Michael Everett
Northeastern
Sparse Variable Projection in Robotic Perception: Exploiting Separable Structure for Efficient Nonlinear Optimization
Dec 08, 2025Abstract:Robotic perception often requires solving large nonlinear least-squares (NLS) problems. While sparsity has been well-exploited to scale solvers, a complementary and underexploited structure is \emph{separability} -- where some variables (e.g., visual landmarks) appear linearly in the residuals and, for any estimate of the remaining variables (e.g., poses), have a closed-form solution. Variable projection (VarPro) methods are a family of techniques that exploit this structure by analytically eliminating the linear variables and presenting a reduced problem in the remaining variables that has favorable properties. However, VarPro has seen limited use in robotic perception; a major challenge arises from gauge symmetries (e.g., cost invariance to global shifts and rotations), which are common in perception and induce specific computational challenges in standard VarPro approaches. We present a VarPro scheme designed for problems with gauge symmetries that jointly exploits separability and sparsity. Our method can be applied as a one-time preprocessing step to construct a \emph{matrix-free Schur complement operator}. This operator allows efficient evaluation of costs, gradients, and Hessian-vector products of the reduced problem and readily integrates with standard iterative NLS solvers. We provide precise conditions under which our method applies, and describe extensions when these conditions are only partially met. Across synthetic and real benchmarks in SLAM, SNL, and SfM, our approach achieves up to \textbf{2$\times$--35$\times$ faster runtimes} than state-of-the-art methods while maintaining accuracy. We release an open-source C++ implementation and all datasets from our experiments.
Practical and Performant Enhancements for Maximization of Algebraic Connectivity
Nov 11, 2025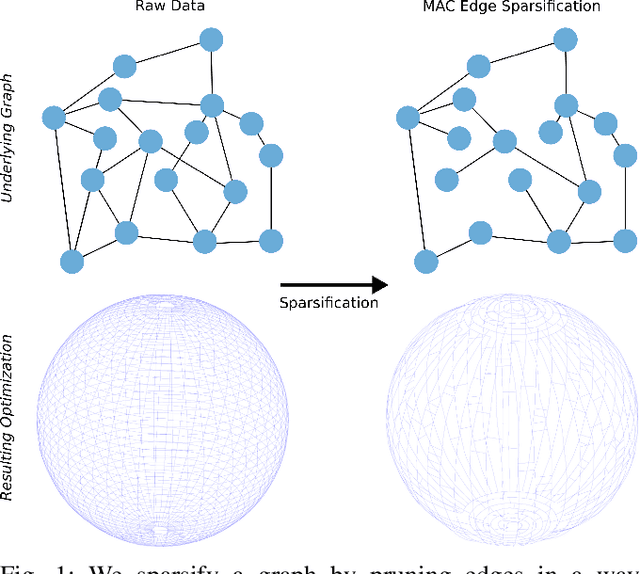
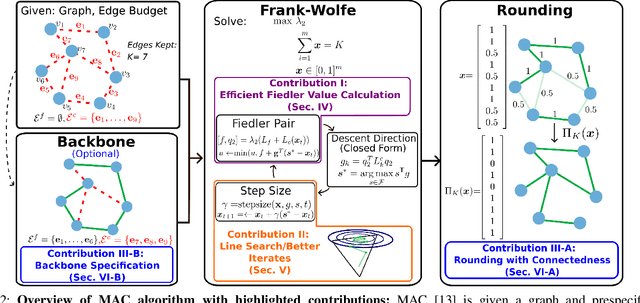
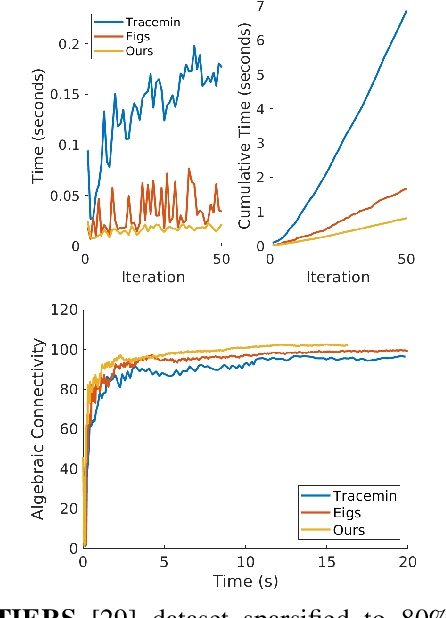
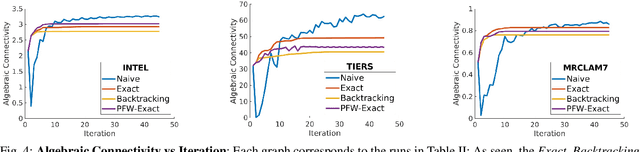
Abstract:Long-term state estimation over graphs remains challenging as current graph estimation methods scale poorly on large, long-term graphs. To address this, our work advances a current state-of-the-art graph sparsification algorithm, maximizing algebraic connectivity (MAC). MAC is a sparsification method that preserves estimation performance by maximizing the algebraic connectivity, a spectral graph property that is directly connected to the estimation error. Unfortunately, MAC remains computationally prohibitive for online use and requires users to manually pre-specify a connectivity-preserving edge set. Our contributions close these gaps along three complementary fronts: we develop a specialized solver for algebraic connectivity that yields an average 2x runtime speedup; we investigate advanced step size strategies for MAC's optimization procedure to enhance both convergence speed and solution quality; and we propose automatic schemes that guarantee graph connectivity without requiring manual specification of edges. Together, these contributions make MAC more scalable, reliable, and suitable for real-time estimation applications.
Uncertainty-Aware Ankle Exoskeleton Control
Aug 28, 2025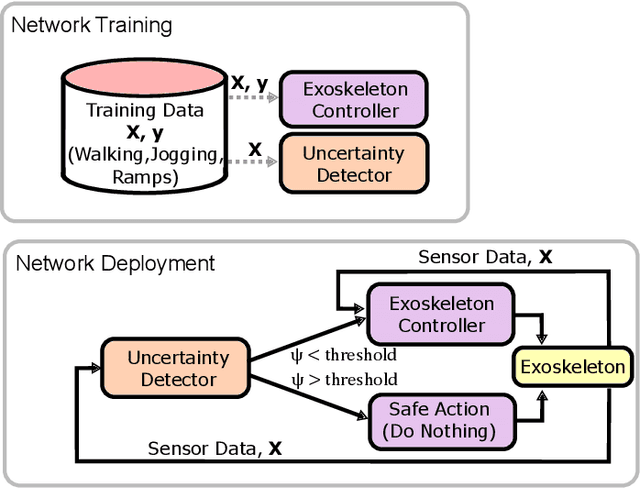
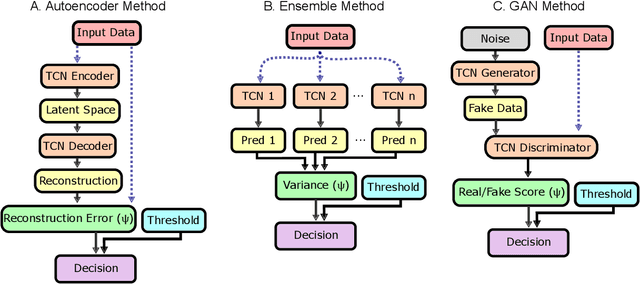
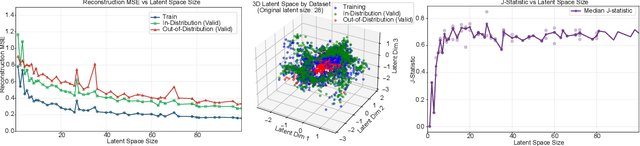
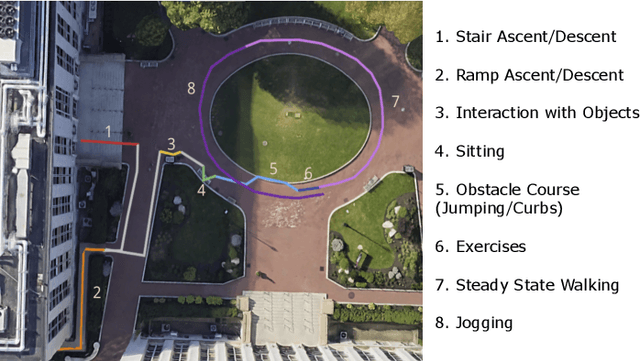
Abstract:Lower limb exoskeletons show promise to assist human movement, but their utility is limited by controllers designed for discrete, predefined actions in controlled environments, restricting their real-world applicability. We present an uncertainty-aware control framework that enables ankle exoskeletons to operate safely across diverse scenarios by automatically disengaging when encountering unfamiliar movements. Our approach uses an uncertainty estimator to classify movements as similar (in-distribution) or different (out-of-distribution) relative to actions in the training set. We evaluated three architectures (model ensembles, autoencoders, and generative adversarial networks) on an offline dataset and tested the strongest performing architecture (ensemble of gait phase estimators) online. The online test demonstrated the ability of our uncertainty estimator to turn assistance on and off as the user transitioned between in-distribution and out-of-distribution tasks (F1: 89.2). This new framework provides a path for exoskeletons to safely and autonomously support human movement in unstructured, everyday environments.
Learning Smooth State-Dependent Traversability from Dense Point Clouds
Jun 04, 2025Abstract:A key open challenge in off-road autonomy is that the traversability of terrain often depends on the vehicle's state. In particular, some obstacles are only traversable from some orientations. However, learning this interaction by encoding the angle of approach as a model input demands a large and diverse training dataset and is computationally inefficient during planning due to repeated model inference. To address these challenges, we present SPARTA, a method for estimating approach angle conditioned traversability from point clouds. Specifically, we impose geometric structure into our network by outputting a smooth analytical function over the 1-Sphere that predicts risk distribution for any angle of approach with minimal overhead and can be reused for subsequent queries. The function is composed of Fourier basis functions, which has important advantages for generalization due to their periodic nature and smoothness. We demonstrate SPARTA both in a high-fidelity simulation platform, where our model achieves a 91\% success rate crossing a 40m boulder field (compared to 73\% for the baseline), and on hardware, illustrating the generalization ability of the model to real-world settings.
Learning Verifiable Control Policies Using Relaxed Verification
Apr 23, 2025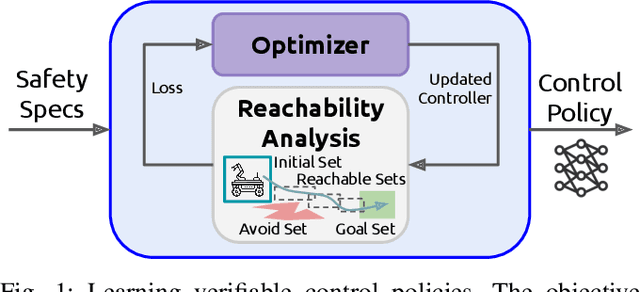
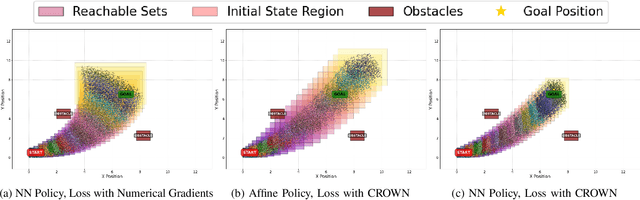
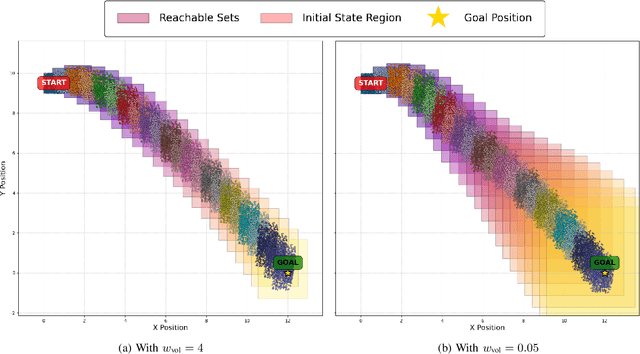
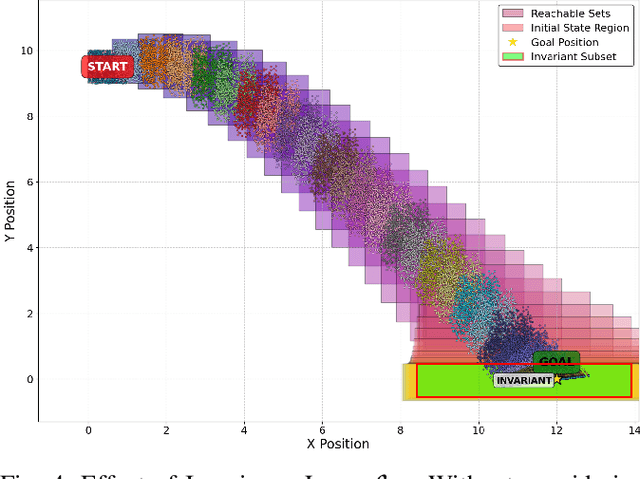
Abstract:To provide safety guarantees for learning-based control systems, recent work has developed formal verification methods to apply after training ends. However, if the trained policy does not meet the specifications, or there is conservatism in the verification algorithm, establishing these guarantees may not be possible. Instead, this work proposes to perform verification throughout training to ultimately aim for policies whose properties can be evaluated throughout runtime with lightweight, relaxed verification algorithms. The approach is to use differentiable reachability analysis and incorporate new components into the loss function. Numerical experiments on a quadrotor model and unicycle model highlight the ability of this approach to lead to learned control policies that satisfy desired reach-avoid and invariance specifications.
Active Learning For Repairable Hardware Systems With Partial Coverage
Mar 20, 2025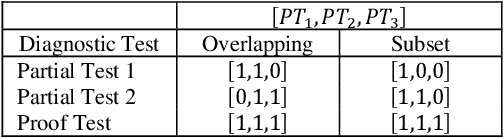
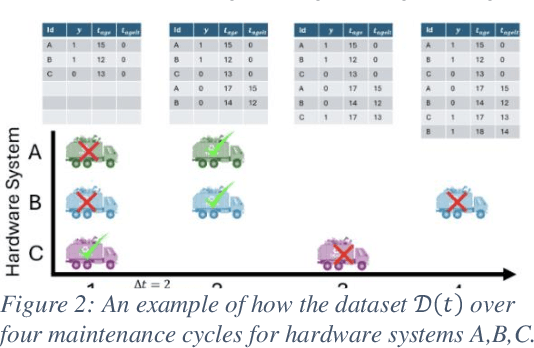
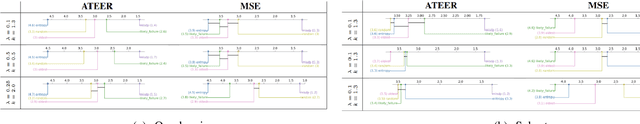
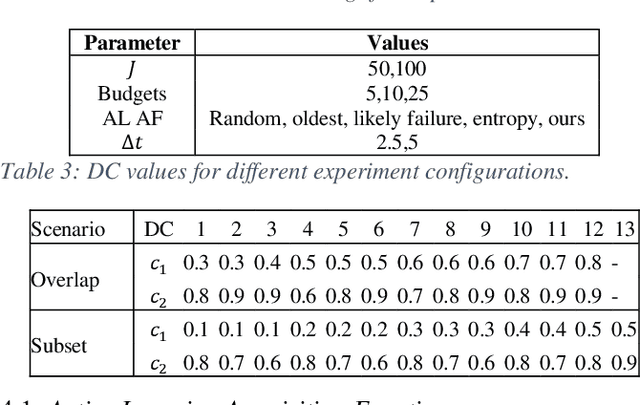
Abstract:Identifying the optimal diagnostic test and hardware system instance to infer reliability characteristics using field data is challenging, especially when constrained by fixed budgets and minimal maintenance cycles. Active Learning (AL) has shown promise for parameter inference with limited data and budget constraints in machine learning/deep learning tasks. However, AL for reliability model parameter inference remains underexplored for repairable hardware systems. It requires specialized AL Acquisition Functions (AFs) that consider hardware aging and the fact that a hardware system consists of multiple sub-systems, which may undergo only partial testing during a given diagnostic test. To address these challenges, we propose a relaxed Mixed Integer Semidefinite Program (MISDP) AL AF that incorporates Diagnostic Coverage (DC), Fisher Information Matrices (FIMs), and diagnostic testing budgets. Furthermore, we design empirical-based simulation experiments focusing on two diagnostic testing scenarios: (1) partial tests of a hardware system with overlapping subsystem coverage, and (2) partial tests where one diagnostic test fully subsumes the subsystem coverage of another. We evaluate our proposed approach against the most widely used AL AF in the literature (entropy), as well as several intuitive AL AFs tailored for reliability model parameter inference. Our proposed AF ranked best on average among the alternative AFs across 6,000 experimental configurations, with respect to Area Under the Curve (AUC) of the Absolute Total Expected Event Error (ATEER) and Mean Squared Error (MSE) curves, with statistical significance calculated at a 0.05 alpha level using a Friedman hypothesis test.
Contingency Constrained Planning with MPPI within MPPI
Dec 13, 2024
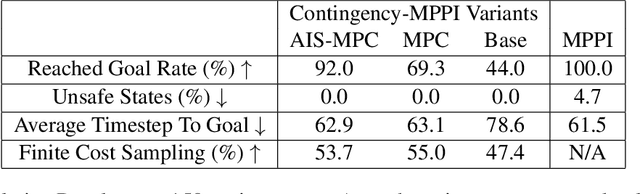


Abstract:For safety, autonomous systems must be able to consider sudden changes and enact contingency plans appropriately. State-of-the-art methods currently find trajectories that balance between nominal and contingency behavior, or plan for a singular contingency plan; however, this does not guarantee that the resulting plan is safe for all time. To address this research gap, this paper presents Contingency-MPPI, a data-driven optimization-based strategy that embeds contingency planning inside a nominal planner. By learning to approximate the optimal contingency-constrained control sequence with adaptive importance sampling, the proposed method's sampling efficiency is further improved with initializations from a lightweight path planner and trajectory optimizer. Finally, we present simulated and hardware experiments demonstrating our algorithm generating nominal and contingency plans in real time on a mobile robot.
Chance-Constrained Convex MPC for Robust Quadruped Locomotion Under Parametric and Additive Uncertainties
Nov 05, 2024



Abstract:Recent advances in quadrupedal locomotion have focused on improving stability and performance across diverse environments. However, existing methods often lack adequate safety analysis and struggle to adapt to varying payloads and complex terrains, typically requiring extensive tuning. To overcome these challenges, we propose a Chance-Constrained Model Predictive Control (CCMPC) framework that explicitly models payload and terrain variability as distributions of parametric and additive disturbances within the single rigid body dynamics (SRBD) model. Our approach ensures safe and consistent performance under uncertain dynamics by expressing the model friction cone constraints, which define the feasible set of ground reaction forces, as chance constraints. Moreover, we solve the resulting stochastic control problem using a computationally efficient quadratic programming formulation. Extensive Monte Carlo simulations of quadrupedal locomotion across varying payloads and complex terrains demonstrate that CCMPC significantly outperforms two competitive benchmarks: Linear MPC (LMPC) and MPC with hand-tuned safety margins to maintain stability, reduce foot slippage, and track the center of mass. Hardware experiments on the Unitree Go1 robot show successful locomotion across various indoor and outdoor terrains with unknown loads exceeding 50% of the robot body weight, despite no additional parameter tuning. A video of the results and accompanying code can be found at: https://cc-mpc.github.io/.
LiDAR Inertial Odometry And Mapping Using Learned Registration-Relevant Features
Oct 03, 2024Abstract:SLAM is an important capability for many autonomous systems, and modern LiDAR-based methods offer promising performance. However, for long duration missions, existing works that either operate directly the full pointclouds or on extracted features face key tradeoffs in accuracy and computational efficiency (e.g., memory consumption). To address these issues, this paper presents DFLIOM with several key innovations. Unlike previous methods that rely on handcrafted heuristics and hand-tuned parameters for feature extraction, we propose a learning-based approach that select points relevant to LiDAR SLAM pointcloud registration. Furthermore, we extend our prior work DLIOM with the learned feature extractor and observe our method enables similar or even better localization performance using only about 20\% of the points in the dense point clouds. We demonstrate that DFLIOM performs well on multiple public benchmarks, achieving a 2.4\% decrease in localization error and 57.5\% decrease in memory usage compared to state-of-the-art methods (DLIOM). Although extracting features with the proposed network requires extra time, it is offset by the faster processing time downstream, thus maintaining real-time performance using 20Hz LiDAR on our hardware setup. The effectiveness of our learning-based feature extraction module is further demonstrated through comparison with several handcrafted feature extractors.
Continuously Optimizing Radar Placement with Model Predictive Path Integrals
May 30, 2024Abstract:Continuously optimizing sensor placement is essential for precise target localization in various military and civilian applications. While information theory has shown promise in optimizing sensor placement, many studies oversimplify sensor measurement models or neglect dynamic constraints of mobile sensors. To address these challenges, we employ a range measurement model that incorporates radar parameters and radar-target distance, coupled with Model Predictive Path Integral (MPPI) control to manage complex environmental obstacles and dynamic constraints. We compare the proposed approach against stationary radars or simplified range measurement models based on the root mean squared error (RMSE) of the Cubature Kalman Filter (CKF) estimator for the targets' state. Additionally, we visualize the evolving geometry of radars and targets over time, highlighting areas of highest measurement information gain, demonstrating the strengths of the approach. The proposed strategy outperforms stationary radars and simplified range measurement models in target localization, achieving a 38-74% reduction in mean RMSE and a 33-79% reduction in the upper tail of the 90% Highest Density Interval (HDI) over 500 Monte Carl (MC) trials across all time steps. Code will be made publicly available upon acceptance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge