Merey Ramazanova
Pixels or Positions? Benchmarking Modalities in Group Activity Recognition
Nov 16, 2025Abstract:Group Activity Recognition (GAR) is well studied on the video modality for surveillance and indoor team sports (e.g., volleyball, basketball). Yet, other modalities such as agent positions and trajectories over time, i.e. tracking, remain comparatively under-explored despite being compact, agent-centric signals that explicitly encode spatial interactions. Understanding whether pixel (video) or position (tracking) modalities leads to better group activity recognition is therefore important to drive further research on the topic. However, no standardized benchmark currently exists that aligns broadcast video and tracking data for the same group activities, leading to a lack of apples-to-apples comparison between these modalities for GAR. In this work, we introduce SoccerNet-GAR, a multimodal dataset built from the $64$ matches of the football World Cup 2022. Specifically, the broadcast videos and player tracking modalities for $94{,}285$ group activities are synchronized and annotated with $10$ categories. Furthermore, we define a unified evaluation protocol to benchmark two strong unimodal approaches: (i) a competitive video-based classifiers and (ii) a tracking-based classifiers leveraging graph neural networks. In particular, our novel role-aware graph architecture for tracking-based GAR directly encodes tactical structure through positional edges and temporal attention. Our tracking model achieves $67.2\%$ balanced accuracy compared to $58.1\%$ for the best video baseline, while training $4.25 \times$ faster with $438 \times$ fewer parameters ($197K$ \vs $86.3M$). This study provides new insights into the relative strengths of pixels and positions for group activity recognition. Overall, it highlights the importance of modality choice and role-aware modeling for GAR.
OpenTAD: A Unified Framework and Comprehensive Study of Temporal Action Detection
Feb 27, 2025Abstract:Temporal action detection (TAD) is a fundamental video understanding task that aims to identify human actions and localize their temporal boundaries in videos. Although this field has achieved remarkable progress in recent years, further progress and real-world applications are impeded by the absence of a standardized framework. Currently, different methods are compared under different implementation settings, evaluation protocols, etc., making it difficult to assess the real effectiveness of a specific technique. To address this issue, we propose \textbf{OpenTAD}, a unified TAD framework consolidating 16 different TAD methods and 9 standard datasets into a modular codebase. In OpenTAD, minimal effort is required to replace one module with a different design, train a feature-based TAD model in end-to-end mode, or switch between the two. OpenTAD also facilitates straightforward benchmarking across various datasets and enables fair and in-depth comparisons among different methods. With OpenTAD, we comprehensively study how innovations in different network components affect detection performance and identify the most effective design choices through extensive experiments. This study has led to a new state-of-the-art TAD method built upon existing techniques for each component. We have made our code and models available at https://github.com/sming256/OpenTAD.
Combating Missing Modalities in Egocentric Videos at Test Time
Apr 23, 2024

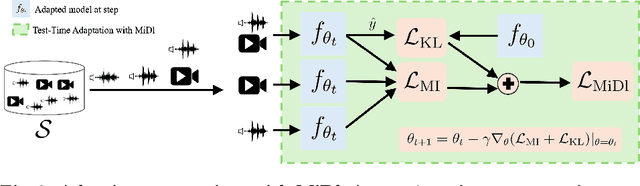

Abstract:Understanding videos that contain multiple modalities is crucial, especially in egocentric videos, where combining various sensory inputs significantly improves tasks like action recognition and moment localization. However, real-world applications often face challenges with incomplete modalities due to privacy concerns, efficiency needs, or hardware issues. Current methods, while effective, often necessitate retraining the model entirely to handle missing modalities, making them computationally intensive, particularly with large training datasets. In this study, we propose a novel approach to address this issue at test time without requiring retraining. We frame the problem as a test-time adaptation task, where the model adjusts to the available unlabeled data at test time. Our method, MiDl~(Mutual information with self-Distillation), encourages the model to be insensitive to the specific modality source present during testing by minimizing the mutual information between the prediction and the available modality. Additionally, we incorporate self-distillation to maintain the model's original performance when both modalities are available. MiDl represents the first self-supervised, online solution for handling missing modalities exclusively at test time. Through experiments with various pretrained models and datasets, MiDl demonstrates substantial performance improvement without the need for retraining.
Exploring Missing Modality in Multimodal Egocentric Datasets
Jan 21, 2024Abstract:Multimodal video understanding is crucial for analyzing egocentric videos, where integrating multiple sensory signals significantly enhances action recognition and moment localization. However, practical applications often grapple with incomplete modalities due to factors like privacy concerns, efficiency demands, or hardware malfunctions. Addressing this, our study delves into the impact of missing modalities on egocentric action recognition, particularly within transformer-based models. We introduce a novel concept -Missing Modality Token (MMT)-to maintain performance even when modalities are absent, a strategy that proves effective in the Ego4D, Epic-Kitchens, and Epic-Sounds datasets. Our method mitigates the performance loss, reducing it from its original $\sim 30\%$ drop to only $\sim 10\%$ when half of the test set is modal-incomplete. Through extensive experimentation, we demonstrate the adaptability of MMT to different training scenarios and its superiority in handling missing modalities compared to current methods. Our research contributes a comprehensive analysis and an innovative approach, opening avenues for more resilient multimodal systems in real-world settings.
Ego-Exo4D: Understanding Skilled Human Activity from First- and Third-Person Perspectives
Nov 30, 2023



Abstract:We present Ego-Exo4D, a diverse, large-scale multimodal multiview video dataset and benchmark challenge. Ego-Exo4D centers around simultaneously-captured egocentric and exocentric video of skilled human activities (e.g., sports, music, dance, bike repair). More than 800 participants from 13 cities worldwide performed these activities in 131 different natural scene contexts, yielding long-form captures from 1 to 42 minutes each and 1,422 hours of video combined. The multimodal nature of the dataset is unprecedented: the video is accompanied by multichannel audio, eye gaze, 3D point clouds, camera poses, IMU, and multiple paired language descriptions -- including a novel "expert commentary" done by coaches and teachers and tailored to the skilled-activity domain. To push the frontier of first-person video understanding of skilled human activity, we also present a suite of benchmark tasks and their annotations, including fine-grained activity understanding, proficiency estimation, cross-view translation, and 3D hand/body pose. All resources will be open sourced to fuel new research in the community.
Just a Glimpse: Rethinking Temporal Information for Video Continual Learning
May 28, 2023Abstract:Class-incremental learning is one of the most important settings for the study of Continual Learning, as it closely resembles real-world application scenarios. With constrained memory sizes, catastrophic forgetting arises as the number of classes/tasks increases. Studying continual learning in the video domain poses even more challenges, as video data contains a large number of frames, which places a higher burden on the replay memory. The current common practice is to sub-sample frames from the video stream and store them in the replay memory. In this paper, we propose SMILE a novel replay mechanism for effective video continual learning based on individual/single frames. Through extensive experimentation, we show that under extreme memory constraints, video diversity plays a more significant role than temporal information. Therefore, our method focuses on learning from a small number of frames that represent a large number of unique videos. On three representative video datasets, Kinetics, UCF101, and ActivityNet, the proposed method achieves state-of-the-art performance, outperforming the previous state-of-the-art by up to 21.49%.
Revisiting Test Time Adaptation under Online Evaluation
Apr 10, 2023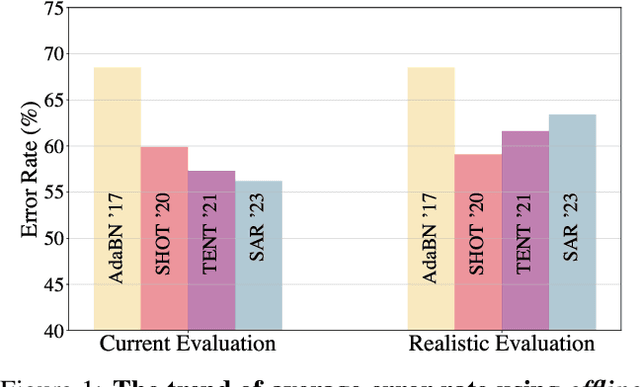

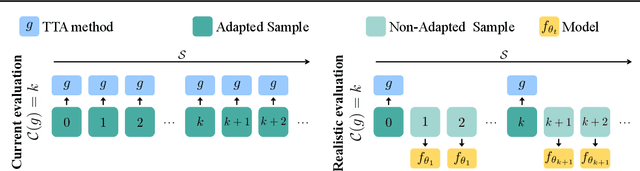
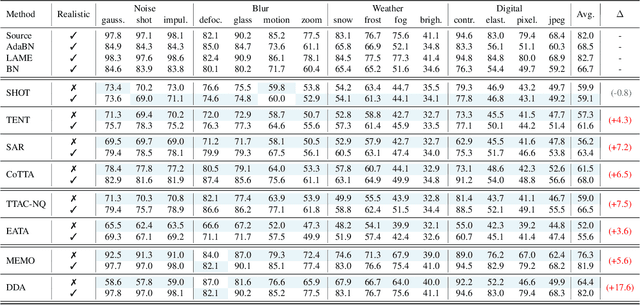
Abstract:This paper proposes a novel online evaluation protocol for Test Time Adaptation (TTA) methods, which penalizes slower methods by providing them with fewer samples for adaptation. TTA methods leverage unlabeled data at test time to adapt to distribution shifts. Though many effective methods have been proposed, their impressive performance usually comes at the cost of significantly increased computation budgets. Current evaluation protocols overlook the effect of this extra computation cost, affecting their real-world applicability. To address this issue, we propose a more realistic evaluation protocol for TTA methods, where data is received in an online fashion from a constant-speed data stream, thereby accounting for the method's adaptation speed. We apply our proposed protocol to benchmark several TTA methods on multiple datasets and scenarios. Extensive experiments shows that, when accounting for inference speed, simple and fast approaches can outperform more sophisticated but slower methods. For example, SHOT from 2020 outperforms the state-of-the-art method SAR from 2023 under our online setting. Our online evaluation protocol emphasizes the need for developing TTA methods that are efficient and applicable in realistic settings.
SegTAD: Precise Temporal Action Detection via Semantic Segmentation
Mar 03, 2022



Abstract:Temporal action detection (TAD) is an important yet challenging task in video analysis. Most existing works draw inspiration from image object detection and tend to reformulate it as a proposal generation - classification problem. However, there are two caveats with this paradigm. First, proposals are not equipped with annotated labels, which have to be empirically compiled, thus the information in the annotations is not necessarily precisely employed in the model training process. Second, there are large variations in the temporal scale of actions, and neglecting this fact may lead to deficient representation in the video features. To address these issues and precisely model temporal action detection, we formulate the task of temporal action detection in a novel perspective of semantic segmentation. Owing to the 1-dimensional property of TAD, we are able to convert the coarse-grained detection annotations to fine-grained semantic segmentation annotations for free. We take advantage of them to provide precise supervision so as to mitigate the impact induced by the imprecise proposal labels. We propose an end-to-end framework SegTAD composed of a 1D semantic segmentation network (1D-SSN) and a proposal detection network (PDN).
OWL (Observe, Watch, Listen): Localizing Actions in Egocentric Video via Audiovisual Temporal Context
Feb 14, 2022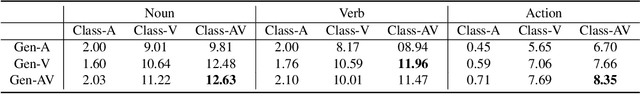
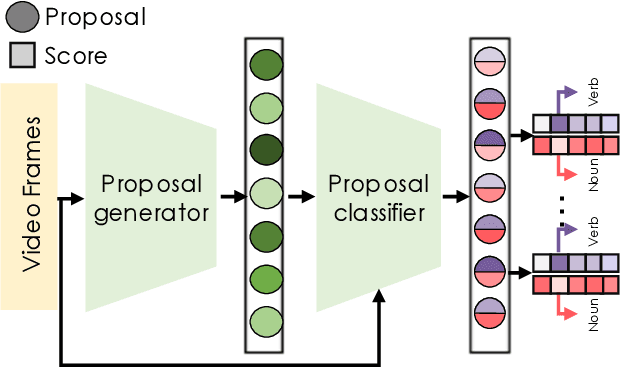
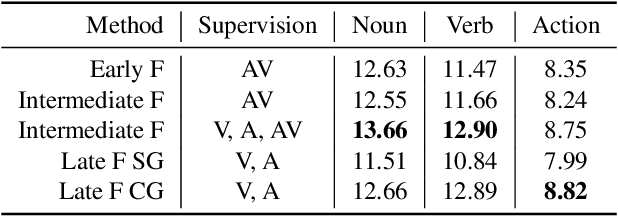
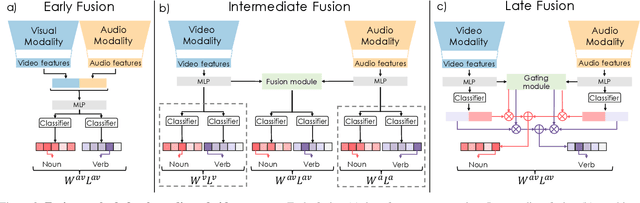
Abstract:Temporal action localization (TAL) is an important task extensively explored and improved for third-person videos in recent years. Recent efforts have been made to perform fine-grained temporal localization on first-person videos. However, current TAL methods only use visual signals, neglecting the audio modality that exists in most videos and that shows meaningful action information in egocentric videos. In this work, we take a deep look into the effectiveness of audio in detecting actions in egocentric videos and introduce a simple-yet-effective approach via Observing, Watching, and Listening (OWL) to leverage audio-visual information and context for egocentric TAL. For doing that, we: 1) compare and study different strategies for where and how to fuse the two modalities; 2) propose a transformer-based model to incorporate temporal audio-visual context. Our experiments show that our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance on EPIC-KITCHENS-100.
Ego4D: Around the World in 3,000 Hours of Egocentric Video
Oct 13, 2021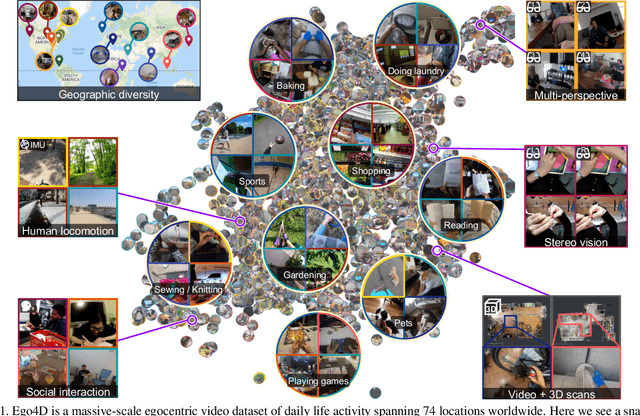
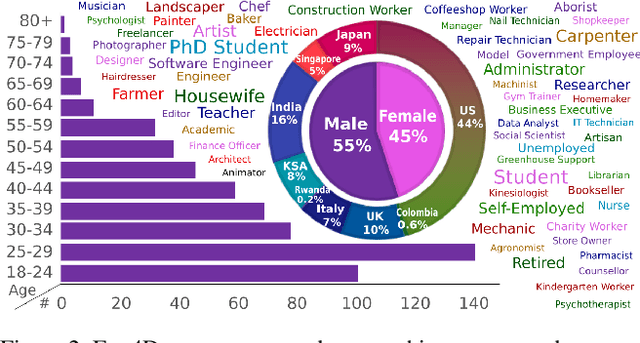

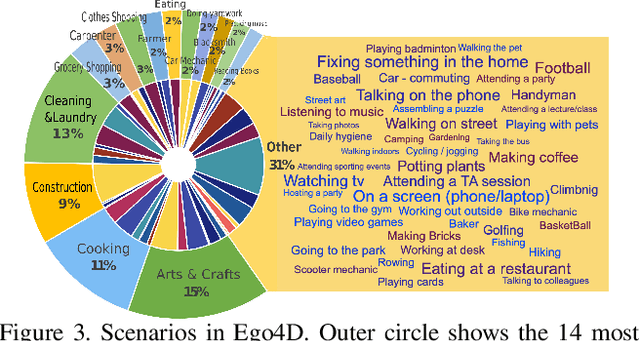
Abstract:We introduce Ego4D, a massive-scale egocentric video dataset and benchmark suite. It offers 3,025 hours of daily-life activity video spanning hundreds of scenarios (household, outdoor, workplace, leisure, etc.) captured by 855 unique camera wearers from 74 worldwide locations and 9 different countries. The approach to collection is designed to uphold rigorous privacy and ethics standards with consenting participants and robust de-identification procedures where relevant. Ego4D dramatically expands the volume of diverse egocentric video footage publicly available to the research community. Portions of the video are accompanied by audio, 3D meshes of the environment, eye gaze, stereo, and/or synchronized videos from multiple egocentric cameras at the same event. Furthermore, we present a host of new benchmark challenges centered around understanding the first-person visual experience in the past (querying an episodic memory), present (analyzing hand-object manipulation, audio-visual conversation, and social interactions), and future (forecasting activities). By publicly sharing this massive annotated dataset and benchmark suite, we aim to push the frontier of first-person perception. Project page: https://ego4d-data.org/
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge