Mohammad Mahdi Derakhshani
Private PoEtry: Private In-Context Learning via Product of Experts
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:In-context learning (ICL) enables Large Language Models (LLMs) to adapt to new tasks with only a small set of examples at inference time, thereby avoiding task-specific fine-tuning. However, in-context examples may contain privacy-sensitive information that should not be revealed through model outputs. Existing differential privacy (DP) approaches to ICL are either computationally expensive or rely on heuristics with limited effectiveness, including context oversampling, synthetic data generation, or unnecessary thresholding. We reformulate private ICL through the lens of a Product-of-Experts model. This gives a theoretically grounded framework, and the algorithm can be trivially parallelized. We evaluate our method across five datasets in text classification, math, and vision-language. We find that our method improves accuracy by more than 30 percentage points on average compared to prior DP-ICL methods, while maintaining strong privacy guarantees.
Purrception: Variational Flow Matching for Vector-Quantized Image Generation
Oct 01, 2025



Abstract:We introduce Purrception, a variational flow matching approach for vector-quantized image generation that provides explicit categorical supervision while maintaining continuous transport dynamics. Our method adapts Variational Flow Matching to vector-quantized latents by learning categorical posteriors over codebook indices while computing velocity fields in the continuous embedding space. This combines the geometric awareness of continuous methods with the discrete supervision of categorical approaches, enabling uncertainty quantification over plausible codes and temperature-controlled generation. We evaluate Purrception on ImageNet-1k 256x256 generation. Training converges faster than both continuous flow matching and discrete flow matching baselines while achieving competitive FID scores with state-of-the-art models. This demonstrates that Variational Flow Matching can effectively bridge continuous transport and discrete supervision for improved training efficiency in image generation.
NeoBabel: A Multilingual Open Tower for Visual Generation
Jul 08, 2025Abstract:Text-to-image generation advancements have been predominantly English-centric, creating barriers for non-English speakers and perpetuating digital inequities. While existing systems rely on translation pipelines, these introduce semantic drift, computational overhead, and cultural misalignment. We introduce NeoBabel, a novel multilingual image generation framework that sets a new Pareto frontier in performance, efficiency and inclusivity, supporting six languages: English, Chinese, Dutch, French, Hindi, and Persian. The model is trained using a combination of large-scale multilingual pretraining and high-resolution instruction tuning. To evaluate its capabilities, we expand two English-only benchmarks to multilingual equivalents: m-GenEval and m-DPG. NeoBabel achieves state-of-the-art multilingual performance while retaining strong English capability, scoring 0.75 on m-GenEval and 0.68 on m-DPG. Notably, it performs on par with leading models on English tasks while outperforming them by +0.11 and +0.09 on multilingual benchmarks, even though these models are built on multilingual base LLMs. This demonstrates the effectiveness of our targeted alignment training for preserving and extending crosslingual generalization. We further introduce two new metrics to rigorously assess multilingual alignment and robustness to code-mixed prompts. Notably, NeoBabel matches or exceeds English-only models while being 2-4x smaller. We release an open toolkit, including all code, model checkpoints, a curated dataset of 124M multilingual text-image pairs, and standardized multilingual evaluation protocols, to advance inclusive AI research. Our work demonstrates that multilingual capability is not a trade-off but a catalyst for improved robustness, efficiency, and cultural fidelity in generative AI.
Continual Hyperbolic Learning of Instances and Classes
Jun 12, 2025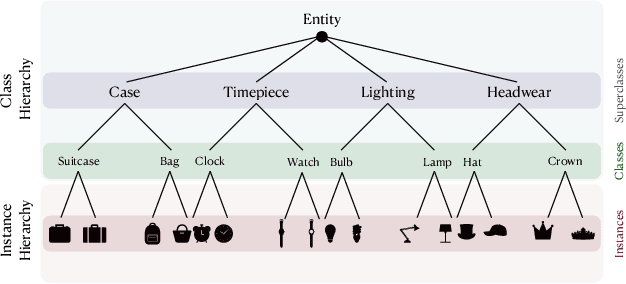
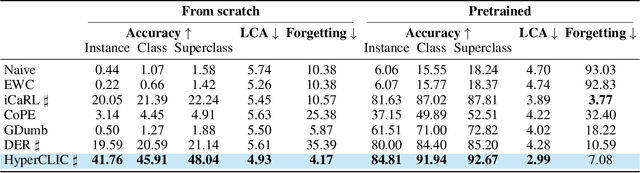
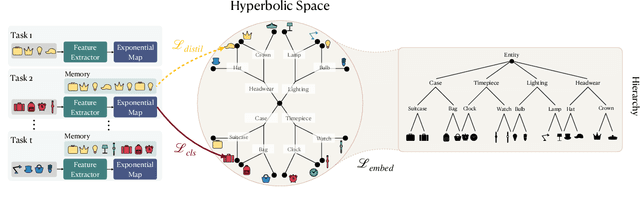
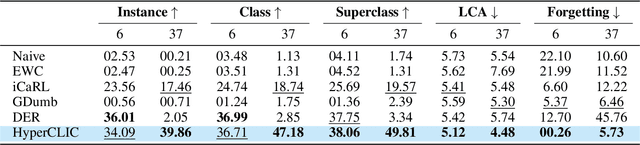
Abstract:Continual learning has traditionally focused on classifying either instances or classes, but real-world applications, such as robotics and self-driving cars, require models to handle both simultaneously. To mirror real-life scenarios, we introduce the task of continual learning of instances and classes, at the same time. This task challenges models to adapt to multiple levels of granularity over time, which requires balancing fine-grained instance recognition with coarse-grained class generalization. In this paper, we identify that classes and instances naturally form a hierarchical structure. To model these hierarchical relationships, we propose HyperCLIC, a continual learning algorithm that leverages hyperbolic space, which is uniquely suited for hierarchical data due to its ability to represent tree-like structures with low distortion and compact embeddings. Our framework incorporates hyperbolic classification and distillation objectives, enabling the continual embedding of hierarchical relations. To evaluate performance across multiple granularities, we introduce continual hierarchical metrics. We validate our approach on EgoObjects, the only dataset that captures the complexity of hierarchical object recognition in dynamic real-world environments. Empirical results show that HyperCLIC operates effectively at multiple granularities with improved hierarchical generalization.
Learning to Ground VLMs without Forgetting
Oct 14, 2024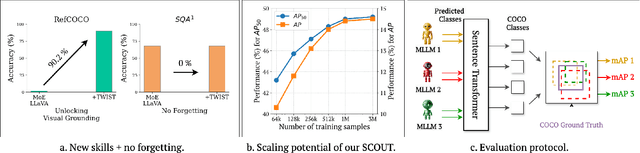
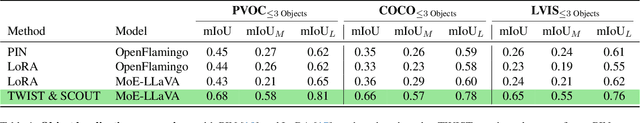
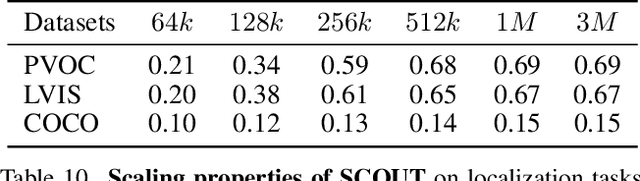
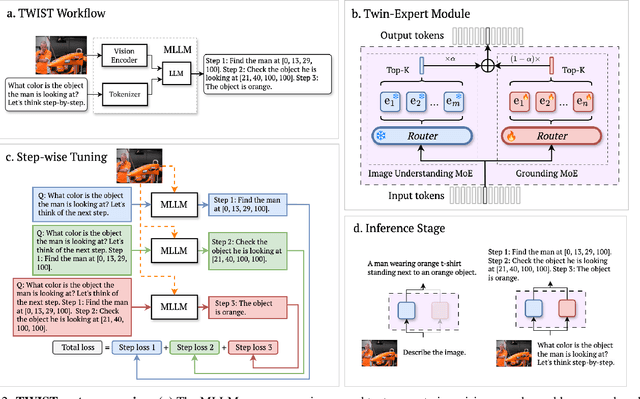
Abstract:Spatial awareness is key to enable embodied multimodal AI systems. Yet, without vast amounts of spatial supervision, current Visual Language Models (VLMs) struggle at this task. In this paper, we introduce LynX, a framework that equips pretrained VLMs with visual grounding ability without forgetting their existing image and language understanding skills. To this end, we propose a Dual Mixture of Experts module that modifies only the decoder layer of the language model, using one frozen Mixture of Experts (MoE) pre-trained on image and language understanding and another learnable MoE for new grounding capabilities. This allows the VLM to retain previously learned knowledge and skills, while acquiring what is missing. To train the model effectively, we generate a high-quality synthetic dataset we call SCouT, which mimics human reasoning in visual grounding. This dataset provides rich supervision signals, describing a step-by-step multimodal reasoning process, thereby simplifying the task of visual grounding. We evaluate LynX on several object detection and visual grounding datasets, demonstrating strong performance in object detection, zero-shot localization and grounded reasoning while maintaining its original image and language understanding capabilities on seven standard benchmark datasets.
TULIP: Token-length Upgraded CLIP
Oct 13, 2024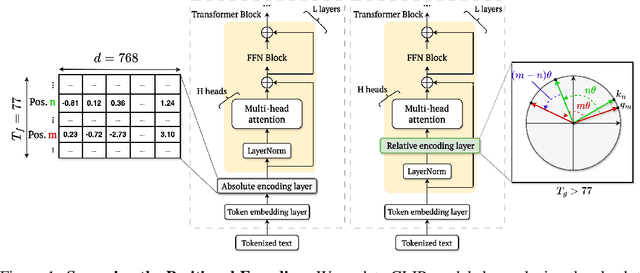
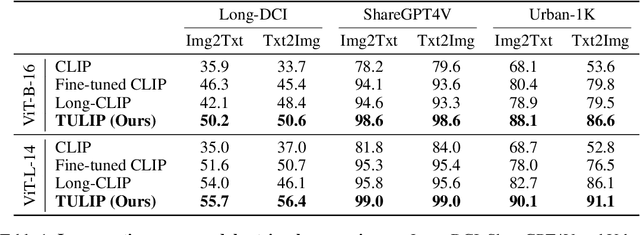
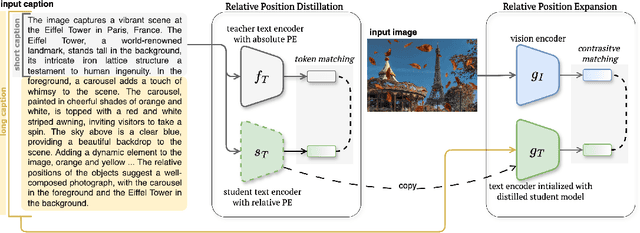
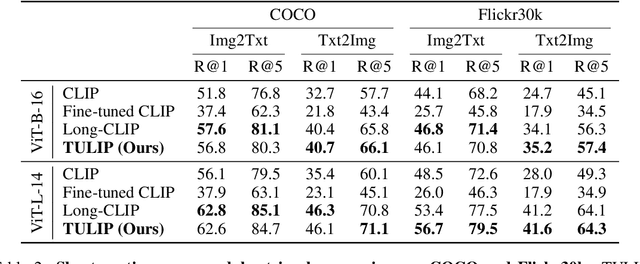
Abstract:We address the challenge of representing long captions in vision-language models, such as CLIP. By design these models are limited by fixed, absolute positional encodings, restricting inputs to a maximum of 77 tokens and hindering performance on tasks requiring longer descriptions. Although recent work has attempted to overcome this limit, their proposed approaches struggle to model token relationships over longer distances and simply extend to a fixed new token length. Instead, we propose a generalizable method, named TULIP, able to upgrade the token length to any length for CLIP-like models. We do so by improving the architecture with relative position encodings, followed by a training procedure that (i) distills the original CLIP text encoder into an encoder with relative position encodings and (ii) enhances the model for aligning longer captions with images. By effectively encoding captions longer than the default 77 tokens, our model outperforms baselines on cross-modal tasks such as retrieval and text-to-image generation.
Any-Shift Prompting for Generalization over Distributions
Feb 15, 2024Abstract:Image-language models with prompt learning have shown remarkable advances in numerous downstream vision tasks. Nevertheless, conventional prompt learning methods overfit their training distribution and lose the generalization ability on test distributions. To improve generalization across various distribution shifts, we propose any-shift prompting: a general probabilistic inference framework that considers the relationship between training and test distributions during prompt learning. We explicitly connect training and test distributions in the latent space by constructing training and test prompts in a hierarchical architecture. Within this framework, the test prompt exploits the distribution relationships to guide the generalization of the CLIP image-language model from training to any test distribution. To effectively encode the distribution information and their relationships, we further introduce a transformer inference network with a pseudo-shift training mechanism. The network generates the tailored test prompt with both training and test information in a feedforward pass, avoiding extra training costs at test time. Extensive experiments on twenty-three datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of any-shift prompting on the generalization over various distribution shifts.
Unlocking Spatial Comprehension in Text-to-Image Diffusion Models
Nov 28, 2023



Abstract:We propose CompFuser, an image generation pipeline that enhances spatial comprehension and attribute assignment in text-to-image generative models. Our pipeline enables the interpretation of instructions defining spatial relationships between objects in a scene, such as `An image of a gray cat on the left of an orange dog', and generate corresponding images. This is especially important in order to provide more control to the user. CompFuser overcomes the limitation of existing text-to-image diffusion models by decoding the generation of multiple objects into iterative steps: first generating a single object and then editing the image by placing additional objects in their designated positions. To create training data for spatial comprehension and attribute assignment we introduce a synthetic data generation process, that leverages a frozen large language model and a frozen layout-based diffusion model for object placement. We compare our approach to strong baselines and show that our model outperforms state-of-the-art image generation models in spatial comprehension and attribute assignment, despite being 3x to 5x smaller in parameters.
Small Visual Language Models can also be Open-Ended Few-Shot Learners
Sep 30, 2023Abstract:We present Self-Context Adaptation (SeCAt), a self-supervised approach that unlocks open-ended few-shot abilities of small visual language models. Our proposed adaptation algorithm explicitly learns from symbolic, yet self-supervised training tasks. Specifically, our approach imitates image captions in a self-supervised way based on clustering a large pool of images followed by assigning semantically-unrelated names to clusters. By doing so, we construct the `self-context', a training signal consisting of interleaved sequences of image and pseudo-caption pairs and a query image for which the model is trained to produce the right pseudo-caption. We demonstrate the performance and flexibility of SeCAt on several multimodal few-shot datasets, spanning various granularities. By using models with approximately 1B parameters we outperform the few-shot abilities of much larger models, such as Frozen and FROMAGe. SeCAt opens new possibilities for research in open-ended few-shot learning that otherwise requires access to large or proprietary models.
Open-Ended Medical Visual Question Answering Through Prefix Tuning of Language Models
Mar 10, 2023



Abstract:Medical Visual Question Answering (VQA) is an important challenge, as it would lead to faster and more accurate diagnoses and treatment decisions. Most existing methods approach it as a multi-class classification problem, which restricts the outcome to a predefined closed-set of curated answers. We focus on open-ended VQA and motivated by the recent advances in language models consider it as a generative task. Leveraging pre-trained language models, we introduce a novel method particularly suited for small, domain-specific, medical datasets. To properly communicate the medical images to the language model, we develop a network that maps the extracted visual features to a set of learnable tokens. Then, alongside the question, these learnable tokens directly prompt the language model. We explore recent parameter-efficient fine-tuning strategies for language models, which allow for resource- and data-efficient fine-tuning. We evaluate our approach on the prime medical VQA benchmarks, namely, Slake, OVQA and PathVQA. The results demonstrate that our approach outperforms existing methods across various training settings while also being computationally efficient.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge