Ce Gao
A Scalable and Cloud-Native Hyperparameter Tuning System
Jun 08, 2020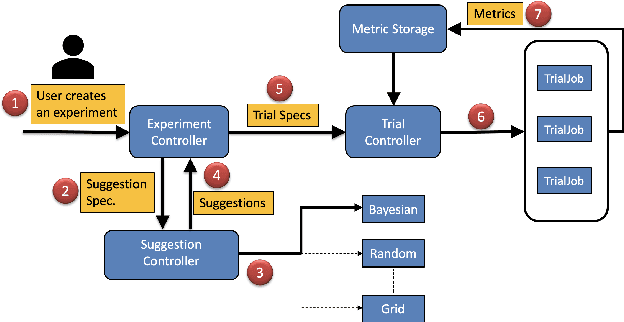
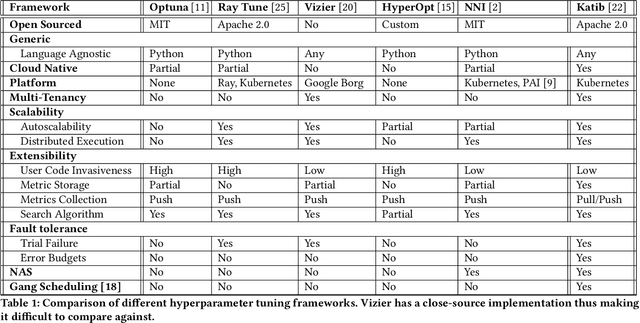
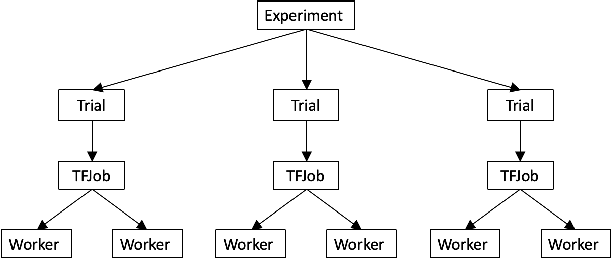
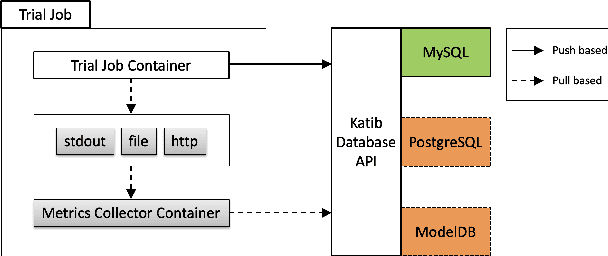
Abstract:In this paper, we introduce Katib: a scalable, cloud-native, and production-ready hyperparameter tuning system that is agnostic of the underlying machine learning framework. Though there are multiple hyperparameter tuning systems available, this is the first one that caters to the needs of both users and administrators of the system. We present the motivation and design of the system and contrast it with existing hyperparameter tuning systems, especially in terms of multi-tenancy, scalability, fault-tolerance, and extensibility. It can be deployed on local machines, or hosted as a service in on-premise data centers, or in private/public clouds. We demonstrate the advantage of our system using experimental results as well as real-world, production use cases. Katib has active contributors from multiple companies and is open-sourced at \emph{https://github.com/kubeflow/katib} under the Apache 2.0 license.
Fine-Grained Age Estimation in the wild with Attention LSTM Networks
May 26, 2018



Abstract:Age estimation from a single face image has been an essential task in the field of human-computer interaction and computer vision which has a wide range of practical application value. Concerning the problem that accuracy of age estimation of face images in the wild are relatively low for existing methods, where they take into account only the whole features of face image while neglecting the fine-grained features of age-sensitive area, we propose a method based on Attention LSTM network for Fine-Grained age estimation in the wild based on the idea of Fine-Grained categories and visual attention mechanism. This method combines ResNets or RoR models with LSTM unit to construct AL-ResNets or AL-RoR networks to extract age-sensitive local regions, which effectively improves age estimation accuracy. Firstly, ResNets or RoR model pre-trained on ImageNet dataset is selected as the basic model, which is then fine-tuned on the IMDB-WIKI-101 dataset for age estimation. Then, we fine-tune ResNets or RoR on the target age datasets to extract the global features of face images. To extract the local characteristics of age-sensitive areas, the LSTM unit is then presented to obtain the coordinates of the age-sensitive region automatically. Finally, the age group classification experiment is conducted directly on the Adience dataset, and age-regression experiments are performed by the Deep EXpectation algorithm (DEX) on MORPH Album 2, FG-NET and LAP datasets. By combining the global and local features, we got our final prediction results. Our experiments illustrate the effectiveness of AL-ResNets or AL-RoR for age estimation in the wild, where it achieves new state-of-the-art performance than all other CNN methods on the Adience, MORPH Album 2, FG-NET and LAP datasets.
Age Group and Gender Estimation in the Wild with Deep RoR Architecture
Oct 09, 2017



Abstract:Automatically predicting age group and gender from face images acquired in unconstrained conditions is an important and challenging task in many real-world applications. Nevertheless, the conventional methods with manually-designed features on in-the-wild benchmarks are unsatisfactory because of incompetency to tackle large variations in unconstrained images. This difficulty is alleviated to some degree through Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) for its powerful feature representation. In this paper, we propose a new CNN based method for age group and gender estimation leveraging Residual Networks of Residual Networks (RoR), which exhibits better optimization ability for age group and gender classification than other CNN architectures.Moreover, two modest mechanisms based on observation of the characteristics of age group are presented to further improve the performance of age estimation.In order to further improve the performance and alleviate over-fitting problem, RoR model is pre-trained on ImageNet firstly, and then it is fune-tuned on the IMDB-WIKI-101 data set for further learning the features of face images, finally, it is used to fine-tune on Adience data set. Our experiments illustrate the effectiveness of RoR method for age and gender estimation in the wild, where it achieves better performance than other CNN methods. Finally, the RoR-152+IMDB-WIKI-101 with two mechanisms achieves new state-of-the-art results on Adience benchmark.
Pyramidal RoR for Image Classification
Oct 01, 2017



Abstract:The Residual Networks of Residual Networks (RoR) exhibits excellent performance in the image classification task, but sharply increasing the number of feature map channels makes the characteristic information transmission incoherent, which losses a certain of information related to classification prediction, limiting the classification performance. In this paper, a Pyramidal RoR network model is proposed by analysing the performance characteristics of RoR and combining with the PyramidNet. Firstly, based on RoR, the Pyramidal RoR network model with channels gradually increasing is designed. Secondly, we analysed the effect of different residual block structures on performance, and chosen the residual block structure which best favoured the classification performance. Finally, we add an important principle to further optimize Pyramidal RoR networks, drop-path is used to avoid over-fitting and save training time. In this paper, image classification experiments were performed on CIFAR-10/100 and SVHN datasets, and we achieved the current lowest classification error rates were 2.96%, 16.40% and 1.59%, respectively. Experiments show that the Pyramidal RoR network optimization method can improve the network performance for different data sets and effectively suppress the gradient disappearance problem in DCNN training.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge