Marvin Klingner
CleverDistiller: Simple and Spatially Consistent Cross-modal Distillation
Mar 12, 2025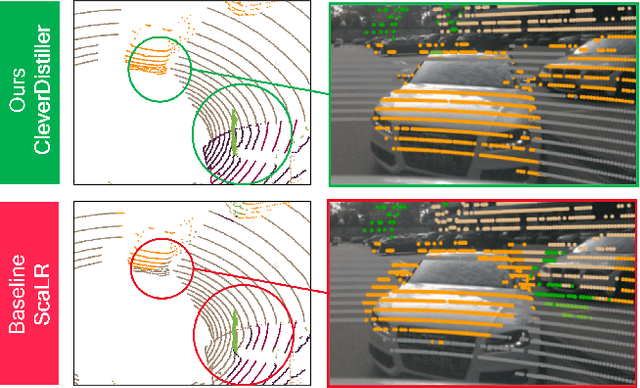
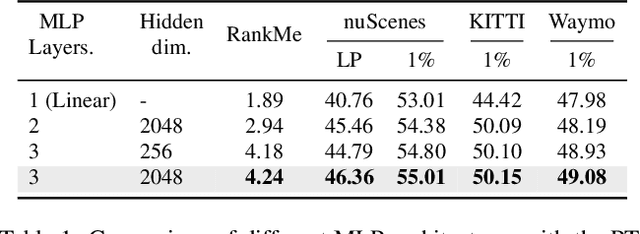
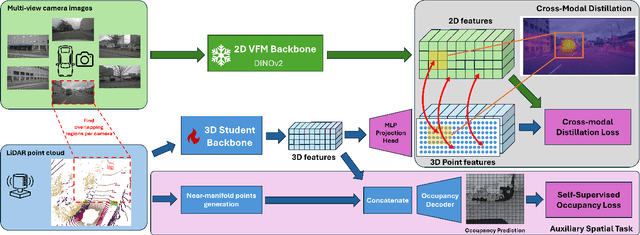
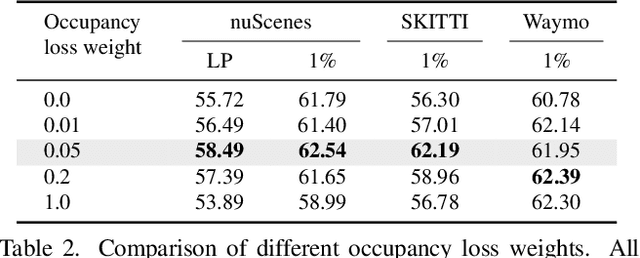
Abstract:Vision foundation models (VFMs) such as DINO have led to a paradigm shift in 2D camera-based perception towards extracting generalized features to support many downstream tasks. Recent works introduce self-supervised cross-modal knowledge distillation (KD) as a way to transfer these powerful generalization capabilities into 3D LiDAR-based models. However, they either rely on highly complex distillation losses, pseudo-semantic maps, or limit KD to features useful for semantic segmentation only. In this work, we propose CleverDistiller, a self-supervised, cross-modal 2D-to-3D KD framework introducing a set of simple yet effective design choices: Unlike contrastive approaches relying on complex loss design choices, our method employs a direct feature similarity loss in combination with a multi layer perceptron (MLP) projection head to allow the 3D network to learn complex semantic dependencies throughout the projection. Crucially, our approach does not depend on pseudo-semantic maps, allowing for direct knowledge transfer from a VFM without explicit semantic supervision. Additionally, we introduce the auxiliary self-supervised spatial task of occupancy prediction to enhance the semantic knowledge, obtained from a VFM through KD, with 3D spatial reasoning capabilities. Experiments on standard autonomous driving benchmarks for 2D-to-3D KD demonstrate that CleverDistiller achieves state-of-the-art performance in both semantic segmentation and 3D object detection (3DOD) by up to 10% mIoU, especially when fine tuning on really low data amounts, showing the effectiveness of our simple yet powerful KD strategy
S3PT: Scene Semantics and Structure Guided Clustering to Boost Self-Supervised Pre-Training for Autonomous Driving
Oct 30, 2024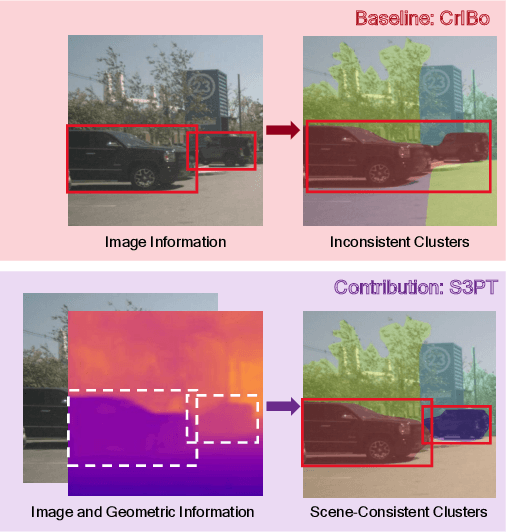
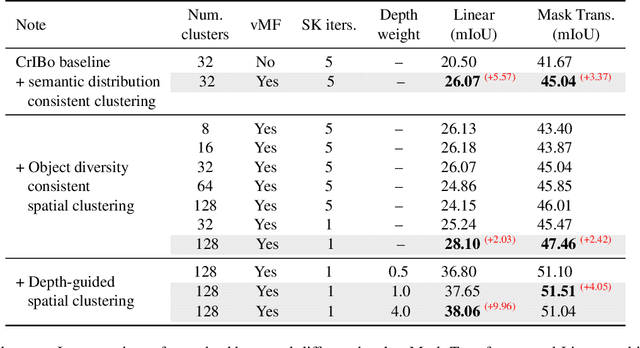
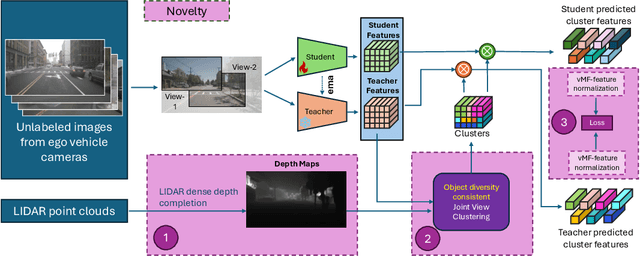
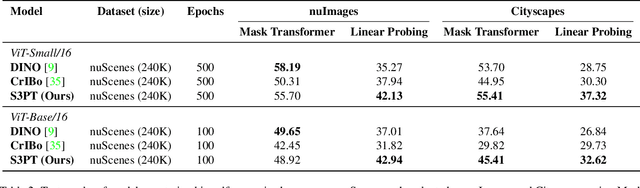
Abstract:Recent self-supervised clustering-based pre-training techniques like DINO and Cribo have shown impressive results for downstream detection and segmentation tasks. However, real-world applications such as autonomous driving face challenges with imbalanced object class and size distributions and complex scene geometries. In this paper, we propose S3PT a novel scene semantics and structure guided clustering to provide more scene-consistent objectives for self-supervised training. Specifically, our contributions are threefold: First, we incorporate semantic distribution consistent clustering to encourage better representation of rare classes such as motorcycles or animals. Second, we introduce object diversity consistent spatial clustering, to handle imbalanced and diverse object sizes, ranging from large background areas to small objects such as pedestrians and traffic signs. Third, we propose a depth-guided spatial clustering to regularize learning based on geometric information of the scene, thus further refining region separation on the feature level. Our learned representations significantly improve performance in downstream semantic segmentation and 3D object detection tasks on the nuScenes, nuImages, and Cityscapes datasets and show promising domain translation properties.
X-Align++: cross-modal cross-view alignment for Bird's-eye-view segmentation
Jun 06, 2023Abstract:Bird's-eye-view (BEV) grid is a typical representation of the perception of road components, e.g., drivable area, in autonomous driving. Most existing approaches rely on cameras only to perform segmentation in BEV space, which is fundamentally constrained by the absence of reliable depth information. The latest works leverage both camera and LiDAR modalities but suboptimally fuse their features using simple, concatenation-based mechanisms. In this paper, we address these problems by enhancing the alignment of the unimodal features in order to aid feature fusion, as well as enhancing the alignment between the cameras' perspective view (PV) and BEV representations. We propose X-Align, a novel end-to-end cross-modal and cross-view learning framework for BEV segmentation consisting of the following components: (i) a novel Cross-Modal Feature Alignment (X-FA) loss, (ii) an attention-based Cross-Modal Feature Fusion (X-FF) module to align multi-modal BEV features implicitly, and (iii) an auxiliary PV segmentation branch with Cross-View Segmentation Alignment (X-SA) losses to improve the PV-to-BEV transformation. We evaluate our proposed method across two commonly used benchmark datasets, i.e., nuScenes and KITTI-360. Notably, X-Align significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art by 3 absolute mIoU points on nuScenes. We also provide extensive ablation studies to demonstrate the effectiveness of the individual components.
X$^3$KD: Knowledge Distillation Across Modalities, Tasks and Stages for Multi-Camera 3D Object Detection
Mar 03, 2023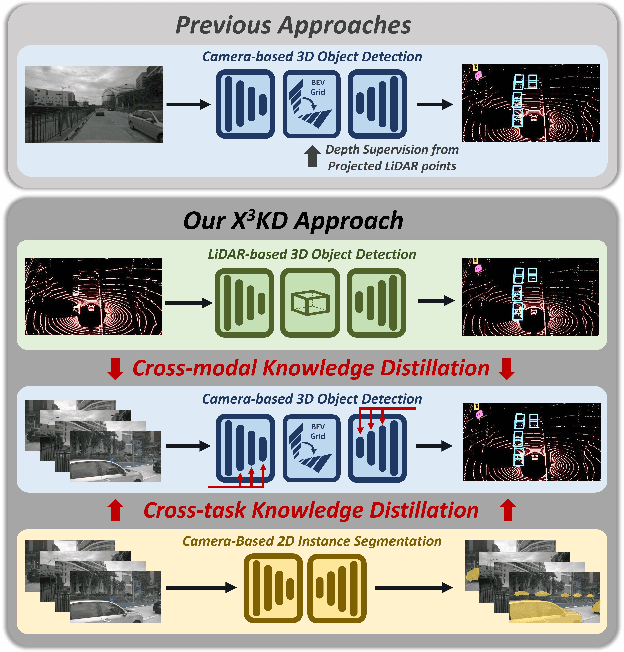
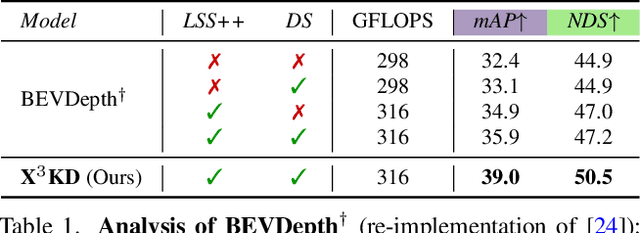
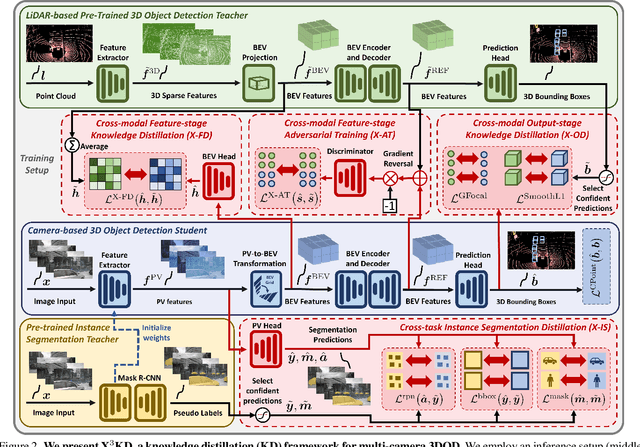
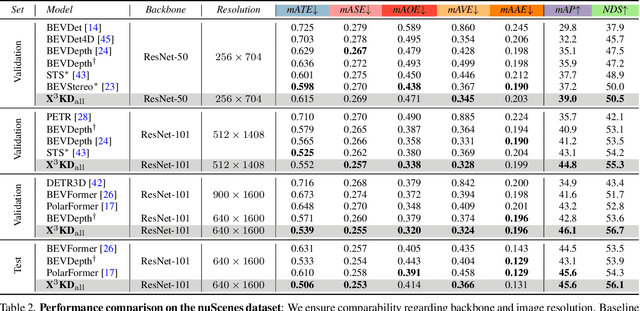
Abstract:Recent advances in 3D object detection (3DOD) have obtained remarkably strong results for LiDAR-based models. In contrast, surround-view 3DOD models based on multiple camera images underperform due to the necessary view transformation of features from perspective view (PV) to a 3D world representation which is ambiguous due to missing depth information. This paper introduces X$^3$KD, a comprehensive knowledge distillation framework across different modalities, tasks, and stages for multi-camera 3DOD. Specifically, we propose cross-task distillation from an instance segmentation teacher (X-IS) in the PV feature extraction stage providing supervision without ambiguous error backpropagation through the view transformation. After the transformation, we apply cross-modal feature distillation (X-FD) and adversarial training (X-AT) to improve the 3D world representation of multi-camera features through the information contained in a LiDAR-based 3DOD teacher. Finally, we also employ this teacher for cross-modal output distillation (X-OD), providing dense supervision at the prediction stage. We perform extensive ablations of knowledge distillation at different stages of multi-camera 3DOD. Our final X$^3$KD model outperforms previous state-of-the-art approaches on the nuScenes and Waymo datasets and generalizes to RADAR-based 3DOD. Qualitative results video at https://youtu.be/1do9DPFmr38.
X-Align: Cross-Modal Cross-View Alignment for Bird's-Eye-View Segmentation
Oct 13, 2022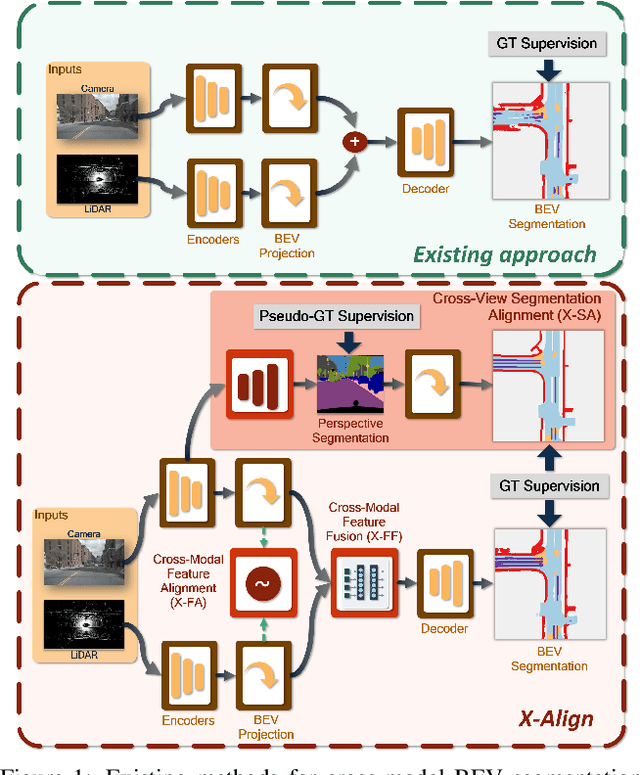
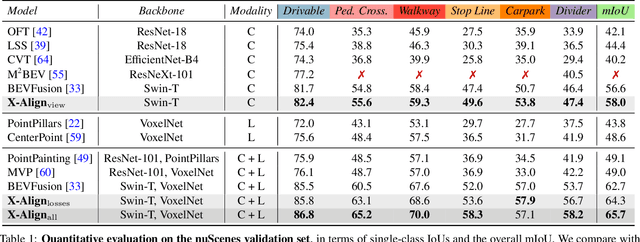
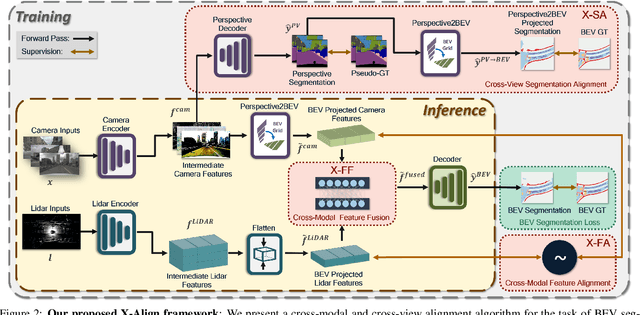
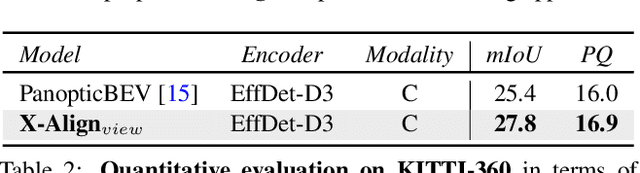
Abstract:Bird's-eye-view (BEV) grid is a common representation for the perception of road components, e.g., drivable area, in autonomous driving. Most existing approaches rely on cameras only to perform segmentation in BEV space, which is fundamentally constrained by the absence of reliable depth information. Latest works leverage both camera and LiDAR modalities, but sub-optimally fuse their features using simple, concatenation-based mechanisms. In this paper, we address these problems by enhancing the alignment of the unimodal features in order to aid feature fusion, as well as enhancing the alignment between the cameras' perspective view (PV) and BEV representations. We propose X-Align, a novel end-to-end cross-modal and cross-view learning framework for BEV segmentation consisting of the following components: (i) a novel Cross-Modal Feature Alignment (X-FA) loss, (ii) an attention-based Cross-Modal Feature Fusion (X-FF) module to align multi-modal BEV features implicitly, and (iii) an auxiliary PV segmentation branch with Cross-View Segmentation Alignment (X-SA) losses to improve the PV-to-BEV transformation. We evaluate our proposed method across two commonly used benchmark datasets, i.e., nuScenes and KITTI-360. Notably, X-Align significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art by 3 absolute mIoU points on nuScenes. We also provide extensive ablation studies to demonstrate the effectiveness of the individual components.
On the Choice of Data for Efficient Training and Validation of End-to-End Driving Models
Jun 01, 2022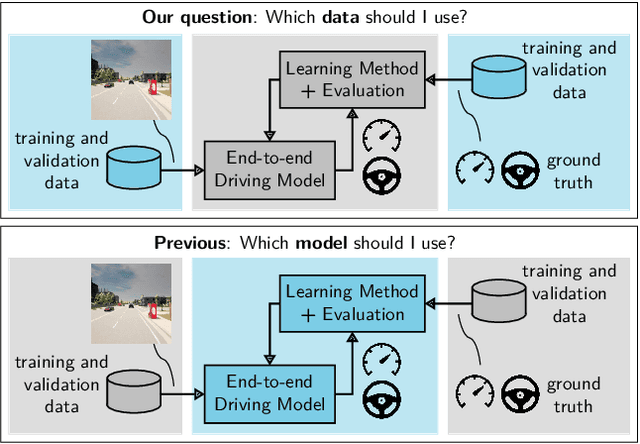
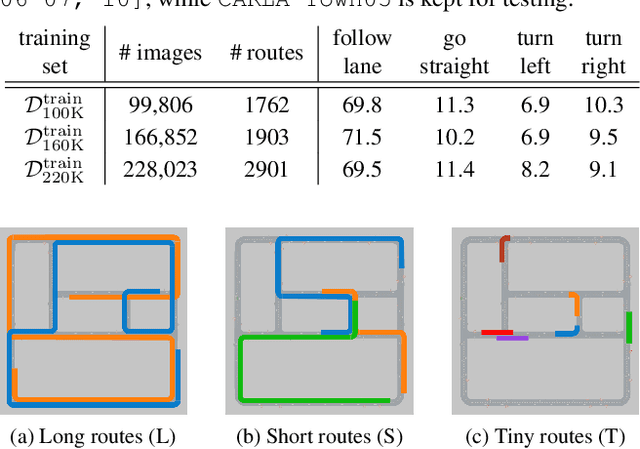
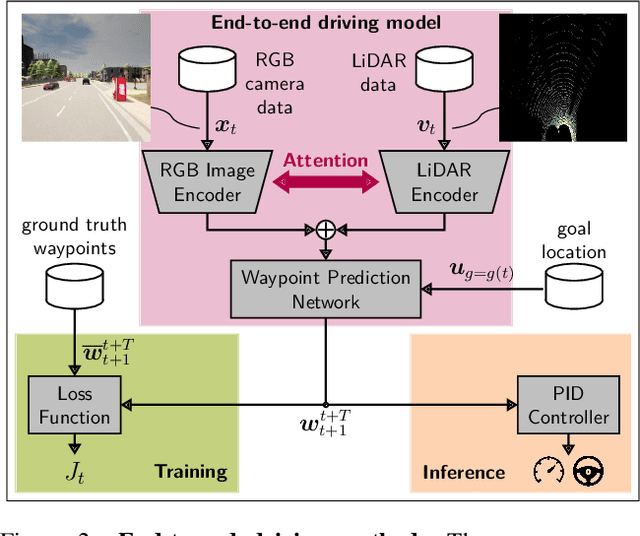
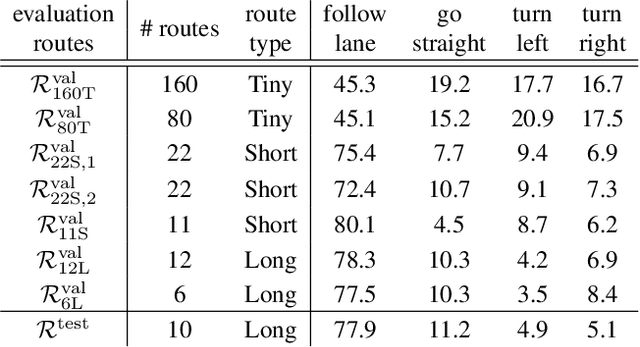
Abstract:The emergence of data-driven machine learning (ML) has facilitated significant progress in many complicated tasks such as highly-automated driving. While much effort is put into improving the ML models and learning algorithms in such applications, little focus is put into how the training data and/or validation setting should be designed. In this paper we investigate the influence of several data design choices regarding training and validation of deep driving models trainable in an end-to-end fashion. Specifically, (i) we investigate how the amount of training data influences the final driving performance, and which performance limitations are induced through currently used mechanisms to generate training data. (ii) Further, we show by correlation analysis, which validation design enables the driving performance measured during validation to generalize well to unknown test environments. (iii) Finally, we investigate the effect of random seeding and non-determinism, giving insights which reported improvements can be deemed significant. Our evaluations using the popular CARLA simulator provide recommendations regarding data generation and driving route selection for an efficient future development of end-to-end driving models.
Detecting Adversarial Perturbations in Multi-Task Perception
Mar 02, 2022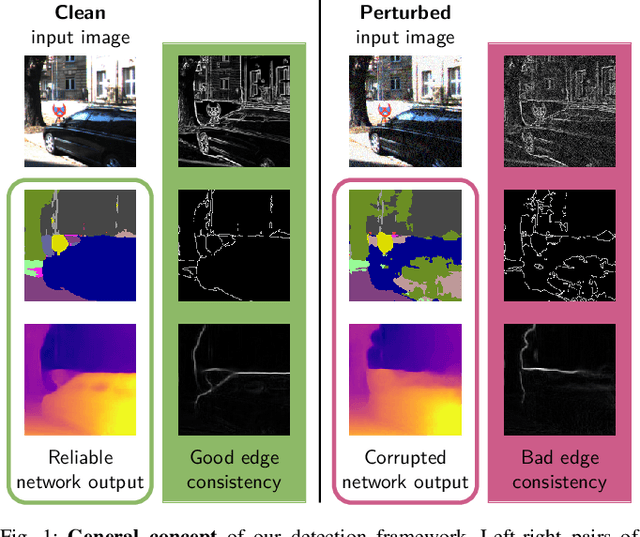
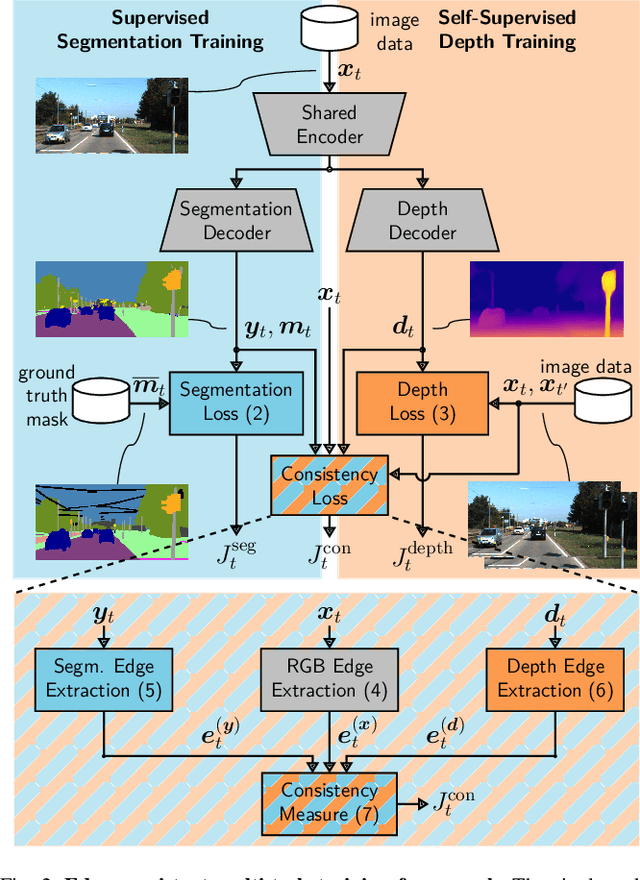
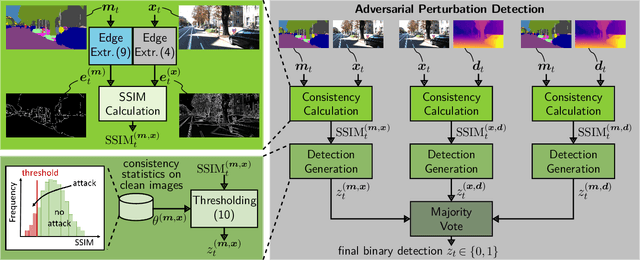
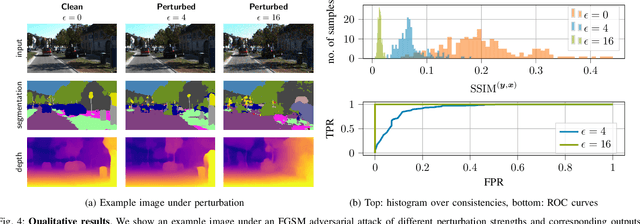
Abstract:While deep neural networks (DNNs) achieve impressive performance on environment perception tasks, their sensitivity to adversarial perturbations limits their use in practical applications. In this paper, we (i) propose a novel adversarial perturbation detection scheme based on multi-task perception of complex vision tasks (i.e., depth estimation and semantic segmentation). Specifically, adversarial perturbations are detected by inconsistencies between extracted edges of the input image, the depth output, and the segmentation output. To further improve this technique, we (ii) develop a novel edge consistency loss between all three modalities, thereby improving their initial consistency which in turn supports our detection scheme. We verify our detection scheme's effectiveness by employing various known attacks and image noises. In addition, we (iii) develop a multi-task adversarial attack, aiming at fooling both tasks as well as our detection scheme. Experimental evaluation on the Cityscapes and KITTI datasets shows that under an assumption of a 5% false positive rate up to 100% of images are correctly detected as adversarially perturbed, depending on the strength of the perturbation. Code will be available on github. A short video at https://youtu.be/KKa6gOyWmH4 provides qualitative results.
Continual BatchNorm Adaptation (CBNA) for Semantic Segmentation
Mar 02, 2022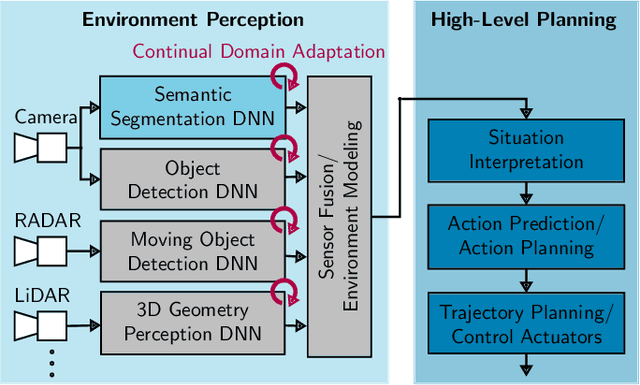
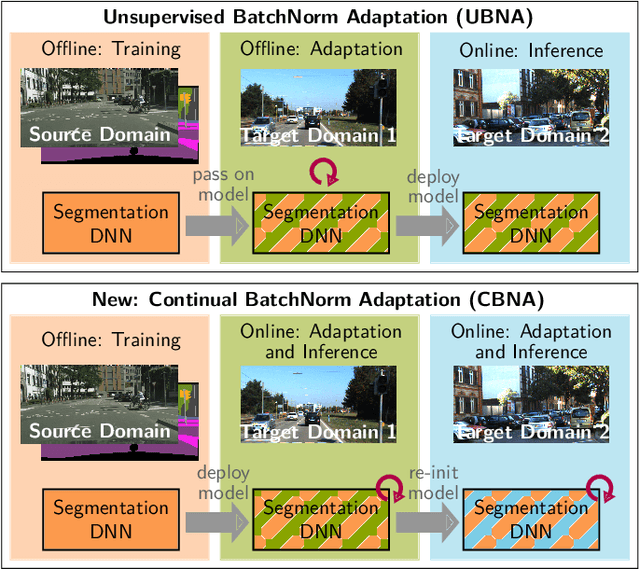
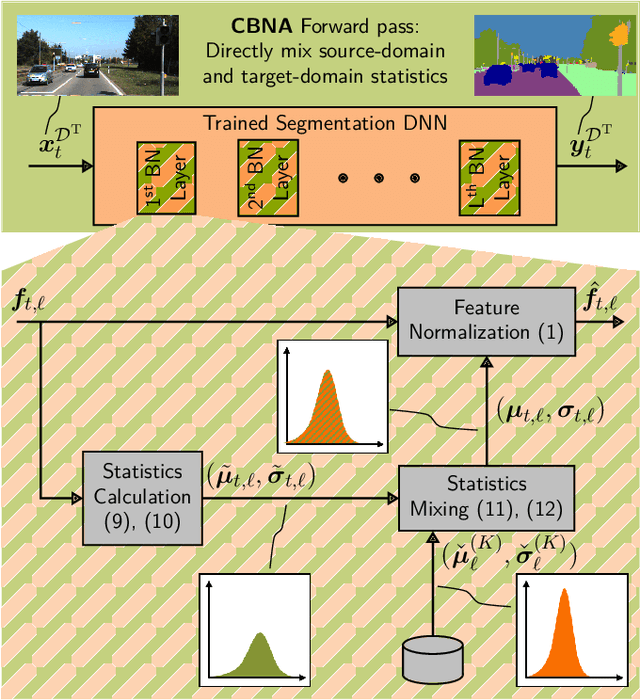
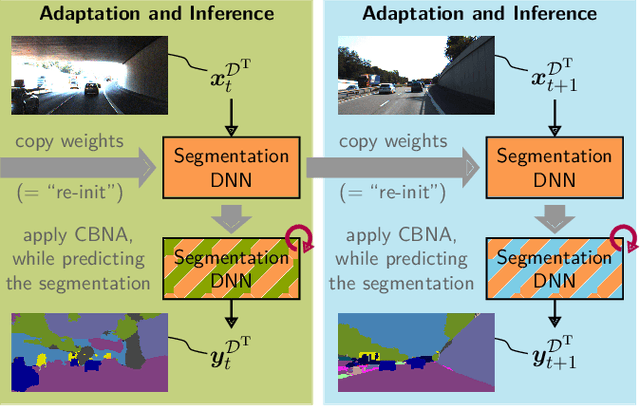
Abstract:Environment perception in autonomous driving vehicles often heavily relies on deep neural networks (DNNs), which are subject to domain shifts, leading to a significantly decreased performance during DNN deployment. Usually, this problem is addressed by unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) approaches trained either simultaneously on source and target domain datasets or even source-free only on target data in an offline fashion. In this work, we further expand a source-free UDA approach to a continual and therefore online-capable UDA on a single-image basis for semantic segmentation. Accordingly, our method only requires the pre-trained model from the supplier (trained in the source domain) and the current (unlabeled target domain) camera image. Our method Continual BatchNorm Adaptation (CBNA) modifies the source domain statistics in the batch normalization layers, using target domain images in an unsupervised fashion, which yields consistent performance improvements during inference. Thereby, in contrast to existing works, our approach can be applied to improve a DNN continuously on a single-image basis during deployment without access to source data, without algorithmic delay, and nearly without computational overhead. We show the consistent effectiveness of our method across a wide variety of source/target domain settings for semantic segmentation. As part of this work, our code will be made publicly available.
Inspect, Understand, Overcome: A Survey of Practical Methods for AI Safety
Apr 29, 2021Abstract:The use of deep neural networks (DNNs) in safety-critical applications like mobile health and autonomous driving is challenging due to numerous model-inherent shortcomings. These shortcomings are diverse and range from a lack of generalization over insufficient interpretability to problems with malicious inputs. Cyber-physical systems employing DNNs are therefore likely to suffer from safety concerns. In recent years, a zoo of state-of-the-art techniques aiming to address these safety concerns has emerged. This work provides a structured and broad overview of them. We first identify categories of insufficiencies to then describe research activities aiming at their detection, quantification, or mitigation. Our paper addresses both machine learning experts and safety engineers: The former ones might profit from the broad range of machine learning topics covered and discussions on limitations of recent methods. The latter ones might gain insights into the specifics of modern ML methods. We moreover hope that our contribution fuels discussions on desiderata for ML systems and strategies on how to propel existing approaches accordingly.
Improving Online Performance Prediction for Semantic Segmentation
Apr 12, 2021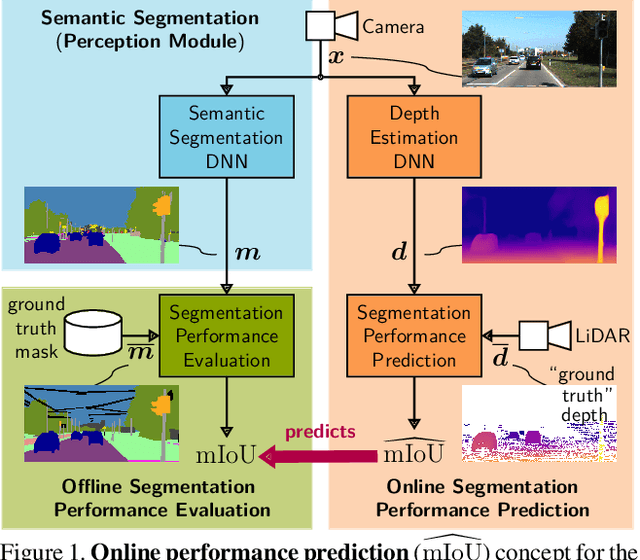
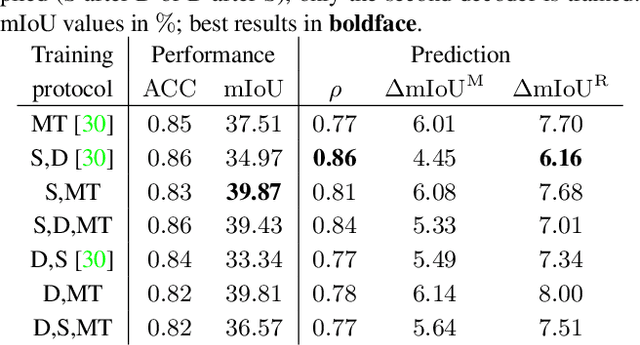
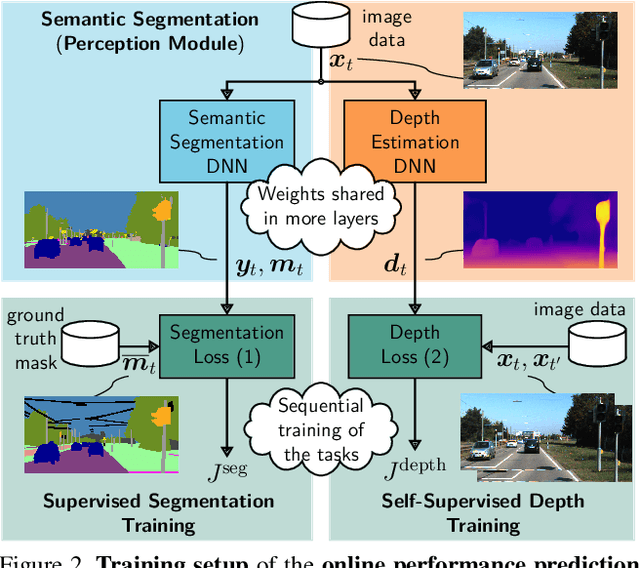
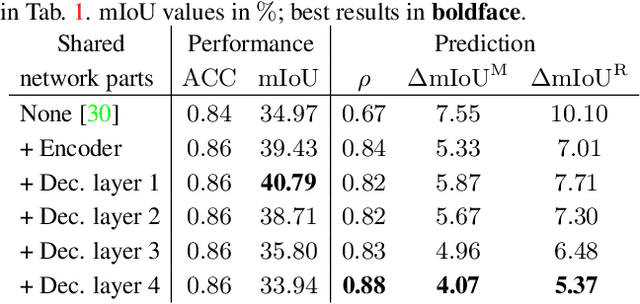
Abstract:In this work we address the task of observing the performance of a semantic segmentation deep neural network (DNN) during online operation, i.e., during inference, which is of high importance in safety-critical applications such as autonomous driving. Here, many high-level decisions rely on such DNNs, which are usually evaluated offline, while their performance in online operation remains unknown. To solve this problem, we propose an improved online performance prediction scheme, building on a recently proposed concept of predicting the primary semantic segmentation task's performance. This can be achieved by evaluating the auxiliary task of monocular depth estimation with a measurement supplied by a LiDAR sensor and a subsequent regression to the semantic segmentation performance. In particular, we propose (i) sequential training methods for both tasks in a multi-task training setup, (ii) to share the encoder as well as parts of the decoder between both task's networks for improved efficiency, and (iii) a temporal statistics aggregation method, which significantly reduces the performance prediction error at the cost of a small algorithmic latency. Evaluation on the KITTI dataset shows that all three aspects improve the performance prediction compared to previous approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge