Mitigating Knowledge Discrepancies among Multiple Datasets for Task-agnostic Unified Face Alignment
Paper and Code
Mar 28, 2025


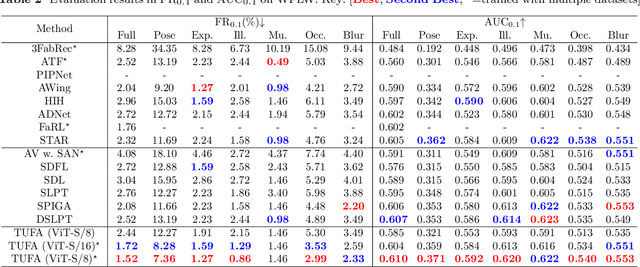
Despite the similar structures of human faces, existing face alignment methods cannot learn unified knowledge from multiple datasets with different landmark annotations. The limited training samples in a single dataset commonly result in fragile robustness in this field. To mitigate knowledge discrepancies among different datasets and train a task-agnostic unified face alignment (TUFA) framework, this paper presents a strategy to unify knowledge from multiple datasets. Specifically, we calculate a mean face shape for each dataset. To explicitly align these mean shapes on an interpretable plane based on their semantics, each shape is then incorporated with a group of semantic alignment embeddings. The 2D coordinates of these aligned shapes can be viewed as the anchors of the plane. By encoding them into structure prompts and further regressing the corresponding facial landmarks using image features, a mapping from the plane to the target faces is finally established, which unifies the learning target of different datasets. Consequently, multiple datasets can be utilized to boost the generalization ability of the model. The successful mitigation of discrepancies also enhances the efficiency of knowledge transferring to a novel dataset, significantly boosts the performance of few-shot face alignment. Additionally, the interpretable plane endows TUFA with a task-agnostic characteristic, enabling it to locate landmarks unseen during training in a zero-shot manner. Extensive experiments are carried on seven benchmarks and the results demonstrate an impressive improvement in face alignment brought by knowledge discrepancies mitigation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge