Marie Piraud
Leveraging Multi-Rater Annotations to Calibrate Object Detectors in Microscopy Imaging
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Deep learning-based object detectors have achieved impressive performance in microscopy imaging, yet their confidence estimates often lack calibration, limiting their reliability for biomedical applications. In this work, we introduce a new approach to improve model calibration by leveraging multi-rater annotations. We propose to train separate models on the annotations from single experts and aggregate their predictions to emulate consensus. This improves upon label sampling strategies, where models are trained on mixed annotations, and offers a more principled way to capture inter-rater variability. Experiments on a colorectal organoid dataset annotated by two experts demonstrate that our rater-specific ensemble strategy improves calibration performance while maintaining comparable detection accuracy. These findings suggest that explicitly modelling rater disagreement can lead to more trustworthy object detectors in biomedical imaging.
Analysis of the MICCAI Brain Tumor Segmentation -- Metastases (BraTS-METS) 2025 Lighthouse Challenge: Brain Metastasis Segmentation on Pre- and Post-treatment MRI
Apr 16, 2025Abstract:Despite continuous advancements in cancer treatment, brain metastatic disease remains a significant complication of primary cancer and is associated with an unfavorable prognosis. One approach for improving diagnosis, management, and outcomes is to implement algorithms based on artificial intelligence for the automated segmentation of both pre- and post-treatment MRI brain images. Such algorithms rely on volumetric criteria for lesion identification and treatment response assessment, which are still not available in clinical practice. Therefore, it is critical to establish tools for rapid volumetric segmentations methods that can be translated to clinical practice and that are trained on high quality annotated data. The BraTS-METS 2025 Lighthouse Challenge aims to address this critical need by establishing inter-rater and intra-rater variability in dataset annotation by generating high quality annotated datasets from four individual instances of segmentation by neuroradiologists while being recorded on video (two instances doing "from scratch" and two instances after AI pre-segmentation). This high-quality annotated dataset will be used for testing phase in 2025 Lighthouse challenge and will be publicly released at the completion of the challenge. The 2025 Lighthouse challenge will also release the 2023 and 2024 segmented datasets that were annotated using an established pipeline of pre-segmentation, student annotation, two neuroradiologists checking, and one neuroradiologist finalizing the process. It builds upon its previous edition by including post-treatment cases in the dataset. Using these high-quality annotated datasets, the 2025 Lighthouse challenge plans to test benchmark algorithms for automated segmentation of pre-and post-treatment brain metastases (BM), trained on diverse and multi-institutional datasets of MRI images obtained from patients with brain metastases.
OneProt: Towards Multi-Modal Protein Foundation Models
Nov 07, 2024



Abstract:Recent AI advances have enabled multi-modal systems to model and translate diverse information spaces. Extending beyond text and vision, we introduce OneProt, a multi-modal AI for proteins that integrates structural, sequence, alignment, and binding site data. Using the ImageBind framework, OneProt aligns the latent spaces of modality encoders along protein sequences. It demonstrates strong performance in retrieval tasks and surpasses state-of-the-art methods in various downstream tasks, including metal ion binding classification, gene-ontology annotation, and enzyme function prediction. This work expands multi-modal capabilities in protein models, paving the way for applications in drug discovery, biocatalytic reaction planning, and protein engineering.
MultiOrg: A Multi-rater Organoid-detection Dataset
Oct 18, 2024Abstract:High-throughput image analysis in the biomedical domain has gained significant attention in recent years, driving advancements in drug discovery, disease prediction, and personalized medicine. Organoids, specifically, are an active area of research, providing excellent models for human organs and their functions. Automating the quantification of organoids in microscopy images would provide an effective solution to overcome substantial manual quantification bottlenecks, particularly in high-throughput image analysis. However, there is a notable lack of open biomedical datasets, in contrast to other domains, such as autonomous driving, and, notably, only few of them have attempted to quantify annotation uncertainty. In this work, we present MultiOrg a comprehensive organoid dataset tailored for object detection tasks with uncertainty quantification. This dataset comprises over 400 high-resolution 2d microscopy images and curated annotations of more than 60,000 organoids. Most importantly, it includes three label sets for the test data, independently annotated by two experts at distinct time points. We additionally provide a benchmark for organoid detection, and make the best model available through an easily installable, interactive plugin for the popular image visualization tool Napari, to perform organoid quantification.
BraTS-PEDs: Results of the Multi-Consortium International Pediatric Brain Tumor Segmentation Challenge 2023
Jul 11, 2024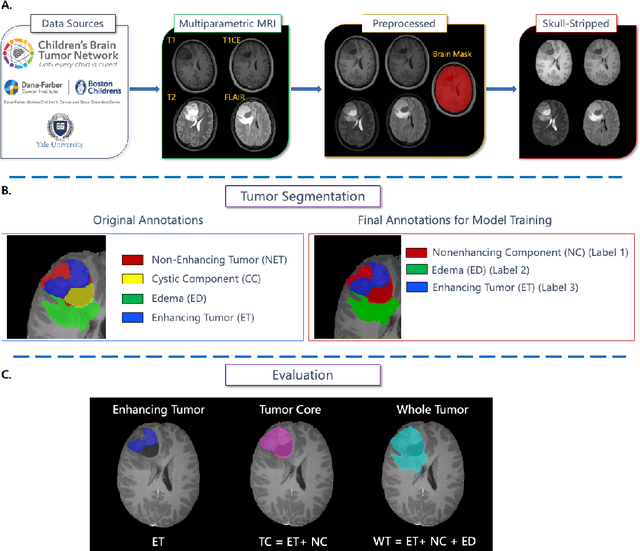

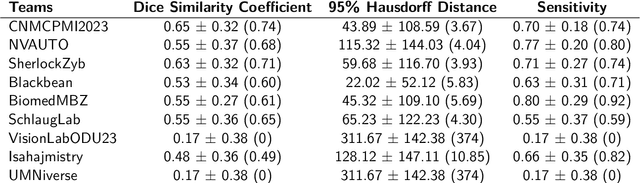
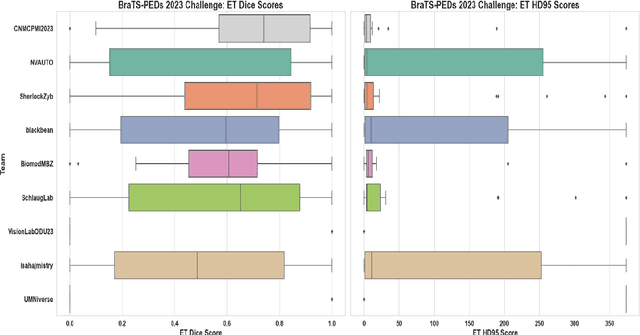
Abstract:Pediatric central nervous system tumors are the leading cause of cancer-related deaths in children. The five-year survival rate for high-grade glioma in children is less than 20%. The development of new treatments is dependent upon multi-institutional collaborative clinical trials requiring reproducible and accurate centralized response assessment. We present the results of the BraTS-PEDs 2023 challenge, the first Brain Tumor Segmentation (BraTS) challenge focused on pediatric brain tumors. This challenge utilized data acquired from multiple international consortia dedicated to pediatric neuro-oncology and clinical trials. BraTS-PEDs 2023 aimed to evaluate volumetric segmentation algorithms for pediatric brain gliomas from magnetic resonance imaging using standardized quantitative performance evaluation metrics employed across the BraTS 2023 challenges. The top-performing AI approaches for pediatric tumor analysis included ensembles of nnU-Net and Swin UNETR, Auto3DSeg, or nnU-Net with a self-supervised framework. The BraTSPEDs 2023 challenge fostered collaboration between clinicians (neuro-oncologists, neuroradiologists) and AI/imaging scientists, promoting faster data sharing and the development of automated volumetric analysis techniques. These advancements could significantly benefit clinical trials and improve the care of children with brain tumors.
Analysis of the BraTS 2023 Intracranial Meningioma Segmentation Challenge
May 16, 2024



Abstract:We describe the design and results from the BraTS 2023 Intracranial Meningioma Segmentation Challenge. The BraTS Meningioma Challenge differed from prior BraTS Glioma challenges in that it focused on meningiomas, which are typically benign extra-axial tumors with diverse radiologic and anatomical presentation and a propensity for multiplicity. Nine participating teams each developed deep-learning automated segmentation models using image data from the largest multi-institutional systematically expert annotated multilabel multi-sequence meningioma MRI dataset to date, which included 1000 training set cases, 141 validation set cases, and 283 hidden test set cases. Each case included T2, T2/FLAIR, T1, and T1Gd brain MRI sequences with associated tumor compartment labels delineating enhancing tumor, non-enhancing tumor, and surrounding non-enhancing T2/FLAIR hyperintensity. Participant automated segmentation models were evaluated and ranked based on a scoring system evaluating lesion-wise metrics including dice similarity coefficient (DSC) and 95% Hausdorff Distance. The top ranked team had a lesion-wise median dice similarity coefficient (DSC) of 0.976, 0.976, and 0.964 for enhancing tumor, tumor core, and whole tumor, respectively and a corresponding average DSC of 0.899, 0.904, and 0.871, respectively. These results serve as state-of-the-art benchmarks for future pre-operative meningioma automated segmentation algorithms. Additionally, we found that 1286 of 1424 cases (90.3%) had at least 1 compartment voxel abutting the edge of the skull-stripped image edge, which requires further investigation into optimal pre-processing face anonymization steps.
The Brain Tumor Segmentation in Pediatrics (BraTS-PEDs) Challenge: Focus on Pediatrics (CBTN-CONNECT-DIPGR-ASNR-MICCAI BraTS-PEDs)
Apr 29, 2024Abstract:Pediatric tumors of the central nervous system are the most common cause of cancer-related death in children. The five-year survival rate for high-grade gliomas in children is less than 20%. Due to their rarity, the diagnosis of these entities is often delayed, their treatment is mainly based on historic treatment concepts, and clinical trials require multi-institutional collaborations. Here we present the CBTN-CONNECT-DIPGR-ASNR-MICCAI BraTS-PEDs challenge, focused on pediatric brain tumors with data acquired across multiple international consortia dedicated to pediatric neuro-oncology and clinical trials. The CBTN-CONNECT-DIPGR-ASNR-MICCAI BraTS-PEDs challenge brings together clinicians and AI/imaging scientists to lead to faster development of automated segmentation techniques that could benefit clinical trials, and ultimately the care of children with brain tumors.
Denoising Diffusion Models for 3D Healthy Brain Tissue Inpainting
Mar 21, 2024



Abstract:Monitoring diseases that affect the brain's structural integrity requires automated analysis of magnetic resonance (MR) images, e.g., for the evaluation of volumetric changes. However, many of the evaluation tools are optimized for analyzing healthy tissue. To enable the evaluation of scans containing pathological tissue, it is therefore required to restore healthy tissue in the pathological areas. In this work, we explore and extend denoising diffusion models for consistent inpainting of healthy 3D brain tissue. We modify state-of-the-art 2D, pseudo-3D, and 3D methods working in the image space, as well as 3D latent and 3D wavelet diffusion models, and train them to synthesize healthy brain tissue. Our evaluation shows that the pseudo-3D model performs best regarding the structural-similarity index, peak signal-to-noise ratio, and mean squared error. To emphasize the clinical relevance, we fine-tune this model on data containing synthetic MS lesions and evaluate it on a downstream brain tissue segmentation task, whereby it outperforms the established FMRIB Software Library (FSL) lesion-filling method.
Panoptica -- instance-wise evaluation of 3D semantic and instance segmentation maps
Dec 05, 2023



Abstract:This paper introduces panoptica, a versatile and performance-optimized package designed for computing instance-wise segmentation quality metrics from 2D and 3D segmentation maps. panoptica addresses the limitations of existing metrics and provides a modular framework that complements the original intersection over union-based panoptic quality with other metrics, such as the distance metric Average Symmetric Surface Distance. The package is open-source, implemented in Python, and accompanied by comprehensive documentation and tutorials. panoptica employs a three-step metrics computation process to cover diverse use cases. The efficacy of panoptica is demonstrated on various real-world biomedical datasets, where an instance-wise evaluation is instrumental for an accurate representation of the underlying clinical task. Overall, we envision panoptica as a valuable tool facilitating in-depth evaluation of segmentation methods.
Framing image registration as a landmark detection problem for better representation of clinical relevance
Jul 31, 2023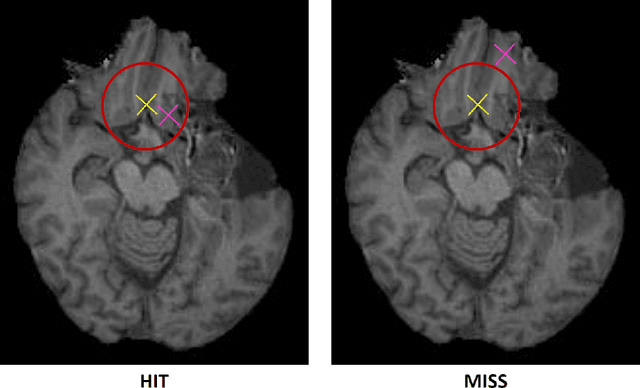
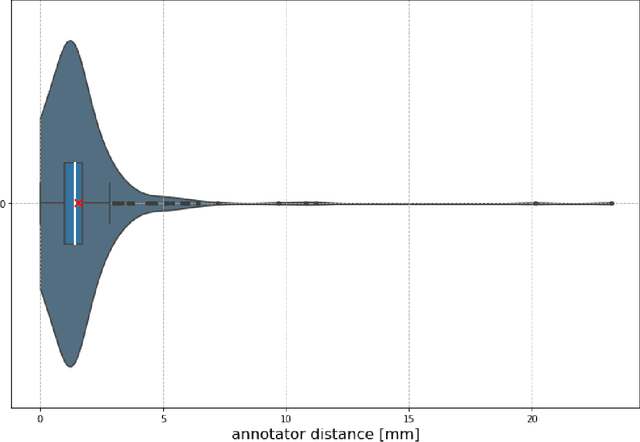
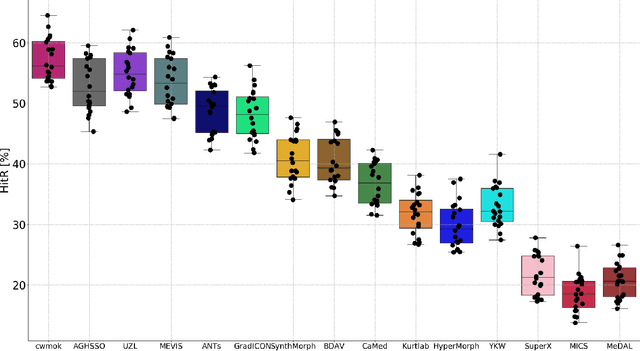
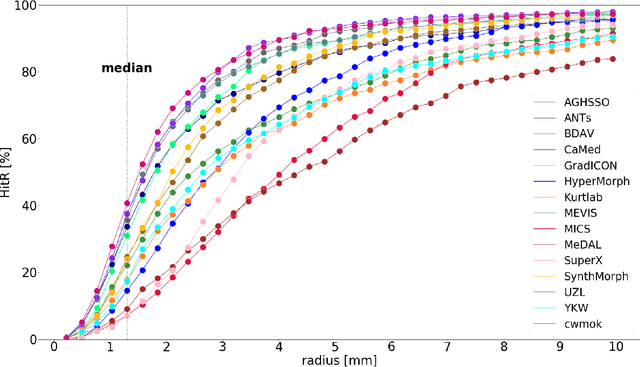
Abstract:Nowadays, registration methods are typically evaluated based on sub-resolution tracking error differences. In an effort to reinfuse this evaluation process with clinical relevance, we propose to reframe image registration as a landmark detection problem. Ideally, landmark-specific detection thresholds are derived from an inter-rater analysis. To approximate this costly process, we propose to compute hit rate curves based on the distribution of errors of a sub-sample inter-rater analysis. Therefore, we suggest deriving thresholds from the error distribution using the formula: median + delta * median absolute deviation. The method promises differentiation of previously indistinguishable registration algorithms and further enables assessing the clinical significance in algorithm development.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge