Min Xu
Carnegie Mellon University
AgentSelect: Benchmark for Narrative Query-to-Agent Recommendation
Mar 04, 2026Abstract:LLM agents are rapidly becoming the practical interface for task automation, yet the ecosystem lacks a principled way to choose among an exploding space of deployable configurations. Existing LLM leaderboards and tool/agent benchmarks evaluate components in isolation and remain fragmented across tasks, metrics, and candidate pools, leaving a critical research gap: there is little query-conditioned supervision for learning to recommend end-to-end agent configurations that couple a backbone model with a toolkit. We address this gap with AgentSelect, a benchmark that reframes agent selection as narrative query-to-agent recommendation over capability profiles and systematically converts heterogeneous evaluation artifacts into unified, positive-only interaction data. AgentSelectcomprises 111,179 queries, 107,721 deployable agents, and 251,103 interaction records aggregated from 40+ sources, spanning LLM-only, toolkit-only, and compositional agents. Our analyses reveal a regime shift from dense head reuse to long-tail, near one-off supervision, where popularity-based CF/GNN methods become fragile and content-aware capability matching is essential. We further show that Part~III synthesized compositional interactions are learnable, induce capability-sensitive behavior under controlled counterfactual edits, and improve coverage over realistic compositions; models trained on AgentSelect also transfer to a public agent marketplace (MuleRun), yielding consistent gains on an unseen catalog. Overall, AgentSelect provides the first unified data and evaluation infrastructure for agent recommendation, which establishes a reproducible foundation to study and accelerate the emerging agent ecosystem.
Handling Supervision Scarcity in Chest X-ray Classification: Long-Tailed and Zero-Shot Learning
Feb 13, 2026Abstract:Chest X-ray (CXR) classification in clinical practice is often limited by imperfect supervision, arising from (i) extreme long-tailed multi-label disease distributions and (ii) missing annotations for rare or previously unseen findings. The CXR-LT 2026 challenge addresses these issues on a PadChest-based benchmark with a 36-class label space split into 30 in-distribution classes for training and 6 out-of-distribution (OOD) classes for zero-shot evaluation. We present task-specific solutions tailored to the distinct supervision regimes. For Task 1 (long-tailed multi-label classification), we adopt an imbalance-aware multi-label learning strategy to improve recognition of tail classes while maintaining stable performance on frequent findings. For Task 2 (zero-shot OOD recognition), we propose a prediction approach that produces scores for unseen disease categories without using any supervised labels or examples from the OOD classes during training. Evaluated with macro-averaged mean Average Precision (mAP), our method achieves strong performance on both tasks, ranking first on the public leaderboard of the development phase. Code and pre-trained models are available at https://github.com/hieuphamha19/CXR_LT.
Constraint-Aware Discrete-Time PID Gain Optimization for Robotic Joint Control Under Actuator Saturation
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:The precise regulation of rotary actuation is fundamental in autonomous robotics, yet practical PID loops deviate from continuous-time theory due to discrete-time execution, actuator saturation, and small delays and measurement imperfections. We present an implementation-aware analysis and tuning workflow for saturated discrete-time joint control. We (i) derive PI stability regions under Euler and exact zero-order-hold (ZOH) discretizations using the Jury criterion, (ii) evaluate a discrete back-calculation anti-windup realization under saturation-dominant regimes, and (iii) propose a hybrid-certified Bayesian optimization workflow that screens analytically unstable candidates and behaviorally unsafe transients while optimizing a robust IAE objective with soft penalties on overshoot and saturation duty. Baseline sweeps ($τ=1.0$~s, $Δt=0.01$~s, $u\in[-10,10]$) quantify rise/settle trends for P/PI/PID. Under a randomized model family emulating uncertainty, delay, noise, quantization, and tighter saturation, robustness-oriented tuning improves median IAE from $0.843$ to $0.430$ while keeping median overshoot below $2\%$. In simulation-only tuning, the certification screen rejects $11.6\%$ of randomly sampled gains within bounds before full robust evaluation, improving sample efficiency without hardware experiments.
From Specialist to Generalist: Unlocking SAM's Learning Potential on Unlabeled Medical Images
Jan 25, 2026Abstract:Foundation models like the Segment Anything Model (SAM) show strong generalization, yet adapting them to medical images remains difficult due to domain shift, scarce labels, and the inability of Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT) to exploit unlabeled data. While conventional models like U-Net excel in semi-supervised medical learning, their potential to assist a PEFT SAM has been largely overlooked. We introduce SC-SAM, a specialist-generalist framework where U-Net provides point-based prompts and pseudo-labels to guide SAM's adaptation, while SAM serves as a powerful generalist supervisor to regularize U-Net. This reciprocal guidance forms a bidirectional co-training loop that allows both models to effectively exploit the unlabeled data. Across prostate MRI and polyp segmentation benchmarks, our method achieves state-of-the-art results, outperforming other existing semi-supervised SAM variants and even medical foundation models like MedSAM, highlighting the value of specialist-generalist cooperation for label-efficient medical image segmentation. Our code is available at https://github.com/vnlvi2k3/SC-SAM.
Reconstructing Training Data from Adapter-based Federated Large Language Models
Jan 24, 2026Abstract:Adapter-based Federated Large Language Models (FedLLMs) are widely adopted to reduce the computational, storage, and communication overhead of full-parameter fine-tuning for web-scale applications while preserving user privacy. By freezing the backbone and training only compact low-rank adapters, these methods appear to limit gradient leakage and thwart existing Gradient Inversion Attacks (GIAs). Contrary to this assumption, we show that low-rank adapters create new, exploitable leakage channels. We propose the Unordered-word-bag-based Text Reconstruction (UTR) attack, a novel GIA tailored to the unique structure of adapter-based FedLLMs. UTR overcomes three core challenges: low-dimensional gradients, frozen backbones, and combinatorially large reconstruction spaces by: (i) inferring token presence from attention patterns in frozen layers, (ii) performing sentence-level inversion within the low-rank subspace of adapter gradients, and (iii) enforcing semantic coherence through constrained greedy decoding guided by language priors. Extensive experiments across diverse models (GPT2-Large, BERT, Qwen2.5-7B) and datasets (CoLA, SST-2, Rotten Tomatoes) demonstrate that UTR achieves near-perfect reconstruction accuracy (ROUGE-1/2 > 99), even with large batch size settings where prior GIAs fail completely. Our results reveal a fundamental tension between parameter efficiency and privacy in FedLLMs, challenging the prevailing belief that lightweight adaptation inherently enhances security. Our code and data are available at https://github.com/shwksnshwowk-wq/GIA.
Domain-invariant Mixed-domain Semi-supervised Medical Image Segmentation with Clustered Maximum Mean Discrepancy Alignment
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:Deep learning has shown remarkable progress in medical image semantic segmentation, yet its success heavily depends on large-scale expert annotations and consistent data distributions. In practice, annotations are scarce, and images are collected from multiple scanners or centers, leading to mixed-domain settings with unknown domain labels and severe domain gaps. Existing semi-supervised or domain adaptation approaches typically assume either a single domain shift or access to explicit domain indices, which rarely hold in real-world deployment. In this paper, we propose a domain-invariant mixed-domain semi-supervised segmentation framework that jointly enhances data diversity and mitigates domain bias. A Copy-Paste Mechanism (CPM) augments the training set by transferring informative regions across domains, while a Cluster Maximum Mean Discrepancy (CMMD) block clusters unlabeled features and aligns them with labeled anchors via an MMD objective, encouraging domain-invariant representations. Integrated within a teacher-student framework, our method achieves robust and precise segmentation even with very few labeled examples and multiple unknown domain discrepancies. Experiments on Fundus and M&Ms benchmarks demonstrate that our approach consistently surpasses semi-supervised and domain adaptation methods, establishing a potential solution for mixed-domain semi-supervised medical image segmentation.
FUGC: Benchmarking Semi-Supervised Learning Methods for Cervical Segmentation
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Accurate segmentation of cervical structures in transvaginal ultrasound (TVS) is critical for assessing the risk of spontaneous preterm birth (PTB), yet the scarcity of labeled data limits the performance of supervised learning approaches. This paper introduces the Fetal Ultrasound Grand Challenge (FUGC), the first benchmark for semi-supervised learning in cervical segmentation, hosted at ISBI 2025. FUGC provides a dataset of 890 TVS images, including 500 training images, 90 validation images, and 300 test images. Methods were evaluated using the Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC), Hausdorff Distance (HD), and runtime (RT), with a weighted combination of 0.4/0.4/0.2. The challenge attracted 10 teams with 82 participants submitting innovative solutions. The best-performing methods for each individual metric achieved 90.26\% mDSC, 38.88 mHD, and 32.85 ms RT, respectively. FUGC establishes a standardized benchmark for cervical segmentation, demonstrates the efficacy of semi-supervised methods with limited labeled data, and provides a foundation for AI-assisted clinical PTB risk assessment.
Imaging-anchored Multiomics in Cardiovascular Disease: Integrating Cardiac Imaging, Bulk, Single-cell, and Spatial Transcriptomics
Jan 10, 2026Abstract:Cardiovascular disease arises from interactions between inherited risk, molecular programmes, and tissue-scale remodelling that are observed clinically through imaging. Health systems now routinely generate large volumes of cardiac MRI, CT and echocardiography together with bulk, single-cell and spatial transcriptomics, yet these data are still analysed in separate pipelines. This review examines joint representations that link cardiac imaging phenotypes to transcriptomic and spatially resolved molecular states. An imaging-anchored perspective is adopted in which echocardiography, cardiac MRI and CT define a spatial phenotype of the heart, and bulk, single-cell and spatial transcriptomics provide cell-type- and location-specific molecular context. The biological and technical characteristics of these modalities are first summarised, and representation-learning strategies for each are outlined. Multimodal fusion approaches are reviewed, with emphasis on handling missing data, limited sample size, and batch effects. Finally, integrative pipelines for radiogenomics, spatial molecular alignment, and image-based prediction of gene expression are discussed, together with common failure modes, practical considerations, and open challenges. Spatial multiomics of human myocardium and atherosclerotic plaque, single-cell and spatial foundation models, and multimodal medical foundation models are collectively bringing imaging-anchored multiomics closer to large-scale cardiovascular translation.
Unsupervised SE(3) Disentanglement for in situ Macromolecular Morphology Identification from Cryo-Electron Tomography
Jan 04, 2026Abstract:Cryo-electron tomography (cryo-ET) provides direct 3D visualization of macromolecules inside the cell, enabling analysis of their in situ morphology. This morphology can be regarded as an SE(3)-invariant, denoised volumetric representation of subvolumes extracted from tomograms. Inferring morphology is therefore an inverse problem of estimating both a template morphology and its SE(3) transformation. Existing expectation-maximization based solution to this problem often misses rare but important morphologies and requires extensive manual hyperparameter tuning. Addressing this issue, we present a disentangled deep representation learning framework that separates SE(3) transformations from morphological content in the representation space. The framework includes a novel multi-choice learning module that enables this disentanglement for highly noisy cryo-ET data, and the learned morphological content is used to generate template morphologies. Experiments on simulated and real cryo-ET datasets demonstrate clear improvements over prior methods, including the discovery of previously unidentified macromolecular morphologies.
Step-GUI Technical Report
Dec 19, 2025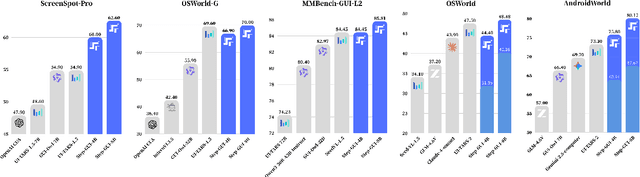
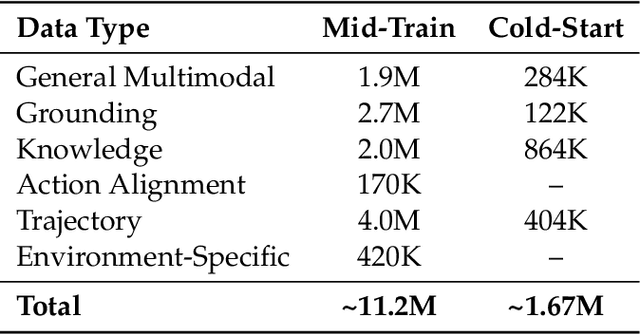
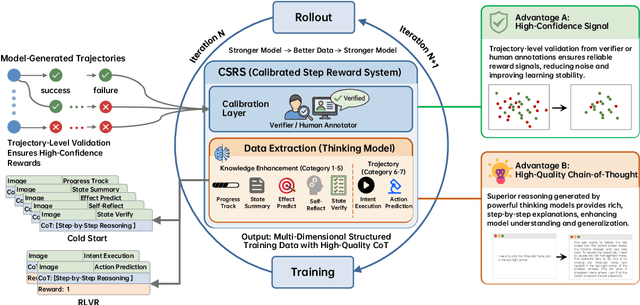

Abstract:Recent advances in multimodal large language models unlock unprecedented opportunities for GUI automation. However, a fundamental challenge remains: how to efficiently acquire high-quality training data while maintaining annotation reliability? We introduce a self-evolving training pipeline powered by the Calibrated Step Reward System, which converts model-generated trajectories into reliable training signals through trajectory-level calibration, achieving >90% annotation accuracy with 10-100x lower cost. Leveraging this pipeline, we introduce Step-GUI, a family of models (4B/8B) that achieves state-of-the-art GUI performance (8B: 80.2% AndroidWorld, 48.5% OSWorld, 62.6% ScreenShot-Pro) while maintaining robust general capabilities. As GUI agent capabilities improve, practical deployment demands standardized interfaces across heterogeneous devices while protecting user privacy. To this end, we propose GUI-MCP, the first Model Context Protocol for GUI automation with hierarchical architecture that combines low-level atomic operations and high-level task delegation to local specialist models, enabling high-privacy execution where sensitive data stays on-device. Finally, to assess whether agents can handle authentic everyday usage, we introduce AndroidDaily, a benchmark grounded in real-world mobile usage patterns with 3146 static actions and 235 end-to-end tasks across high-frequency daily scenarios (8B: static 89.91%, end-to-end 52.50%). Our work advances the development of practical GUI agents and demonstrates strong potential for real-world deployment in everyday digital interactions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge