Miao Sun
eMamba: Efficient Acceleration Framework for Mamba Models in Edge Computing
Aug 14, 2025Abstract:State Space Model (SSM)-based machine learning architectures have recently gained significant attention for processing sequential data. Mamba, a recent sequence-to-sequence SSM, offers competitive accuracy with superior computational efficiency compared to state-of-the-art transformer models. While this advantage makes Mamba particularly promising for resource-constrained edge devices, no hardware acceleration frameworks are currently optimized for deploying it in such environments. This paper presents eMamba, a comprehensive end-to-end hardware acceleration framework explicitly designed for deploying Mamba models on edge platforms. eMamba maximizes computational efficiency by replacing complex normalization layers with lightweight hardware-aware alternatives and approximating expensive operations, such as SiLU activation and exponentiation, considering the target applications. Then, it performs an approximation-aware neural architecture search (NAS) to tune the learnable parameters used during approximation. Evaluations with Fashion-MNIST, CIFAR-10, and MARS, an open-source human pose estimation dataset, show eMamba achieves comparable accuracy to state-of-the-art techniques using 1.63-19.9$\times$ fewer parameters. In addition, it generalizes well to large-scale natural language tasks, demonstrating stable perplexity across varying sequence lengths on the WikiText2 dataset. We also quantize and implement the entire eMamba pipeline on an AMD ZCU102 FPGA and ASIC using GlobalFoundries (GF) 22 nm technology. Experimental results show 4.95-5.62$\times$ lower latency and 2.22-9.95$\times$ higher throughput, with 4.77$\times$ smaller area, 9.84$\times$ lower power, and 48.6$\times$ lower energy consumption than baseline solutions while maintaining competitive accuracy.
SDformer: Efficient End-to-End Transformer for Depth Completion
Sep 12, 2024



Abstract:Depth completion aims to predict dense depth maps with sparse depth measurements from a depth sensor. Currently, Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) based models are the most popular methods applied to depth completion tasks. However, despite the excellent high-end performance, they suffer from a limited representation area. To overcome the drawbacks of CNNs, a more effective and powerful method has been presented: the Transformer, which is an adaptive self-attention setting sequence-to-sequence model. While the standard Transformer quadratically increases the computational cost from the key-query dot-product of input resolution which improperly employs depth completion tasks. In this work, we propose a different window-based Transformer architecture for depth completion tasks named Sparse-to-Dense Transformer (SDformer). The network consists of an input module for the depth map and RGB image features extraction and concatenation, a U-shaped encoder-decoder Transformer for extracting deep features, and a refinement module. Specifically, we first concatenate the depth map features with the RGB image features through the input model. Then, instead of calculating self-attention with the whole feature maps, we apply different window sizes to extract the long-range depth dependencies. Finally, we refine the predicted features from the input module and the U-shaped encoder-decoder Transformer module to get the enriching depth features and employ a convolution layer to obtain the dense depth map. In practice, the SDformer obtains state-of-the-art results against the CNN-based depth completion models with lower computing loads and parameters on the NYU Depth V2 and KITTI DC datasets.
Sub-SA: Strengthen In-context Learning via Submodular Selective Annotation
Jul 08, 2024



Abstract:In-context learning (ICL) leverages in-context examples as prompts for the predictions of Large Language Models (LLMs). These prompts play a crucial role in achieving strong performance. However, the selection of suitable prompts from a large pool of labeled examples often entails significant annotation costs. To address this challenge, we propose \textbf{Sub-SA} (\textbf{Sub}modular \textbf{S}elective \textbf{A}nnotation), a submodule-based selective annotation method. The aim of Sub-SA is to reduce annotation costs while improving the quality of in-context examples and minimizing the time consumption of the selection process. In Sub-SA, we design a submodular function that facilitates effective subset selection for annotation and demonstrates the characteristics of monotonically and submodularity from the theoretical perspective. Specifically, we propose \textbf{RPR} (\textbf{R}eward and \textbf{P}enalty \textbf{R}egularization) to better balance the diversity and representativeness of the unlabeled dataset attributed to a reward term and a penalty term, respectively. Consequently, the selection for annotations can be effectively addressed with a simple yet effective greedy search algorithm based on the submodular function. Finally, we apply the similarity prompt retrieval to get the examples for ICL.
TimeLDM: Latent Diffusion Model for Unconditional Time Series Generation
Jul 05, 2024



Abstract:Time series generation is a crucial research topic in the area of deep learning, which can be used for data augmentation, imputing missing values, and forecasting. Currently, latent diffusion models are ascending to the forefront of generative modeling for many important data representations. Being the most pivotal in the computer vision domain, latent diffusion models have also recently attracted interest in other communities, including NLP, Speech, and Geometric Space. In this work, we propose TimeLDM, a novel latent diffusion model for high-quality time series generation. TimeLDM is composed of a variational autoencoder that encodes time series into an informative and smoothed latent content and a latent diffusion model operating in the latent space to generate latent information. We evaluate the ability of our method to generate synthetic time series with simulated and realistic datasets, benchmark the performance against existing state-of-the-art methods. Qualitatively and quantitatively, we find that the proposed TimeLDM persistently delivers high-quality generated time series. Sores from Context-FID and Discriminative indicate that TimeLDM consistently and significantly outperforms current state-of-the-art benchmarks with an average improvement of 3.4$\times$ and 3.8$\times$, respectively. Further studies demonstrate that our method presents better performance on different lengths of time series data generation. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to explore the potential of the latent diffusion model for unconditional time series generation and establish a new baseline for synthetic time series.
LiDAR-PTQ: Post-Training Quantization for Point Cloud 3D Object Detection
Jan 29, 2024Abstract:Due to highly constrained computing power and memory, deploying 3D lidar-based detectors on edge devices equipped in autonomous vehicles and robots poses a crucial challenge. Being a convenient and straightforward model compression approach, Post-Training Quantization (PTQ) has been widely adopted in 2D vision tasks. However, applying it directly to 3D lidar-based tasks inevitably leads to performance degradation. As a remedy, we propose an effective PTQ method called LiDAR-PTQ, which is particularly curated for 3D lidar detection (both SPConv-based and SPConv-free). Our LiDAR-PTQ features three main components, \textbf{(1)} a sparsity-based calibration method to determine the initialization of quantization parameters, \textbf{(2)} a Task-guided Global Positive Loss (TGPL) to reduce the disparity between the final predictions before and after quantization, \textbf{(3)} an adaptive rounding-to-nearest operation to minimize the layerwise reconstruction error. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our LiDAR-PTQ can achieve state-of-the-art quantization performance when applied to CenterPoint (both Pillar-based and Voxel-based). To our knowledge, for the very first time in lidar-based 3D detection tasks, the PTQ INT8 model's accuracy is almost the same as the FP32 model while enjoying $3\times$ inference speedup. Moreover, our LiDAR-PTQ is cost-effective being $30\times$ faster than the quantization-aware training method. Code will be released at \url{https://github.com/StiphyJay/LiDAR-PTQ}.
EddyNet: A Deep Neural Network For Pixel-Wise Classification of Oceanic Eddies
Nov 10, 2017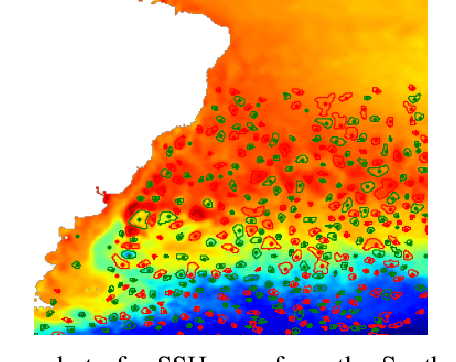
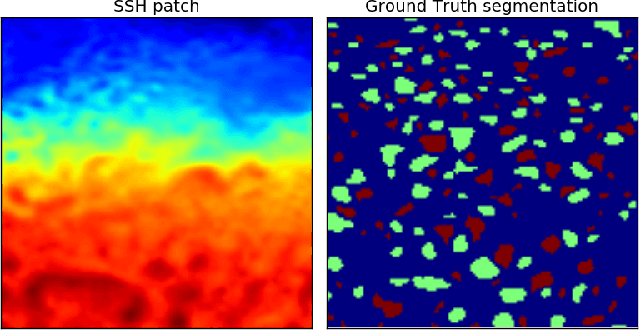
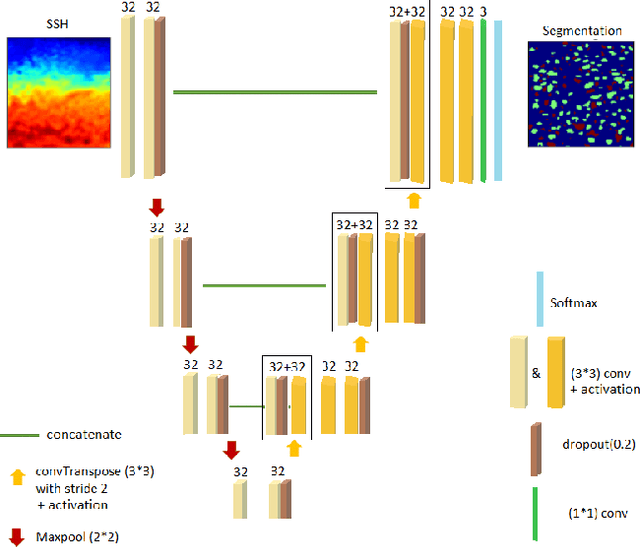
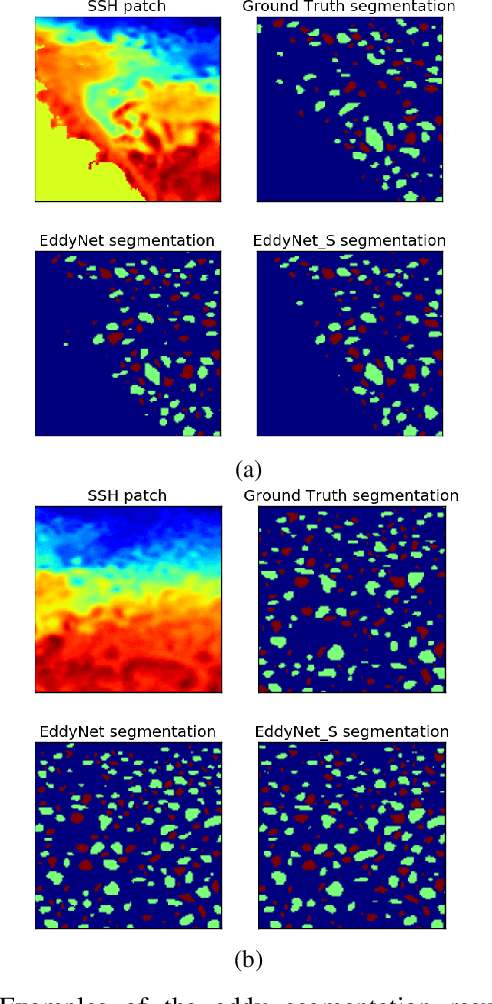
Abstract:This work presents EddyNet, a deep learning based architecture for automated eddy detection and classification from Sea Surface Height (SSH) maps provided by the Copernicus Marine and Environment Monitoring Service (CMEMS). EddyNet is a U-Net like network that consists of a convolutional encoder-decoder followed by a pixel-wise classification layer. The output is a map with the same size of the input where pixels have the following labels \{'0': Non eddy, '1': anticyclonic eddy, '2': cyclonic eddy\}. We investigate the use of SELU activation function instead of the classical ReLU+BN and we use an overlap based loss function instead of the cross entropy loss. Keras Python code, the training datasets and EddyNet weights files are open-source and freely available on https://github.com/redouanelg/EddyNet.
ProLanGO: Protein Function Prediction Using Neural~Machine Translation Based on a Recurrent Neural Network
Oct 19, 2017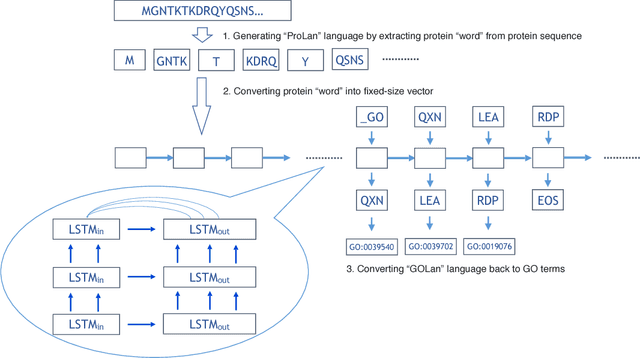
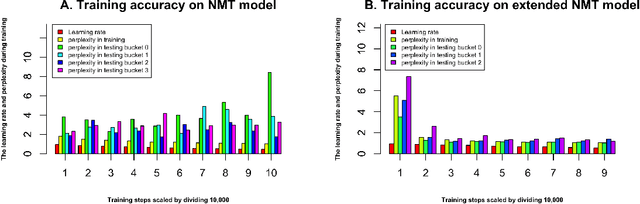
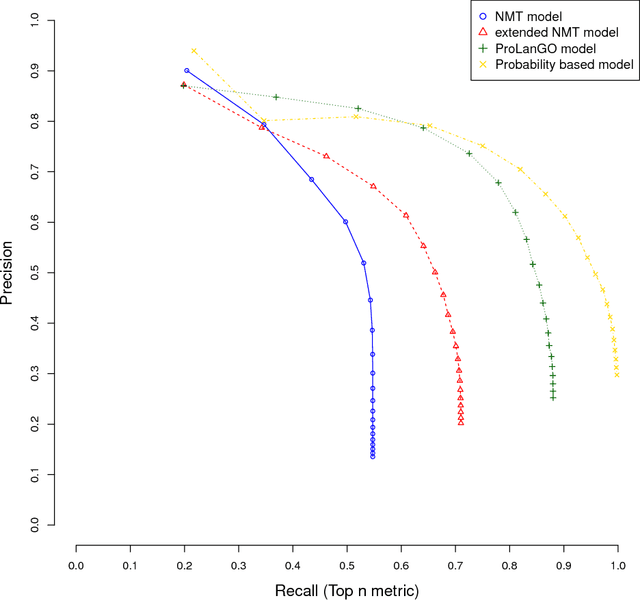
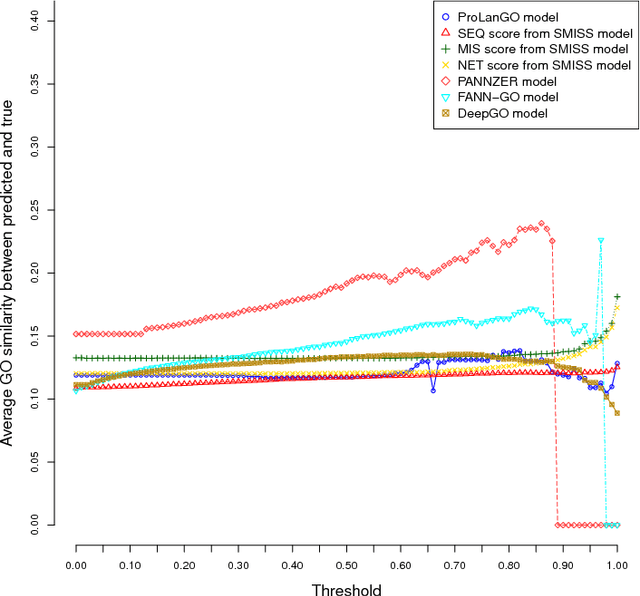
Abstract:With the development of next generation sequencing techniques, it is fast and cheap to determine protein sequences but relatively slow and expensive to extract useful information from protein sequences because of limitations of traditional biological experimental techniques. Protein function prediction has been a long standing challenge to fill the gap between the huge amount of protein sequences and the known function. In this paper, we propose a novel method to convert the protein function problem into a language translation problem by the new proposed protein sequence language "ProLan" to the protein function language "GOLan", and build a neural machine translation model based on recurrent neural networks to translate "ProLan" language to "GOLan" language. We blindly tested our method by attending the latest third Critical Assessment of Function Annotation (CAFA 3) in 2016, and also evaluate the performance of our methods on selected proteins whose function was released after CAFA competition. The good performance on the training and testing datasets demonstrates that our new proposed method is a promising direction for protein function prediction. In summary, we first time propose a method which converts the protein function prediction problem to a language translation problem and applies a neural machine translation model for protein function prediction.
Age Group and Gender Estimation in the Wild with Deep RoR Architecture
Oct 09, 2017



Abstract:Automatically predicting age group and gender from face images acquired in unconstrained conditions is an important and challenging task in many real-world applications. Nevertheless, the conventional methods with manually-designed features on in-the-wild benchmarks are unsatisfactory because of incompetency to tackle large variations in unconstrained images. This difficulty is alleviated to some degree through Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) for its powerful feature representation. In this paper, we propose a new CNN based method for age group and gender estimation leveraging Residual Networks of Residual Networks (RoR), which exhibits better optimization ability for age group and gender classification than other CNN architectures.Moreover, two modest mechanisms based on observation of the characteristics of age group are presented to further improve the performance of age estimation.In order to further improve the performance and alleviate over-fitting problem, RoR model is pre-trained on ImageNet firstly, and then it is fune-tuned on the IMDB-WIKI-101 data set for further learning the features of face images, finally, it is used to fine-tune on Adience data set. Our experiments illustrate the effectiveness of RoR method for age and gender estimation in the wild, where it achieves better performance than other CNN methods. Finally, the RoR-152+IMDB-WIKI-101 with two mechanisms achieves new state-of-the-art results on Adience benchmark.
Residual Networks of Residual Networks: Multilevel Residual Networks
Mar 05, 2017



Abstract:A residual-networks family with hundreds or even thousands of layers dominates major image recognition tasks, but building a network by simply stacking residual blocks inevitably limits its optimization ability. This paper proposes a novel residual-network architecture, Residual networks of Residual networks (RoR), to dig the optimization ability of residual networks. RoR substitutes optimizing residual mapping of residual mapping for optimizing original residual mapping. In particular, RoR adds level-wise shortcut connections upon original residual networks to promote the learning capability of residual networks. More importantly, RoR can be applied to various kinds of residual networks (ResNets, Pre-ResNets and WRN) and significantly boost their performance. Our experiments demonstrate the effectiveness and versatility of RoR, where it achieves the best performance in all residual-network-like structures. Our RoR-3-WRN58-4+SD models achieve new state-of-the-art results on CIFAR-10, CIFAR-100 and SVHN, with test errors 3.77%, 19.73% and 1.59%, respectively. RoR-3 models also achieve state-of-the-art results compared to ResNets on ImageNet data set.
Multiple Instance Learning Convolutional Neural Networks for Object Recognition
Oct 11, 2016



Abstract:Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) have demon- strated its successful applications in computer vision, speech recognition, and natural language processing. For object recog- nition, CNNs might be limited by its strict label requirement and an implicit assumption that images are supposed to be target- object-dominated for optimal solutions. However, the labeling procedure, necessitating laying out the locations of target ob- jects, is very tedious, making high-quality large-scale dataset prohibitively expensive. Data augmentation schemes are widely used when deep networks suffer the insufficient training data problem. All the images produced through data augmentation share the same label, which may be problematic since not all data augmentation methods are label-preserving. In this paper, we propose a weakly supervised CNN framework named Multiple Instance Learning Convolutional Neural Networks (MILCNN) to solve this problem. We apply MILCNN framework to object recognition and report state-of-the-art performance on three benchmark datasets: CIFAR10, CIFAR100 and ILSVRC2015 classification dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge