iii) representation gaps across demographics and diagnoses. Despite exponential growth in dataset sizes, informational novelty across time has somewhat plateaued: Some clusters, such as common neoplasms on fair skin, are densely populated, while underrepresented skin types and many rare diseases remain unaddressed. We further identify structural gaps in coverage: Darker skin tones (Fitzpatrick V-VI) constitute only 5.8% of images and pediatric patients only 3.0%, while many rare diseases and phenotype combinations remain sparsely represented. SkinMap provides infrastructure to measure blind spots and steer strategic data acquisition toward undercovered regions of clinical space.
Explainable AI as a Double-Edged Sword in Dermatology: The Impact on Clinicians versus The Public
Dec 14, 2025Abstract:Artificial intelligence (AI) is increasingly permeating healthcare, from physician assistants to consumer applications. Since AI algorithm's opacity challenges human interaction, explainable AI (XAI) addresses this by providing AI decision-making insight, but evidence suggests XAI can paradoxically induce over-reliance or bias. We present results from two large-scale experiments (623 lay people; 153 primary care physicians, PCPs) combining a fairness-based diagnosis AI model and different XAI explanations to examine how XAI assistance, particularly multimodal large language models (LLMs), influences diagnostic performance. AI assistance balanced across skin tones improved accuracy and reduced diagnostic disparities. However, LLM explanations yielded divergent effects: lay users showed higher automation bias - accuracy boosted when AI was correct, reduced when AI erred - while experienced PCPs remained resilient, benefiting irrespective of AI accuracy. Presenting AI suggestions first also led to worse outcomes when the AI was incorrect for both groups. These findings highlight XAI's varying impact based on expertise and timing, underscoring LLMs as a "double-edged sword" in medical AI and informing future human-AI collaborative system design.
When Large Language Models are Reliable for Judging Empathic Communication
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) excel at generating empathic responses in text-based conversations. But, how reliably do they judge the nuances of empathic communication? We investigate this question by comparing how experts, crowdworkers, and LLMs annotate empathic communication across four evaluative frameworks drawn from psychology, natural language processing, and communications applied to 200 real-world conversations where one speaker shares a personal problem and the other offers support. Drawing on 3,150 expert annotations, 2,844 crowd annotations, and 3,150 LLM annotations, we assess inter-rater reliability between these three annotator groups. We find that expert agreement is high but varies across the frameworks' sub-components depending on their clarity, complexity, and subjectivity. We show that expert agreement offers a more informative benchmark for contextualizing LLM performance than standard classification metrics. Across all four frameworks, LLMs consistently approach this expert level benchmark and exceed the reliability of crowdworkers. These results demonstrate how LLMs, when validated on specific tasks with appropriate benchmarks, can support transparency and oversight in emotionally sensitive applications including their use as conversational companions.
CleanPatrick: A Benchmark for Image Data Cleaning
May 16, 2025Abstract:Robust machine learning depends on clean data, yet current image data cleaning benchmarks rely on synthetic noise or narrow human studies, limiting comparison and real-world relevance. We introduce CleanPatrick, the first large-scale benchmark for data cleaning in the image domain, built upon the publicly available Fitzpatrick17k dermatology dataset. We collect 496,377 binary annotations from 933 medical crowd workers, identify off-topic samples (4%), near-duplicates (21%), and label errors (22%), and employ an aggregation model inspired by item-response theory followed by expert review to derive high-quality ground truth. CleanPatrick formalizes issue detection as a ranking task and adopts typical ranking metrics mirroring real audit workflows. Benchmarking classical anomaly detectors, perceptual hashing, SSIM, Confident Learning, NoiseRank, and SelfClean, we find that, on CleanPatrick, self-supervised representations excel at near-duplicate detection, classical methods achieve competitive off-topic detection under constrained review budgets, and label-error detection remains an open challenge for fine-grained medical classification. By releasing both the dataset and the evaluation framework, CleanPatrick enables a systematic comparison of image-cleaning strategies and paves the way for more reliable data-centric artificial intelligence.
Characterizing Photorealism and Artifacts in Diffusion Model-Generated Images
Feb 17, 2025Abstract:Diffusion model-generated images can appear indistinguishable from authentic photographs, but these images often contain artifacts and implausibilities that reveal their AI-generated provenance. Given the challenge to public trust in media posed by photorealistic AI-generated images, we conducted a large-scale experiment measuring human detection accuracy on 450 diffusion-model generated images and 149 real images. Based on collecting 749,828 observations and 34,675 comments from 50,444 participants, we find that scene complexity of an image, artifact types within an image, display time of an image, and human curation of AI-generated images all play significant roles in how accurately people distinguish real from AI-generated images. Additionally, we propose a taxonomy characterizing artifacts often appearing in images generated by diffusion models. Our empirical observations and taxonomy offer nuanced insights into the capabilities and limitations of diffusion models to generate photorealistic images in 2024.
Deceptive AI systems that give explanations are more convincing than honest AI systems and can amplify belief in misinformation
Jul 31, 2024Abstract:Advanced Artificial Intelligence (AI) systems, specifically large language models (LLMs), have the capability to generate not just misinformation, but also deceptive explanations that can justify and propagate false information and erode trust in the truth. We examined the impact of deceptive AI generated explanations on individuals' beliefs in a pre-registered online experiment with 23,840 observations from 1,192 participants. We found that in addition to being more persuasive than accurate and honest explanations, AI-generated deceptive explanations can significantly amplify belief in false news headlines and undermine true ones as compared to AI systems that simply classify the headline incorrectly as being true/false. Moreover, our results show that personal factors such as cognitive reflection and trust in AI do not necessarily protect individuals from these effects caused by deceptive AI generated explanations. Instead, our results show that the logical validity of AI generated deceptive explanations, that is whether the explanation has a causal effect on the truthfulness of the AI's classification, plays a critical role in countering their persuasiveness - with logically invalid explanations being deemed less credible. This underscores the importance of teaching logical reasoning and critical thinking skills to identify logically invalid arguments, fostering greater resilience against advanced AI-driven misinformation.
How to Distinguish AI-Generated Images from Authentic Photographs
Jun 12, 2024Abstract:The high level of photorealism in state-of-the-art diffusion models like Midjourney, Stable Diffusion, and Firefly makes it difficult for untrained humans to distinguish between real photographs and AI-generated images. To address this problem, we designed a guide to help readers develop a more critical eye toward identifying artifacts, inconsistencies, and implausibilities that often appear in AI-generated images. The guide is organized into five categories of artifacts and implausibilities: anatomical, stylistic, functional, violations of physics, and sociocultural. For this guide, we generated 138 images with diffusion models, curated 9 images from social media, and curated 42 real photographs. These images showcase the kinds of cues that prompt suspicion towards the possibility an image is AI-generated and why it is often difficult to draw conclusions about an image's provenance without any context beyond the pixels in an image. Human-perceptible artifacts are not always present in AI-generated images, but this guide reveals artifacts and implausibilities that often emerge. By drawing attention to these kinds of artifacts and implausibilities, we aim to better equip people to distinguish AI-generated images from real photographs in the future.
Towards Reliable Dermatology Evaluation Benchmarks
Sep 13, 2023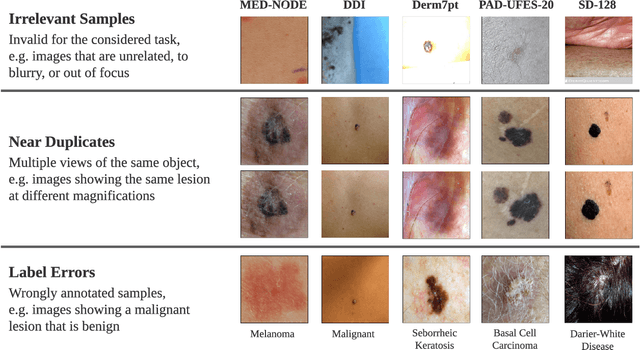
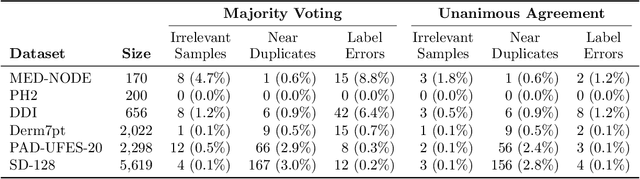
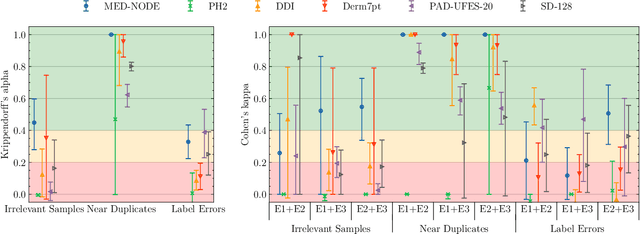
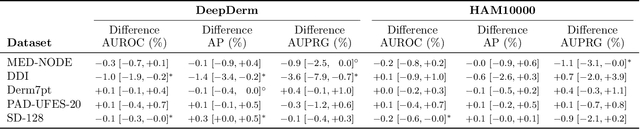
Abstract:Benchmark datasets for digital dermatology unwittingly contain inaccuracies that reduce trust in model performance estimates. We propose a resource-efficient data cleaning protocol to identify issues that escaped previous curation. The protocol leverages an existing algorithmic cleaning strategy and is followed by a confirmation process terminated by an intuitive stopping criterion. Based on confirmation by multiple dermatologists, we remove irrelevant samples and near duplicates and estimate the percentage of label errors in six dermatology image datasets for model evaluation promoted by the International Skin Imaging Collaboration. Along with this paper, we publish revised file lists for each dataset which should be used for model evaluation. Our work paves the way for more trustworthy performance assessment in digital dermatology.
Augmenting medical image classifiers with synthetic data from latent diffusion models
Aug 23, 2023



Abstract:While hundreds of artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms are now approved or cleared by the US Food and Drugs Administration (FDA), many studies have shown inconsistent generalization or latent bias, particularly for underrepresented populations. Some have proposed that generative AI could reduce the need for real data, but its utility in model development remains unclear. Skin disease serves as a useful case study in synthetic image generation due to the diversity of disease appearance, particularly across the protected attribute of skin tone. Here we show that latent diffusion models can scalably generate images of skin disease and that augmenting model training with these data improves performance in data-limited settings. These performance gains saturate at synthetic-to-real image ratios above 10:1 and are substantially smaller than the gains obtained from adding real images. As part of our analysis, we generate and analyze a new dataset of 458,920 synthetic images produced using several generation strategies. Our results suggest that synthetic data could serve as a force-multiplier for model development, but the collection of diverse real-world data remains the most important step to improve medical AI algorithms.
Art and the science of generative AI: A deeper dive
Jun 07, 2023Abstract:A new class of tools, colloquially called generative AI, can produce high-quality artistic media for visual arts, concept art, music, fiction, literature, video, and animation. The generative capabilities of these tools are likely to fundamentally alter the creative processes by which creators formulate ideas and put them into production. As creativity is reimagined, so too may be many sectors of society. Understanding the impact of generative AI - and making policy decisions around it - requires new interdisciplinary scientific inquiry into culture, economics, law, algorithms, and the interaction of technology and creativity. We argue that generative AI is not the harbinger of art's demise, but rather is a new medium with its own distinct affordances. In this vein, we consider the impacts of this new medium on creators across four themes: aesthetics and culture, legal questions of ownership and credit, the future of creative work, and impacts on the contemporary media ecosystem. Across these themes, we highlight key research questions and directions to inform policy and beneficial uses of the technology.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge