Mi Luo
HOI-Swap: Swapping Objects in Videos with Hand-Object Interaction Awareness
Jun 11, 2024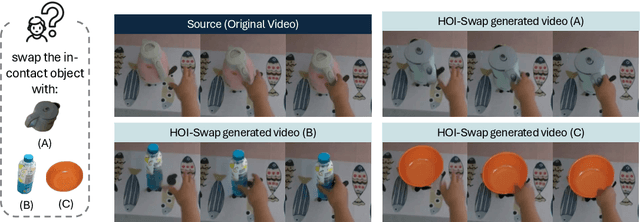

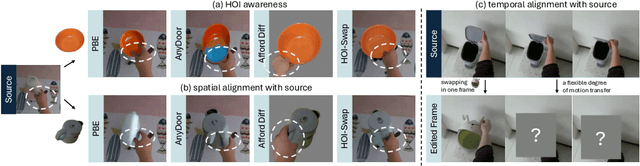
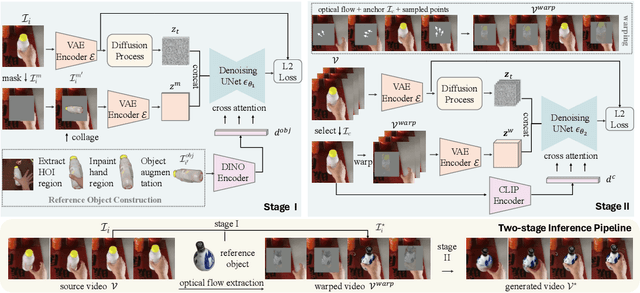
Abstract:We study the problem of precisely swapping objects in videos, with a focus on those interacted with by hands, given one user-provided reference object image. Despite the great advancements that diffusion models have made in video editing recently, these models often fall short in handling the intricacies of hand-object interactions (HOI), failing to produce realistic edits -- especially when object swapping results in object shape or functionality changes. To bridge this gap, we present HOI-Swap, a novel diffusion-based video editing framework trained in a self-supervised manner. Designed in two stages, the first stage focuses on object swapping in a single frame with HOI awareness; the model learns to adjust the interaction patterns, such as the hand grasp, based on changes in the object's properties. The second stage extends the single-frame edit across the entire sequence; we achieve controllable motion alignment with the original video by: (1) warping a new sequence from the stage-I edited frame based on sampled motion points and (2) conditioning video generation on the warped sequence. Comprehensive qualitative and quantitative evaluations demonstrate that HOI-Swap significantly outperforms existing methods, delivering high-quality video edits with realistic HOIs.
Put Myself in Your Shoes: Lifting the Egocentric Perspective from Exocentric Videos
Mar 11, 2024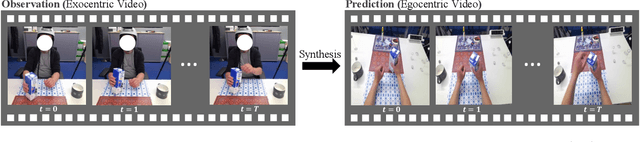
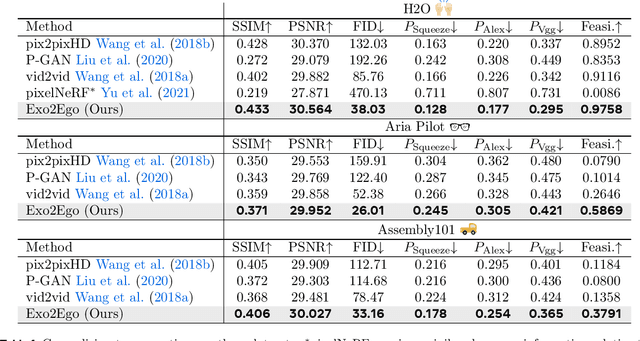
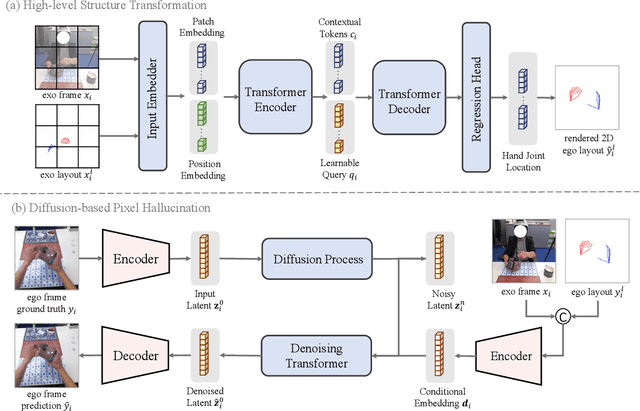
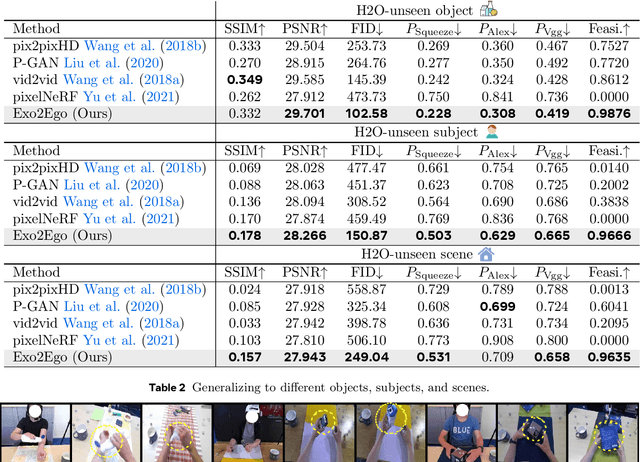
Abstract:We investigate exocentric-to-egocentric cross-view translation, which aims to generate a first-person (egocentric) view of an actor based on a video recording that captures the actor from a third-person (exocentric) perspective. To this end, we propose a generative framework called Exo2Ego that decouples the translation process into two stages: high-level structure transformation, which explicitly encourages cross-view correspondence between exocentric and egocentric views, and a diffusion-based pixel-level hallucination, which incorporates a hand layout prior to enhance the fidelity of the generated egocentric view. To pave the way for future advancements in this field, we curate a comprehensive exo-to-ego cross-view translation benchmark. It consists of a diverse collection of synchronized ego-exo tabletop activity video pairs sourced from three public datasets: H2O, Aria Pilot, and Assembly101. The experimental results validate that Exo2Ego delivers photorealistic video results with clear hand manipulation details and outperforms several baselines in terms of both synthesis quality and generalization ability to new actions.
Ego-Exo4D: Understanding Skilled Human Activity from First- and Third-Person Perspectives
Nov 30, 2023



Abstract:We present Ego-Exo4D, a diverse, large-scale multimodal multiview video dataset and benchmark challenge. Ego-Exo4D centers around simultaneously-captured egocentric and exocentric video of skilled human activities (e.g., sports, music, dance, bike repair). More than 800 participants from 13 cities worldwide performed these activities in 131 different natural scene contexts, yielding long-form captures from 1 to 42 minutes each and 1,422 hours of video combined. The multimodal nature of the dataset is unprecedented: the video is accompanied by multichannel audio, eye gaze, 3D point clouds, camera poses, IMU, and multiple paired language descriptions -- including a novel "expert commentary" done by coaches and teachers and tailored to the skilled-activity domain. To push the frontier of first-person video understanding of skilled human activity, we also present a suite of benchmark tasks and their annotations, including fine-grained activity understanding, proficiency estimation, cross-view translation, and 3D hand/body pose. All resources will be open sourced to fuel new research in the community.
MetaFormer Baselines for Vision
Oct 24, 2022



Abstract:MetaFormer, the abstracted architecture of Transformer, has been found to play a significant role in achieving competitive performance. In this paper, we further explore the capacity of MetaFormer, again, without focusing on token mixer design: we introduce several baseline models under MetaFormer using the most basic or common mixers, and summarize our observations as follows: (1) MetaFormer ensures solid lower bound of performance. By merely adopting identity mapping as the token mixer, the MetaFormer model, termed IdentityFormer, achieves >80% accuracy on ImageNet-1K. (2) MetaFormer works well with arbitrary token mixers. When specifying the token mixer as even a random matrix to mix tokens, the resulting model RandFormer yields an accuracy of >81%, outperforming IdentityFormer. Rest assured of MetaFormer's results when new token mixers are adopted. (3) MetaFormer effortlessly offers state-of-the-art results. With just conventional token mixers dated back five years ago, the models instantiated from MetaFormer already beat state of the art. (a) ConvFormer outperforms ConvNeXt. Taking the common depthwise separable convolutions as the token mixer, the model termed ConvFormer, which can be regarded as pure CNNs, outperforms the strong CNN model ConvNeXt. (b) CAFormer sets new record on ImageNet-1K. By simply applying depthwise separable convolutions as token mixer in the bottom stages and vanilla self-attention in the top stages, the resulting model CAFormer sets a new record on ImageNet-1K: it achieves an accuracy of 85.5% at 224x224 resolution, under normal supervised training without external data or distillation. In our expedition to probe MetaFormer, we also find that a new activation, StarReLU, reduces 71% FLOPs of activation compared with GELU yet achieves better performance. We expect StarReLU to find great potential in MetaFormer-like models alongside other neural networks.
MetaFormer is Actually What You Need for Vision
Nov 29, 2021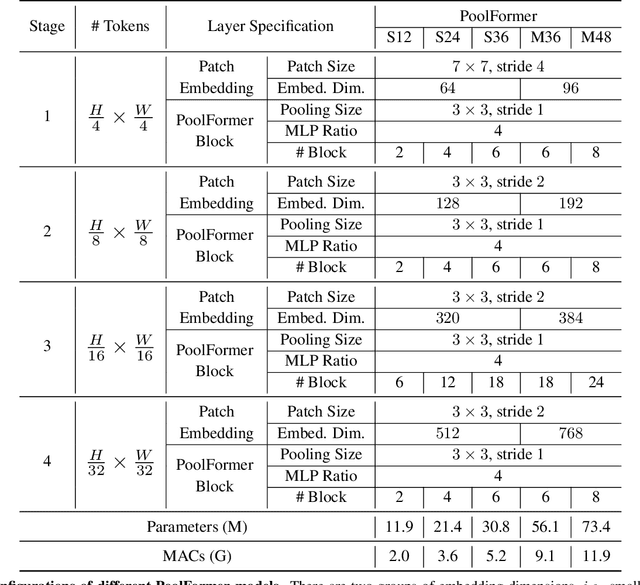
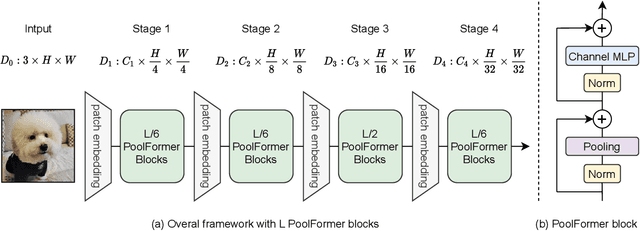
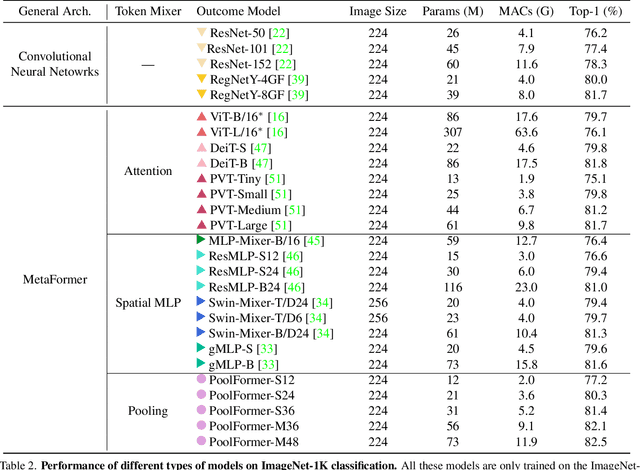
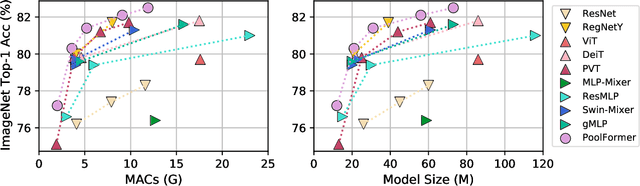
Abstract:Transformers have shown great potential in computer vision tasks. A common belief is their attention-based token mixer module contributes most to their competence. However, recent works show the attention-based module in transformers can be replaced by spatial MLPs and the resulted models still perform quite well. Based on this observation, we hypothesize that the general architecture of the transformers, instead of the specific token mixer module, is more essential to the model's performance. To verify this, we deliberately replace the attention module in transformers with an embarrassingly simple spatial pooling operator to conduct only the most basic token mixing. Surprisingly, we observe that the derived model, termed as PoolFormer, achieves competitive performance on multiple computer vision tasks. For example, on ImageNet-1K, PoolFormer achieves 82.1% top-1 accuracy, surpassing well-tuned vision transformer/MLP-like baselines DeiT-B/ResMLP-B24 by 0.3%/1.1% accuracy with 35%/52% fewer parameters and 48%/60% fewer MACs. The effectiveness of PoolFormer verifies our hypothesis and urges us to initiate the concept of "MetaFormer", a general architecture abstracted from transformers without specifying the token mixer. Based on the extensive experiments, we argue that MetaFormer is the key player in achieving superior results for recent transformer and MLP-like models on vision tasks. This work calls for more future research dedicated to improving MetaFormer instead of focusing on the token mixer modules. Additionally, our proposed PoolFormer could serve as a starting baseline for future MetaFormer architecture design. Code is available at https://github.com/sail-sg/poolformer
No Fear of Heterogeneity: Classifier Calibration for Federated Learning with Non-IID Data
Jun 09, 2021



Abstract:A central challenge in training classification models in the real-world federated system is learning with non-IID data. To cope with this, most of the existing works involve enforcing regularization in local optimization or improving the model aggregation scheme at the server. Other works also share public datasets or synthesized samples to supplement the training of under-represented classes or introduce a certain level of personalization. Though effective, they lack a deep understanding of how the data heterogeneity affects each layer of a deep classification model. In this paper, we bridge this gap by performing an experimental analysis of the representations learned by different layers. Our observations are surprising: (1) there exists a greater bias in the classifier than other layers, and (2) the classification performance can be significantly improved by post-calibrating the classifier after federated training. Motivated by the above findings, we propose a novel and simple algorithm called Classifier Calibration with Virtual Representations (CCVR), which adjusts the classifier using virtual representations sampled from an approximated gaussian mixture model. Experimental results demonstrate that CCVR achieves state-of-the-art performance on popular federated learning benchmarks including CIFAR-10, CIFAR-100, and CINIC-10. We hope that our simple yet effective method can shed some light on the future research of federated learning with non-IID data.
MetaSelector: Meta-Learning for Recommendation with User-Level Adaptive Model Selection
Feb 13, 2020


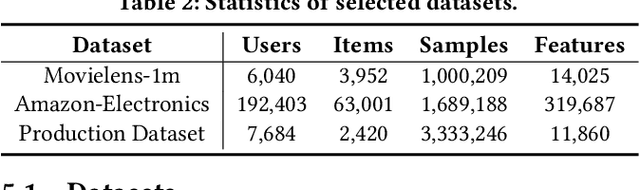
Abstract:Recommender systems often face heterogeneous datasets containing highly personalized historical data of users, where no single model could give the best recommendation for every user. We observe this ubiquitous phenomenon on both public and private datasets and address the model selection problem in pursuit of optimizing the quality of recommendation for each user. We propose a meta-learning framework to facilitate user-level adaptive model selection in recommender systems. In this framework, a collection of recommenders is trained with data from all users, on top of which a model selector is trained via meta-learning to select the best single model for each user with the user-specific historical data. We conduct extensive experiments on two public datasets and a real-world production dataset, demonstrating that our proposed framework achieves improvements over single model baselines and sample-level model selector in terms of AUC and LogLoss. In particular, the improvements may lead to huge profit gain when deployed in online recommender systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge