Fabian Gröger
A Global Atlas of Digital Dermatology to Map Innovation and Disparities
Dec 27, 2025Abstract:The adoption of artificial intelligence in dermatology promises democratized access to healthcare, but model reliability depends on the quality and comprehensiveness of the data fueling these models. Despite rapid growth in publicly available dermatology images, the field lacks quantitative key performance indicators to measure whether new datasets expand clinical coverage or merely replicate what is already known. Here we present SkinMap, a multi-modal framework for the first comprehensive audit of the field's entire data basis. We unify the publicly available dermatology datasets into a single, queryable semantic atlas comprising more than 1.1 million images of skin conditions and quantify (i) informational novelty over time, (ii) dataset redundancy, and (iii) representation gaps across demographics and diagnoses. Despite exponential growth in dataset sizes, informational novelty across time has somewhat plateaued: Some clusters, such as common neoplasms on fair skin, are densely populated, while underrepresented skin types and many rare diseases remain unaddressed. We further identify structural gaps in coverage: Darker skin tones (Fitzpatrick V-VI) constitute only 5.8% of images and pediatric patients only 3.0%, while many rare diseases and phenotype combinations remain sparsely represented. SkinMap provides infrastructure to measure blind spots and steer strategic data acquisition toward undercovered regions of clinical space.
Clinical Uncertainty Impacts Machine Learning Evaluations
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:Clinical dataset labels are rarely certain as annotators disagree and confidence is not uniform across cases. Typical aggregation procedures, such as majority voting, obscure this variability. In simple experiments on medical imaging benchmarks, accounting for the confidence in binary labels significantly impacts model rankings. We therefore argue that machine-learning evaluations should explicitly account for annotation uncertainty using probabilistic metrics that directly operate on distributions. These metrics can be applied independently of the annotations' generating process, whether modeled by simple counting, subjective confidence ratings, or probabilistic response models. They are also computationally lightweight, as closed-form expressions have linear-time implementations once examples are sorted by model score. We thus urge the community to release raw annotations for datasets and to adopt uncertainty-aware evaluation so that performance estimates may better reflect clinical data.
Is Hyperbolic Space All You Need for Medical Anomaly Detection?
May 27, 2025Abstract:Medical anomaly detection has emerged as a promising solution to challenges in data availability and labeling constraints. Traditional methods extract features from different layers of pre-trained networks in Euclidean space; however, Euclidean representations fail to effectively capture the hierarchical relationships within these features, leading to suboptimal anomaly detection performance. We propose a novel yet simple approach that projects feature representations into hyperbolic space, aggregates them based on confidence levels, and classifies samples as healthy or anomalous. Our experiments demonstrate that hyperbolic space consistently outperforms Euclidean-based frameworks, achieving higher AUROC scores at both image and pixel levels across multiple medical benchmark datasets. Additionally, we show that hyperbolic space exhibits resilience to parameter variations and excels in few-shot scenarios, where healthy images are scarce. These findings underscore the potential of hyperbolic space as a powerful alternative for medical anomaly detection. The project website can be found at https://hyperbolic-anomalies.github.io
CleanPatrick: A Benchmark for Image Data Cleaning
May 16, 2025Abstract:Robust machine learning depends on clean data, yet current image data cleaning benchmarks rely on synthetic noise or narrow human studies, limiting comparison and real-world relevance. We introduce CleanPatrick, the first large-scale benchmark for data cleaning in the image domain, built upon the publicly available Fitzpatrick17k dermatology dataset. We collect 496,377 binary annotations from 933 medical crowd workers, identify off-topic samples (4%), near-duplicates (21%), and label errors (22%), and employ an aggregation model inspired by item-response theory followed by expert review to derive high-quality ground truth. CleanPatrick formalizes issue detection as a ranking task and adopts typical ranking metrics mirroring real audit workflows. Benchmarking classical anomaly detectors, perceptual hashing, SSIM, Confident Learning, NoiseRank, and SelfClean, we find that, on CleanPatrick, self-supervised representations excel at near-duplicate detection, classical methods achieve competitive off-topic detection under constrained review budgets, and label-error detection remains an open challenge for fine-grained medical classification. By releasing both the dataset and the evaluation framework, CleanPatrick enables a systematic comparison of image-cleaning strategies and paves the way for more reliable data-centric artificial intelligence.
Evaluation of Deep Audio Representations for Hearables
Feb 10, 2025Abstract:Effectively steering hearable devices requires understanding the acoustic environment around the user. In the computational analysis of sound scenes, foundation models have emerged as the state of the art to produce high-performance, robust, multi-purpose audio representations. We introduce and release Deep Evaluation of Audio Representations (DEAR), the first dataset and benchmark to evaluate the efficacy of foundation models in capturing essential acoustic properties for hearables. The dataset includes 1,158 audio tracks, each 30 seconds long, created by spatially mixing proprietary monologues with commercial, high-quality recordings of everyday acoustic scenes. Our benchmark encompasses eight tasks that assess the general context, speech sources, and technical acoustic properties of the audio scenes. Through our evaluation of four general-purpose audio representation models, we demonstrate that the BEATs model significantly surpasses its counterparts. This superiority underscores the advantage of models trained on diverse audio collections, confirming their applicability to a wide array of auditory tasks, including encoding the environment properties necessary for hearable steering. The DEAR dataset and associated code are available at https://dear-dataset.github.io.
Towards Scalable Foundation Models for Digital Dermatology
Nov 08, 2024Abstract:The growing demand for accurate and equitable AI models in digital dermatology faces a significant challenge: the lack of diverse, high-quality labeled data. In this work, we investigate the potential of domain-specific foundation models for dermatology in addressing this challenge. We utilize self-supervised learning (SSL) techniques to pre-train models on a dataset of over 240,000 dermatological images from public and private collections. Our study considers several SSL methods and compares the resulting foundation models against domain-agnostic models like those pre-trained on ImageNet and state-of-the-art models such as MONET across 12 downstream tasks. Unlike previous research, we emphasize the development of smaller models that are more suitable for resource-limited clinical settings, facilitating easier adaptation to a broad range of use cases. Results show that models pre-trained in this work not only outperform general-purpose models but also approach the performance of models 50 times larger on clinically relevant diagnostic tasks. To promote further research in this direction, we publicly release both the training code and the foundation models, which can benefit clinicians in dermatological applications.
PASSION for Dermatology: Bridging the Diversity Gap with Pigmented Skin Images from Sub-Saharan Africa
Nov 07, 2024Abstract:Africa faces a huge shortage of dermatologists, with less than one per million people. This is in stark contrast to the high demand for dermatologic care, with 80% of the paediatric population suffering from largely untreated skin conditions. The integration of AI into healthcare sparks significant hope for treatment accessibility, especially through the development of AI-supported teledermatology. Current AI models are predominantly trained on white-skinned patients and do not generalize well enough to pigmented patients. The PASSION project aims to address this issue by collecting images of skin diseases in Sub-Saharan countries with the aim of open-sourcing this data. This dataset is the first of its kind, consisting of 1,653 patients for a total of 4,901 images. The images are representative of telemedicine settings and encompass the most common paediatric conditions: eczema, fungals, scabies, and impetigo. We also provide a baseline machine learning model trained on the dataset and a detailed performance analysis for the subpopulations represented in the dataset. The project website can be found at https://passionderm.github.io/.
* MICCAI 2024
Self-Supervised and Few-Shot Learning for Robust Bioaerosol Monitoring
Jun 14, 2024


Abstract:Real-time bioaerosol monitoring is improving the quality of life for people affected by allergies, but it often relies on deep-learning models which pose challenges for widespread adoption. These models are typically trained in a supervised fashion and require considerable effort to produce large amounts of annotated data, an effort that must be repeated for new particles, geographical regions, or measurement systems. In this work, we show that self-supervised learning and few-shot learning can be combined to classify holographic images of bioaerosol particles using a large collection of unlabelled data and only a few examples for each particle type. We first demonstrate that self-supervision on pictures of unidentified particles from ambient air measurements enhances identification even when labelled data is abundant. Most importantly, it greatly improves few-shot classification when only a handful of labelled images are available. Our findings suggest that real-time bioaerosol monitoring workflows can be substantially optimized, and the effort required to adapt models for different situations considerably reduced.
Hyperbolic Metric Learning for Visual Outlier Detection
Mar 22, 2024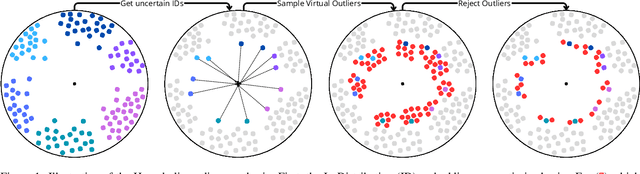
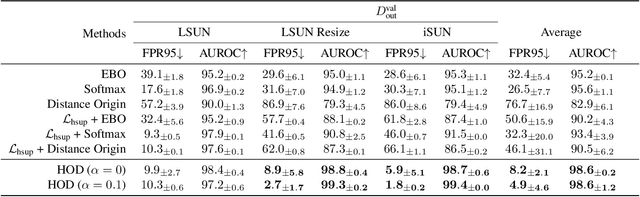
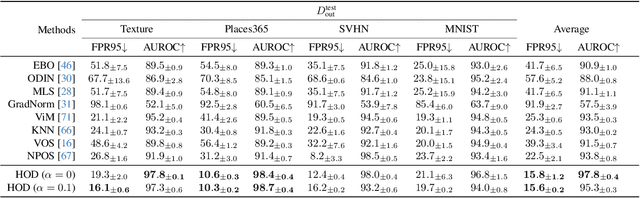
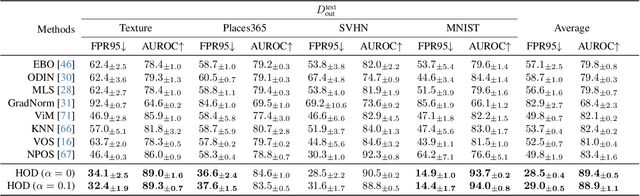
Abstract:Out-Of-Distribution (OOD) detection is critical to deploy deep learning models in safety-critical applications. However, the inherent hierarchical concept structure of visual data, which is instrumental to OOD detection, is often poorly captured by conventional methods based on Euclidean geometry. This work proposes a metric framework that leverages the strengths of Hyperbolic geometry for OOD detection. Inspired by previous works that refine the decision boundary for OOD data with synthetic outliers, we extend this method to Hyperbolic space. Interestingly, we find that synthetic outliers do not benefit OOD detection in Hyperbolic space as they do in Euclidean space. Furthermore we explore the relationship between OOD detection performance and Hyperbolic embedding dimension, addressing practical concerns in resource-constrained environments. Extensive experiments show that our framework improves the FPR95 for OOD detection from 22\% to 15\% and from 49% to 28% on CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100 respectively compared to Euclidean methods.
Towards Reliable Dermatology Evaluation Benchmarks
Sep 13, 2023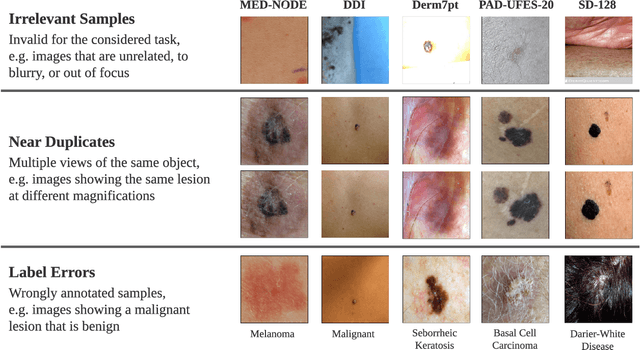
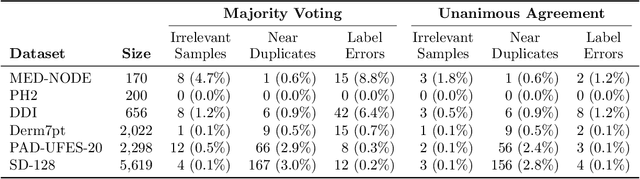
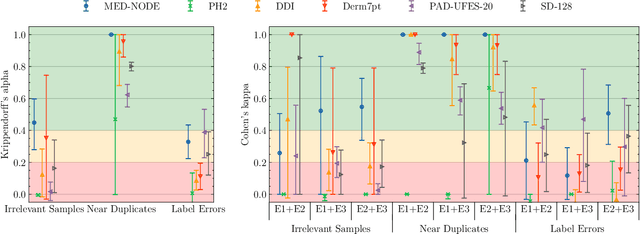
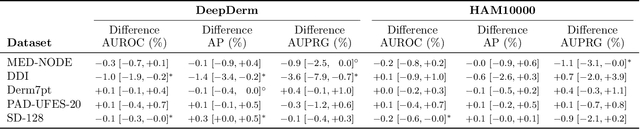
Abstract:Benchmark datasets for digital dermatology unwittingly contain inaccuracies that reduce trust in model performance estimates. We propose a resource-efficient data cleaning protocol to identify issues that escaped previous curation. The protocol leverages an existing algorithmic cleaning strategy and is followed by a confirmation process terminated by an intuitive stopping criterion. Based on confirmation by multiple dermatologists, we remove irrelevant samples and near duplicates and estimate the percentage of label errors in six dermatology image datasets for model evaluation promoted by the International Skin Imaging Collaboration. Along with this paper, we publish revised file lists for each dataset which should be used for model evaluation. Our work paves the way for more trustworthy performance assessment in digital dermatology.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge